What it is
Benign hemangioma is a tumor-like defect arising from blood vessel cells.
On this topic
- Skin covering
Tumor on the face
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 10, 2020
This is a widespread pathology, since in children it occurs in 45% of cases of tumor damage to soft tissue structures. The disease is considered congenital, although it sometimes develops in adults.
Hemangioma is characterized by an aggressive course. In the first months of a child’s life, the neoplasm often increases rapidly. In addition to cosmetic discomfort, the progressive disease leads to the destruction of nearby tissues.
Causes
To date, doctors have not been able to determine the exact cause of why hemangioma occurs in adults on the arm or any other part of the body.
The nature of the congenital form of the lesion is as follows: during the period of growth, the body produces an excessive amount of connective tissue, which is why it has to become denser. The luminaries of modern medicine do not have the necessary equipment that would allow them to identify hemangioma on the body in adults in the early stages, a photo of which you can easily find on the Internet.
A hemangioma on the leg of an adult, which manifests itself as a bright red tumor, will not grow over time or torment you with unpleasant sensations. It is not known for certain what causes an adult body to manifest such an ailment on the skin. Common causes of hemangioma in the adult population include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Environmental influence.
- Diseases of internal organs, in particular the endocrine system.
- Disorders in the cardiovascular system.
- Exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet radiation.
Classification
Depending on the types of blood vessels, hemangiomas are divided into the following types:
- Capillary. This type is considered the most common. Such tumors form small superficial capillaries.
- Arterial, venous. Hemangiomas of these types consist of large vessels, as a result of which they affect a significant area of deep tissue layers.
- Racemic. Neoplasms develop from excessively tortuous vessels with thick walls.
- Cavernous. Tumors are formed from elements of the circulatory system with thin walls and significant lumen. Cavernous hemangiomas are characterized by the accumulation of blood in the cavities. Cavernous neoplasms affect both the superficial layers of the skin and deep tissue structures.
It is important to distinguish hemangioma from lymphangioma, which arises from lymphatic vessels. The latter pathology often occurs on the thighs and buttocks and is extremely aggressive.
Clinical picture
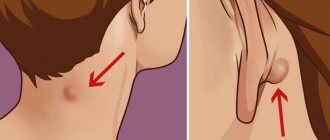
An external sign of the disease is the presence of a reddish or blue spot on the skin. The defect has clear contours and rises above the surface of the epithelium. When located in the deep layers of the soft tissues of the thigh or on the femur, the disease is asymptomatic for a long time.
In this case, a voluminous neoplasm located in the muscles is easily palpated. A deep-lying tumor often leads to various complications. As a result, the patient experiences pain in the hip joint, blood circulation deteriorates, and innervation is disrupted.
Due to the presence of pain in the hip, the patient begins to limp, which significantly increases the load on the pelvis, spine and joints of the lower extremities.
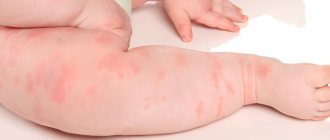
Hemangioma in newborns
Infantile hemangiomas have characteristics: sometimes they grow quickly and unpredictably. Tumor growth causes tumor cells to damage nearby healthy tissue. Because of this, cosmetic and functional defects occur. For example, a vascular tumor may be located in the nose, upper respiratory tract, or mouth. This may make it difficult for your child to breathe or swallow. Moreover, up to 8% of hemangiomas disappear on their own without treatment. But most often this happens after the first year of life and in full-term children.
Infantile hemangioma develops in several stages:
- The first phase is active tumor growth until the first 6-12 months of life. During this period, particularly rapid growth of pathological cells is observed.
- After a year, the second stage begins - the stability phase, when the growth of the hemangioma slows down.
- After the stability phase and up to 6-7 years, the regression phase begins. At this stage, in 5-7% of cases the tumor completely disappears, in the rest, regression is accompanied by the appearance of a scar.
A typical hemangioma has a red color, a bumpy surface and slightly rises above the skin. If you press on it, the tumor will shrink, but after a few seconds it will recover to its previous size.
Hemangiomas in children are different. They are divided into local and segmental. 90% of infant vascular tumors are local. This means that the tumor has clear contours and grows from a central point. Hemangiomas are superficial, that is, they grow on the skin and sometimes protrude above it. There are deep ones, when they grow deep into the skin. There is also a mixed variant, when the tumor spreads over the skin and deep into it. Typically, such hemangiomas are discovered during the first weeks of examination by a doctor. The first sign is a small red spot. Its size remains almost unchanged until 2-3 months, after which it begins to actively grow.
Segmental hemangiomas grow in large spots. They appear in the neck and head, on the lower back and tailbone. Typically, segmental vascular neoplasms are combined with abnormal development of blood vessels or pathology of internal organs. This combination of hemangioma and other defects is called PHACES syndrome. In this case, defects of the chest, aorta and heart defects are usually found in children. Children with PHACES syndrome are prone to infections and peptic ulcers.
Other syndromes also occur in children - a combination of hemangioma and pathologies in the pelvis and sacrum. Common signs: bone growths, abnormally developing bladder, spinal cord and spinal cord membranes.
There are special forms of hemangiomas in newborns:
- congenital rapidly self-limiting hemangioma. It is characterized by rapid growth immediately after the birth of the child. Often children are born with an already formed vascular tumor. This variety passes quickly and completely disappears by the third year of life;
- congenital non-involutional hemangioma. This tumor does not disappear, but it does not grow either.
Most often, hemangiomas are small in size. They do not create cosmetic defects and do not create discomfort for the child. But in some cases, vascular tumors can be dangerous to health and cause complications:
- hemangioma in the eye or eyelid area. Prevents the child from opening and closing his eyes. As a result, visual acuity decreases. If a tumor appears in this area, you need to consult an ophthalmologist;
- hemangioma on the face. Creates a cosmetic defect for the child and can interfere with the work of facial muscles;
- hemangioma in the mouth area. Prevents the child from eating and chewing food. May lead to deformation of the lips, teeth and lower jaw;
- hemangioma in the nasal area. It provokes deformation of the nasal septum, impaired ventilation of the nasal turbinates, and makes it difficult to breathe through the nose. May be complicated by rhinitis;
- hemangioma in the ear area. Deforms the ears, thickens the ear cartilage. Creates a cosmetic defect, increasing the size of the affected ear;
- hemangioma in the upper respiratory tract. It can grow into the lumen of the trachea and interfere with breathing.
Hemangiomas of the liver lead to heart failure, and hemangiomas of the digestive organs lead to gastrointestinal bleeding. However, local complications occur in only 5% of children.
Causes
Almost always, hemangioma develops even before birth due to disturbances in the formation of the circulatory system. In infants, this disease occurs in 10% of cases.
On this topic
- Skin covering
Treatment methods for atheroma without surgery
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2020
At the same time, girls are most susceptible to pathology. In children, in most cases, the tumor occurs on the face, under the scalp, on the skin of the extremities, while damage to the soft tissues of the thigh is considered a rare occurrence.
The exact causes of the disease in adults have not yet been identified. However, there are the following factors that provoke the development of the pathological process:
- The presence of vascular diseases that impair blood circulation.
- Permanent microdamages of congenital minor hemangiomas, previously not diagnosed.
- Prolonged exposure to open sunlight , frequent visits to the solarium.
- Regular hypothermia.
- Unfavorable ecological state of the environment.
In addition, constant nervous strain and various stressful situations can also lead to the appearance of vascular tumors on the thigh.
Information about the disease
Spinal hemangioma occurs in 10-11.5% of the population. In total, the disease occurs in 1.5-2% of cases of the total mass of benign skeletal neoplasms. It has no predisposition to become malignant. Such cases are exceptional and constitute no more than 1% of the total mass.
The most common hemangioma of the thoracic spine is in the 6th vertebra. Lesions of the sacral and cervical spine are rarely detected. The formations are often located within one vertebra.
In the modern classification, there are 4 types of hemangiomas, different in histological structure:
- capillary - formed by the interweaving of capillaries, the layers are separated by a layer of fibrous and fatty tissues;
- recematous - include large veins and arteries;
- cavernous - consist of layers of connective tissue covered with endothelium, include many cavities with different sizes and shapes;
- mixed - combines features characteristic of hemangiomas of all listed types.
There are aggressive and non-aggressive course of the disease. The first case is characterized by a rapid increase in the size of the tumor and the appearance of pronounced symptoms. Non-aggressive ones have a favorable course. Tumor growth cannot be traced. Education progresses slowly and asymptomatically. There are clinical cases confirming the possibility of spontaneous resorption.
The main reason for the formation of spinal hemangioma is hereditary predisposition. This factor is confirmed by statistics. The risk of developing a tumor for a person increases when pathology is detected in his close relatives. The likelihood of progress increases with spinal injuries and tissue hypoxia.
The disease often progresses in women before the age of 40. The frequency of detection of pathology is compared with men after reaching menopause. Doctors attribute this to the stabilization of hormonal levels and a decrease in estrogen levels in the blood.
Symptoms of the tumor process depend on the size and location of the tumor in relation to the vertebral body. For a long period, the disease occurs in a latent form, without causing the emergence of a clinical picture. Pathology is detected by chance, during an examination after injury or for other indications.
At an early stage of development of the pathology, pain syndrome appears. The pain itself is mild and appears periodically. Its intensity increases as the hemangioma grows, and in the end it becomes unbearable. New growths larger than 1 cm in diameter are dangerous. They provoke not only pain. Long-term progression leads to neurological spectrum disorders, manifested due to disruption of the vertebral structure and compression of the spinal cord.
Pain that occurs at night or intensifies after physical activity helps to suspect a problem at an early stage of development. It should be localized in the area of the affected vertebra. Numbness, paresis and paralysis of the affected area are possible.
The following methods are used to diagnose pathology:
- X-ray examination in several projections;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Atypical vertebral hemangioma is also confirmed using these methods. An X-ray can identify a spinal tumor, but it is not enough to make a diagnosis. Accurate information is obtained after a CT scan. MRI is indicated for patients with suspected hemangioma of the cervical spine .
With an aggressive course, the signs of spinal hemangioma appear clearly. It is possible that serious complications may arise, the list of which includes:
- compression fractures of the vertebral body;
- compression of the spinal cord and its roots;
- paresis and paralysis;
- dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
It is almost impossible to prevent the development of a tumor process in individuals with a hereditary predisposition. A calm lifestyle with abstinence from excessive physical activity helps reduce the likelihood of pathology; it is important to avoid injuries.
Diagnostics
If the neoplasm is localized in the upper layers of the epidermis, then diagnosis will be simple. An experienced dermatologist will easily identify hemangioma during a visual examination, since such tumors are clearly visible and palpable.
When deeper tissue structures are affected, instrumental diagnostic methods such as ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are used to determine the type, size, and nature of the growth of the formation.
Treatment
Minimally invasive surgeries are used to eliminate hemangiomas of the soft tissues of the thigh. Unlike standard surgical removal, the use of laser or cryodestruction has a number of advantages. Such methods of therapy do not damage adjacent healthy tissues and have a minimal risk of scars or cicatrices after healing.
In addition, treatment with laser or liquid nitrogen significantly reduces the likelihood of infection, protects against bleeding and is characterized by a small number of contraindications to the use of manipulation.
If the deep layers of the thighs are affected, sclerotherapy is used. The essence of this operation is the introduction of a special drug that glues abnormally overgrown blood vessels.
On this topic
- Skin covering
Why does the wen itch?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 5, 2020
Sometimes, when the tumor is large and has grown into nearby tissues, surgical intervention is prescribed. Surgical treatment is often combined with conservative therapy to prevent the recurrence of hemangioma.
Other medications are used if there are contraindications to the tumor removal procedure. To slow down the progression of the pathological process, cystostatics are prescribed. Corticosteroids are also used as a conservative treatment.
Treatment of hemangioma
For spots that do not grow and do not cause complications, a wait-and-see approach is often used. Hemangiomas with progressive growth, infected and bleeding are subject to treatment or removal.
Removal methods
The following removal methods are available:
- radiotherapy - used in hard-to-reach places;
- laser coagulation of blood vessels;
- dithermoelectrocoagulation – removal of small formations;
- cryodestruction – exposure to liquid nitrogen (freezing);
- sclerodestruction - administration of a sclerosing drug;
- hormone therapy to stop the growth.
- surgical removal.
Let's celebrate! In practice, combined methods are used: surgical removal with radiation therapy, cryodestruction with hormone therapy.
Surgery
Hemangioma, which grows and destroys the body of the spine, puts pressure on neighboring organs, actively grows, is localized near the eyes, ears, and genitals and requires surgical intervention.
But now more and more preference is given to minimally invasive treatment methods, since surgical operations cannot be performed due to a possible cosmetic defect or for other reasons.
Note! In such situations, close-focus radiotherapy is used - radiation exposure. Targeted gamma rays destroy tumor cells, having minimal effect on nearby organs.
Traditional methods
Basic recipes for folk remedies to combat hemangioma:
- Kombucha compress. The compress is applied to the area of the growing vascular tumor for the whole day. the course of treatment consists of three weeks.
- Treatment with copper sulfate. Add a tablespoon of vitriol to half a glass of water, and wipe the stain with this solution. Treatment lasts for 10 days. In parallel with this, you should take a hot bath with baking soda at night (a pack of baking soda per bath).
- Fresh celandine juice is also used in various infusions: from wormwood, coltsfoot, St. John's wort, yarrow, calendula and so on.
Likely consequences
Hemangioma does not transform into a malignant neoplasm. However, the disease progresses aggressively, grows into nearby tissues, and affects neighboring organs, disrupting their functionality. An increasing defect compresses nerve endings and blood vessels, impairs innervation, disrupts blood circulation and nutrition of the affected area.
Reduced blood circulation in the hip tissue causes increased fragility of the femur, as a result of which the patient begins to suffer from frequent fractures.
Damage to the tumor is dangerous due to the development of severe bleeding. This complication is especially dangerous in people with large hemangioma, low platelet levels, and poor blood clotting.