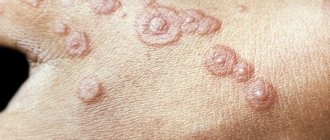
Symptoms and treatment of fungus on the skin of the face + photo.
Can there be a fungus on the face? The answer is yes.
Fungus on the face does not manifest itself as often as mycosis (fungal infection) that affects the skin of the body, feet or nail plates.
But in any case, superficial skin mycoses, in particular, fungus on the face (photo) disfigures the skin and can provoke a severe allergic reaction.
Children, especially infants and the elderly, are most susceptible to this disease, since the infection is activated when the body's immune forces cannot resist microscopic pathogens.
- Causes of fungus on the face
- Symptoms of fungus on the face
- Treatment of fungus on the face
- Traditional medicine for fungus on the face
Why does fungus appear on the face?
Fungus on the face appears due to the penetration of pathogenic microflora through damaged skin (scratches, microcracks). In this case, mycosis of the beard develops only against the background of decreased immunity.
The following factors weaken the body’s defense mechanisms:
- diabetes;
- vascular diseases;
- dysfunction of the digestive system;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hyperhidrosis;
- infectious pathologies.
Mycosis of the beard develops if personal hygiene is not maintained.
The cause of the disease may also be due to the negative influence of the external environment. Under the influence of these factors, fungi begin to actively multiply, and therefore an inflamed area forms on the forehead, cheek and other parts of the skin.
Beard mycosis is a contagious pathology. The infection can enter the body through clothing or other objects that contain particles of skin or nails containing fungal microflora. Possible causes of infection include direct contact with the affected area on the body of other people. This explains the high prevalence of mycoses among children.
Common causes of mycosis
You should not start treatment and panic just because epidermophytes live on your face. In fact, these are quite harmless microorganisms. Dead cells of the epidermis provide food for them, and the best conditions for development, as for all fungi, are a moist and warm environment.
That is why on dry areas of the skin the fungus develops almost asymptomatically.
There are only three main causes of mycosis:
- microtrauma of the skin,
- increased humidity and sweating,
- warm environment.
In no case should we forget about the basic rules of personal hygiene. After all, you can easily become infected from an already sick person. Typically this happens through the following items:
- towels and washcloths,
- cosmetic devices,
- someone else's shoes, if we are talking about foot fungus.
The first on the list of places where infection most often occurs are bathhouses, saunas, communal showers, swimming pools and similar public institutions.
For many people, persistent itching of the feet and skin between the toes caused by the fungus does not seem to be such a concern that it is worth seeking immediate treatment. Moreover, you can put on socks and shoes, and this disease will be securely hidden from prying eyes. There is no way to do this if the fungus appears on the face.
For early diagnosis of such a disease, general symptoms of fungal diseases are used:
- quite severe itching
- peeling of the skin,
- the appearance of painful rashes, cracks and ulcers.
In laboratory conditions, a detailed examination of the affected skin can be carried out. To do this, a test scraping is taken, which contains flakes of skin.
Some people are most susceptible to a disease such as mycosis. This is the so-called risk group. It includes:
- athletes,
- military personnel,
- people who sweat excessively
- people who neglect personal hygiene.
Classification
There are many varieties of fungi that affect different parts of the body.
Trichophytosis
Mycoses on the face come mainly in the following forms:
- trichophytosis;
- candidiasis;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- rubromycosis;
- microsporia.
The activity of trichophytosis leads to the appearance of inflamed areas on a person. The disease caused by this pathogen provokes the formation of large spots on the skin, inside of which small nodules form. The development of pathology is accompanied by suppuration of the skin.
Candidiasis occurs due to infection of dermal tissues by yeast fungi. The latter mainly provoke the development of thrush or stomatitis, depending on the zone of localization of the pathogenic microflora (genital organs and oral cavity, respectively). More often, candidiasis occurs in children.
Manifestation of candidiasis on the face
Tinea versicolor also occurs due to the activity of yeast-like microorganisms. This type of fungus appears as a small spot that has a reddish or pink tint. Without treatment, the affected area increases. As the disease progresses, the number of spots that merge with each other increases.
Seborrheic dermatitis in rare cases provokes mycosis of the beard. The disease affects the scalp and causes dandruff. If adequate therapy is not carried out, then as the infection spreads to the face (mainly the forehead), the skin begins to peel off. Subsequently, hemorrhagic crusts form in the problem area.
Rubromycosis rarely develops on the facial part of the head. This is explained by the fact that the fungus Trichophyton rubrum mainly affects the feet or large folds of skin. But sometimes an infection develops in the vellus hair growth area. The course of the inflammatory process characteristic of rubromycosis is accompanied by the formation of papules.
Microsporia develops as a result of infection of the body with a fungus that is transmitted through contact with animals or soil. The course of the pathology is accompanied by the formation of a large red spot surrounded by a cushion.
Microsporia
General symptoms
The nature of the clinical picture for mycoses on the face depends on what kind of infection people have become infected with. However, the course of most fungal diseases is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- formation of red (pink) spots of various sizes;
- peeling of the upper layers of the skin;
- intense itching in the affected area;
- rashes, ulcers.
At the last stage of development of mycoses, cracks often form in the problem area, which creates favorable conditions for the addition of a secondary infection. The latter, having penetrated into the subcutaneous layers, provokes suppuration of local tissues and increases the intensity of the manifestation of the underlying disease.
The development of the inflammatory process caused by fungi is accompanied by dry skin. In some cases, the disease occurs in an atypical form, which is characterized by the absence of itching and peeling. Due to the influence of fungal microflora on the skin, pigment spots are formed.
It is recommended to begin treatment of mycoses at the initial stages of development of the inflammatory process, when itching and red spots appear on the face. In this case, drugs used against fungi are prescribed only after the type of pathogenic agent has been established.
Treatment of mycosis
At an advanced stage, the fungus can greatly harm a person’s appearance. Even looking at photos of people with similar problems can cause disgust, and seeing such a picture “live” is not worth talking about. The patients themselves understand this, but due to ignorance, their independent treatment comes down to the use of extremely ineffective, and sometimes even aggravating, methods.
A terrible appearance is not the only danger that mycosis poses. Other consequences are also possible:
- large-scale spread of the disease (up to internal organs),
- various complications due to side infections,
- the likelihood of developing chronic pathology of blood vessels,
- allergic reactions.
All this is a consequence of everyday poisoning of the body with waste products of fungi.
Since his very appearance, man has cohabited on the planet with such an enemy, so many means have been developed to combat him. But despite this, treatment of the disease is difficult.
As a rule, general therapy includes several methods that act in many ways:
- application of ointments, aerosols and creams,
- taking medications that stimulate immunity.
Recent developments in the production of creams and ointments are the most effective, but their disadvantage is high toxicity and allergenicity. Therefore, for some people they are simply contraindicated.
In cases where the disease manifests itself on the face, the situation becomes even more complicated. After all, some drugs have an extremely aggressive effect, so treating areas with delicate skin with them is undesirable.
In this case, mycoses on the face are no exception. The sooner the diagnosis is made, the greater the chance of preventing the spread of the disease.
As for choosing a specific drug, you need to pay attention first of all to the following criteria:
- application area,
- the amount of active substance in the composition,
- safety,
- contraindications.
Treatment is most effective if drugs such as Orungal, Duflucan and Lamisil are used. They can be freely used on the face.
Drug therapy
In the treatment of mycoses, a complex of methods is used, providing for local, systemic and symptomatic treatment of the pathology.
To get rid of fungus on the face, you need the following medications:
- vitamin complexes;
- antifungal drugs;
- probiotics, enzymes;
- antihistamines.
The list of the best agents that suppress fungal microflora includes ointments and creams:
- "Mikoket." The cream is based on ketoconazole, which destroys yeast-like fungi. The product is applied to the skin for two weeks or longer.
- "Miconazole". The active components of the product destroy fungi of various strains. Miconazole is recommended to be applied twice a day.
- "Orungal." The drug has a good antimycotic effect. The product inhibits the production of a special enzyme by fungi that supports the vital activity of pathogenic microflora. "Orungal" is effective against most strains.
In advanced cases, complex drug treatment will be required, including taking medications in the form of tablets and treating the problem area with effective topical medications.
The first include:
- "Diflucan";
- "Orungal";
- "Lamisil";
- "Clotrimazole".
To avoid secondary infection, antiseptic compounds should be applied to the skin after the formation of open wounds. If ulcers appear in the problem area, you need to treat the skin with Cephalexin for several days. Solutions based on Gentamicin or syntomycin ointment will help relieve inflammation.
Folk recipes
Treatment of mycoses at home can be supplemented with traditional medicine:
- Lemon juice. The latter should be applied to problem areas several times a day. Lemon juice is not recommended for treating open wounds.
- Chopped onion or garlic with butter. The mass obtained by mixing the ingredients must be applied to problem areas and left for about 30 minutes. The product should not be used if you are hypersensitive to garlic and onions.
- Raisin. The dried fruit should be cut in half and rubbed several times a day into the affected tissue.
- Horsetail decoction. You should rinse your face with the product 3-4 times a day.
- Celandine lotion. To prepare the product you will need 10 g of dried plant and a liter of boiling water. Celandine is soaked in water for 10 minutes. Wipe the skin with a warm solution twice a day.
Freshly brewed coffee without sugar helps suppress itching. If you are not allergic to honey, it is recommended to treat problem areas with propolis tincture. This remedy prevents the addition of a secondary infection and suppresses the inflammatory process.
Prevention
To avoid the development of mycoses, it is necessary to constantly maintain immunity. Proper nutrition and regular intake of vitamin complexes help achieve this.
Skin care is also important. It is highly recommended not to use other people's towels or cosmetics. Prevention of mycoses involves limiting contact with persons during periods of exacerbation of similar diseases.
In addition, you need to monitor the condition of the dermis. Dry skin should be treated with moisturizing creams, and wounds with antiseptic compounds.
Mycoses develop against the background of infection of the body by fungal microflora. The activity of the latter is suppressed by a strong immune system. But under the influence of provoking factors, fungi cause itching and flaking of the skin. In the treatment of mycoses, a complex of drugs with local and systemic action is used.
Treatment options
Effective treatment of skin fungus can only be achieved if you have found out which species caused your disease. For this reason, you should not put off visiting a dermatologist.
Different types of infections will be treated completely differently. However, there are some drugs that are mandatory in the treatment of fungus - antimicrobial agents, as well as some antifungal drugs. In addition, vitamin complexes should be prescribed.
For example, we can cite some drugs that are included in the treatment of fungus, however, you should not use them without prescription and without the supervision of a dermatologist, since each of them has its own list of contraindications:
- amphotericin,
- ketoconazole,
- fluconazole,
- various solutions and ointments for external use (levorin ointment, triderm and others).
Most antifungal drugs are very effective, but many of them have a big drawback - they are toxic. Therefore, treatment with such drugs is prohibited for people who suffer from:
- renal or liver failure,
- oncological diseases,
- metabolic disorders,
- blood diseases,
- pathology of the vessels of the extremities.
Even if the patient does not have the above diseases, serious consequences can still occur with frequent use of such drugs.
It is especially necessary to carefully monitor the prescription of such drugs to children, since the toxic effects of such drugs are more dangerous for them than for adults.
Also, treatment of the fungus should be carried out immediately because the presence of mycoses in the body for a long time has a detrimental effect on humans. Thus, the waste products of these parasites have a poisonous and toxic effect on the body, which can cause viral and bacterial complications.