Candidiasis
Candidiasis includes fungal infection of the mucous membrane of internal organs, mucous membranes of the mouth, nasopharynx, and vagina.
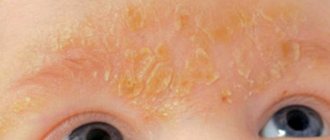
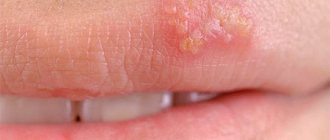
Oral mycosis is most often caused by fungi of the Candida albicans family. Even infants who become infected with a fungus (thrush) through their mother's milk are susceptible to the disease. The fungus affects the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, the red border of the lips (cheilitis) and the corners of the mouth.
Most often, children suffer from two types of fungal infections in the throat:
- Yeast cheilitis. Lips turn red and swell. The skin begins to peel off and become covered with a grayish film. When you try to remove it, bleeding begins. The child may complain of itching and burning.
- Yeast erosions in the corners of the mouth. They are a consequence of yeast cheilitis. Forms in the corners of the mouth. The skin begins to peel, crack, and redness is pronounced. It is painful for the child to open his mouth.
Candida fungus in children is difficult to treat and is recurrent.
Candidal lesions of the gastrointestinal tract
- Candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract
Among fungal infections in newborns, gastrointestinal candidiasis ranks third. The causative agents of this disease, Candida fungi, can quite often cause damage to various organs and affect the development of:
- gastroduodenitis;
- enterocolitis;
- erosive gastritis;
- esophalitis;
- enteritis;
- other types of diseases.
In the gastrointestinal tract, lesions appear when a colony of fungi outgrows a certain amount. Candidiasis can affect both individual organs and the entire gastrointestinal tract.
Gastrointestinal candidiasis very often occurs along with skin candidiasis localized around the anus, or in the form of inflammation on the skin of the buttocks. Candidiasis of visible mucous membranes may be accompanied by intestinal or gastrointestinal candidiasis.
- Candidal esophagitis.
This disease manifests itself already on the 2nd day of the baby’s life. For all cases of intestinal candidiasis, the characteristic features for children are:
- excessive regurgitation;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- “rumbling” in the intestines;
- bloating;
- decreased appetite;
- anxiety when feeding.
With this type of candidiasis, the vomit may acquire a whitish or greenish color and contain admixtures of mucous fractions. The stool is greenish-yellowish in color and is characterized by a mucous consistency mixed with whitish lumps.
Candidiasis in newborns, better known as thrush, is a disease caused by yeast-like fungi belonging to the genus Candida and which are opportunistic microorganisms.
This disease is very common in pediatric practice, since children are characterized by an imperfect immune system. Defects in care also play a role in this.
Dermatomycosis
- Pityriasis versicolor. Most often occurs in school-age children prone to hypersweating. Area of infection: rashes on the chest, back, abdomen, neck, arms and legs. Symptoms: yellowish spots on the skin, peeling of the skin, depigmentation in the affected area.
- Microsporia. Most often the causative agent is a zooanthropophilic dermatophyte (when the carrier of the disease is an animal). The incubation period of the disease is up to seven days.
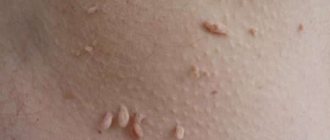
- Epidorphytia. The fungus primarily affects the child's nails and body. The fungus is localized in the groin area and foot area. The route of infection is household items.
- Favus. Chronic disease of nails, internal organs, hair. Most often found in hot countries with high humidity (Africa, Türkiye). The fungus is transmitted through household contact.
- Sporotrichosis. Lives in soil or plants. After entering the human body it causes suppuration and ulcers.
- Rubrophytia. Symptoms are pinkish-red lesions on any part of the skin. The skin becomes covered with blisters, papules and crusts.
Let's recognize the cause of the phenomenon
Nail fungus in infants and newborns, like a number of other diseases, is most often associated with a genetic predisposition. Other reasons are:
Overheating and dampness can cause nail fungus in infants
- excessive humidity and dampness in the house (this is a favorable environment for the growth and development of various types of fungi);
- presence of chronic diseases;
- reduced immunity;
- vitamin deficiency (initially, hangnails and white spots appear on the nail plates);
- using nail care products that were used by another family member (for a newborn child, personal hygiene products must be individual);
- mechanical damage (nail injuries).
Doctors note that most fungal infections affect the toenails, so be sure to keep them clean, warm and dry. A baby can also become infected from an adult if he or she has similar problems.
Medical treatment of fungus in children
At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor. The first thing you need to do is undergo a visual inspection. Then, based on the data obtained, the specialist writes out a referral for the following tests: scraping from the affected area, analysis of the blood and contents of erosions.
Today, dermatologists recommend the following general-spectrum medications to combat mycosis in children:
- Diflucan;
- Nizoral;
- Nystatin;
- Clotrimazole;
- Flucostat;
- Exoderil.
Medicine can only be prescribed by a dermatologist after examining the patient. Before using the prescribed drug, you must carefully read the instructions.
Also, a specialist for treating certain types of fungi (seeds, cheilitis) will prescribe solutions for treating the affected area, for example, iodine, salicylic acid, glycerin, naphthalan-salicylic ointment. After completion of treatment, it is necessary, as a preventive measure, to drink a complex of vitamins B, C and K.
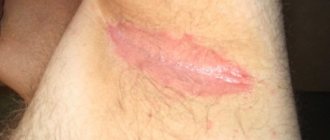
Variants of skin candidiasis in newborns
Cutaneous candidiasis in newborns affects either the folds of the skin, or directly smooth skin, or exists in the form of a mixed version.
In the first case, wetting occurs in various folds of the skin, for example, in the groin or armpits, and sometimes in the neck area, the skin acquires a reddish tint, and its upper layers die to form an eroded surface.
In the second case, pink papules with uneven scalloped edges form on the baby’s tummy, back, limbs and face. Bubbles appear on the top of these formations, which soon burst, leaving behind erosions.
If there is a mixed variant of skin candidiasis in a newborn, the clinical picture will show a combination of the above symptoms.
In most cases, there is a mild variant of the disease with a small number of rash elements. In premature babies, a severe variant may develop, in which the rash covers the entire body and the general condition of the baby is disrupted. Such children cry all the time, have difficulty latching on the breast, and have difficulty falling asleep. If a bacterial infection is added to the fungal infections, the child’s condition will worsen in many ways.
Folk remedies
If the first signs of fungal infection are noticeable in children, then folk remedies that can be used as a preventive measure for the disease will help relieve the unpleasant symptoms of itching and burning:
- Herbal baths. Boil 500 grams of wormwood and boil. Let it brew, then strain and pour into a bowl. Steam your child's feet before bed.
- Sea salt . You can also steam the legs in regular salt. It is enough to add 4-5 tablespoons of salt to warm water. Hold the area where the fungus appears in the bath, then wipe it off and wrap yourself in warm clothes.
- Mint . Used for mycosis of the feet. It is necessary to cut 50 g of fresh leaves and pour them into two bags, which must be put on and carried for two hours.
- Tea tree oil . Excellent for treating fungus-affected areas. Use the product for at least two weeks.
Such measures are effective only in the initial stages of the disease, when symptoms such as redness and peeling appear.
Traditional methods will alleviate the symptoms of fungus, but will not cure the disease!
Fungal infections in children must be treated and the disease not progressed.
Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis in newborns
From an oral cavity infected with pathogenic fungi, the causative agent of the described disease may well enter the digestive tract and exert its pathological effect on it. This happens when food is swallowed.
The most significant manifestations of intestinal candidiasis in a newborn are symptoms such as diarrhea, increased gas production and intestinal cramps that occur after feeding. The stool is usually yellow in color and may also contain white flakes.
It is not at all necessary that the baby will develop all these signs of the disease. Some symptoms may not be observed or may occur in the form of minor changes in the baby’s condition.
Fungus prevention and child hygiene
As practice shows, children catch the fungus in public places. Therefore, parents need to pay attention to hygiene procedures for themselves and their child in order to prevent the disease. Use the following tips:
- High quality shoes. Choose shoes according to the season and from natural materials. The baby's feet should not swell during the warm season. Treat the surface of shoes and insoles with an antimycotic spray in a timely manner;
- Public places. Use rubber slippers in the pool and on the beach;
- Animal carriers. Prohibit contact with street animals - cats, dogs, pigeons;
- Hygiene. Use personal care products (scissors, files). After a shower, you need to dry your feet.
Traditional medicine to help
Despite such a large selection of medicines, many still prefer traditional medicine methods, and believe that they work no worse than the “chemistry” we are used to.
However, it is worth noting that a child’s body is more susceptible to allergic reactions than an adult, therefore, when choosing traditional medicine methods, you need to be especially careful. Among the “natural” medicines are:
- Infusions: strong green tea, chamomile infusions, and aloe;
- Natural oils: flax, rosehip, peach.
Dear parents, if your child, who is old enough to eat everything, has a fungus, then please limit his food during treatment. That is, put you on a diet to avoid complications. Limit your child's consumption of fatty, sour, and spicy foods, as such foods help spread the disease.
Forbidden:
- Fat meat;
- Sweet;
- Tea coffee;
- Spices, ketchup, mayonnaise, etc.
- Not fatty meat;
- Cereals;
- Vegetables;
- Greenery;
- Dairy products.
How to deal with fungus on a child's feet
It’s a rare person who won’t be moved by touching photos of a newborn’s tiny feet that fit in the mother’s palm. New mothers are delighted with their baby's pink fingers and miniature nails. Unfortunately, often the skin and nails of children are affected by such an unpleasant disease as mycosis, or, more simply, fungus.
Unlike adults, foot fungus in a child, and in particular its treatment and diagnosis, is quite complex. Firstly, the younger the child, the more difficult it is to make a diagnosis: many forms of mycosis are asymptomatic, children cannot talk about their discomfort. Secondly, most antifungal drugs can cause allergies and are usually prescribed after the age of two years.
- 5 Prevention
Mycosis in children and its types
Mycosis (from other Greek “mushroom”) is an infectious disease, the appearance of which is provoked by various types of parasitic microorganisms. In the case of foot fungus in a child, these are usually the dermatophytes Trichophyton rubrum (more than 50%) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes (about 30%). Lesions may spread to the soles of the feet, between the toes and nails.
There are 4 clinical types of mycosis of the feet. This classification is relevant for both children and adults:
- Intertriginous (interdigital or membrane) form of the disease. It is characterized by the presence of ulcers, cracks or weeping, and, possibly, on the contrary, flaking skin in the interdigital area. The affected skin appears pale, and in some cases greenish. We will feel a slight itch. This manifestation of the fungus predominates in the warm season under conditions of high humidity, which is aggravated by wearing tight or simply uncomfortable shoes. This is the most common type of fungus on a child's feet.
- Squamous-hyperkeratotic form (moccasin / “athlete’s foot”). It is the destruction of epithelial cells and the proliferation of the stratum corneum of the skin, which provokes the appearance of rough calluses and deep cracks on the heels. Visually, it looks like a “mark” covering the foot in the form of flaky skin. Additionally, this form of the disease also affects the nails. They look like wood dust: they lose their shape and pinkish color, lag behind the nail bed, lose transparency, change their structure and begin to crumble.
- Dyshidrotic (vesicular) form. A rare form of mycosis, extremely difficult to diagnose and treat. Manifests itself in the form of the appearance of vesicles on the entire surface of the foot. These blisters are filled with fluid, which soon pours out of them, forming erosions on the skin right up to the ankles.
- Erased form. This type of disease is also quite difficult to diagnose. It is characterized by interdigital microcracks invisible to the eye and flour-like peeling of the upper layers of the skin. May cause burning and itching. Typically, this form of mycosis is diagnosed only after the transition to the next stage - onychomycosis (fungal infection of the nail).
How to identify mycosis in a child: symptoms
Since children's skin contains more water than the body of an adult, the course of the disease is more acute and “wet”. Sometimes, due to the fact that a child’s nail plates are renewed twice as fast as those of adults, the baby’s nails do not have time to deform appropriately during the development of the disease. But in any case, some changes will be present. The most common ones are:
Even if a child has several symptoms from the list, the final diagnosis can only be made by a dermatologist, based on scraping microscopy or DNA testing. Also, only a specialist should prescribe treatment. Self-medication, and even more so the use of systemic therapy, which is hepatoxic (negatively affects the liver), in the case of children can do more harm than good.
Causes of mycosis
Before starting treatment for foot fungus in a child, you should try to determine the causes of mycosis. By eliminating them, you have already done half the battle, eliminating subsequent relapses.
It would seem that the fungus is a contact disease and extremely contagious. But how can a child become infected, especially if he is a baby a few months old? Let's look at the most common causes of infection with fungal diseases:
- Close contact with those closest to you - parents and other household members;
- Hereditary predisposition to fungal diseases;
- Wearing tight shoes made of low-quality materials, which provokes the appearance of microcracks on the skin of the feet, through which microorganisms can penetrate;
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards: trying on shoes in a store on bare feet, exchanging shoes with other children, being barefoot in the pool or other public places;
- Long or excessively short toenails.
Additionally, children who have undergone antibiotic treatment and are exposed to stress are at risk. As well as those suffering from such serious diseases and conditions as:
- Immunodeficiency;
- Metabolic disease;
- Diabetes;
- Flat feet;
- Avitaminosis;
- Excess weight;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- Congenital vascular diseases of the legs.
Treatment and prevention of foot fungus in children
Drug treatment of mycosis in children
The greatest effectiveness in curing foot fungus in a child comes from a combination of systemic therapy (medicines for oral administration) and local external treatment. But the choice of this type of therapy is not always rational. For example, systemic therapy is contraindicated for children under 2 years of age and children with liver problems. Doctors take special care when prescribing medications for infants: treatment can harm them more than the mycosis itself. In this situation, the baby is indicated for maintenance therapy while waiting for the moment when it grows to be effective.
The most common drugs for the treatment of fungus on the legs of a child:
- Terbinafine (terbizil);
- Diflucan;
- Nizoral;
- Flucostat;
- Exoderil;
- Clotrimazole;
- Itraconazole and ketoconazole - dermatologists have an ambiguous attitude towards these drugs (the drugs have a wide spectrum of effects and are quite effective, but at the same time they are quite hepatoxic);
- Lamisil is prescribed from the age of 12 due to the fact that the effect of the medicine has not yet been sufficiently studied.
Treatment of fungus with folk remedies
Almost all types of fungus on a child’s feet are susceptible to traditional medicine. Unfortunately, they will not cope with severe stages of squamous-hyperkeratotic or vesicular forms of mycosis, but they can significantly alleviate the condition by relieving itching and drying out weeping ulcers.
- A paste of crushed garlic and butter in a one to one ratio is applied to the affected area at night.
- A compress of 35% salicylic ointment is applied in a thin layer, wrapped in cling film and put on a sock.
- Hot salt baths - steam your feet in a saline solution at the rate of 200 grams of salt per liter of water. It is more effective to use sea salt.
- Baths of wormwood decoction - 2 liters of liquid per 0.5 kg of fresh wormwood.
- Compresses from crushed rowan leaves, onions or burdock - keep on your leg for 24 hours.
- Treatment of feet with calendula tincture - for 250 grams of flowers - 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 30 - 40 minutes.
Prevention
- Wear only your own shoes that fit.
- Selection of highly breathable natural materials for children's shoes.
- Wear appropriate footwear at the beach, pool and other public places.
- Airing your shoes after every walk.
- A selection of socks made from high-quality natural materials.
- Control your foot temperature to avoid overheating and sweating. A moist, warm environment is an ideal place for microorganisms to multiply.
- Using individual files, scissors and nail clippers, treating tools with alcohol after manipulating nails.
With any illness, time plays against you.
Prevention
But you must admit that it is better to be careful than to treat an advanced fungus, as with any disease. Candidiasis can be prevented, namely, you need to provide your baby with:
- Balanced diet;
- Have a rational diet for mom;
- Treat pacifiers, pacifiers, etc.
Therefore, we can conclude: Fungus in the mouth of a newborn is a fairly common disease. It can bring a lot of trouble, but you shouldn’t be afraid of it. You need to be able to correctly and timely identify a child’s illness, immediately visit a doctor, only he will be able to establish the correct treatment and outline your further actions. Be healthy you and your children!
Affected area
A fungal disease can also affect the skin of a newborn. In this case, red spots appear on certain areas of the skin. The number of leukocytes in the blood increases sharply, which indicates the presence of inflammation. Then bubbles appear on the reddened areas and become covered with a white coating.
Diaper dermatitis is a type of thrush. Affects the groin area, perineum, and area between the buttocks. The reason for the development of pathogenic microorganisms is the constant wearing of diapers made of low-quality material.
There are rare cases of nail plate fungus in children. A special feature is thickening or, conversely, thinning of the nail surface. Its color becomes yellowish. The nail becomes lumpy. If the area around the nail is affected, it becomes red and swollen.
In children, you can encounter thrush of the genital organs. This is most often caused by taking antibiotics, allergies or poor hygiene. Both boys and girls experience a cheesy discharge from the genitals.
The genitals look swollen and red. The child feels a burning sensation, itching, which leads to changes in behavior. The baby becomes capricious and whiny.
Treatment methods
How is fungus treated in children? Treatment must be carried out at home, but under the supervision of a doctor. You can use medications, as well as additional folk recipes.
Therapeutic therapy is carried out in several stages.
If there is damage to smooth skin on the face, head, feet, or nails on the toes and fingers, it is necessary to treat it every day with a 2% iodine solution. It helps wounds heal much faster. Before going to bed, you need to apply a moisturizing ointment to avoid drying out and itching at night. It must contain amphotericin A, miconazole and nystatin.
It is necessary to use complex therapy in the form of external and internal means. The following medications are suitable for this: Lamisil, Clotrimazole, Miconazole and Exoderil. All ointments and creams should be applied to the skin 3 times throughout the day. The course of treatment ranges from 2 weeks to 1.5 months. Even after the symptoms have disappeared, treatment must continue for some time to prevent recurrence of the disease.
When treating fungus, special attention should be paid to the area between the fingers, as well as the skin that surrounds the nail plate. You can additionally wipe this area with an antiseptic solution.
The drug Diflucan has a rapid effect. This product has powerful fungicidal properties. It is considered absolutely safe in the treatment of fungus in children. This may be an intravenous solution, a tasty suspension or capsules.
In advanced stages of the disease, it is necessary to take an additional course of treatment with antifungal drugs. From 3 years of age, Terbinafine can be used for treatment. Calculate the proportion depending on age and weight. The course of treatment is 10 days, then a break of 10 days and repeating the course again.
If you have a fungus that affects the throat and tonsils, it is necessary to treat with drugs that contain fluconazole, levorin or nystatin.
It is very important to disinfect bedding and clothing during treatment. Things should be boiled in a 1% soap solution. Then, for the best effect, you need to iron it several times with a hot iron.
How effective the skin treatment was is checked using a fluorescent lamp. It is with its help that you can determine whether the disease has been cured or not.
If the disease has been advanced and problems appear in the functioning of internal organs, it is necessary to carry out therapy that will be aimed at eliminating toxins from the body. The baby should undergo treatment using droppers, through which saline solutions are infused.
It is necessary to additionally use drugs to stimulate the immune system and the body’s protective properties. It is also advisable to harden yourself, play sports, drink a lot of water and eat right.
Features of the disease
In infants, fungal pathogens mainly affect the oral cavity. The main symptom is a white coating with lumps. Hence the popular name - thrush; in medicine it is called candidiasis.
The first degree of the disease is characterized by the formation of red areas on the tongue, cheeks and gums. Gradually the area becomes covered with a white coating. Body temperature does not increase. The child's behavior changes slightly. He becomes moody and restless.
If treatment is started at this stage, the disease goes away quickly.
Second (moderate) degree of severity. The affected areas enlarge and unite with each other. The pain increases and becomes the reason for refusing to eat. Sleep is disturbed, the baby becomes capricious, whiny, refuses to communicate and play. It becomes more difficult to get rid of plaque; the affected area may bleed. Sometimes your body temperature may rise.
The third (severe) degree of severity of the disease is characterized by a high rise in temperature. The fungus spreads to the mucous membrane of the larynx and extends to the lips. The oral cavity is completely covered with a cheesy coating. Treatment is most often carried out in a hospital.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, a consultation with a mycologist is necessary.
After clarifying the patient’s complaints and reviewing the provided medical documentation, the specialist prescribes a list of laboratory tests, which include:
- visual examination of the patient under a Wood's lamp, revealing uncharacteristic glow of the scales;
- collection of clinical material to determine the type and tissue form of mycoses;
- Sowing the scrapings separated for microflora helps to determine the susceptibility of a particular fungal disease to chemotherapy drugs.
Symptoms
The description of symptoms depends on the form and location of the disease:
- A characteristic symptom for a fungal infection on the skin of the face and torso is the appearance of a scaly, ring-shaped rash with pustules and a clear outline. As the disease progresses, the number of elements increases and the affected area increases.
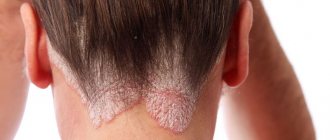
- A feature of a fungal infection of the scalp in a child is the appearance of itchy bald spots with remnants of broken, dull hair.
Almost all fungal diseases spread on the skin, manifesting themselves in the form of rashes (papules) and the formation of skin scabs. The disease is most severe in young children, especially infants, causing diaper dermatitis.
Symptoms of the disease are characterized by the following manifestations:
- hyperemic skin that itches, cracks and peels;
- the rash has a bumpy border with healthy skin;
- when scratching, scab formation is observed;
- bacterial development contributes to the formation of a purulent rash;
- possible imbalance of immune and humoral functions;
- increased sweating, burning at the site of the rash;
- Diaper dermatitis and weeping rash are possible.
In addition, general symptoms such as hyperthermia, increased fatigue and weakness may occur.