HPV and pregnancy: features of the course
The causative agent of papillomavirus is a complex organism that parasitizes in the upper sphere of the mucous membranes. Infection occurs during contact with a virus carrier. The risk of getting sick increases in women with microtraumas of the skin and insufficient immune status.
There are usually several routes of infection:
- sexual intercourse (the risk remains even with oral and anal intercourse);
- household contact with a contaminated object (for example, someone else's razor);
- visiting public places (for example, dentistry, cafes, nail salons);
- airborne droplets;
- intrauterine infection.
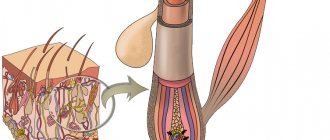
Having penetrated the female body, the virus settles in the epithelial cells of the mucous membrane or epidermis. In the process of its life activity, the virus modifies tissues and causes neoplasms. In this case, HPV does not penetrate into the blood or internal organs.
On a note! The incubation period for HPV development is about 3 months. But in a body with excellent immunity, the virus can hide for several years and become active only at times of decreased immune function, for example, during pregnancy.
The most unprotected organ in the female body, which is most often damaged by HPV, is the cervix. The virus provokes transformation of its tissues, which leads to atypical dysplastic changes, which often precede cervical cancer or other benign tumors.
Research shows that women with HPV types 16 and 18 have an increased risk of cervical cancer during pregnancy, which can develop between 2 and 40 years. Moreover, the average age of HPV infection is 22-23 years. Of the total number of women, the number of infected is more than 30%.
Important! There are 30 known types of HPV, which are divided into oncogenic and conditionally safe (cause only benign growths). Only the following types of HPV are considered dangerous: 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56-59, as well as 66, 68, 73, 82.
Diagnosis of HPV
Often, papillomas are discovered during a gynecological examination during the initial consultation with a doctor about pregnancy. Some mothers have complaints about the appearance of genital warts in the area of the external genitalia. Such patients are prescribed special diagnostic tests:
- cytological analysis of a fragment of the cervical canal mucosa;
- colposcopy;
- antibody titer study;
- Digene test (amplification);
- PCR diagnostics.
This is interesting: How to cure HPV type 16 forever
Analysis of sequential chain reactions makes it possible to most accurately determine DNA, HPV strains, the degree of their oncogenicity, and how long ago a person was infected. The material for the study is blood, urine, and amniotic fluid. Based on the results obtained, the doctor selects a treatment regimen.
Important! In cervical cancer, highly oncogenic strains of papillomavirus are detected, most often types 16, 18. Patients are referred for consultation and further examination to an oncologist.
How to protect yourself from relapses of papilloma and not become infected with a new type of virus
HPV is transmitted through household and sexual contact. It penetrates the body even when using a condom, during oral sex and kissing with a carrier of the infection.
Papillomavirus is transmitted through the use of unsterile instruments or their improper handling. Caution should be exercised during cosmetic procedures such as manicure trims, eyebrow shaping, and hair removal to remove ingrown hairs.
It is worth purchasing individual tweezers, manicure clippers, and bringing them to each cosmetic procedure.
The most important thing with papillomavirus in pregnant women is maintaining the body’s defenses. Strong immunity inhibits the growth of old growths and prevents the formation of new ones. A woman expecting a child needs to rest more and be less nervous, eat a balanced diet and sleep at least 8 hours a day.
HPV during pregnancy - symptoms
If papillomas grow on the skin, the presence of HPV in a pregnant woman can be detected without diagnosis. If papillomas grow on the cervix, you can find out about the disease only after a gynecological examination. However, there are several symptoms that may suggest you have HPV infection.
If the following symptoms appear during pregnancy, it is advisable to immediately consult a gynecologist:
- unusual vaginal discharge (changes in its color, abundance, smell);
- the appearance of condylomas on the genitals or near the anus;
- pain discomfort in the pubic area;
- discomfort when urinating;
- burning sensation during intercourse.
On a note! Activation of HPV in women during pregnancy may be accompanied by intoxication. Weakness, low-grade fever, irritability, dizziness, and vomiting occur.
The impact of HPV on child development
Modern scientific research has shown that a mother with HPV can give birth to a completely healthy baby without papillomavirus in the body or other pathologies. It can only become infected with the virus when passing through the birth canal, but this probability is extremely low.
As for the effect of the virus on the developing fetus and the appearance of any deviations from the norm, there is currently no such information, so the expectant mother should not worry about this.
Even if a pregnant woman’s immune system is weakened and the human papillomavirus causes condylomas to appear on the skin, the child is still well protected by her immunity at this time. His antibodies easily cope with HPV.
How does HPV affect pregnancy?
Not only women, but also doctors themselves are very concerned about the effect of the papilloma virus on pregnancy. There are many cases that prove the fact that HPV can interfere with conception and the process of bearing a fetus. There is also some evidence that infection of the baby during childbirth can cause respiratory diseases and damage to the genital organs.
HPV types 16 and 18 are characterized by increased oncogenicity. They form flat condylomas on the surface of the body, the appearance of which requires regular examination of the cervix using a colposcope and taking a sample for histological examination (biopsy).
The presence of these types of viruses during the gestational period should cause particular concern, since the baby may become infected while passing through the birth canal. As a result, he may develop papillomatosis of the respiratory tract. Therefore, the current method of delivery for women with active HPV during pregnancy remains cesarean section.
As a rule, the woman’s condition is regularly monitored throughout pregnancy, and if nothing threatens her and the baby, the growths are not removed. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to the removal of flat papillomas during pregnancy using cryofreezing or electrocoagulation.
More recently, gynecological oncologists have begun to focus on 31 types of HPV. At first it was assumed that this virus did not have oncogenic activity. Now there is official evidence that the effect of HPV 31 on pregnancy is quite aggressive and ranks second in the risk of cancer.
The growths caused by this virus resemble squamous processes. They are noticeable in the genital area and on the cervix. Genital warts are not typical for HPV 31.
The danger during pregnancy of this virus is the formation of bowenoid papulosis, as well as neoplasia. There is also a risk of infection of the fetus at the time of birth.
HPV 33, despite its oncogenicity, does not affect the course of pregnancy and is extremely rarely transmitted to the baby. But given the reduced immunity of a pregnant woman, the virus can significantly worsen her health. First of all, the risk of developing cervical cancer increases. Therefore, if this strain of the virus is detected, a woman needs regular histological examination and cytology.
In addition, the growth of papillomas more often begins in places of friction, in the groin, and a woman can often damage these growths, and this opens the door to all kinds of infections. If the growths are present in the vagina, cervix, or cervical canal, bleeding may occur.
HPV during pregnancy
Often women become carriers of the disease, but are not aware of it. During pregnancy, HPV is activated as a woman's hormonal levels undergo changes. The virus has hundreds of strains, of which only 130 have been studied, and each of them makes its own adjustments to the host.
Once in the human body, the papillomavirus penetrates into the deepest layers of the epithelium. It is unrealistic to guess that the infection is inside. The infected cells then inject DNA into healthy cells and begin to chaotically produce their own cells—in other words, mutate.
Lack of proper treatment can cause cervical cancer, making pregnancy impossible. How did the virus itself enter the body of the unfortunate woman? This happens in the following ways:
- through bed - sexual intercourse with an untested partner is the most common way of becoming infected with papillomavirus with a high degree of oncogenicity;
- through household items - a common comb, washcloth, razor, etc.;
- a child can become infected if genital warts or anogenital warts form on the birth canal .
Reasons for HPV activation
For signs of HPV to appear on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes in the form of condylomas, papillomas or warts, the introduction of the virus into the body is not enough. Provoking factors such as:
- presence of bad habits – alcoholism, smoking, taking psychotropic drugs;
- frequent injury to mucous membranes or skin;
- colds or chronic diseases;
- harmful working conditions – often associated with industrial production;
- hormonal imbalances – pregnancy itself can cause growths to appear;
- increased sweating – the virus spreads more easily in a humid environment;
- excess fat deposits;
- sedentary pastime as a way of life.
Symptoms
Since the papillomavirus does not manifest itself externally for years, its presence in the body can only be judged by the state of immunity. The sequence of the disease may be as follows:
- UNDER a certain area of the mucous membrane or skin, modified epithelial cells begin to grow - in the cervix, on the neck, face, etc.;
- In a short period of time, cells multiply chaotically and occupy a large area, which affects the appearance of papillomas already on the surface of the body or mucous membrane;
- A person may notice the growth of papillomas, warts or condylomas. Why “may notice”? Because papillomas can appear in the larynx or inside the genital organs, where only the attending physician can see their appearance.
Is it dangerous
The growths do not interfere with the course of pregnancy and often disappear after childbirth. Removal using various methods will not affect the situation; the papilloma may pop up in another area of the skin.
It is advisable to undergo HPV treatment when planning a pregnancy. It will relieve you from unnecessary worries while carrying a child. You can get vaccinated against human papillomavirus before you become sexually active.
Only topical medications are prescribed.
| Name | Action | Mode of application |
| Kipferon | Suppositories for rectal and vaginal administration. Helps cope with condylomas in the vagina. The action is aimed at increasing immunity, eliminating papillomavirus. The drug has anti-inflammatory properties. | Suppositories are inserted into the vagina, 1-2 pieces (depending on symptoms), 2 times a day. Therapy lasts about 10 days. |
| Galavit | Suppositories designed to combat the HPV virus. The drug has an anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating effect that changes virus cells. | Take one suppository once a day for 10 days, then one suppository every other day. A full course of therapy requires 25 suppositories. |
| Viferon | Available in the form of suppositories and ointments. Helps cope with growths in the vagina, stimulates the immune system, controls formations, thanks to its antiviral properties. | One suppository is administered rectally. The course is about 10 days. The ointment is applied to the affected area of the skin, mucous membrane or vagina. Apply a thin layer of ointment to the formation 4 times a day for 5 days. Take a break for 5 days, repeat the course again. |
| Infagel | A drug for the treatment of viral diseases, has anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating, antitumor effects. Suppresses the growth of infection, provokes drying out and detachment of the wart. | The product is applied to the damaged area of the skin or mucous membrane. Wait until it dries completely and a protective film forms. Use twice a day for 5 days. |
| Solcoderm | The solution for removing papillomas, due to the action of acids, causes the growth to dry out and fall off. | It is recommended that the treatment procedure be carried out by a doctor. Application should be spot-on due to the high risk of burning healthy skin. After the fourth procedure, the result will become noticeable, the papilloma will begin to peel off. |
Pharmaceutical drugs are used only after a doctor's prescription.
When papillomas appear in places subject to mechanical stress, and condylomas prone to rapid growth, it is recommended to remove the elements using surgical methods. Indications for getting rid of growths are: bloody, purulent discharge from the surface of papillomas, itching, burning, discoloration, peeling.
| Method name | Description |
| Cryodestruction | A method of removing growth using liquid nitrogen, which has a freezing effect. |
| Laser therapy | A painless, gentle method of getting rid of growths using a laser. Leaves no marks or scars. Removal is possible in hard-to-reach places, mucous membranes and vagina. There is no risk of bleeding; the edges of the tissue are burned. |
Other hardware methods: DEC and Surgitron are not used during pregnancy. After removal of the formations, it is recommended to increase immunity to prevent relapse and the appearance of new growths in other parts of the body.
Regardless of the type of reason for the appearance of papilloma on the neck during pregnancy or on another area of the dermis, a pregnant woman must show it to the doctor. In medicine, there is an opinion that the activity of papillomavirus and the growth of formations during the period of bearing a baby has the following consequences: infection of the child. The virus can be transmitted to the baby during childbirth.
The following symptoms of papillomatosis should alert the expectant mother and go to the hospital:
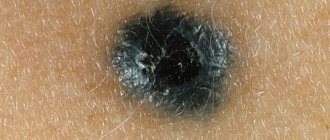
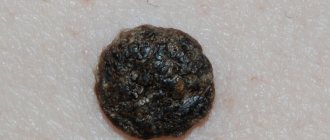
- An elongated, elongated form of a formation having a length of 1.5 to 2 mm. Such a growth is easy to injure; it can become infected and provoke the development of inflammation.
- High growth rate and rapid increase in the number of condylomas.
- Change in color of the growth. They are usually flesh-colored or slightly brownish, and redness of the lesion indicates damage.
- Bleeding indicates damage to the papilloma.
Having realized the danger from formations on the skin, the expectant mother should consult a doctor who, using modern diagnostic methods, will determine the type of virus and prescribe the necessary treatment. Therapy should be comprehensive; it is preferable to remove the growth. The use of antiviral drugs is necessary, sometimes the use of folk remedies is acceptable.
Recommendations from doctors when detecting manifestations of papillomavirus in a pregnant woman
Many women are interested in treating growths or removing them only because of their own complexes (ugly, not aesthetically pleasing). Indeed, growths negatively affect a woman’s appearance. Especially if the warts are located on exposed parts of the body. It is not recommended to treat and remove growths in the following situations:
- Neoplasms do not cause discomfort to the expectant mother.
- The growths do not constantly come into contact with clothing.
- The color and shape of papillomas do not change, they do not become inflamed.
If the situation is completely opposite, then papillomas can be removed by removing tumors from a pregnant woman. They are used: liquid nitrogen freezing method, laser coagulation or radio wave excision.
Treatment with medications during pregnancy with tablets or ointments is extremely rare. Most medications have contraindications for use by pregnant women, so they cannot be used in treatment.
Why is treatment for HPV papillomavirus undesirable while pregnant? The reasons are as follows:
- medication treatment involves stress for the mother’s body, which naturally affects the baby;
- most neoplasms that arise during pregnancy go away on their own after childbirth;
- Removal of papillomas during pregnancy is carried out using local anesthetic drugs, the components of which, when entering the mother’s bloodstream, have a negative effect on the fetus.
Radiofrequency removal of papilloma
HPV and pregnancy: what to do
Every second woman can be diagnosed with at least one type of HPV, so there is no need to worry when making such a diagnosis. It is only important to remember that the development of the virus is possible under favorable conditions, and during pregnancy, a weakening of the immune system always occurs. Therefore, you need to take this diagnosis calmly and focus your efforts on improving your overall health.
Is it possible to get tested for HPV during pregnancy? If the doctor has suspicions, then the woman must be prescribed an examination. The standard list of diagnostic procedures includes:
- Visual examination of a woman to detect condylomas on the body.
- Colposcopy of the cervix (helps to notice dangerous cell changes in time).
- PCR study of the type of virus (identifies the virus in the body by its DNA).
- Cytological examination (necessary to identify atypical cells).
- Biopsy followed by histology (study of cervical tissue).
- Standard gynecological examination with smears (assess the degree of proliferation of condylomas, the presence of infection).
HPV treatment
Human papillomavirus infection that develops during pregnancy does not always require immediate treatment. Doctors' intervention is only necessary if unwanted changes begin to occur in the cervix. In other cases, treatment is delayed until the baby is born.
It is impossible to remove papillomas during pregnancy - any stress on the body can lead to unpleasant consequences. Only in the most extreme cases do medical specialists decide to eliminate papillomas using traditional surgery, laser therapy or electrocoagulation. There is also such a method as burning papillomas with liquid nitrogen, but it is not particularly popular due to the high probability of damage to healthy tissue. Drug treatment is usually not prescribed - the drugs can adversely affect the growing fetus. The only thing a doctor can recommend is taking additional vitamins, especially vitamin C to strengthen the immune system.
This is interesting: HPV analysis Voronezh
HPV during pregnancy: consequences for the child
The human papillomavirus does not have a significant effect on the embryonic development of the fetus. All risks are associated with deterioration of the woman’s health and complications during childbirth. However, some types of HPV can be transmitted to the baby during birth and cause a condition called papillomatosis.
The essence of the pathology is the focal proliferation of condylomas on the mucous membranes of the newborn. The throat, trachea, eyes, and genitals may be affected. If papillomatosis affects the bronchi, there is a risk of asphyxia (suffocation) of the baby.
Does the appearance of papillomas affect the fetus and is it possible to give birth?
Papilloma during pregnancy does not affect the fetus throughout pregnancy, the baby in the womb is protected. If a woman was diagnosed with genital warts before pregnancy, with the onset of pregnancy, their growth may increase, followed by vaginal discharge. The abundance of discharge affects the growth of papillomas, creating a favorable environment for the virus.
A child can become infected with HPV when passing through the genital tract during childbirth; close contact with the infection occurs. In most cases, the virus does not pose a threat to the baby’s body; the immune system copes on its own. The disease does not manifest symptoms and does not provoke consequences.
Weakened immunity leads to infection with papillomavirus, which affects the vocal cords and respiratory organs. This type of disease is rare, treatment will require a lot of effort and patience.
During childbirth, the baby becomes infected with a virus, which manifests itself as formations on the larynx, bronchi, genitals, and anus. The presence of a virus is not an indication for surgery. Condylomas can occur in women diagnosed with AIDS.
The virus can be transmitted from mother to child through the birth canal, directly through contact. Papillomas after childbirth can disappear on their own, leaving no traces.
HPV during pregnancy - treatment
There is no specific treatment that would completely destroy HPV. Only temporary elimination of the virus occurs by the woman’s immune system. Medical care is limited to surgical removal of papillomas, if there are indications for this. It has been proven that removing growths reduces the percentage of transmission of the virus to a sexual partner, and also reduces the risk of cancer.
Important! Most condylomas disappear on their own after childbirth, so there is practically no need for their excision.
When a woman is diagnosed with HPV during pregnancy, drug treatment can be prescribed to maintain immunity if it absolutely cannot cope with the virus. However, taking medications is allowed only from the second trimester.
To normalize immune function and suppress HPV, a woman can be prescribed the herbal drug Anaferon, which stimulates the production of antibodies to this virus. An excellent immunomodulatory agent that prevents the growth of papillomas is Viferon.
Important! Any antiviral medications can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Women have an important role to play in HPV treatment. She needs to lead a healthy lifestyle so that her body is able to contain the virus. Doctors recommend following simple rules:
- to eat well;
- be in the fresh air;
- be regularly examined by a doctor;
- do not be nervous;
- get a full night's sleep.
Causes of papillomas during pregnancy
The formation of papillomas during pregnancy is due to the following factors:
- weakened immunity, which is necessary for successful childbearing;
- changes in hormonal levels , which provoke intradermal transformations due to the active growth of epidermal cells;
- diabetes mellitus in a woman;
- chronic diseases aggravated during pregnancy;
- skin damage caused by sudden weight gain, especially in the 3rd trimester.
Prevention
To avoid pathogen activation during pregnancy, you need to carefully monitor your health and follow the following recommendations:
- avoid hypothermia, overheating, drafts;
- treat concomitant diseases in a timely manner;
- avoid stressful situations and excessive worries;
- eat properly and drink vitamin and mineral complexes;
- spend more time in the fresh air and do moderate physical activity.
If you are one of the small number of people who are not infected with the virus, you need to carefully select your sexual partner to reduce the risk of infection. It is necessary to use protection during sex. You cannot use other people’s things and personal hygiene products.
HPV when planning pregnancy
Detection of HPV at the stage of pregnancy planning is not an obstacle to successful conception if the woman does not have underlying gynecological diseases. In exceptional cases, the virus can negatively affect the immune program of the reproductive system, and female immune cells begin to incorrectly perceive sperm. This condition can significantly complicate the fertilization process.
To avoid any problems, a woman needs to approach pregnancy planning wisely and responsibly. To do this, you need to undergo a full examination, and if there are any violations, follow the doctor’s instructions. If all the rules are followed, HPV will not harm either the woman or her baby.
Chances of conceiving with HPV
Women who have been diagnosed with papillomavirus are interested in information about HPV type 16 and pregnancy: is it possible to conceive and carry a healthy child while being a carrier? Those who plan to be cured first should know that HPV of any type cannot be completely eliminated from the body. The patient can only maintain immunity and stop viral manifestations.
The barrier to conception is not the virus itself, but its harmful effect on the reproductive organs. An infected female body has less chance of fertilization naturally - this is a scientific fact. The likelihood of a problem-free pregnancy is also reduced.
If there is a viral infection with a high oncogenic danger in the female body, the doctor prescribes a cytology test for the patient. If the cervix is normal, planning a pregnancy is acceptable. If there are significant pathologies, a woman must first undergo a course of treatment and only then solve the problem of conception. However, HPV detected after pregnancy is not an indicator of its termination and resolution by cesarean section.
HPV does not affect the likelihood of conception
HPV and pregnancy - reviews
HPV has long instilled fear and terror in women with cancer phobia. Fearing cervical cancer, they are shocked when they hear they are infected with the virus. But having understood the situation, they understand that following the doctor’s advice practically eliminates any complications during pregnancy.
Many pregnant women experience rapid growth of papillomas on the body. There are especially many of them on the neck, nipples, and genitals. But if you study most reviews, other than a cosmetic defect, they do not create anything. And some time after giving birth, papillomas disappear as suddenly as they appeared.
HPV is not the worst thing that can happen to a pregnant woman. There is no risk of miscarriage or abnormalities in the fetus. Also, the virus does not affect a woman’s well-being, although there are exceptions. In general, there is nothing dangerous about this virus if you maintain your immunity. But you must always remember that HPV causes cervical cancer, so after childbirth you need to regularly visit a gynecologist.
general information
The appearance of papillomas on the body of the expectant mother, as a rule, occurs in HPV carriers. There are more than 100 types of human papillomavirus, but only a few of them are oncogenic:
- HPV 16;
- HPV 18;
- HPV 36;
- HPV 45.
Almost always, symptoms of HPV disease do not clearly appear in its carrier. Despite the fact that more than 100 different types of papillomavirus have now been identified, the appearance of papilloma during pregnancy is possible only with certain types of the disease.
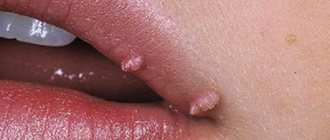
As a rule, neoplasms appear on the following parts of the body:
- on the neck;
- on the face;
- on the armpits;
- on the chest - papillomas are possible on the nipples, between the breasts or under them;
- in the groin area.
Papilloma on the nipple is one of the most unpleasant manifestations of the virus. Such growths on the chest cause discomfort, because... rub against clothes, causing discomfort. There is also a risk that they may develop into a tumor. If a papilloma on the nipple causes concern to a pregnant woman, then it is better to remove it immediately, without waiting for it to worsen.
If a girl develops papillomas during pregnancy, this may be due to several factors. Possible reasons for the appearance of growths:
- the expectant mother’s immunity weakens, which provokes an increase in HPV symptoms during pregnancy;
- The virus is more likely to appear in overweight women;
- during the last trimester of pregnancy, papillomas may occur after friction or minor damage to some areas of the skin;
- The cause of papillomas during pregnancy can be an exacerbation of diabetes mellitus caused by an increase in hormone levels.
In most cases, the papillomavirus ceases to manifest itself after childbirth. A few months after the baby is born, most formations go away on their own.