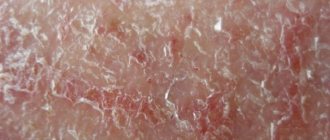
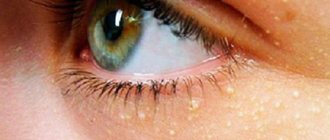
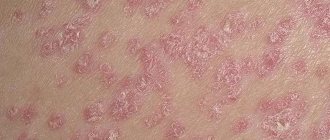
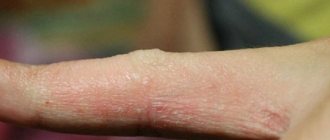
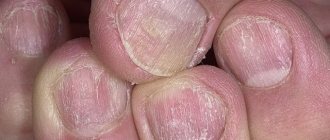
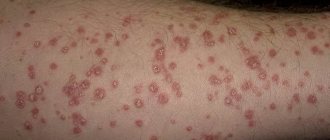
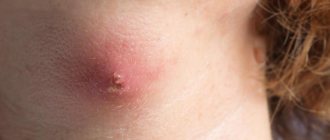
Microbial eczema is an itchy, inflammatory process that occurs in areas of the skin affected by a fungus or microbe. The rash appears in areas of ulcers, cracks and wounds. This disease is characterized by pyoderma, that is, purulent inflammation of the skin, the causative agents of which are streptococci and staphylococci. In pathogenesis, endogenous (related to the internal environment of the body) disorders in combination with exogenous (external) influences on the skin play a huge role. Microbial eczema most often occurs in people with a weakened immune system, or in those who have often been exposed to severe stress and nervous stress.
For each type of dermatoses, you need to look for your own approach to treatment, which is selected for different patients, depending on the form of the disease.
In the international classification of diseases, microbial eczema is classified as infectious or unspecified dermatitis.
Description of the disease
post-traumatic (microbial) eczema
One of the forms of eczema is microbial (bacterial), which has its own specifics. The development of this pathology can be provoked by:
- immune disorders,
- nervous system disorders,
- allergic reactions.
The disease is prone to frequent relapses. It is classified as a secondary pathology, due to its development against the background of an existing disease.
Microbial eczema can develop into its true form if not treated in a timely manner. In almost all cases, lesions are located on the skin of the upper and lower extremities.
It should be noted that the dermis is very important in the excretory system, ensuring the removal of toxic substances. Thus, if a person has problems with the kidneys, liver, or gastrointestinal tract, then the skin has to remove more of the toxins than it should normally. Harmful metabolites have a negative effect on it and can trigger the development of eczema. In other words, one of the main causes of various dermatoses is a disruption in the functioning of internal organs.
If we consider microbial eczema, then the main factor influencing the occurrence of the problem is infection, which reduces the protective functions of the skin and lowers human immunity. As a result, the processes of stopping the access of pathogenic microorganisms into the bloodstream are disrupted. Diagnosis consists of analyzing a smear for bacteriological culture and scraping for fungus.
Treatment of this disease in children
Unfortunately, children are no exception to the rule; their skin is also affected by eczema. This form of the disease is extremely rare; basically, eczema occurs as a result of severely reduced immunity, with frequent acute respiratory viral infections. When the body's resistance is low, it is easier for bacteria to penetrate a wound or abrasion.
Eczema develops quite quickly in children
In a child, microbial eczema develops very rapidly - the wound quickly festers as a result of the active proliferation of staphylococcus or fungus. As with adults, it is necessary to diagnose eczema so as not to confuse it with another skin pathology or form of the disease.
For an accurate diagnosis, keratinized scales will be needed to determine the nature of the origin of eczema. Treatment of eczema in a child is based on changes in diet, taking allergy medications and local antipruritic ointments.
The principle of treatment is similar to adult therapy, with the exception of the use of corticosteroids: here the decision is made by the treating dermatologist.
Therapy includes:
- exclusion of allergenic foods from the diet: citrus fruits, eggs, chocolate, strawberries, tomatoes;
- taking antihistamines: Claritin, Zyrtec, Zodak, Erius, Eden;
- compresses from a solution of fucorcin or resorcinol;
- use of drugs against intestinal dysbiosis: Lactofiltrum, Bifidumbacterin; application of local anti-itching agents: Fenistil, Flucinar, zinc paste.
Read: Instructions for metronidazole suppositories
In severe cases, it is possible to prescribe hormonal ointments based on methylprednisolone (Advantan) or hydrocortisone ointment. In the treatment of microbial eczema, it is important to add lotions and compresses from medicinal plants: chamomile, calendula, string. The main thing is to make sure that the child does not have an allergy to herbs.
As a preventative measure, it is recommended to treat children's wounds with syntomycin liniment.
Types of microbial eczema
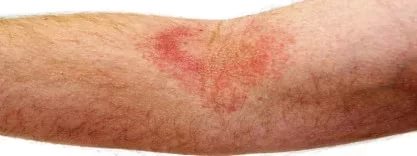
The following types of microbial eczema are distinguished:
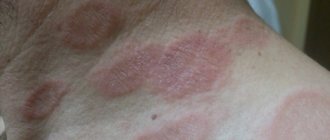
- Coin-shaped (plaque): Itchy, round lesions that resemble coins. The diameter of such “coins” is usually from 1 to 3 cm. A characteristic feature is the elevation of the plaques above the surface of the skin. The rashes are very itchy, which often causes problems sleeping. Liquid (exudate) may be released from the plaques, which is accompanied by weeping. Often, crusts appear at the site of peeling, which can subsequently crack. Symptoms include: hyperthermia, nervous anxiety, general weakness. This dermatosis is in most cases localized in the legs and arms.
- Varicose: appears in patients with varicose veins, thrombophlebitis and other disorders of the blood vessels.
The area most often affected is the skin of the calf muscle. Stagnation of blood in the lower extremities is the main factor in this pathology. As a result, the veins become inflamed, which leads to the accumulation of fluid in the body tissues and lymphostasis. Contraction of skeletal muscles is the best prevention for this disease. An active lifestyle helps prevent not only varicose veins, but also many other diseases. varicose eczema According to statistics from the most famous medical associations, almost every third woman and every tenth man suffers from varicose veins. Most often, varicose eczema occurs in older people. To get rid of this disease, you first need to treat the cause, not the symptoms. To do this, they often resort to surgical operations and wearing special underwear to improve lymphatic drainage. Do not forget about physical therapy as the simplest and most accessible method of preventing varicose veins. Itching and inflammation are relieved with medication. - Post-traumatic: develops due to trauma to areas of the skin against a background of weakened immunity. With a weak immune response, any mechanical injury takes quite a long time to heal and is a vulnerable place for various antigens to enter. This type of microbial eczema is observed quite rarely. It is characterized by itching, redness, rashes and crust formation. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy is prescribed.
- Sycosiform: Caused by staphylococci and affects people with chronic inflammation of the hair follicles. Location: chin, armpits, upper lip and area near hair follicles. Pustules appear on the affected areas, containing fluid and pus. There is itching of varying degrees, which brings discomfort to the patient. The course of treatment can only be prescribed by a specialist, since the disease is located on the face.
- Nipple eczema: the areola of the mammary glands is affected. It can develop due to poor hygiene or due to scratching during scabies. At first, rashes similar to small pimples form, but then they transform into blisters and brownish crusts. If not treated in a timely manner, the area near the lesion may become dry or enter a weeping stage, which is difficult to treat.
It is important to remember that this disease belongs to the group of non-contagious ones, that is, not transmitted from person to person. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment, depending on the stage of eczema.
Types and stages of eczema
Eczema is a peculiar chronic recurrent inflammatory disease of the epidermis with possible spread of the process to the papillary layer of the dermis. The pathology occurs with periodic exacerbations and short-term remissions.
Eczema occurs at any age (childhood, occupational, microbial) with the appearance of typical symptoms (rash with itching and weeping) of different localization, with a certain degree of manifestation, which differs in different patients in the stage and evolution of the inflammatory reaction. At the same time, the pathogenesis necessarily involves activation of the allergic reaction against the background of various provoking and predisposing factors.
There are three stages of development of eczema: acute, chronic and subacute, which differ in the characteristics of the transformation of the elements of the rash.
Stages of eczema
Features of manifestation
Redness of the skin (erythema) with swelling and the formation of papules and vesicles. Cracks in the inflamed epidermis, opening of vesicles, release of serous exudate and formation of crusts.
Formation of erythema with subsequent thickening of the skin and impaired pigmentation (lichenization), the appearance of excoriations and scales.
Chronic
The formation of erythema with lichenification and subsequent hypo- or hyperpigmentation is noted.
In addition to the main types of eczema: true, microbial, seborrheic and occupational, there are several forms that are less common and have their own characteristics.
Localization
Rash elements
Complications
Dyshidrotic eczema
Arms and legs (fingers, palms, feet)
Multiple sago-like blisters with extensive skin hyperemia without opening erosions. A distinctive feature is excruciating itching
Attachment of a secondary infection, with the formation of infected wounds and fistulas
Atopic eczema
Has different localization, specific rashes develop as a result of a complicated course of atopic dermatitis
A rash in the form of blisters that burst over time, forming a weeping surface with severe itching
Mycotic eczema
The back parts of the hands and feet, less often the scalp.
Develops on areas of the skin affected by inflammation of the fungal flora, which have a long and/or chronic course
The lesion has a clearly limited shape, is covered with lamellar crusts with detachment of the stratum corneum at the edges, and after removal of the crusts a weeping surface is formed
Development of pronounced swelling of the hands and feet with the addition of pyococcal (purulent) infection
Varicose eczema
This type of eczema develops against the background of varicose veins with prolonged stagnation of blood, which leads to a weakening of the protective properties of the skin, impaired trophism, and a tendency to form superficial ulcers and erysipelas.
READ ALSO: Wen on the eyelids: reasons for their appearance and how to get rid of them
It develops more often in older people.
Large lesions with jagged edges. Rash in the form of blisters, cracks and crusts with severe itching, which intensifies after contact with water
Attachment of a secondary infection in the form of microbial and fungal flora. Fistula formation.
Coin eczema
Upper limbs with exacerbations in the cold season
Rounded lesions (in the form of coins) with pronounced infiltration of areas of hyperemia and lichenification (thickening of the skin and impaired pigmentation)
Horny (tilotic) eczema
Plantar surface of feet and hands
The lesions have jagged edges. A distinctive feature is considered to be hyperkeratic processes with the formation of multiple, deep and painful cracks with weeping and itching during periods of exacerbation
Secondary infection, with the formation of infected fissures and fistula tracts
Contact eczema
(eczematous dermatitis)
Hands, face and neck, in men it may spread to the genitals
One of the subtypes of occupational eczema.
Multiple vesiculopapular elements against a background of severe skin hyperemia with severe itching. After the vesicles open, pinpoint erosions form and serous fluid is released. When contact with the allergen is eliminated, symptoms quickly disappear
Attachment of a secondary infection in the form of microbial and fungal flora
Allergic eczema
It can occur on any part of the body. It is seasonal in nature with exacerbations in the autumn-winter period against the background of a significant decrease in immunity
Multiple vesiculopapular elements against the background of severe skin hyperemia with itching. After opening the vesicles, erosions are formed, which after opening have the appearance of “wells” filled with serous fluid
Development of pronounced swelling of the skin with the addition of pyococcal (purulent) infection or fungal flora
Numular eczema
Back of wrists and lower extremities (feet and legs)
The rashes look like oval, round spots (about 3 cm) with clearly defined edges and protruding above the surface of healthy skin.
Weeping eczema
Face, backs of hands and forearms, feet, legs
The rash looks like redness and swelling, then small blisters and papules appear, which merge to form an erosive, weeping surface with itching and burning.
Attachment of a secondary infection in the form of microbial and fungal flora
Causes of microbial eczema
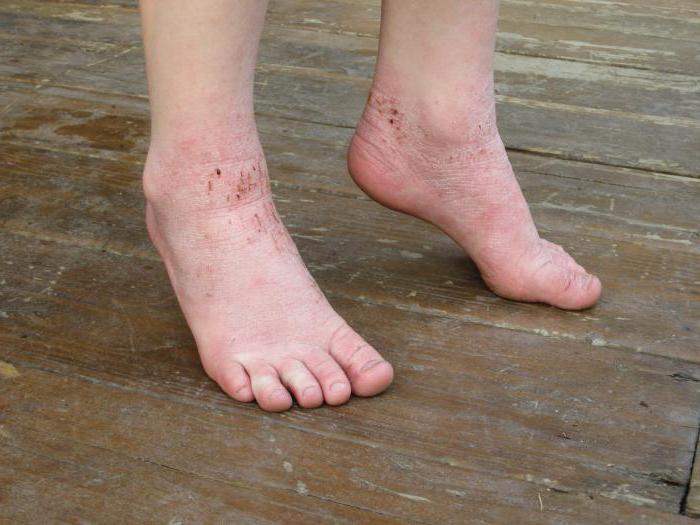
There are several factors that can cause the development of dermatosis. The causes are divided into common for all types of eczema:
- Disruption of the endocrine system.
- Weak immunity.
- Constant stress, VSD.
- Chronic inflammatory processes.
and specific only to microbial eczema:
- Sensitivity to the infectious agent.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Skin injuries (ulcers, abrasions, scratches, burns).
- Fungal and bacterial skin lesions.
Kinds
Depending on how the clinical picture of the disease manifests itself and its etiology, the following subtypes of microbial eczema are distinguished.
- Post-traumatic. It occurs as a violation of skin healing at the site of injury, burns or frostbite. An example is parawound eczema, which occurs at the site of sutures after surgery.
- Nummular. This is a fairly common microbial eczema. Foci of inflammation in this form most often occur on the hands. They look like round plaques ranging in size from 1 to 3 cm. The surface of such rashes is usually moist, swollen and over time becomes overgrown with dry purulent or serous crusts.
- Varicose microbial eczema. It occurs against the background of existing varicose veins or venous insufficiency. Ulcers, swelling and inflammation sometimes form near diseased veins. A slight itching may also occur. Microbial eczema on the legs can appear due to injury or as a result of maceration (swelling of the skin as a reaction to prolonged exposure to liquid).
- Sycosiform. The cause of this form is sycosis - damage to the epidermis, accompanied by the release of pus, the causative agent of which is Staphylococcus aureus. It is localized on the beard and mustache, pubis, hair and armpits. If eczema is added to sycosis, then itching and weeping areas appear at the sites of inflammation.
- Mycotic. It appears when there is a fungal infection on the hands or nails.
- Eczema of the nipples. Breastfeeding women sometimes suffer from it due to frequent nipple injuries. The disease can also appear in patients with scabies. Red, itchy spots form around the nipple, and the nipple itself becomes covered with painful cracks.
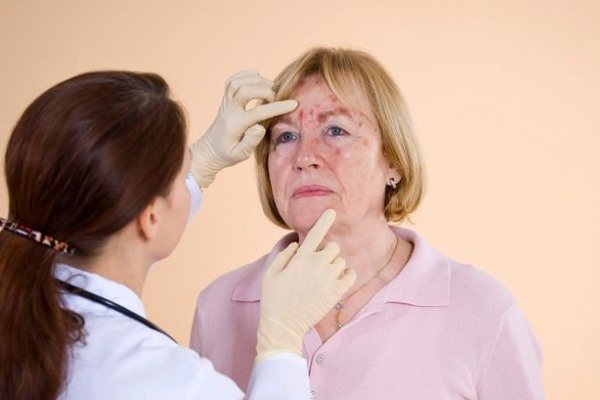
Symptoms of microbial eczema
Symptoms include inflammatory processes in the dermis, which are accompanied by rashes in the form of papules or vesicles, as well as a weeping stage. There is varying degrees of itching and redness of the skin. It happens that the burning sensation is so strong that it disrupts the patient’s daily routine. In such situations, intravenous injections of sedatives are used. Layers of dead epidermis (white or yellow) are observed locally. The disease develops around abrasions, scratches, ulcers and other wounds. The top thin layer of skin is easy to remove by touch; underneath it there will be a large accumulation of pus. Foci of bacterial eczema have uneven edges (except for the nummular form).
Symptoms
External manifestations of this disease can occur in any place:
- hands, arms, between fingers;
- stomach;
- chin;
- in the scalp;
- legs;
- neck;
- nipples;
- in the pubic area and armpits;
- upper lip.
However, most often the disease affects the legs, since many people have impaired blood circulation. Lesions of eczema are usually large, tend to grow, affecting normal skin, and may not have healthy areas in between.
The rash looks like papules or vesicles, the surface of the inflamed areas is red, swollen and wet and gradually becomes covered with dry purulent crusts.
Rashes with microbial eczema are accompanied by severe itching and peeling and have an asymmetrical shape.
The danger of the disease is that if not treated correctly, the disease affects healthy skin. In addition, allergic rashes may appear, and microbial eczema will turn into true eczema, which will be much more difficult to cope with. Scars and welts may appear at the site of deep ulcers. And if there are numerous areas of inflammation, then there is a risk of viral infection, including Kaposi's eczema, infection of which can be fatal.
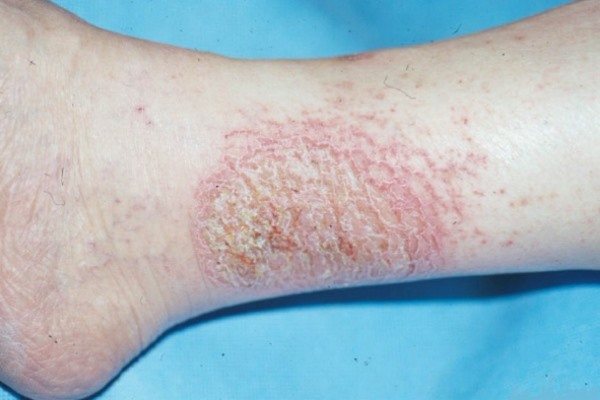
Features of microbial eczema on the hands
microbial eczema on the hands
Microbial eczema on the hands is localized due to constant contact of this part of the human body with microorganisms. In this case, it is necessary to completely stop contact of the free upper limb with infectious agents. Of course, it is impossible to completely isolate your hand from the external environment, but you can use disinfectant creams to protect yourself. If you have jewelry, you should remove it from your fingers and hands. Advantan and Dermovate have proven themselves to be effective against itching.
Water only provokes the development of microbial eczema on the hands, so it is necessary to minimize contact with it. For disinfection, you can use special creams or solutions of alcohol or potassium permanganate. It is worth switching to neutral soap and washing your hands with hypoallergenic hygiene products.
Features of therapy with folk remedies
Traditional methods are aimed at reducing the symptoms of microbial eczema: relieve itching, irritation, and accelerate tissue regeneration. In the complex treatment of eczema, lotions, compresses, infusions and decoctions of medicinal plants will not be superfluous.
Traditional medicine is used for treatment
The following methods are used:
- compress of coltsfoot and milk - a plant passed through a meat grinder, mixed with fresh milk, the mixture is applied to the eczema and wrapped in cellophane overnight;
- applying sea buckthorn oil - applied to the affected areas daily, the composition of the oil helps reduce itching, pain, and swelling;
- viburnum decoction - used as a natural immunomodulating agent, recommended for all types of eczema;
- baths with herbs - you can soothe inflamed skin with a bath with the addition of oak bark, chamomile, celandine, string, yarrow;
- infusions of dandelion roots, burdock, birch leaves - used as a natural anti-inflammatory agent;
- grated potato compresses - raw crushed potatoes are used as an application for microbial eczema to help the tissues recover faster.
Read: Pectusin should not be given to children
The patient needs to remember that folk recipes will not replace drug treatment due to the cause of microbial eczema.
Features of microbial eczema on the legs
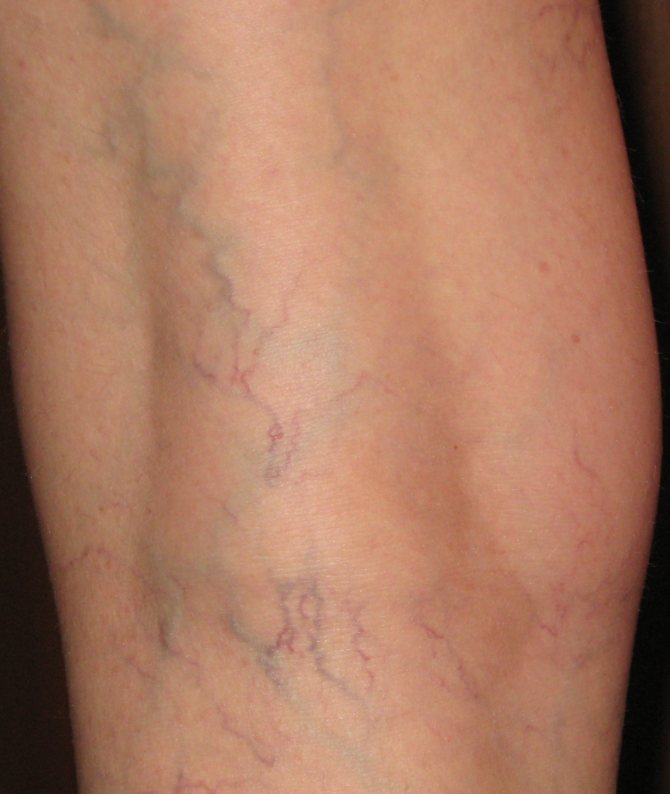
For microbial eczema of the legs, almost the same remedies are used as for lesions of the arms. Often, microbial eczema on the legs is accompanied by varicose veins, and then, in addition to local treatment, special underwear and medications are prescribed to tone the blood flow. Symptoms include redness of the skin, a grayish coating at the site of cracks and severe itching. At first, the affected areas have scalloped edges, but if not properly treated they can grow, affecting large areas of the leg.
The decisive factor in the appearance of purulent plugs is poor foot hygiene. Provoking factors include:
- maceration of the epidermis (a process in which swelling of the epidermis occurs if the skin comes into contact with water for a long time),
- trophic ulcers,
- skin injuries in areas of varicose veins.
It should be remembered that you should not put a lot of physical stress on your legs, as this can only aggravate the process. It is strictly forbidden to use socks made of synthetics or wool, as they provoke the development of pathology. Before going to bed, your feet are placed on a hill; you can make herbal lotions to increase the effectiveness of treatment.
Symptoms and signs of microbial eczema
There are several types of microbial eczema, but they have common symptoms:
- redness,
- severe itching of the skin,
- burning,
- sleep disturbance,
- skin peeling,
- the appearance of a wet or dry rash resembling psoriasis,
- separation of pus. The wound remains wet for a long time and heals slowly. Eczematous boundaries have a clear contour. With successful elimination of symptoms and inflammation, the skin remains deformed and darkened (develops on previously damaged areas: abrasions, cuts, purulent lesions). In the center of the affected area there are white formations filled with serous fluid.
Such manifestations require immediate medical attention.
Types of eczema and their symptoms
- Plaque - sizes vary from 3 to 5 cm. There is constant redness of the epithelium, swelling and a weeping surface. The appearance of a purulent crust is characteristic. It only spreads on the hands.
- Varicose veins - accompanied by dilation of veins in the affected area. Itching is moderate. It is possible that ulcers may form near the vessels.
- Sycosiform - inflammation of the hair follicles. Characterized by wetness. Localized in the scalp, armpits, and pubic area. The causative agent is Staphylococcus aureus.
- Nipple - manifests itself in women at the end of lactation, and in persons with scabies. The surrounding skin becomes covered with small cracks, itches and turns red. In addition, severe pain appears.
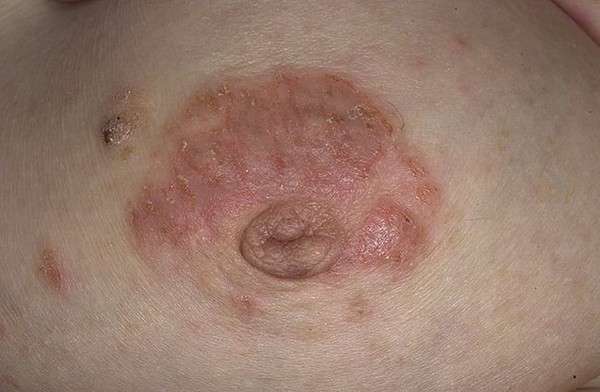
All these signs are typical for adults and children. The chronic form is distinguished by a large area of damage and is called true.
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosis is bacteriological examination. For this procedure, scraping is performed from the affected areas of the skin. The main goal is to identify the type of causative agent of the rash. The degree of penetration of infection into the tissue is determined by histological examination of the biomaterial.
In addition to laboratory tests, visual inspection is used. This procedure is carried out in a well-lit room at a comfortable body temperature. Visual analysis can assess the degree of swelling, localization and external manifestations of the disease. It is advisable to order additional studies to differentiate it from psoriasis, dermatitis and other forms of eczema.
What ointments are used to treat microbial dermatosis
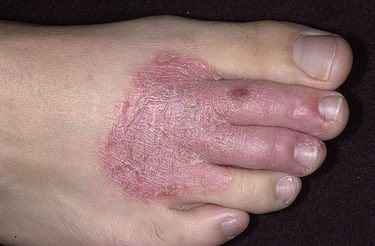
As you know, the fundamental element of therapy for any type of dermatosis is external agents. The microbial form of eczema cannot be cured with one ointment. A whole combined complex is needed, which will consist only of effective drugs that have real therapeutic significance.
In order not to make a mistake in choosing an external medication, i.e. ointments for microbial eczema, at the first signs of the disease you should contact a dermatologist without experimenting with self-medication. He will select the most effective remedies in a particular case, based on anamnesis, medical history, and probable causes of the development of dermatosis.
Today, ointments of various categories are used to treat microbial eczema:
- Corticosteroids for external use.
- Non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments.
- Antibacterial and antifungal medications for the treatment of microbial eczema
- Antihistamines and antiallergic drugs of local action.
Glucocorticosteroids and non-hormonal drugs for skin diseases
Speaking about the types of hormonal ointments for microbial eczema, the list of the most effective remedies should start with safe, but less effective medications:
- hydrocortisone ointment;
- prednisolone ointment;
- Lokoida;
- Afloderma.
These glucocorticosteroids contain synthetic compounds that are almost identical in structure to the natural hormones produced by the human adrenal cortex.
In fact, hormonal ointments have a wide range of effects on the skin, eliminating the symptoms of the pathology without much difficulty:
- inflammation;
- swelling;
- itching and burning;
- pain syndrome;
- toxic effects.

To treat microbial eczema, doctors prescribe hormonal ointments.
Medications of weak and moderate action can in some cases be used to treat microbial eczema in children, pregnant and lactating women. Since the etiology of the bacterial form of eczema differs in many respects from idiopathic or any other type of this skin disease, the choice of hormonal ointment largely depends on the individual characteristics of the disease.
If a stronger medicinal effect is necessary, the following means are used:
- Soderm;
- Advantan;
- Sinalar;
- Dermovate.
These drugs help relieve pain syndromes, relieve inflammation and are indispensable for the recurrence of the disease.
A separate group of external medications includes preparations for eczema that do not contain hormonal substances. The absence of corticosteroids is usually advisable at the onset of the disease. It is rational to use such medications also after a course of hormones, because glucocorticosteroids cannot be used for a long time. They are able to provide a strong therapeutic blow to the symptoms that bring suffering and discomfort, but they will not be able to get rid of eczema in a few days. Therefore, there is an urgent need for anti-inflammatory therapy using safe means without side effects.
Some of the most popular non-hormonal drugs for dermatosis are the following ointments:
- Vishnevsky;
- ichthyol;
- boric naphthalene;
- Radevit;
- Eplan;
- Losterol;
- indomethacin.
Antibiotics and antifungal medications for bacterial eczema
Antibacterial treatment of microbial eczema with ointment can rightfully be called one of the fundamental points in the treatment of skin diseases. Since this type of dermatosis is of pathogenic origin, the presence of antibiotics in the therapeutic complex of external medications is mandatory. Meanwhile, the pharmacy assortment and price variety do not allow patients to obtain specific information about which antibacterial or antimycotic agent is better.
For bacterial eczema, the presence of antibiotics in the therapeutic complex of external medications is mandatory!
Based on the type of microbial pathogen, the doctor will prescribe a medication with the most suitable acting and healing element. Among the antibacterial ointments that are used in the treatment of microbial eczema, the most common ones should be noted:
- Levomekol;
- Erythromycin;
- Terramycin;
- Tetracycline;
- Oflocaine.
Instead of an antibacterial effect on the epidermis affected by dermatosis, the use of antimycotic agents may be necessary, especially when it comes to widespread fungal infection of the lower extremities.
Effective ointments for the treatment of microbial eczema on the legs (the list will allow you to get a detailed idea of the most popular products):
- Mycozoral;
- Lamisil;
- Exoderil;
- Terbizil;
- Mikonorm;
- Nizoral;
- Zalain;
- Bifosin.
All of the above remedies affect the condition of the epidermis by the principle of providing a fungistatic effect on representatives of various fungi. Such preparations contain astringent components that accelerate tissue healing, eliminating the unpleasant symptoms of burning and itching of the skin. Just like steroid and antibacterial ointments for microbial eczema, antifungal agents should be prescribed by a doctor.
Antiallergic drugs to relieve itching and other symptoms
A separate category includes antihistamine external ointments, which help get rid of pain, severe unbearable itching and burning. To eliminate all the unpleasant sensations that you encounter during the course of dermatosis, you should pay attention to antiallergic drugs with an anti-inflammatory component. Such drugs do not contain hormones and are relatively safe, but in any case you should consult a doctor before using them.
Antihistamine ointments for microbial eczema, which doctors most often prescribe to patients:
- Hyoxyzone;
- Fenistil;
- Protopic;
- Gistan;
- Radevit;
- Elidel;
- Skin Cap;
- Bepanten;
- Lidocaine;
- Losterine.
These preparations are applied to clean, dry epidermis at least 3-4 times a day. If a remedy prescribed by a doctor does not bring the expected result, the patient must inform a specialist who will review the treatment regimen. In addition, the effectiveness of the ointment for microbial eczema can be neutralized due to improper or irregular treatment of wounds. If there are cracks, minor scratches and abrasions, we must not forget about the use of an antiseptic and the use of a bactericidal patch.
Antihistamine external ointments help get rid of pain, severe unbearable itching and burning.
Ointments for microbial dermatosis according to folk recipes
Therapy for the skin disease in question may also include the use of folk recipes. Treatment is carried out with simple pharmacy and household ingredients. Several simple ointment recipes for microbial eczema will help you quickly get rid of the disease and restore healthy epidermis. But it should be remembered that folk remedies are not always safe - the risk of an allergic reaction almost always remains, even if we are talking about products that have been repeatedly used for their main purpose without any negative consequences.
Dermatologists often give recommendations to patients regarding the use of home recipes. Do not hesitate to ask your doctor whether one or another of the following remedies can be used in a particular case:
- Ointment based on sour cream and copper sulfate . Prepared in the following ratio: 3 tbsp. l. dairy product per 1 tsp. copper sulfate. Mix thoroughly and apply a thin layer to the affected areas of the epidermis twice a day. The course of treatment is 10 days. Before each procedure, a fresh composition should be prepared.
- Ointment with ash . To prepare this remedy you will need rosehip branches, which you need to burn and collect the ashes, and then mix with baby cream or Vaseline. For 3 parts of the base, use 1 part of ash. After mixing until smooth, apply to eczematous erosions several times a day. The product effectively eliminates itching and redness.
- Ointment based on birch tar, fish oil and vinegar . All components are mixed in equal quantities and used for microbial eczema twice a day. The procedure can be performed every other day.
- Ointment made from honey and aloe . Prepare a large leaf of the plant, wash it thoroughly and wipe it with a paper towel. Remove the skin from the aloe and grind until mushy. Add honey to the mixture in a 1:1 ratio. After mixing the raw materials, you can begin treatment by applying homemade ointment to areas affected by microbial eczema.

Honey and aloe ointment is an excellent folk remedy for treating microbial eczema.
Treatment methods
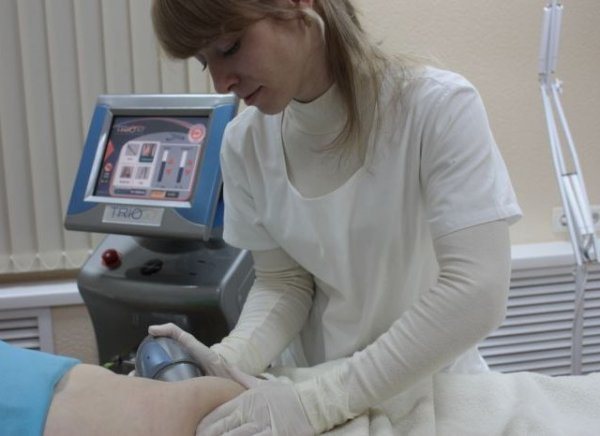
For the effectiveness of treatment, an integrated approach is used, which consists of the use of external and systemic drugs. External treatment of microbial eczema:
- Lotions made from lead water, using a solution of resorcinol.
- Ointments containing antibiotics: Dettol, Bactroban.
- Antifungal ointments.
- For complications, ointments containing corticosteroids (Lokoid, Block) are used.
To achieve maximum efficiency, you must follow the following rules:
- Avoid microtraumas and overheating.
- Maintain hygiene but limit contact with water.
- Wear underwear made from natural material that does not cause an allergic reaction.
- Follow the diet prescribed by your dermatologist.
Systemic treatment:
- The use of broad-spectrum antibiotics (Azithromycin, Cefazolin, Doxycyline).
- Flucanazole is often prescribed as an antimycotic.
- Use of cytostatics and glucocorticosteroids.
- Antihistamines (Loratadine, Suprastin).
- Sedatives (tinctures of valerian, motherwort, St. John's wort, peony and even sleeping pills).
- Taking vitamins A and B.
- Physiotherapy, which includes ultraviolet light, ozone therapy, phototherapy and laser therapy.
Home treatment
Even at home, it is important to take good care of your skin to reduce inflammation. For this use:
- lotions with resorcinol,
- Castellani liquid,
- ointments with zinc,
- tar,
- ichthyol.

In acute cases, they are treated with brilliant green or aniline dyes. If the infection is bacterial in nature. Then the doctor recommends ointments with antibiotics, for example:
- Dettol,
- Drapolene.
If a fungus is detected, use antifungal drugs, such as:
- Loceril,
- Exoderil.
If the lesions are especially on the legs, treatment includes hormonal drugs:
- Advantan,
- Elokom
- and Celestoderm.
When the disease is not very advanced, non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs cope well with it:
- Eplan,
- Radevit,
- Losterine.
Calcivirin inhibitors have become very popular lately:
- Tacrolimus,
- Pimecrolimus.
They cope well with lesions even on large areas of the skin and relieve inflammation and itching.
Physiotherapy may be prescribed by your doctor:
- ozone and cryotherapy,
- laser therapy,
- UFO and UHF.
Folk remedies for treating microbial eczema

treatment of eczema with herbs
- Lotions based on herbal infusions. You need to take about 20 grams of herbal collection of nettle, string, St. John's wort. For a glass of boiling water - 1 spoonful of the resulting mixture. This substance is infused for about two hours. Keep on affected areas for no more than 30 minutes.
- Dandelion tincture to strengthen the immune system. Strictly observe the proportion: for 1 tablespoon of chopped dandelion root - 400 ml of boiled water. Let it steep all night. Already in the morning you can take the first portion of the tincture and drink 50 ml 3 times a day.
- Black elderberry compress. This plant has a high antiseptic effect. First you need to collect and wash the elderberry leaves. Next, beat and chop. Apply the resulting substance to the affected area of the skin and wrap it with gauze for half an hour. The procedure should be repeated every day until the purulent scales disappear.
The prognosis for microbial eczema is favorable. With proper treatment, stable remissions can be quickly achieved. The main thing is not to self-medicate and strictly follow the instructions of your doctor.
Treatment
Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the infectious focus and the underlying disease. The plan is drawn up based on the etiological factor. Treatment should be comprehensive, using not only local drugs, but also intravenous ones.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy involves local or course treatment. For pyoderma eczema (staphylococcus, streptococcus), medication is indicated. It applies:
- antihistamines;
- complex vitamins (mainly group B);
- sedatives;
- antibacterial and antifungal ointments for topical use;
- antiseptics;
- astringents.
They treat fungal-affected areas and treat ulcers and sycosis.
Physiotherapy
- Magnetic therapy.
- Ozone therapy.
- Laser therapy.
- Ultraviolet irradiation.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy.
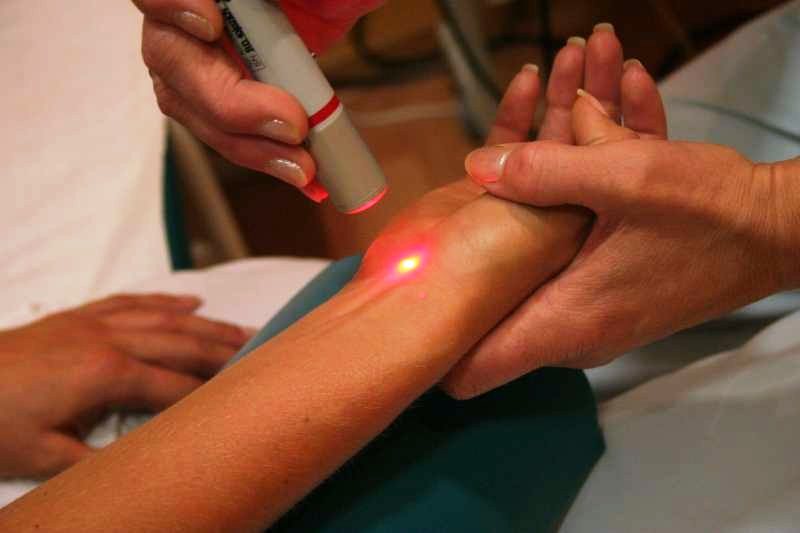
Laser therapy
In addition to eliminating the underlying problem, physical therapy can help get rid of traces of the rash.
It is important to use a gentle diet that excludes foods that cause allergies (if eczema has become true).
Traditional medicine recipes
Treatment with folk remedies includes local application of herbal lotions and is used only as an additional therapy to the main treatment.
Effective lotions from plant decoctions:
- calendula;
- celandine;
- series;
- nettle;
- St. John's wort;
- yarrow;
- birch.
Wetting with infusion of pine needles and cones: add 1 liter of water per 100 grams, leave for about 15 minutes and apply to eczema.
Elderberry leaves have a pronounced antiseptic effect. They need to be mashed so that they release juice, applied to the skin and wrapped in cling film.
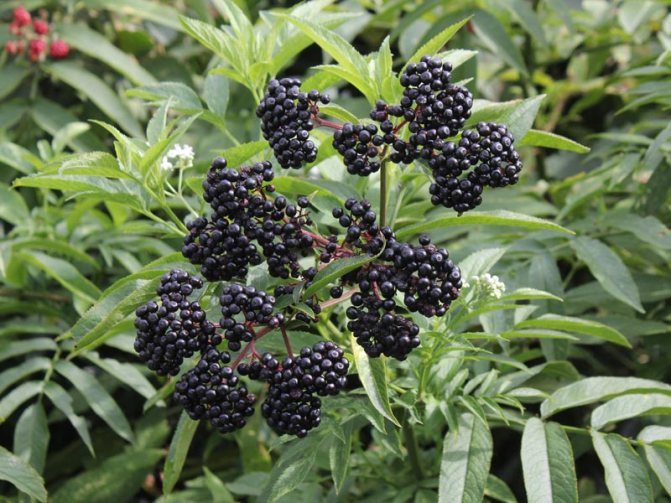

Elder
Inflammation can also be favorably influenced from the inside. To do this, you need to make tea from dandelion root. The brewing process lasts up to 12 hours, drink several times a day. This drink improves the functioning of the immune system and helps cope with the bacterial component in the skin.