Skin burns occur due to human contact with a burning or hot substance, the temperature of which is significantly higher than permissible for humans.
Chemical burns occur from skin contact with aggressive chemicals, regardless of the temperature of the latter. As a result of their action, a chemical reaction occurs between living cells and a chemical compound, which can lead to complete destruction of the skin. Therefore, chemical burns are especially dangerous, but most of them can be treated at home.
Important! The effect of chemicals on the skin occurs even after cessation of contact with the aggressive substance!
Degree of damage
A chemical burn is serious damage to the skin and soft tissues of the human body. The severity of such an injury is determined by the symptoms.
- First degree: minor injury with virtually no consequences other than a cosmetic skin defect. It affects a small area of the skin and does not penetrate soft tissue. The disorder is limited to the upper epidermis. The most severe manifestations: slight swelling, severe redness. The pain is sharp, but short-lived - it is easily relieved, there is a burning sensation.
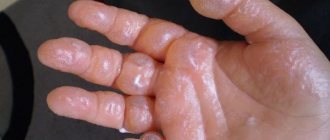
- Second degree: the wound is more widespread and quickly goes deeper into the tissue. Severe swelling and redness affects healthy areas of the skin. Blisters filled with serous water form on the wound. The pain is severe and growing.
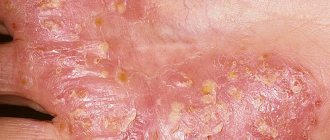
- The third degree has two categories: “a” and “b”. The symptoms remain exactly the same, aggravated by skin necrosis. In category “a” there are intact areas of the skin and soft tissues. Category “b” is characterized by deep damage - tissue begins to die. Sensitivity disappears, the blisters are larger in size and filled with bloody fluid.
- The fourth degree is unpredictable. The symptoms are the same, necrosis affects tendons and muscles, and can reach bones. It is almost impossible to cure; specialized help is required.
Sulfuric acid burn: first aid and further treatment
The most dangerous injury to the skin is a burn from sulfuric acid. If previously this substance was found exclusively in industry, today you can encounter it even in everyday life. By its nature, a chemical burn differs from ordinary thermal damage from boiling water or steam and, accordingly, requires special treatment.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Heparin ointment for burns. 5 best remedies for burns
Sulfuric acid is a potent substance that can penetrate into the deep layers of the epidermis. Chemical burns often occur in industrial plants.
It is used to purify petroleum products. In the chemical industry it is used for the production of dyes and fibers, the production of fertilizers, leather dressing, etc.
In the domestic sphere, sulfuric acid is used by car owners to prepare electrolyte for batteries.
There are several types of sulfuric acid with different percentages:
- concentrated - 98%,
- tower - 75%,
- battery - 30%,
- diluted (sulphurous) - 10%.
Depending on what type is used, the depth of exposure of the chemical depends. The main causes of acid burns are:
- failure to comply with safety regulations,
- industrial injuries,
- casual contact in everyday life,
- unprofessional use in cosmetology.
Most often, injuries are local in nature, i.e. a small area of skin is affected. Working with a toxic substance can lead to poisoning by its vapors - internal burns. If acid gets into your eyes, it can have the most dire consequences.
The degree of exposure to sulfuric acid depends on its concentration, the time of exposure to the skin, the depth of penetration and timely provision of assistance to the victim. There are four stages of chemical injury.
- In the first stage, only the upper layer of the epithelium is affected. After providing first aid and removing acid from the body, skin hyperemia appears, which disappears after a few days without drug treatment. Sometimes a burning sensation and itching may occur.
- In the second stage, the skin becomes blistered and swollen. The acid penetrates into the deeper subcutaneous layers, the patient feels a strong burning sensation. Timely assistance provided leads to a favorable outcome, without scarring.
- The third stage is characterized by blistering of the affected area with a cloudy liquid inside, sometimes with blood. The acid penetrated deep into all layers of the skin, including the fat layer. The patient experiences a painful shock and his temperature rises. The affected area turns red, then quickly darkens, and tissue necrosis is observed. The third stage is treated only in a hospital setting.
- At the fourth stage, the chemical penetrates through all layers of the epidermis, affecting tendons and bone tissue. Even with timely medical care, the prognosis can be unfavorable, even death.
There are also types of chemical burns: superficial, when the external parts of the body are affected, vapor poisoning - the poison enters the internal organs and eye burns. The latter is considered the most dangerous, because it is impossible to determine the depth of penetration of the chemical and correctly assess the scale of the damage.
It is believed that the lethal dose of sulfuric acid ingested is 5 mg.
A slight effect of a weak acid solution on the skin is manifested by slight redness with a light crust around the edges. If the substance is not removed in time, bubbles may form. At first, the damaged epidermis will be whitish, then the skin will darken to a gray or brown tint.
The symptoms of a chemical burn with sulfuric acid differ from ordinary thermal injury and depend on the location of the substance.
Classification
Injuries are characterized primarily by the chemical reagent that caused them. A person can be injured both at home and at work, so a number of “culprits” are identified from which this happens most often:
- various acids, the most common are sulfuric and nitric;
- alkalis;
- flammable mixtures (kerosene, gasoline, etc.);
- phosphorus;
- hydroxyl complexes;
- oil (bitumen).
A weak solution of these compounds will easily cause skin burns upon prolonged contact. The effects of all substances negatively affect the human body, in addition, many of them are toxic. The severity of the injury will be equal to the time the connection is exposed to the injury site.
The damaged area is gradually covered with a crust or plaque. A burn with alkali is the most dangerous - it penetrates deeply, the coating is white. Sulfuric acid, on the contrary, is recognized by the gray color of the skin, nitric acid by its yellow-green color, and yellow is a clear sign of hydrochloric acid. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide severely burns the skin and is recognized by a gray coating.
Burns of the 3rd and 4th degrees, sometimes 2nd, leave serious consequences. Skin regeneration at the site of injury is irreversibly impaired. The wound takes a terribly long time to heal, and a scar forms in its place. The following functions of the skin are often disrupted: motor and excretory. An inflammatory process may begin, and suppuration may affect healthy tissue around the injury. Complications can be prevented by starting to provide assistance to the victim as soon as possible.
It is important to take into account the area of injury - the larger it is, the higher the risk of death, the stronger the pain shock. It is possible to accurately determine the danger to a person only after a week, when suppuration and scabs form.
Characteristic symptoms
Symptoms of a chemical skin burn vary depending on its severity:
- 1st degree (the upper layer of skin, the epidermis, is affected). In this case, swelling of the skin and slight redness are observed. Mild pain may also occur.
- 2nd degree . Bubbles appear on the reddened, swollen skin, containing transparent contents.
- 3rd degree . The deeper layers of the skin down to the subcutaneous fatty tissues are affected. In this case, bubbles appear, inside of which there is a cloudy liquid or bloody contents. Sensitivity is impaired, and there is no pain in the burn area.
- 4th degree . All skin tissues, muscles, tendons and even bones are affected.
Chemical burns of the 3rd and 4th degrees occur most often. If the cause of the burn is acid or alkali, a crust (scab) forms in its place. After an alkali burn, it will be soft, loose and whitish, affecting adjacent tissues without clear contours. Alkaline liquids are more dangerous than acidic ones because they can penetrate deep into tissues.
If the burn was caused by acids, the scab is usually hard and dry, with clear lines where it transitions to undamaged areas. Such burns are usually superficial. The shade of the damaged skin will be determined by the color of the chemical.
Symptoms and treatment of hypertensive crisis at home. How to provide emergency assistance?
How to treat intestinal colitis using folk remedies? Read in this article.
First aid
Providing first aid consists of a simple rule: first you need to neutralize the chemical, only then begin to treat. At the same time, it is important to know what substance caused the violation, because otherwise the wound can be aggravated. You can remove almost any chemical from the skin with plain water, but only within half an hour after it gets in.
Actions to take immediately:
- hold the damaged area under running water;
- Neutralization of acid burns occurs with a weak soap solution, alkaline burns with a solution of water and vinegar, lime damage with sugar;
- remove clothing and accessories, it is likely that the chemical could get on them;
- Chemicals in powder form should be shaken off and only then rinsed;
- the injury site should be carefully, loosely bandaged with a sterile bandage or bandaged with a clean cloth.
A cold compress - ice wrapped in a cloth, frozen semi-finished products - will help prevent swelling and partially relieve pain. They should be applied only after the chemicals have been neutralized. The wound must be treated with iodine to prevent infection.
Under no circumstances should wounds resulting from hydroxyl complexes or organic substances react with aluminum be washed. Water will act as a solvent on these types of substances, thereby expanding and deepening the area of damage.
A common mistake that aggravates an injury is that the victim begins to rub the sore spot. The substance is rubbed even deeper, thereby aggravating the situation. You cannot use wet wipes; it is better to simply water the damaged area.
You can treat the injury before doctors arrive with burn ointment. Thanks to their composition, such ointments have an analgesic and calming effect. You can protect the skin from spreading with fat - just lubricate the affected area.
Treatment for chemical skin burns at home involves the use of sea buckthorn oil. It will relieve itching, burning, and calm the pain a little. Taking painkillers will help relieve some of the pain, stopping the onset of pain shock.
What to do if you have a burn to the esophagus
Treatment of a chemical burn of the esophagus is carried out in a medical facility. Only qualified medical intervention will help avoid negative consequences for the human body. Correctly provided first aid will reduce tissue trauma. Therefore, if aggressive substances enter the digestive system, it is necessary to resort to the following:
- First aid for a burn of the esophagus is gastric lavage . It is necessary to give the person to drink a large amount of water (at least a liter), and then induce vomiting.
- If the victim drank an acid-containing substance, you need to offer him a weak soda solution. If it was lye, you should use water with a little vinegar. After all manipulations, vomiting is repeated.
- If it is impossible to determine the nature of the substance drunk, the victim is given 400-500 ml of warm milk, which neutralizes the negative effects of chemical compounds.
- The patient is sent to a medical facility, where he undergoes further treatment.
Drug treatment
Outpatient treatment or hospitalization - depends on the area of damage, the extent and correctly provided first aid. Victims often refuse hospitalization, incorrectly assessing the damage caused.
Treatment with medications consists of treating the skin around the wound with a 3% solution of boric acid. The wound itself is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide. To prevent the development of sepsis and, as a consequence, tissue necrosis, the wounds are watered with a solution of Chlorhexidine, Lavasept and Miramistin.
The use of Levomel and Dermazin ointments will allow wounds to heal quickly. These drugs have an antiseptic effect. Ointments are used in the treatment of 2nd degree damage. Furacilin and gentamicin ointments are effective in treatment.
Causes of chemical skin burns
The degree of skin damage, methods of providing first aid, further treatment of burns and the possibility of skin rehabilitation directly depend on the reagent that affected the skin.
The most dangerous chemicals are:
· Acids (especially concentrated: hydrochloric, sulfuric, nitric, hydrofluoric, etc.);
· Alkalis (caustic potassium, caustic soda, quicklime, ammonia);
· Some metals and their salts (sodium, potassium, mercury, heavy metals);
· Non-metals (phosphorus);
· Gases (vapors of gasoline, acids, phenol, nitrogen oxides, bromine, etc.);
· Some medications (benzoyl peroxide, baziron, etc.), especially in case of overdose;
· Organic substances (hot bitumen, oil vapors, etc.);
· Oxidizing agents (hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, etc.).
Folk recipes
Treatment for chemical skin burns at home involves the use of folk remedies. Sometimes they are even more effective than drug treatment. A huge number of recipes allows you to choose the optimal one and begin treating a chemical burn at home.
Symptoms of 3rd degree burns are relieved by soft compresses of onion pulp. Boil the onion, crush until mushy, after which a couple of drops of linseed oil are added. The compress is applied twice a day, usually used until the skin is completely restored.
A simple cabbage leaf will help eliminate pain and swelling. Cabbage should be fresh; it has an astringent effect on the damaged area. The sheet is washed in clean water, after which it is applied to the burn and secured with a sterile bandage.
Grated potatoes will be indispensable when providing first aid for 1st degree burns. The potatoes should be grated and then squeezed. A compress of grated potatoes is made twice a day, a fresh one is applied at night. This procedure will relieve pain, reduce swelling, and starch will prevent the formation of blisters. The potato mass is fixed with a gauze bandage and loosely bandaged with a bandage.
Starch can be used in other ways. Dry starch is mixed with soda in equal parts, after which the wound is sprinkled. Prevents the appearance of bubbles. Do not forget that this method will be dangerous for alkaline burns.
There are phytotherapeutic recipes. Young St. John's wort is mixed with sunflower oil, the mixture is boiled for half an hour. After cooling and filtering, lotions and compresses are made from the mixture.
Not only sea buckthorn oil, but also fir oil will be effective against blisters at the burn site. A bandage is applied to the wound: a napkin in oil is fixed with a sterile bandage. This type of dressing is changed 4-5 times a day.
A decoction of elderberry roots, chamomile and garden rose flowers, beets and onions will provide an excellent therapeutic effect. Make compresses on the wound from the cooled broth, change them several times a day after complete drying. Preparing such a decoction is quite simple: grate the beets and cut the onion. Chamomile is enough on the tip of a spoon, and elderberry - a couple of tablespoons. All this is boiled in one liter of water and filtered.
A decoction of milk and elderberry leaves will have a relieving effect and stop the appearance of blisters. The milk is mixed with elderberry leaves, kept in a water bath and cooled. For dressings, napkins are soaked and placed on the burn.
There are plenty of traditional medicine recipes, but don’t forget - they will only give an effect for the first and second degrees of burn. More complex injuries are best treated by doctors, as tissue necrosis can spread throughout the body.
What to do if you inhale vapors of aggressive substances
A lung burn is accompanied by destruction of the mucous membranes, which leads to disruption of their function. If the upper respiratory tract is affected, the person feels a sharp pain in the throat and chest. Unpleasant sensations almost always intensify during exhalation . The degree of negative changes in the lungs depends on the duration of exposure to the aggressive substance.
First aid for chemical burns of this type is as follows:
- the victim is taken out into fresh air;
- the person must take a reclining position;
- when the victim is unconscious, he is placed on his side to prevent vomit from entering the respiratory tract;
- the mouth and throat should be rinsed with clean water;
- in case of an acid burn, the oral cavity can be treated with a solution of soda, and in case of an alkaline burn - with a solution of acetic acid;
- the victim is required to be sent for further treatment to a medical facility.
Precautionary measures
A burn at home always occurs due to negligence, because this is the place where we feel safe. It’s easy to prevent this - be careful about the household chemicals you buy for your home.
Proper storage of chemicals and compliance with the rules for working with them is the key to safe work. Working with chemicals requires special equipment, which should not be neglected. Following the instructions will help completely eliminate even the possibility of chemical damage to the skin.
Anyone can get a chemical burn; no one is immune from such injuries in everyday life. Following simple rules, paying close attention to your job responsibilities, and getting the right help can help prevent injury or reduce exposure to chemicals. It is worth remembering that self-medication does not lead to good results. It is always better to seek specialized help.
Preventive measures
The most effective prevention of burns is compliance with all safety rules when working with chemicals, as well as in everything related to the rules for their storage.
In production, special clothing and shoes, masks, goggles, protective screens and other similar devices are used to protect against harmful substances. We must not forget about safety in everyday life.
Before using any substance, be sure to read the instructions and strictly follow them. You should only work with gloves and protective clothing; it is important to store chemicals in closed containers and in places inaccessible to children.
Watch a useful video on the topic of the article:
What not to do
For burns on the face and body from sulfuric acid, it is important not to harm the victim. Remember what not to do:
- do not apply fatty ointments, starch, etc. to injured areas;
- do not pop blisters;
- Do not wipe the acid with a napkin, towel, or tampon.
If you do not know what substance has come into contact with your skin, do not try to neutralize it. Simply wash the area with water or baking soda solution. Be sure to seek professional help.