What it is?
A cavity with its own membrane and fluid (mucous, lipid contents) inside is a cyst. Atheroma is a cystic pathology of the skin that affects areas covered with hair, that is, the entire body except the feet and palms, especially places densely dotted with sweat and sebaceous glands. The latter are necessary for the body to produce a fatty secretion that covers the body with a protective film. The stronger the negative effects of the environment on the skin - hot dry air, dirt, insufficient and excessive hygiene, etc., the more secretion is produced.
Violations lead to blockage of the ducts. The small fat factory turns out to be closed, but continues to operate. As the cyst fills, it increases in size. After an individual period, the gland stops functioning. As a result, a person is left with an education, some the size of a pea, another the size of a chicken egg. It moves in relation to the bone, but is attached to a specific area of the skin. Therefore, a cyst cannot be called a fixed formation.
In relation to the human ear, the following localization sites are distinguished:
- Behind the lobe. There is a cluster of sebaceous glands here. It grows to quite large sizes and has a reddish color.
- The external auditory canal, middle ear and eardrum are affected by such formations due to trauma. Epidermal and serous cysts form here. More often observed in men.
- One or more dense balls appear in the tissues of the lobe. They are painless and can sometimes be detected only by touch. Occasionally there are tumors that are really large in size, the size of a quail or chicken egg. More often this is a consequence of a disruption of the endocrine system or increased production of the sebaceous gland.
Clinical picture of atheroma
A cyst, which is located on the skin anywhere around the ear and on the lobe, is visible to the naked eye. There are no symptoms such as discomfort, pain or other manifestations. A formation in the ear canal is characterized by problems with hearing and the feeling of a foreign object.
Signs of cyst suppuration:
- Hyperemia – redness and increased temperature in the tumor area;
- Pain and throbbing;
- Itching;
- Edema;
- In advanced cases, signs of fever.
Carefully! Infectious inflammation in skin tissue can lead to abscess and sepsis.
Photo
The danger of atheroma on the ear for health
With the natural course of a benign neoplasm, it does not bother people in any way - the nodule in the form of a soft brush transforms gradually and imperceptibly into a dense lump. This process does not cause any pain. In this case, there is no danger to human health.
In case of atheroma with purulent contents, immediate consultation with a doctor is required to prevent such serious complications as an auricle abscess with penetration of necrotic masses into the inner ear. In the absence of adequate massive therapy, otitis media develops first, and then meningitis.
In case of severe infection of the whole body, a diagnosis of sepsis is made, which leads to death.
A timely consultation with a specialist helps to avoid such a health hazard - at the first visible or palpable changes in the tissues of the retroauricular area or the shell itself. In the early stages of cyst formation, even surgical intervention is not required; conservative therapy can be used.
Causes of the disease
Clogging of the sebaceous glands leads to disruption of the process of subcutaneous fat release, which is inherent in people with excessive sweating or prone to seborrhea. In addition, the occurrence of a disease, including atheroma of the auricle, can provoke: metabolic disorders at the cellular level;
- imbalance of substances produced by internal secretion organs;
- malfunction of the sebaceous glands, which contributes to an increase in the fat layer of the human skin;
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- the use of certain cosmetics that narrow the ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- unfavorable environmental conditions, prolonged stay in dusty, dirty rooms;
- hereditary predisposition to the disease;
- skin injury;
- prolonged exposure to the cold.
Considering that in children the immune defense of the body may decrease due to various diseases, including chronic ones, the appearance of atheroma of the auricle in a child is quite common.
Reasons for development
The main reason causing the development of atheroma is the inability to remove lipid substances due to blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. Typically, this formation appears in people prone to seborrhea, acne rashes and increased sweating. Such a tumor can appear in various parts of the body, for example, on the face, chest, neck or head. Atheroma that occurs in the concha of the ear can be caused by piercing the ears using an unsterile instrument.
In addition to this, there are other factors that cause the appearance of a cyst in the ear area:
- lack of proper hygiene;
- hormonal disorders;
- impaired metabolic processes;
- mechanical damage to the skin of the ear;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- heredity and genetic predisposition;
- presence of hyperhidrosis.
Another appearance of atheroma behind the earlobe or in its shell can occur due to a sharp deterioration of immunity, which is often observed with chronic infections. If atheroma appears in the ear area, in the absence of inflammation or suppuration, it does not pose a health hazard. However, a cyst in the tissues of the ear can significantly increase in size and will be noticeable to others, causing a person to feel some discomfort. If atheroma becomes infected with bacteria, suppuration occurs in the tissues of the ear, during which the cyst will begin to hurt, turn red and increase in size. Without timely treatment, purulent inflammation can easily spread to nearby soft tissue around the ear and lead to the development of sepsis. Atheroma that arises in the structures of the ear can very rarely transform into a cancerous tumor. More often, such neoplasms, especially those arising in the concha, lead to serious hearing impairment.
Symptoms of the disease
Not many people know what atheroma of the earlobe is, so patients often seek the help of specialists only when inflammation or other complications of this disease occur. Atheroma has a round shape and size from 3 to 45 millimeters, while at the initial stage of development the cyst does not cause any concern.
We recommend reading Anaplastic astrocytoma - causes, symptoms, treatment
The rapid enlargement of an ear cyst begins when it becomes inflamed. Other symptoms of this process also appear:
- redness of the skin around the inflamed area;
- constant burning and itching in the ear area;
- swelling of the ear;
- fever;
- pain in the ear area, aggravated by pressure.
Often, during infection, when suppuration occurs, the cyst can open on its own, and its contents flow out. At the same time, its capsule is still located inside the ear and continues to accumulate sebaceous secretions.
The process of inflammation of the cyst may be accompanied by general clinical manifestations:
- constant feeling of weakness;
- headache;
- aching joints;
- loss of appetite;
- bad dream.
Small atheromas that appear in the area behind the ear do not cause harm to health, but due to the existing risk of complications, it is necessary to seek medical help immediately after detecting tumors.
Appearance, localization, symptoms
In appearance, ear atheroma resembles bumps or balls, ranging in size from 5 mm to 40 mm. Such seals on the skin appear due to blockage of the sebaceous glands. A capsule is formed where subcutaneous fat, dead cells of the outer layer of human skin accumulate, and the process is accompanied by a gradual increase.
Causes of appearance and proper treatment of atheroma behind the ear, as well as modern methods of removal
A small round formation on the auricle or in the thickness of the earlobe is not always given due importance.
Therefore, this pathology is detected much less frequently than it actually occurs.
As a rule, people with ear atheromas seek medical help when inflammation develops or when the formation is large.
Although the general prognosis for atheroma is favorable, if such a thickening is discovered, it is better to consult an ENT doctor or surgeon , undergo an examination and rule out a malignant neoplasm.
The exact reasons causing the formation of atheroma behind the ear have not been identified.
The formation of a cyst occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland; its secretion begins to accumulate inside the capsule. The contents of the atheroma have a sharp, unpleasant odor .
This is interesting: Causes of ulcers on legs
A number of predisposing factors are important in the occurrence of atheroma:
- ear injuries and hematomas;
- burns and scarring of the ear;
- animal and insect bites;
- cosmetic piercing of the lobe;
- seborrhea;
- hormonal and endocrine diseases;
- disruption of neuroendocrine regulation of the sebaceous glands;
- oily skin type;
- wearing low-quality jewelry;
- wearing traumatic products, ear tunnels;
- chronic inflammatory skin diseases;
- violation of hygiene of the behind-the-ear area - compulsive cleansing of the skin, or its contamination.
The formation of ear atheroma is gradual and asymptomatic. A round, densely elastic formation appears in the thickness of the skin, the skin above it is not changed.
Over time, atheroma increases in size. It is most often localized in the thickness of the earlobe and in the posterior fold of the ear.
In the second case, the patient cannot sleep comfortably on the affected side due to pressure on the formation.
If the location of the atheroma in the tissues compresses the peripheral nerve endings, then minor discomfort or itching appears.
When pressed, there is usually no discharge from the atheroma, but when it grows into the skin layers there may be a small light, fatty discharge of soft consistency.
With a complicated course, the postauricular atheroma can become inflamed and suppurate. The area of atheroma becomes painful, the skin over it is bright red or bluish, hot and swollen. If the tumor is located in the earlobe, then the earlobe becomes sharply enlarged and turns blue. When the tumor is compressed, sharp pain and purulent discharge appears.
With deep behind-the-ear localization, the ear will protrude. It is possible to narrow the external part of the auditory canal with conductive hearing impairment, i.e. due to mechanical obstruction.
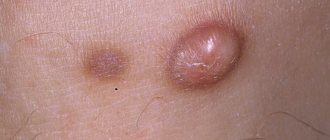
See what atheroma looks like behind the ear in the photo, as well as on the earlobe:
How to recognize a wen?
Atheroma of the earlobe ranges in size from a few millimeters to 5 cm. In the early stages, the tumor may not cause any concern to its owner. The festering wen increases sharply, which leads to pain and hyperemia of the skin. Swelling and a local increase in temperature are often observed. Itching and burning in the earlobe are no less common signs of atheroma inflammation. The tumor can fester due to infection, attempts to independently remove its contents, or constant irritation of the skin.
Communication with the administration
Make an appointment with a specialist directly on the website. We will call you back within 2 minutes.
We will call you back within 1 minute
Papillomas are polyps on a thin stalk that are the color of normal skin or brown (light brown to dark brown)
This is interesting: The cause of irritation, redness and itching of the skin
method of laser destruction of dense round keratinized skin nodules of a viral nature
Purulent pathologies of the skin and fatty layer of tissue are more often (up to 90% of case reports) caused by infection with staphylococcus
a branch of medicine that studies the structure and function of the skin in normal and pathological conditions, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of skin diseases
Health Risk Factors
The formation of atheroma behind the auricle is not always detected at an early stage. A significant increase in the size of the tumor becomes noticeable, and at this time not only the inflammatory process can develop, but also the purulent content of the tumor can form.
The accumulation of pus in the ear area can provoke infection of the entire body by pathogenic microbes through the blood. Given the proximity of the blood vessels supplying the brain, the infection can get there along with the blood, which can often be fatal.
Medical practice knows cases of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one, which significantly complicates the treatment process. However, this happens extremely rarely.
Failure to timely seek medical help for the treatment of atheroma of both the postauricular area, the auricle, and earlobe, in some cases, affects hearing deterioration, up to its partial loss.
Diagnostics
A dermatologist or surgeon can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. At the first stage, an examination is carried out, during which the doctor determines the location, diameter of the tumor, and also prescribes other diagnostic procedures.
Ultrasound of the auricle.
To clarify the type and structure of the seal, the following types of examinations are carried out:
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray of the head;
- Audiometry is additionally used to determine a possible decrease in hearing sensitivity;
- take a swab from the ear canal;
- perform otoscopy;
- blood and urine tests are prescribed to exclude the development of an inflammatory process.
Only after completion of diagnostic measures does the attending physician decide on the choice of therapeutic course.
How to treat ear atheroma
The main method of treating atheroma is its surgical removal. If it is inflamed, then before the operation the doctor may prescribe medications to eliminate the inflammatory process.
At home, many people prefer to treat atheroma on the ear with folk remedies, but this is not the best option, since traditional therapy, if used incorrectly, will not correct the situation, but will only do harm.
It is better not to experiment and coordinate any of your actions with your doctor, even if you want to try folk remedies.
Local preparations
Treatment of earlobe atheroma when it is inflamed is carried out primarily with folk remedies and medications for external use. Systemic medications (tablets and injection solutions) are prescribed only in advanced cases. Effective local medications for the treatment of atheroma are:
- Ichthyol ointment;
- ammonia;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- antimicrobial ointments Levomycetin, Tetracycline.
You need to treat the tumor with ointments 3-5 times a day, and make lotions with ammonia as follows: moisten cotton wool generously, apply it to the sore spot of the ear, wrap it with a warm cloth on top, and hold it for as long as possible.
Among the folk remedies to get rid of atheroma in the ear, you can try:
- Compress from coltsfoot. Tape a few fresh leaves to your ear and keep it there overnight. Repeat the procedure until the inflammation stops.
- A compress made from a film that lines the inside of chicken egg shells. Carefully separate the film from the shell and apply it to the tumor. When it dries out, change it.
- Fat ointment. Melt the lamb fat, cool and smear the tumor 6-8 times a day.
- Garlic compress. Grind a head of garlic, mix with vegetable oil (2 tablespoons), rub the product into the tumor three times a day.
Conservative treatment methods will relieve inflammation, but will not be able to remove atheroma completely, since the sebaceous gland cyst is prone to recurrence - it grows again in the same place. To get rid of atheroma forever, you will have to remove it surgically.
Conservative treatment
Medicines are prescribed to relieve the infection and treat the underlying cause of the pathology. The need, choice of drugs and duration are determined by the doctor based on the patient’s condition.
Features of treatment
Atheroma may not make itself felt for a long period.
However, the earlobe is a place where it is clearly visible, so it cannot go unnoticed. Especially if the ball starts to hurt and hang down. If atheroma occurs in a woman wearing jewelry, then the risk of infection of the formation becomes significantly higher. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the cyst cavity through a clogged duct in the sebaceous gland, causing inflammation.
It is important to prevent infection , as it can cause serious complications.
Removing atheroma is quite simple.
If it appears, go to the doctor as soon as possible. If you do this at an early stage, then twenty minutes will be enough for the doctor to remove the formation, and no traces of the atheroma will remain.
Please note that treating atheroma at home is impossible. To properly remove it, you need to peel off the membrane, which requires skills in surgical interventions. And even with such skills, it is impossible to carry out manipulations on your own without serious risks.
Therefore, only a qualified surgeon can remove your atheroma . While its size is small, it will be as simple as possible.
There are many folk methods that are aimed at combating atheroma. In fact, none of them can rid you of a tumor. However, they can slow down its growth . Therefore, it is advisable to resort to them only when, for a certain time, the operation is impossible for one reason or another. Then folk remedies will help prevent education from growing.
Radical removal methods
Removal of atheroma on the ear is carried out in three ways:
- standard surgical way - using a scalpel;
- laser;
- radio waves.
Standard surgery is the most affordable option. Under local anesthesia, the skin is cut and the contents of the atheroma are removed, then the cavity is treated with special antimicrobial drugs and sutured. When removing small tumors, sutures are usually not applied, since the cysts are elastic, so they can be reached even through a small hole.
Laser therapy is used to remove only small atheromas on the ears and consists of evaporating the tumor, namely the capsule along with its contents, and cauterizing its bed. Thanks to this, relapses are prevented. The operation is quick, painless, minimally traumatic, and leaves no traces. The laser immediately seals the blood vessels, so there is no bleeding after surgery. The rehabilitation period lasts no more than a week, after which the patient can begin normal life. The only drawback of this treatment method is the high cost: 6,000-20,000 rubles. for the operation.
Features of development in a child
In children, the occurrence of atheroma in the ear area is often caused by excessive production of sebaceous secretions. The functioning of the sebaceous glands in a child is normalized only at the age of five or six years. Also, such a neoplasm can form during puberty. At this time, hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands occurs, and fat accumulates in the ducts.
Such growths usually do not hurt and do not bother the baby, but a large tumor has a tendency to suppurate. For children under seven years of age, atheroma removal is performed using general anesthesia, and for older children, local anesthesia is used. There are cases when the formation of atheroma in a child’s ear is congenital. Then its development should be constantly monitored until the baby turns three years old, only then an operation is performed to remove the tumor in the ear.
Treatment options
When ear atheroma is diagnosed, treatment should begin immediately. If you start the development of a tumor, complications will arise after a certain time, and the treatment process will take much longer. There are different methods to get rid of tumors behind the ear, but the main one is surgery.
Treatment methods for atheroma largely depend on the stage of its development. If inflammation has already begun, before surgery, patients are prescribed medications whose action is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process. You can get rid of a cyst in the tissues of the ear through traditional surgery, as well as more modern methods, for example, laser and radio waves.
Causes
The mechanisms of development of a benign tumor are associated with blockage of the excretory ducts. Because of this, the contents of the glands begin to accumulate under the skin. This is caused by the following factors:
Mechanical ear injuries.
- insufficient personal hygiene (impurities are not washed off the skin and the ducts become clogged);
- endocrine disorders and diseases;
- increased sweating;
- increased skin oiliness;
- tendency to acne and other rashes;
- metabolic failures;
- mechanical injuries in the ear area;
- hereditary factor;
- using non-sterile instruments when piercing the lobe.
Some infectious diseases can provoke the appearance of atheroma of the auricle. Due to the presence of the inflammatory process, immunity deteriorates, which causes a disruption in the outflow of secretion.
What to do if the ball in your earlobe hurts or is inflamed
If you notice the appearance of atheroma, consult a doctor as soon as possible, especially if the formation causes uncomfortable pain.
The doctor will probably prescribe antibacterial drugs. You will also need a surgeon who will open the atheroma and remove its contents.
After the inflammatory process is completed, another surgical intervention will be needed. In this case, the capsule will be removed.
If the last operation is not performed, the atheroma will grow and recur an infinite number of times.
Prevention of ear atheroma
First, you need to see a doctor to undergo a complete examination of the body. If you have any disease, you should try to cure it as soon as possible. If this is not done, then an inflammatory process may begin in the body and ear atheroma may reappear.
In addition, it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene. This will be the best preventive measure against relapse of the disease. After going outside, don’t forget to wash not only your hands and face, but also your neck and ears with soap.
Proper nutrition is also the prevention of ear atheroma.
In conclusion, I would like to note that this disease cannot be treated on its own. This can lead to the most dire consequences.
Signs of atheroma
Externally, ear atheroma looks like a rounded growth with clear contours. The tumor is elastic, mobile on palpation, painless, a clogged sebaceous duct (black dot) is noticeable in the center. The nodes can be single or multiple, localized around or inside the auricle, on the lobe, and can even close the ear canal. The tumor is constantly growing and can reach very large sizes.
This is interesting: What tests should a man undergo for HPV?
Large atheromas often cause discomfort to the patient; they rub, are compressed when wearing hats, and are injured by a comb or hairdressing equipment. This leads to the penetration of pathogenic organisms into the capsule cavity and the development of the inflammatory process. Large-diameter cysts can compress surrounding blood, lymphatic vessels and nerve endings. This is accompanied by pain and swelling of soft tissues.
With secondary infection, the atheroma begins to fester.
The skin turns red, becomes hot, the node thickens, and severe pain appears. Unpleasant sensations radiate to the neck, head, lower jaw, and body temperature rises. After spontaneous opening, a thick, fat-like mass of yellow or yellow-green color is released from the purulent nodes. If the cystic capsule is not surgically removed, a non-healing ulcer remains or a tumor forms again.
With advanced purulent atheromas, cartilage tissue melts, the auricle becomes deformed, and a bacterial infection spreads into the ear canal. The disease can be complicated by otitis media, hearing impairment, phlegmon and subcutaneous abscess.
Possible consequences
Without treatment, the development of atheroma can cause the following complications:
- Gradual replacement of healthy connective tissue. This occurs against the background of the natural development of atheroma. The process of tissue replacement proceeds unnoticed. It does not cause pain. A dense nodule is formed in the problem area, which persists for a long time.
- Replacement with fibrous tissue against the background of inflammation. The consequence of this process is also the formation of a dense nodule, which does not disappear throughout the patient’s life.
- rupture due to purulent inflammation. The fluid penetrates deep into the ear canal and affects the middle and inner ear. This leads to deformation of the shell and destruction of cartilage.
If abscesses develop, there is a high probability of developing sepsis, which ultimately leads to death.
Bottom line
Atheroma is a fairly common phenomenon that appears for various reasons, the most common being the accumulation of subcutaneous fat. The formation itself in most cases does not pose a threat, however, in rare cases, the disease can become chronic or even lead to complications.
We must always remember the principle: it is better to prevent than to cure. Early contact with specialists will help to avoid both complex operations and reduce the risk of atheroma.
Sources
- https://StopKista.ru/kista/za-uhom.html
- https://boleznikogi.com/ateroma-uha
- https://pro-rak.ru/dobrokach/ateroma-uha.html
- https://UralKozha.ru/bolezni/ateroma-vozle-uha.html
- https://rakuhuk.ru/opuholi/ateroma-za-uhom
- https://dermatologia.ru/ateroma/za-uhom/
- https://StopRodinkam.ru/obrazovaniya/ateromy/ateroma-uxa.html
- https://tden.ru/health/na-uhe
- https://modernsurgeon.ru/napravleniya/dermatoonkologiya/ateroma/ateroma_mochki_ukha/
- https://kakiebolezni.ru/kozhnyie-zabolevaniya/ateroma/ateroma-za-uhom.html
- https://kozh-med.com/novoobrazovaniya/ateroma/za-uhom.html
- https://webdermatolog.ru/zabolevaniya_kozhi/ateroma/v_mochke_uha/
- https://mixfacts.ru/articles/%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B0-%D1%83%D1%85%D0% B0-%D0%BF%D1%80%D0%B8%D1%87%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%8B-%D1%81%D0%B8%D0%BC%D0%BF%D1% 82%D0%BE%D0%BC%D1%8B-%D0%BB%D0%B5%D1%87%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5
- https://uhoonline.ru/bolezni-uha/drugie/pochemu-poyavlyaetsya-ateroma-za-uhom-i-kak-ot-neyo-izbavitsya