The human body contains a certain number of pathogenic microorganisms that do not cause any discomfort. But favorable conditions for them become a predisposing factor for their activation and rapid reproduction. As a result, they affect the beneficial microflora of the body, upset the balance and lead to various diseases. One of these pathologies is armpit fungus.
Causes of the disease
In the armpit there is a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, people with severe sweating, diabetes and excess weight are susceptible to armpit diseases. This is often influenced by a hygienic factor: hair removal with a razor, which creates microtraumas into which microbes can enter. According to statistics, the most common cause of the disease is frequent stress. In addition, there are the following predisposing factors:
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, menopause or puberty;
- heredity;
- thyroid diseases;
- viral infections;
- tuberculosis.
The development of fungus in the armpits is influenced by reduced immunity, use of antibiotics and childhood, at which mycosis manifests itself in the form of diaper rash. Doctors identify the following as aggravating factors:
- scratching under the arms;
- lack of hygiene;
- wearing clothes made from non-natural materials;
- poor nutrition.
In adults, the reasons are supplemented:
- frequent shaving, as a result of which the skin becomes dry and microtraumas appear;
- increased sweating;
- vegetation under the arms.
Mycosis of the armpit also manifests itself with decreased immunity.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a patient suspects lichen or fungal diseases, or if red itchy spots appear in the groin area or armpits, be sure to make an appointment with a dermatologist for diagnosis. It is important to determine what the cause of the disease is - lichen, candida or a fungus of another origin.
Dermatologists are admitted free of charge; if you have a medical policy, all costs will be borne by the Insurance Company. If the patient wants to undergo an examination anonymously, he can contact a paid diagnostic center.
Symptoms and signs
Any fungal infection of the skin does not go away without obvious symptoms:
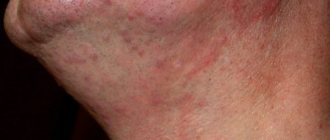
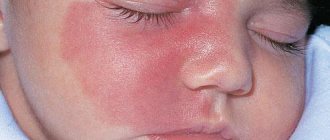
- the skin under the arms takes on a red tint;
- severe itching appears;
- the smell of sweat intensifies;
- microtraumas appear;
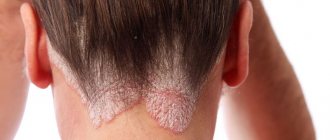
- the skin under the arms becomes hard.
Often, fungal skin infections are accompanied by a secondary infection, after which rashes and peeling appear. They can be in the form of small blisters or ulcers.
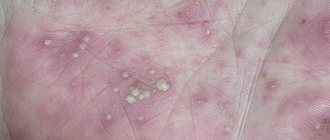
Also signs of mycosis are redness of the affected area and white plaque in the folds of the skin. In addition, there is severe itching and a sour smell of sweat. Since there is always a warm and humid environment under the armpits, the disease can develop into a complicated form without treatment.
Symptoms
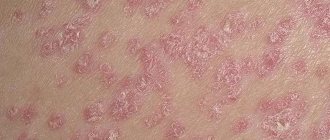
The proliferation of fungi in the armpit is accompanied by symptoms similar to other skin diseases (neurodermatitis, dermatitis, pityriasis rosea), so mycosis of the armpits is easy to confuse. The main symptom is a characteristic powdery white coating on the hair in the armpits. A fungal infection in a severe stage can affect the hair on the entire body and nails, which become yellowish-dirty in color. The main symptoms of mycosis of the armpits:
- peeling and roughening of the skin;
- redness accompanied by itching;
- cracks and sores, which over time begin to itch unbearably;
- unpleasant smell.
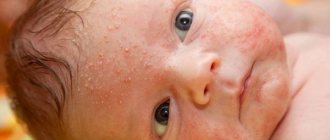
A child has a red spot under his armpit
Red spots in the armpits of children do not always indicate mycosis. This may be erythrasma, a pathology that has a similar etiology to fungal infections. The red spot may be a consequence of the development of ring-shaped lichen or neurodermatitis. In any case, if such a symptom is detected, the child should be shown to a dermatologist, but under no circumstances should he treat it himself. With incorrect therapy, you can not only aggravate the situation, but also provoke serious complications.
Types of fungus under the arms
This type of disease can manifest itself in different forms, which have certain symptoms:
- Linear - appears in the form of small spots and lines. They can be pale pink or brown in color. The skin is very itchy and flaky.
- Pink – dozens of small spots. They are pink in color and covered with scales. Sometimes small bubbles may appear.
- Pityriasis - appears as small brown spots, which may later change color to pink, yellow or red.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, a dermatologist must first examine the affected area and give a referral for examination. In such cases, he prescribes:
- Urine analysis for the presence of inflammatory processes in the body and for sugar.
- Taking a smear from the affected area (this is one of the accurate methods of diagnosis). It is taken by scraping from the site of the fungus, which is placed in a special environment, where the doctor observes it for about 2 weeks. During the growth process, the type of fungus can be determined. The disadvantage of this procedure is its duration.
- Wood's lamp - UV rays cause the fungus to glow. Using this method, you can quickly and accurately make a diagnosis.
Your doctor may order a test in which the affected area is coated with aniline dye and iodine.
If the skin becomes dark, it means the patient has a fungus. Only after this is an accurate diagnosis established: psoriasis, lichen or seborrhea, and a treatment method is selected.
Modern diagnostic methods
As a rule, to determine the type of fungus, it is enough to take a scraping from the affected area. Experienced doctors sometimes only need to conduct a visual examination and listen to the patient’s complaints in order to accurately determine the cause of the pathology.
The sooner treatment begins, the greater the chance that it will be successful and the fungus will not spread to large areas of the skin. In some cases, if chronic diseases of internal organs are suspected, a dermatologist may also refer the patient to undergo a general or biochemical blood test. This is required in order to identify the underlying disease (perhaps the patient has diabetes, problems with hormones, liver or pancreas diseases) - and treat it, which will have a positive effect on the condition of the skin.
Drug therapy
As a medicinal treatment, a set of drugs is selected to disinfect the affected area. During the treatment process, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- choose clothes only from natural materials;
- take a shower more often, especially in hot weather;
- do not visit public swimming pools and baths;
- have personal hygiene items;
- take vitamins and minerals;
- eat right, eat more proteins and exclude bread, kvass, sweets and spicy foods from your diet.
Before applying any drug to the skin, you need to:
- take a shower and dry your skin;
- treat the affected area with an antiseptic;
- apply an antifungal drug;
- wear clothes made from natural fabric.
Fukortsin, Iodine 2%, and hydrogen peroxide can be used as antiseptics. Ointments are usually prescribed:
- Tinedol;
- Lamisil;
- Clotrimazole;
- Terbinafine;
- Salicylic or zinc ointment;
- Nystatin ointment - it destroys fungal cells even at advanced stages of the disease.
Antifungal agents may also be prescribed, such as:
- Exifin;
- Fungoterbin;
- Mikonorm.
Treatment with medications
To get rid of the disease, complex treatment is used, which combines external medications in the form of ointments and solutions with systemic tablets. The choice of drug depends on the stage of infection and the general condition of the patient. In the early stages of the disease, when the symptoms are mild, the fungus can be cured with topical medications:
- Terbizil, a product in the form of an ointment, the active elements of which penetrate the cellular structure of the pathogen and destroy it from the inside, relieves inflammatory processes, eliminates peeling;
- Terbinafine, an antimycotic ointment, can be used in the form of a spray, helps against all types of pathogens, including yeast;
- Lamisil, a drug based on terbinafine, has a similar effect, suppresses the activity of the parasite, causing its death;
- Exifin destroys the cellular structure of all types of fungal infections, eliminates the external symptoms of the disease;
- Atifin, another cream with the active ingredient terbinafine, depending on the type of pathogen, acts through the destruction of cellular structure or suppression of its activity;
- Fungoterbin, when used as a spray, is sprayed onto the affected area, in the form of a cream, applied in a thin layer under gauze;
- Clotrimazole acts as it accumulates in the skin, is most effective at an early stage, and belongs to the category of the most effective antifungal agents;
- Mikonorm destroys all types of fungal infections, including lichen, and can be used as a prophylactic.
More on Med-Gribok.Ru:
Fungus in the ears: symptoms, causes and treatment
Salicylic or zinc ointment is used as cheap analogues of the listed drugs. To effectively use the listed drugs, the skin at the site of the lesion must be:
- washed thoroughly;
- dried with a soft towel that does not injure the affected area;
- coated with a thin layer of cream or ointment.
The frequency of use and duration of the course are determined by the instructions or instructions of the attending physician. It usually takes 2 to 6 months for complete recovery. The list of contraindications for ointments is small, usually it includes:
- intolerance to components;
- periods of pregnancy and lactation;
- age restrictions for children.
In the later stages of the disease, complex treatment with systemic drugs is required. In severe cases, injectable medications may be prescribed, but these are mainly medications in tablet form:
- Fluconazole.
- Itraconazole
- Ketoconazole.
- Mikozan.
It is not recommended to use these drugs on your own; you can expect positive results only if prescribed by a doctor. In addition to drug treatment, a physiotherapeutic method using ultraviolet irradiation is used. The procedure is carried out in a clinic, the session takes up to 20 minutes. The course includes 4 to 5 sessions.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of combating armpit fungus are quite effective, but they only help overcome unpleasant symptoms, so their use is rational only together with medications. The most common ways are:
- Treat the affected area with a strong solution of potassium permanganate. It can also destroy germs that have not yet penetrated deep into the skin.
- Lotions made from a decoction of valerian root, licorice, elecampane, burdock, jasmine and violets. They need to be taken in equal proportions, 1 tsp each, and poured with a liter of water. Put all this on the fire and boil for several minutes.
- Lubricating the armpit with a tincture of carrot juice and apple cider vinegar in equal proportions or a solution of novocaine.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor your health and follow certain rules:
- Do not use other people's towels and personal hygiene products.
- Do not wear synthetic clothes and give preference to natural materials.
- Change T-shirts and T-shirts more often.
- Use antiperspirants.
- Monitor your diet and weight.
- During armpit treatment, avoid hair removal.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, you can cure armpit fungus quickly and forever.
Causes of mycosis of the armpits
In addition to excessive sweating, the cause of armpit fungus can be:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Decreased immunity: condition after acute infections, cancer, HIV.
- Endocrine diseases - hyperthyroidism, diabetes, obesity.
- Hormonal “bursts”: puberty, menopause.
- Acute and chronic stress, depression, neuroses.
- Work in hot and dirty rooms.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
More on the topic: Simple remedies to combat underarm sweating
Risk factors include microtrauma to the skin caused by shaving, the use of aggressive deodorants, or rubbing with tight or synthetic clothing.
In infants, the fungus can develop due to an allergic reaction, prickly heat, or poor hygiene. In addition, the skin of a newborn has an increased moisture content, which creates favorable conditions for the development of fungus.