Genital warts during pregnancy are not uncommon. Many expectant mothers are interested in the question of whether it is necessary to treat or remove emerging condylomas? Not all women know that the nature of the origin of such elements on the skin is viral, so there is a certain probability of infecting the child with the virus. Today, the issue of treating genital warts is relevant, as the prevalence of this infectious skin pathology is gaining momentum.
Causes of genital warts in pregnant women
The culprit for the appearance of warts on the body, as well as on the genitals, is the human papillomavirus (HPV) of low oncogenic risk.
Every person encounters this virus during their life, but not everyone becomes the owner of warts. The main reason for the spread of infection is considered to be a decrease in immune activity. This is why condylomas appear so often in pregnant women. Immune suppression is a natural mechanism during this period, so that the developing fetus is not rejected by the mother's immune system.
Laser therapy during pregnancy
Laser removal of condylomas during pregnancy has its advantages:
- the laser beam carefully removes pathological tissue in 1 or several procedures;
- there is no risk of damage to healthy tissue;
- no scars appear that could interfere with the birth process;
- there is no risk of infection;
- the possibility of bleeding is excluded.
In order for the procedure to be carried out efficiently and with minimal risk to the health of the expectant mother and fetus, you should approach the choice of a specialist and clinic responsibly. It is better to carry out laser removal during the 2-3 trimester. The only downside is some pain during removal and the use of anesthesia in connection with this.
Routes of infection
Warts that appear in the genital area are called genital warts. The virus enters the skin in the following ways:
- For any type of sexual intercourse. The source of infection is an infected sexual partner, on whose skin and mucous membranes there may be genital warts or warts. If there are cracks, wounds, or abrasions, the likelihood of virus penetration increases.
- In an artificial way - through the implementation of nosocomial infection. If during diagnosis and treatment medical personnel use non-sterile medical gloves, contaminated instruments, and neglect the rules of antisepsis and asepsis, then in such cases the risk of transmitting HPV to a woman during a gynecological examination increases.
Condylomas may appear for the first time during pregnancy if the woman became infected with the virus directly during this period. They may begin to grow more rapidly if infection occurred earlier. Pregnancy in this case is a trigger for the development of infection. In such cases, treatment of condylomas is carried out.
Condylomas treatment with folk remedies during pregnancy
Have you been trying to cure PAPILLOMAS and WARTS for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure papillomas by taking it every day...
Read more "
[content]
Warts are growths on the skin that are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). In fact, such a virus lives in the body of almost 90% of the world's population. However, some of its types can be dangerous. That is why pregnant women undergo a special test that helps identify the presence of dangerous types of HPV.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use Papilite to treat papillomas. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Warts themselves do not threaten health, but they can become a source of infection for others and discomfort for their owner.
Are warts dangerous during pregnancy?
In most cases, warts pose no danger to either the pregnant woman or the unborn child. Even if they are caused by some aggressive types of HPV.
There can be danger if warts are in the birth canal. These are so-called genital warts, which form in the vagina and on the cervix.
They pose a threat in that during childbirth the child may be infected with this virus.
Most doctors agree that if the warts do not cause too much discomfort and do not form again in significant quantities, then there is no need to touch them during pregnancy.
Removing warts during pregnancy becomes relevant in cases where they are in the birth canal or are really bothering the pregnant woman. For example, there are warts that constantly cling to clothing and become injured. Sometimes pregnancy reduces a woman’s immunity so much that warts begin to form in large quantities on the hands, face, and neck.
In these cases, it is necessary to resort to their removal, but many medications (even externally) cannot be used by pregnant women. Antiviral drugs also need to be used with great caution.
Doctors usually advise to “be patient” until all the child’s organs are formed in order to minimize the harm from the use of various drugs.
Thus, if a pregnant woman needs to remove warts, it is better to do this not in the early stages, but after 28 weeks.
Products for removing warts in pregnant women
The most important thing is that removing warts during pregnancy does not harm the unborn child. It means that:
- You should not self-medicate, but you should definitely consult a doctor,
- You should not use celandine, as it is a very poisonous plant,
- You should also not use the drug Superchistotel,
- It is not recommended to cauterize warts with liquid nitrogen.
- It should be taken into account that laser removal and electrocoagulation are not dangerous for the child, but the anesthesia that is used is extremely undesirable during pregnancy.
How and with what to remove common warts?
If a dermatologist still recommends removing warts during pregnancy, or a woman experiences too much discomfort because of them, then there are not many methods left.
To remove warts, the expectant mother can use:
- Laser or electrocoagulation, but without the use of anesthesia,
- Folk remedies: onion, garlic, chalk.
As a matter of fact, all other means are either dangerous or highly questionable. Some people remove warts using acetic acid. But this is a very aggressive chemical liquid. It is hardly worth experimenting with the health of the unborn baby, because everything that a woman uses, even externally, passes through the placenta to the child.
Removing warts with chalk
This is a very simple method, but it is not always effective. Take a piece of chalk and spread it thickly on the wart or sprinkle it with crushed chalk and apply a bandage for a day. Then we repeat the procedure for about two weeks. During this time, the wart may dry out.
Garlic for warts
There are quite a lot of recipes using garlic. The simplest and safest thing is to rub the wart with a cut garlic clove. This should be done 2-3 times a day under a bandage for 2-3 weeks.
However, don't expect miracles. Many people will try several wart removal methods before one works for them. Each person’s body is unique, and a pregnant woman’s body can react unpredictably to any treatment. Therefore, we repeat once again: perform any actions to remove warts only in consultation with your doctor.
Removal of genital warts
If you have warts in the birth canal, you should definitely undergo a Pap test and possibly a biopsy, which will determine whether the genital warts contain atypical cells.
The fact is that some types of HPV are dangerous due to the possibility of degeneration into oncology.
Further actions to monitor, treat and remove warts will be taken by the doctor depending on the results of the test and other examinations.
Source: https://papilloma-simptom.ru/lechenie/kondilomy-lechenie-narodnymi-sredstvami-pri-beremennosti/
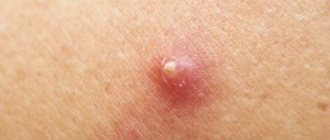
Why are genital warts dangerous during pregnancy?
photo of condyloma acuminata (venereal wart)
Condyloma is the epicenter of virus content. This happens due to the pathogenesis of HPV infection. After the virus enters the skin or mucous membranes, it penetrates the basal, lowest layer of the integumentary epithelium. There, the pathogen invades the nuclei of immature cells and gradually reaches the upper layer of the skin and mucous membranes, where a new viral particle is formed. Then HPV enters the surrounding healthy tissue, where it is able to give rise to new elements.
If a person’s immunity maintains its normal activity, the pathogen is destroyed or persists for a long time without manifesting itself. During pregnancy, condylomas may begin to grow. Infection with HPV for the first time during this period will ensure the implementation of the infectious process on the skin or mucous membranes of the genital organs.
Primary HPV infection during pregnancy is more dangerous than having condylomas in the past. This is due to the fact that during primary infection in a woman’s body there is no protective antibody titer that protects the fetus from HPV. Treatment of such condylomas is necessary.
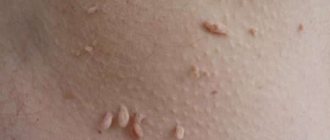
Genital warts can be located in the following places:
- Genital warts grow most often on the skin of the external genitalia.
- In the area of the vestibule of the vagina.
- On the walls of the vagina.
- On the surface of the cervix.
Danger of condylomas during pregnancy:
- HPV can be transmitted from mother to fetus both during natural birth and during fetal development through ascending infection through the membranes, as well as through the blood through the placenta.
- The causative agent of condylomas can negatively affect the development of the fetus. Against the background of an intensified infection, changes occur in the placenta. She gets fatter and ages earlier. In such cases, the nutrition of the fetus is disrupted, and the child is born with low birth weight. In addition, the risks of intrauterine infection increase due to the penetration of other bacteria and viruses into the fetus.
- HPV during pregnancy significantly disrupts the normal vaginal microflora composition, leading to dysbiosis, which provokes an exacerbation of chronic sexually transmitted infections, as well as the proliferation of opportunistic flora.
- During natural delivery, HPV enters the child's respiratory tract, which can lead to a very dangerous disease - respiratory papillomatosis.
Treatment of condylomas during pregnancy, localized on the cervix and vagina, is mandatory due to the anatomical proximity of the organs to the fetal membranes. In addition, this arrangement of elements will more quickly lead to the transmission of HPV through the blood.
Treatment of respiratory papillomatosis is complex. Children are treated with hormonal, cytostatic, immunostimulating drugs, as well as surgical treatment. There may be several operations. Often a child becomes disabled.
Oddly enough, numerous studies have established that infection of a child occurs both during passage through the natural birth canal and during cesarean section. Therefore, condylomas in pregnant women are not an indication for cesarean section. Doctors focus their actions not on the type of delivery, but on the full treatment and removal of such formations during pregnancy.
Popular types of treatment for pregnant women
The chief physician of Moscow City Hospital No. 62 describes his vision on this matter. Anatoly Nakhimovich Makhson Medical practice: more than 40 years.
“I have been treating people’s papillomas and warts for many years. I’m telling you as a doctor, papillomas along with HPV and warts can really lead to serious consequences if they are not dealt with.
The human papillomavirus is present in everyone on whose body there are papillomas, moles, warts and other pigmented formations. According to rough estimates, 80-85% of the planet's population has it. By themselves they are not dangerous. The problem is that an ordinary papilloma can become melanoma at any time.
These are incurable malignant tumors that kill a person in just a few months and from which there is no salvation.
Unfortunately, in Russia and the CIS countries, pharmaceutical corporations sell expensive medications that only relieve symptoms, thereby hooking people on one drug or another. That is why in these countries there is such a high percentage of cancer diseases and so many people suffer from “non-working” drugs.
The only drug that I want to recommend, and it is also officially recommended by WHO for the treatment of papillomas and warts, is Papinol. This drug is the only remedy that has an effect not only on external factors (that is, it removes papillomas), but also acts on the virus itself.
To find out more, read this article.
For the treatment of condylomas during pregnancy, each woman is given an individual regimen. The therapeutic course is selected taking into account all possible risks. If condylomas appear only in the anus, then removal is postponed until the postpartum period. The same situation applies to growths located on the outside of the genital organs. This doctor’s decision is due to the fact that the risk of infection is too small, and any actions can lead to a miscarriage.
In cases where the condition of a pregnant woman worsens, the following remedies are used to remove condylomas:
- acid solutions;
- laser removal;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen;
- exposure to radio waves;
- surgical removal with a scalpel.
Along with the destruction of the tumor, treatment is carried out with antiviral drugs. Most often, expectant mothers are prescribed rectal suppositories. Removal of condylomas is possible only from the fourth month of pregnancy. The optimal time for therapy is considered to be the last trimester of pregnancy. At this stage, the fetus is already practically formed and medications will not have a serious effect on it.
Due to disturbances in hormone levels during pregnancy, the clinical picture can be varied. Since blood circulation in the pelvic organs increases in pregnant women, the growths take on unusual shapes and develop at high speed.
DETAILS: Genital warts in women and men: treatment, removal, causes
It is advisable to check for the presence of human papillomavirus in advance, because treatment of condyloma during pregnancy is carried out only in the first trimester (with a risk - in the second).
Doctors often recommend removing pointed formations, because there is a danger of their uncontrolled growth in the future, which poses a risk of infection of the child during the passage of the birth canal (the newborn may develop laryngeal papillomatosis).
Some doctors insist that there is no need to treat these formations, because after childbirth they can resolve on their own. Most specialists prescribe treatment, possibly removal (only up to 28 weeks).
Removal of condylomas during pregnancy is a somewhat dangerous procedure that can affect the development of the baby. If it has been decided not to take risks and leave the growths intact, a cesarean section is prescribed instead of a natural birth (if the warts are localized in the vagina and its vestibule).
Since treatment and removal of condylomas during pregnancy with liquid nitrogen, laser and cytostatic drugs is contraindicated, doctors have to choose from the remaining methods:
- Use of acid solutions (Solcoderm combination ointment):
- Electrosurgery;
- Immunocorrection with interferon drugs (Cycloferon, Laferobion, Genferon, Viferon);
- Removal of growths using excision with a scalpel.
It is forbidden to take folk remedies without a doctor’s prescription, because they can harm an unformed fetus. If the formations are not located in the genital area on the mucous membranes, and they are not so extensive, you can use traditional medicine for targeted removal:
- Fresh juice or alcohol tincture of greater celandine;
- Castor oil;
- Juices of garlic, pineapple, dandelion;
- Juice or pulp from aloe and Kalanchoe leaves;
- Onion;
- Vinegar solution.
To prevent condylomas during pregnancy (see photo), it is necessary to avoid casual unprotected sexual intercourse, as well as strengthen the immune system so as not to catch ARVI and infectious diseases.
You can get rid of condyloma in pregnant women in a variety of ways. There are many innovative and completely painless options, but the situation here is much more complicated. Because during pregnancy, treatment options are limited.
So there are two treatment options left. The first involves direct exposure to lesions of epithelial tissue. And the second is based on working with the immune system, improving its functioning so that it can fight infections on its own. You can also combine them.
Is it possible to remove condylomas during pregnancy using surgical excision? This procedure is one of the oldest and, unfortunately, not very safe. It is prescribed when a woman has large tumors, as well as to those who, for financial reasons, cannot afford a safer method.
The disadvantages of the procedure are the following factors:
- high risk of bleeding;
- possible infection;
- stitches after the procedure;
- long recovery period, etc.
Not all tumors can be removed by surgical excision. For example, nulliparous women are prohibited from undergoing the procedure. In any case, you should consult your doctor before starting the procedure.
Treatment of condylomas in pregnant women
Carrying out colposcopy
If a woman develops genital warts during pregnancy, she should contact a gynecologist to decide on the method of removing the elements and the volume of treatment.
In what cases is it worth removing and treating condylomas during pregnancy?
- Multiple condylomas of the external genitalia and anal area.
- Localization of elements in the vagina and cervix.
A single wart located on the inner surface of the thighs or on the skin of the genital organs, away from the vestibule of the vagina, does not need to be removed. Such formations usually regress after childbirth.
Treatment of anogenital warts is carried out using medicinal and surgical methods permitted during pregnancy.
- Acids – Collomak, Duofilm. Local acid-based preparations cauterize the wart. Acids are used in the presence of elements of small size and quantity (total affected area no more than 5 cm). Removal must be carried out on an outpatient basis. Only a doctor can accurately apply the genital warts to the area.
- Immunomodulators (Viferon, Genferon, Cycloferon) are used for a large area of damage and for localization of formations on the cervix and vagina. Treatment is carried out after the 12th week of pregnancy.
- antiviral drugs (Panavir) for severe illness, as well as in combination with other diseases that suppress the immune system (HIV, hepatitis, tuberculosis, any chronic infections).
- Removal condylomas by physical means:
- Laser method.
- Cryodestruction.
Physical treatment is carried out without pain relief. There are no pain receptors on the cervix, so manipulation only brings discomfort.
After removal of formations in the vagina or cervix, the doctor must prescribe immunomodulators. During manipulations to remove warts, the virus spreads to healthy tissue, so it is necessary to prevent their regrowth with medications.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
Genital condylomas are one of the forms of papillomatosis. The culprit of this disease is the human papillomavirus or HPV. Infection occurs exclusively through contact.
The favorite location of condylomas is the reproductive organs of both women and men, the perianal fold, the anus and urethra, the rectum, the inner part of the urethra, the buttock area, the cervix and, in rare cases, the tongue and larynx.
- severe itching at the site of virus penetration;
- pain in the area where condylomas appear;
- problems urinating or defecating if the wart appears in the rectum or urethra;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- bleeding when tumors are damaged.
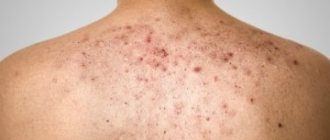
In appearance, condylomas resemble broccoli or cauliflower inflorescences. The color of the neoplasms ranges from flesh-colored to pink on the mucous membranes to brown on the skin in the anal area. The size of a single vegetation does not exceed 0.7 cm. If several neoplasms merge, the diameter can reach several centimeters. If growths or any alarming symptoms appear, you should contact your local gynecologist.
Diagnosis of condyloma in pregnant women is carried out according to standard medical protocols:
- Visual examination by a doctor of the external intimate organs and examination of the internal walls of the vagina and cervix in the mirrors.
- Smear test for sexually transmitted diseases to rule out bacterial infections.
- PCR analysis to confirm the diagnosis and determine the type of virus. There are 2 types of HPV - low-oncogenic strains - that is, the likelihood of degeneration into a cancerous tumor is insignificant and highly oncogenic strains. The latter provoke the development of cervical cancer pathologies.
An indirect sign of a highly oncogenic formation is the location of the tumor - on the cervix - and its appearance. If a classic pointed papilloma is detected, then the risk of degeneration is low, since such neoplasms are caused by low-oncogenic strains. If a flat, wide wart is diagnosed that grows deep into the tissue, then a biopsy of the tumor is indicated to determine the nature of the growth. The likelihood of developing cervical cancer in this case is extremely high.
Prevention of the growth of condylomas during pregnancy
In order to protect yourself and your child from the dangers of HPV, every pregnant woman needs:
- Plan a pregnancy. The doctor will prescribe an examination for all infections, including viral ones. Often, various types of virus persist in the genital tract of women, both high-risk carcinogenesis - causing dysplasia and cancer, and low-risk - initiating the growth of condylomas. Therefore, prescribed antiviral and immunomodulatory treatment before conception will avoid the growth of warts with decreased immunity. In addition, during examination, the doctor will differentiate benign neoplasms of the skin of the genital organs and will advise their removal.
- If genital warts do appear during pregnancy, they need to be treated and removed. The drugs and methods used are safe for the fetus.
- After pregnancy, you should visit your doctor regularly. The specialist will notice changes in the skin and cervix in time.
- It is worth protecting yourself from hospital-acquired infection. Before the upcoming gynecological examination, you need to purchase disposable kits at the pharmacy, including a gynecological speculum, sterile gloves and a diaper, a Volkmann spoon and a cytobrush. You should not be embarrassed to remind the doctor to wash and treat your hands with antiseptic if he did not do so before the examination.
By following the recommendations of a gynecologist, a pregnant woman will protect her child from the dangers of the human papillomavirus. At the initial stages of growth of condylomas, modern treatment methods can completely prevent the effect of the infectious agent on the health of the mother and fetus.
Types of growths
Condylomas can be of various shapes, their parameters vary from 2 mm to several centimeters. The color of the growths is most often gray or pale pinkish. At the initial stage of the disease, condylomas develop separately from each other and represent single neoplasms. Over time, if left untreated, the growths can grow together, forming large, extensive areas of damage. From a medical point of view, such growths are divided into 2 types:
- Flat. This type of condylomas grows on the cervix. Their size is so small that it is almost impossible to examine them without a microscope. It is this feature that makes diagnosis and timely treatment difficult, increasing the risk of cancer and oncological processes in the uterus.
- Pointed. The most common type of condylomas. They are often found in the vagina, clitoris, anus and labia. Genital warts can also be found in the groin, buttocks and thighs.
You can, if you wish and in accordance with the recommendations of your doctor, choose the following method:
- using radio waves - in this case you can be completely calm, all problems will be solved within a few seconds, and you will not experience any unpleasant sensations, everything is done with modern equipment;
- Using liquid nitrogen freezing is also a popular method. It is carried out only by a specialist. There is no pain during the removal process. The only unpleasant sensation that may occur is a burning sensation.
- using a laser - it acts quickly and effectively, but doctors do not recommend using it in cases where the formations are large in size, since a mark may remain on the epithelial tissue;
- using a scalpel - in this case, anesthesia is used, a rather rare technology, carried out mainly in those who have a risk of developing a malignant tumor.
DETAILS: Condylomas and papillomas difference photo
After the doctor conducts therapy, you do not say goodbye to him. Immunotherapy will be prescribed to prevent the virus from becoming active. Over time, you will be able to completely get rid of this problem. But doctors still recommend visiting your gynecologist about this at least once every six months to prevent serious problems.