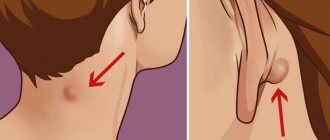
What is a boil?
What is the difference between a boil and a carbuncle? To answer the question, you need to provide definitions of these terms.
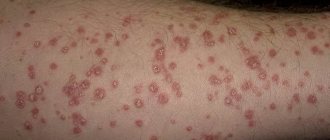
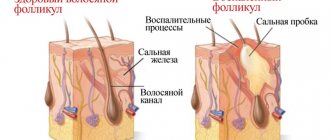
A boil may also be known as a boil or abscess. This is the name for purulent inflammation of the hair follicle (the “root” of the hair) and the adjacent sebaceous gland. Outwardly, it looks like a swollen redness, a red nodule on the skin. Over time, a purulent “head” forms in its center. The size of such a formation can be within 0.5-3 cm. If a person suffers from multiple boils, the phenomenon is called furunculosis.
What is a carbuncle?
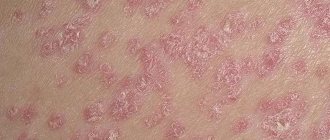
A carbuncle is a purulent inflammation of several hair follicles at once. The sebaceous gland may be affected, as well as the subcutaneous tissue. Compared to boils, this is a more serious purulent lesion. Outwardly, this is a much more extensive inflammatory focus: many purulent “heads”, skin reddened to a purple state.
What is the difference between a boil and a carbuncle? If furunculosis is a local inflammation, local symptoms, then with the development of a carbuncle the general well-being of a person worsens. Body temperature rises, muscle pain and general weakness appear.
Characteristics of the carbuncle
With a carbuncle, several hair follicles become inflamed, forming a continuous infiltrate, and later purulent-necrotic rods are formed. Multi-chamber abscesses in the skin and subcutaneous fat, numerous pustules and holes through which pus leaks out are typical differences between a boil and a carbuncle. The skin under and around the formation swells, becomes purplish-red and warm to the touch. Carbuncle differs in its effect on the body as a whole. It is a more serious skin lesion, but it goes through the same stages of development. Body temperature rises, sharp pain in the affected area radiates to nearby areas.
A general blood test indicates all the signs of the inflammatory process: the ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) increases, the number of leukocytes increases. In purulent-necrotic diseases, neutrophilic leukocytosis is observed.
Effective treatment leads to the fact that after a few days, fluctuation zones appear in the area affected by the carbuncle. It differs from other purulent formations by the presence of several rods inside. After getting rid of the formation, the skin becomes covered with ulcers and heals slowly (up to a month). At the site of the infiltration, an ugly scar with uneven edges, resembling a star, remains.
What do they have in common?
We look at the difference between a boil and a carbuncle. But let's see what unites them.
Both inflammations, as a rule, appear in locations that are subject to friction with clothing, parts of the body that sweat a lot, and are covered with vellus hair. Therefore, such formations often affect the face, neck, armpits, and legs. Often appear in the genital areas.
The development of boils and carbuncles on the face, body, and limbs is provoked by a bacterial infection. Most often these are streptococci and staphylococci, which inhabit the surface of the skin in large numbers. They can get under the skin as a result of both large cuts, abrasions, scratches, and microtraumas (for example, pricks from plant thorns). If the body's immune forces are reduced for one reason or another, inflammation develops.
Boils and carbuncles (you can see photos of inflammation in the article) are not contagious. But we must keep in mind that when the purulent “cap” with its contents is opened, new pathogenic bacteria can enter the surface of the skin. If they spread to neighboring wounds, this causes new inflammation. Therefore, during treatment you need to be careful about hygiene - wash your hands when touching a boil or carbuncle, change the bandages periodically.
Any skin abscess, boil or carbuncle of the face should never be squeezed out, cut or pierced by yourself! This risks spreading the infection into deeper tissues. The infection can enter the blood and sepsis will develop. It can also be carried into the brain through the blood, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
What is the difference between boils and carbuncles
The disease usually develops with a combination of external and internal factors and a decrease in the body's defenses.
The reasons for the appearance of a carbuncle include:
- Active reproduction of pathogenic organisms on human skin.
- Violation of the integrity of the epidermis (wounds, scratches, splinters, insect bites, calluses, scratches, bruises, abrasions).
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Disruption of the sebaceous glands.
- Poor facial and body hygiene.
- Endocrine pathologies (disorders of the thyroid or parathyroid glands, adrenal glands) and metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity).
- Immunodeficiencies and hypovitaminosis.
- Frequent infectious diseases (ARVI, influenza, parainfluenza, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis).
- Serious chronic pathologies (arthritis, myocarditis, hepatitis).
- Poor nutrition and inactive lifestyle.
- Stress and psycho-emotional stress.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Wen on the forehead causes of appearance
Doctors define the disease as a dermatological and surgical disease caused by staphylococci and streptococci and identify several stages in its development:
- Infiltration (its duration is 1-2 weeks). It begins from the moment microorganisms enter the surface layers of the epidermis and the base of the hair follicle, then an inflammatory process begins in the area of infection with reactions of redness and swelling of the skin, which rapidly spreads and covers already healthy areas of the skin.
Photo of the first stage
At the same time, the blood in the capillaries becomes very viscous and therefore blood clots appear, so the site of inflammation quickly darkens or turns black. - Suppuration (lasts 10-20 days). It begins with the formation of purulent-necrotic masses in the center of the carbuncle, and in some places holes appear from which purulent exudate flows.
Stage of suppuration
At this stage, the lesion resembles a large ulcer that penetrates the soft tissues right down to the bones; they quickly become saturated with purulent fluid and die, which is why large areas of necrosis are visible around the base of the carbuncle.
One of the external signs of how a carbuncle differs from a boil is that the stage of spontaneous release of pus to the surface does not exist in the first, but in the second it does, therefore, in case of a carbuncle, in order to completely cleanse its cavity, it is recommended to surgically open it and aseptically clean the resulting cavity . Conservative therapy is usually used at the first stage of development of this pathological formation.
General damage to the body during carbuncle includes: fever, intoxication, general weakening of the body.
Drug therapy is used at the infiltration stage and can help avoid further development of the disease, suppuration and tissue necrosis.
Your doctor will recommend how to treat carbuncle at home quickly and effectively.
Typically, surgeons or dermatologists prescribe a course of antibiotics to which staphylococci are sensitive (Ampiox, Ceftriaxone, Gentamicin, Doxycycline, etc.), and ointments or emulsions (synthomycin, streptomycin, levomikol) are prescribed locally for outpatient use. Additionally, the carbuncle is pricked with antibacterial agents and its surface is treated with antiseptics (usually a 70% alcohol solution), but this is already in a clinic setting.
If such treatment methods are applied in a timely manner, it is possible to initiate a reverse mechanism for the regression of the carbuncle and achieve resorption of the infiltrate and complete restoration of the skin and its functions.
In the stage of suppuration, the main guarantee of recovery is surgical opening of the abscess and removal of the pathological contents from it.
Carbuncle: photo
After the operation, the resulting cavity is tamponed using proteolytic enzymes and a hypertonic NaCl solution or, if necessary, drained, and a sterile dressing is applied on top, which is changed daily.
With a large area and depth of damage, the wound surface heals with the formation of scar tissue.
For their regeneration, after opening the carbuncle and fusion of the wound edges, physiotherapeutic methods are used (UVR, UHF, ultraviolet or intravenous laser irradiation of blood), and long-term intake of vitamins and mineral complexes is prescribed.
Indications for hospitalization are severe symptoms of intoxication (dehydration, high temperature, severe weakness), localization of the carbuncle on the face or head, the presence of underlying diseases (systemic, autoimmune, diabetes, anemia, malignant neoplasms, immunodeficiencies).
Depending on which particular flora caused the formation of the carbuncle, the following types of suppuration are distinguished:
- Emphysematous. The disease has an acute course. Only cattle suffer from such carbuncles. People do not become infected with this type of carbunculosis.
- Purulent. This type of carbuncles is diagnosed more often than others.
- Anthrax. The symptoms of this disorder are very specific. Such carbuncles can occur in both humans and animals (domestic and wild).
- Plague. Pathology is rarely detected. The causative agent is the plague bacillus.
This disease is caused by bacterial flora from the class of clostridia, namely Clostridium chauvoei. Artiodactyl animals most often suffer from emphysematous carbuncles; in humans, the disease is practically not diagnosed. When cattle are affected, tumors are palpated in their muscles and produce a specific crunching sound.
Most often the disease is found in young animals. In most cases, carbuncles lead to the death of individuals. The peak incidence occurs in summer and autumn.
Purulent carbuncle
Most often, people have a purulent carbuncle caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Other pathogenic flora cause inflammation less frequently. A person experiences suppuration of the epidermis and fiber that surrounds the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Single carbuncles tend to merge into large foci, forming an infiltrate.
This type of disease often requires the help of a surgeon, as it threatens the development of serious complications.
Anthrax carbuncle looks like a small red pimple that itches all the time. After just 2 days, a pustule forms at the site of the lesion. It looks like a bubble containing a reddish liquid inside. Taking the contents from the pustule for bacterial culture allows you to identify anthrax bacilli.
After some time, the bubble opens and a crust forms on its surface. The scab quickly darkens. After a few hours, the crust becomes hard and completely black, with new small bubbles appearing around it. These bubbles also contain liquid inside. The tissue surrounding the carbuncle swells and then dies.
Inflammation develops under the influence of toxins released by bacteria. They provoke disruption of tissue nutrition. Swelling increases in the affected area, and then necrosis occurs.
Symptoms of anthrax infection:
- Pain in the affected area is barely noticeable or absent at all.
- After opening the papule, a scab begins to form instead.
- New blisters appear around the scab.
- There is no pus in the affected area.
- The area of inflammation loses its former sensitivity, the skin in this area becomes numb.
Plague Carbuncle
A plague carbuncle forms in the area of the body that was affected by the plague pathogen.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Intense pain.
- Significant swelling.
- Suppuration. There will be a lot of pus in the affected area.
- Tissue necrosis.
Carbuncles appear due to the fault of pathogenic flora that affects a living organism. These can be staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, etc.
In order for an infectious agent to enter the hair follicle and suppuration to occur, the body must be affected by one or more pathological factors at once, including:
- Excessive activity of sebaceous glands or sweat glands
- Contamination of the skin with certain substances (coal, sand, cement).
- Skin injuries.
Staphylococcal carbuncle is formed due to the fault of staphylococci. The source of the spread of infection is humans. Staphylococci belong to the opportunistic flora. This means that until a certain point in time they will exist peacefully on human skin, without causing any harm to the body.
Anthrax carbuncle is a contagious disease. The infection spreads through contact. A person can become infected from domestic animals, for example, from a pig, goat or cow. Ulcer spores penetrate through injured skin; less often, mucous membranes become the gateway for infection. Pathogenic flora quickly spreads throughout the body, affecting the lymph nodes. This leads to their inflammation.
Risk factors that can provoke carbunculosis:
- A decrease in the body's defenses, which often occurs after illness.
- The presence of a chronic source of infection in the body.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Anemia.
- Diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disorders.
- Exhaustion of the body.
- Psychological overload.
Goals to be achieved during carbuncle therapy:
- Approximate the time of ripening of the abscess.
- Do not allow purulent masses to spread to nearby tissues and organs.
- Remove the central part of the suppuration and thoroughly clean the ulcer of dead tissue.
- Do not allow the bacterial flora to cause severe intoxication of the body.
- Direct efforts to prevent complications of the disease.
If the carbuncle is small and located on the arms, legs or body, then treatment is carried out at home. Specific recommendations depend on the stage of the abscess. Provided that a person consults a doctor before a purulent-necrotic focus has formed, there is the possibility of drug correction. Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment.
Inpatient therapy is indicated for patients at a late stage of the disease, when there is already a focus of necrosis. Such patients require surgery. It is carried out as an emergency if the disease is severe, the abscess is large, and is located on the face. When the main symptoms of the disease are eliminated and the person’s well-being returns to normal, he will be prescribed physiotherapeutic treatment.
- A traditional carbuncle forms on the face, body, limbs and torso and develops according to classical canons in several stages.
- Kidney carbuncle. Occurs as a complication after suffering pyelonephritis. Its manifestation is similar to inflammatory kidney diseases and is sometimes difficult to distinguish from them. Symptoms of the disease include fever, intoxication and pain in the lumbar region. Differential diagnosis using X-ray and ultrasound methods helps to identify pathology.
- Emphysematous carbuncle. It does not develop in humans; it affects cattle. When infected with a pathogenic microorganism, many swellings are found on the body of animals, they quickly weaken and die from cardiac and respiratory failure.
- Anthrax carbuncle. It is formed when a person is infected with the anthrax bacillus, has a severe course and is extremely contagious to others.
- Infiltration (its duration is 1-2 weeks). It begins from the moment microorganisms enter the surface layers of the epidermis and the base of the hair follicle, then an inflammatory process begins in the area of infection with reactions of redness and swelling of the skin, which rapidly spreads and covers already healthy areas of the skin.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Toenail fungus: symptoms and causes
Difference between inflammations
Let us now present the main differences between boils and carbuncles. By the way, there are not so many of them.
Boils most often appear in men. Especially among young people, teenagers. Additionally, people who prefer tight clothes and do not care about the hygiene of their body are susceptible to inflammation. Reduced immunity for some reason is also of great importance.
Another difference between boils and carbuncles: the latter are much less common. Men are also more susceptible to them, but they are already middle-aged and elderly. People whose health is weakened by a serious general chronic disease are also at risk. For example, diabetes.
What is the difference between a carbuncle and a boil? The photos, as you can see, don't really convey their difference. An important difference is in the treatment of these inflammations. A boil can be easily treated at home. Especially at the initial stage, before the formation of an abscess. If a carbuncle develops, you should always consult a doctor. Especially if it appears on the face and you feel a general malaise.
Causes of boils
If you look at the photo of a boil and a carbuncle, you can immediately understand what the difference is. B. area of inflammation. As for the reasons, some differences can also be identified.
In most cases, the cause is infection of the hair follicle with Staphylococcus aureus. Under normal conditions, these bacteria live on the surface of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, and skin, without causing harm to the body. Approximately 20% of people on the globe are carriers of staphylococcus.
A boil develops when bacteria enter the skin through cuts, scrapes, or other injuries. The immune system reacts to this by sending white blood cells to the foreign agent. The result of their “war” among themselves is that same pus. It consists of dead bacteria and dead immune cells.
Factors that provoke inflammation include the following:
- Adolescence in men. During this period of life, the skin becomes more oily, which promotes the growth of bacteria.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- Close contact with people who have boils on their skin.
- Engaging in a sport that involves increased sweating, friction of tight clothing against the skin, close contact with other athletes (as in the case of rugby, for example).
- Living in unfavorable sanitary and hygienic conditions.
- Skin diseases - scabies, atopic dermatitis, etc.
- Excessive body weight.
But boils can also appear in a person whose life does not have any of the provoking factors. If this problem comes back again and again, there is a reason to check your health. Since this is one of the symptoms of chronically reduced immunity, which may indicate many hidden serious pathologies.
Predisposing factors
Carbuncle does not develop in physically healthy and active people. This is a disease of a weakened body. The formation of inflammation is promoted by:
- unfavorable working conditions (dusty premises, dirty workplace and special clothing);
- contamination of the skin in places of contact with clothing;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (rare showers);
- increased sweating;
- avitaminosis;
- decreased immunity;
- unhealthy diet (fast food, a lot of spices, sweet and salty);
- alcohol abuse;
- systemic diseases (endocrine, gastrointestinal lesions);
- long-term infectious diseases.
A combination of several reasons reduces the body’s resistance to staphylococcus, and inflammation develops.
Causes of carbuncle
Just like boils, carbuncles are caused by the same Staphylococcus aureus. They develop against the background of a deeper spread of infection into the subcutaneous layers. Several sebaceous glands and hair follicles are also involved in the process.
The risk group here includes people with chronically reduced immunity. This may occur with the following diseases and conditions:
- Diabetes.
- AIDS.
- Prescribing a long course of treatment with steroid drugs.
- Chemotherapy.
- Acute lack of vitamins and essential micro- and macroelements in the daily human diet.
- Skin diseases affecting large areas of the body.
- Addiction to drugs (especially when administered intravenously).
- Diseases of the blood, blood vessels and heart.
Complications of carbuncle
The occurrence of a carbuncle is fraught with various complications. This is due to the fact that the causative agent of the disease penetrates the body tissues through the vessels and enters the blood. Complications in the presence of a carbuncle can be observed in people who practically do not receive adequate treatment, and their health is already weakened during the course of the disease.
In soft tissues, under the influence of infection, phlegmon, or abscess, forms. If bones become infected, there is a risk of osteomyelitis. If the infection spreads to the blood vessels, a person may develop thrombophlebitis; patients often experience bleeding. In complex forms of the disease, erysipelas of the skin may develop in parallel.
Carbuncles that appear on the face can lead to serious complications. Such formations, if untreated, can provoke the disease of purulent meningitis if the infection affects the brain. The pathogen enters the blood, sepsis develops in the body, this process often leads to death of the patient.
Symptoms of a boil
Now you know the difference between a boil and a carbuncle. Let's look at their symptoms.
As a rule, three factors are sufficient for the appearance of a boil: skin friction, increased sweating, and the presence of hair follicles. That's why their most common locations are the face, neck, armpits, groin, buttocks, and thighs.
First a red spot appears. Over time, it increases and becomes dense. The site of inflammation begins to hurt. Then a purulent yellowish head appears in its center.
Over time, the inflammation opens and pus leaks out. The pain goes away, the wound heals, and a scar appears in its place. The process can take from a couple of days to two weeks.
The most dangerous location is the appearance of a boil in the area of the nasolabial triangle. The fact is that the vessels feeding this zone also reach the brain. If you squeeze out a boil and introduce an infection, it may well reach the brain, which will trigger the development of meningitis - a life-threatening infectious disease that requires immediate hospitalization.
The most painful are boils in the nose, ear, and genitals. They swell and increase in size. This is due to the presence of loose subcutaneous tissue, in which the inflammatory process quickly develops.
Carbuncle
A carbuncle is a purulent formation, which is mainly localized in the neck. Also found on the shoulder blades and buttocks. The disease is characterized by the appearance of ulcers that affect the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Accompanied by necrosis of skin tissue and skin necrosis. Carbuncles occur in the singular or plural. The initial stage manifests itself as a small infiltrate, which after a certain time becomes a painful abscess.
Causes of carbuncle
The appearance of a carbuncle is caused by the presence of streptococci or staphylococci in the body. In addition, certain reasons contribute to the appearance of a carbuncle; only the most common of them are given here.
- Failure to comply with personal skin hygiene standards. Prolonged contact of the epidermis with substances such as fuel oil, machine oil, and other petroleum products. Untimely change of linen, too high air humidity, excess heat, etc.
- Even minor damage to the skin surface. For example, scratching after insect bites, squeezing out pimples. The presence of an irritating factor in the form of coal, lime, cement dust.
- Insufficiently good sanitary conditions at home or at work, impaired metabolism due to diabetes.
- An unbalanced diet, in which there is a lack of minerals and vitamins.
- The causes of carbuncle can be explained by diseases that lead to general exhaustion of the body - various anemias, fatigue of a neuropsychic nature, etc.
These and many associated causes are a factor determining the occurrence of carbuncles, as well as boils, and various skin diseases. As practice shows, this disease most often occurs on the back of the neck, which is facilitated by prolonged friction with the sweaty collar of a shirt or jumper. Much less frequently, areas of the body such as the cheeks, lips, buttocks and back are affected. Moreover, younger patients more often suffer from carbuncles in the facial area, and older people complain of the appearance of the disease on the torso, limbs, and neck.
Symptoms of the disease and main signs
Often a carbuncle is confused with a boil. But it should be remembered that the symptoms of carbuncle are somewhat different. Carbuncles often occur singly, while boils, on the contrary, occur in the plural. The area of epidermal damage varies, from one centimeter in diameter to the size of a child's palm.
- At the beginning of the disease, a slight elevation in the form of a nodule forms on the neck or in another part of the body, which begins to increase in size and becomes severely painful.
- An inflamed area begins to form around the nodule; in the area of infiltration, the skin becomes purplish-red in color, often with a bluish tint.
- The surface is covered with purulent foci in large quantities, in appearance they resemble plugs. They are surrounded by swelling and redness. There is a feeling of “tugging” pain.
- The opening of the pustules occurs gradually, and the upper part of the carbuncle looks like a sieve. Purulent contents are released from numerous holes, and sometimes particles of dead epidermal cells appear.
- After some time, the focus of the disease begins to take a crater-shaped shape, the surface becomes ulcerative-necrotic. This is a characteristic feature of a carbuncle, and the necrosis can extend very deeply.
The inflammatory process subsides slowly, pus and dead cells are rejected. The edges of the carbuncle are filled with granulations, in some cases there is a delay in rejection in the center of the inflamed area. The process ends with scarring.
General phenomena with carbuncle
This disease also causes general symptoms such as headache, nausea and vomiting, and fever. The body temperature rises to forty degrees, the pulse quickens, and the general condition is characterized as serious.
Against this background, lymphadenitis, thrombophlebitis, and lymphangitis may occur. The complications that arise are aggravated by intoxication, and often result in sepsis.
If the carbuncle occurs on the face (upper lip, corners of the mouth), then the course of the disease is especially difficult. This is especially true for patients with diabetes and the elderly.
Anthrax carbuncle
The described symptoms make it possible to recognize that the disease is precisely a carbuncle. But it should be borne in mind that the disease may turn out to be anthrax carbuncle. If the treatment of a regular type of carbuncle sometimes cannot be done without surgical intervention, then in the case of anthrax, conservative methods are sufficient. They consist of carrying out anti-epidemic procedures and isolating the patient.
Signs of anthrax carbuncle
This type of disease is characterized by the appearance of a small red nodule. The process develops from twelve hours to two days, during which time a purplish-bluish bubble with cloudy contents forms. In this case, the patient feels severe itching.
The vesicle bursts quickly and a dark red scab forms at the site of the wound. It hardens, and after a day it looks black and becomes hard. That is why the disease was called carbuncle.
Often a kind of corolla forms around the scab. It consists of small blisters with serous fluid inside. Next, severe swelling occurs, after which tissue necrosis, lymphadenitis and lymphangitis occur.
If the disease is particularly severe, then there are septic signs. But, as a rule, the patient’s general condition remains unchanged.
Another difference between anthrax carbuncle and a common disease can be considered its relative painlessness.
Diagnosis of carbuncle
In medical practice, there are no difficulties in diagnosing a carbuncle. But there are cases when it is necessary to differentiate from anthrax, called anthrax carbuncle.
The clinical picture at some stages is similar, and this is facilitated by the development in some cases of a necrotic crust carbuncle. Sometimes there are only minor reactions around the boil site, but this is quite rare. If there is any doubt, doctors prescribe a bacterioscopic examination.
If the clinical picture does not give an accurate picture, then in order to diagnose a carbuncle or furuncle, blood tests are performed - leukocytosis, an increase in ESR, a shift to the left in the leukocyte formula.
Treatment of carbuncle
Outpatient treatment of carbuncle is carried out if there is no pronounced intoxication of the body, and the source of the disease is located on the torso or limbs. If treatment is started in a timely manner, that is, immediately after the inflammatory infiltrate has formed, the patient is prescribed a course of treatment with antibacterial therapy.
When treating carbuncles, ultraviolet irradiation has a good effect, and UHF therapy is used.
The surface of the skin affected by the disease must be treated with ethyl alcohol (70%), apply a bandage with an antiseptic, for example, Vishnevsky ointment, methyluracil ointment, vinylin.
Until relatively recently, this disease was treated exclusively surgically. But these days, therapy is based on antibiotics and sulfa drugs. Surgical treatment is used in extremely rare cases. Specialists use the combined effect of streptomycin, penicillin, terramycin, biomycin, or another antibiotic drug. Quite large doses are used.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics and synthetic antibacterial drugs. At the same time, the patient takes medications with an analgesic effect, as well as heart medications.
Penicillin is administered both intramuscularly and the technique of puncturing the lesion is used. The total daily dose may be 1,000,000 units. It is impossible to determine the exact duration of treatment; it is carried out until the general symptoms of the disease disappear and inflammation decreases.
Streptocide is used, dosage – 0.5 g. every four to six hours. Norsulfazole one gram four times a day. These drugs are used for treatment from a week to ten days.
Symptoms of carbuncle
In addition to the differences in the photo, the differences between a carbuncle and a boil can be seen in their symptoms. One of the signs of carbuncles is that this inflammation develops on the neck, back or thighs. The process is more severe, as inflammation spreads to deep-lying tissues. Subcutaneous fat is affected. The patient notes general malaise: weakness, nausea, headaches and muscle pain, high body temperature.
A carbuncle is a large-scale focus of inflammation. Bright red skin and many purulent heads are its distinguishing features. The size of a mature carbuncle can range from 3 to 10 cm. Pus can ooze from several heads at the same time. Visually, this makes the inflammation look like a honeycomb. Sometimes all the holes merge into one, from which pus flows.
Treatment methods
In a hospital setting, the doctor opens both the carbuncle and the furuncle, followed by drainage of the affected cavity. Thus, purulent-necrotic masses come out, which promotes rapid healing. An open wound can become infected, so the use of antibiotics is rational. How does the treatment of different types of purulent-necrotic diseases differ? The degree of complexity of the lesion plays a role. In severe cases, antibiotics are necessarily prescribed to combat Staphylococcus aureus. When carbuncles or multiple furunculosis appear, it is appropriate to take drugs orally to reduce general intoxication. Having gotten rid of the painful seal, it is necessary to treat the ulcers until they are completely healed. For such purposes, antibacterial ointments that promote rapid regeneration are used.
In the treatment of purulent-inflammatory skin diseases the following are used:
- staphylococcal bacteriophages, toxoids;
- proteolytic enzymes (“Trypsin”, “Chymopsin”) for the rejection of anesthetized masses;
- antiseptics. Shower with disinfecting soap or gel (“Povidone-iodine”);
- local treatment. Antibacterial ointments (for example, Mupirocin).
Warming the affected area helps the purulent lumps mature faster. Following the rules of antiseptics will protect the patient from the addition of accompanying bacteria. A special diet with B vitamins and antioxidants is recommended. If the disease often recurs, it is worth assuming the presence of a chronic inflammatory process. In this case, a general examination of organs and systems is prescribed to find the cause of skin infiltrates.
Diagnostics
As a rule, an experienced specialist diagnoses a boil or carbuncle by the appearance of the inflammation and the patient’s complaints about his condition. But in some cases additional diagnostic procedures are required:
- The inflammation is not eliminated by conventional treatment. Most likely, it is caused not by staphylococcus, but by another bacterium.
- There are several pockets of boils or carbuncles on the human body.
- The inflammation reappeared after treatment.
- The patient has been diagnosed with diabetes, AIDS, and is undergoing chemotherapy.
In this case, a smear is taken from the skin, and the contents of the abscess are sent for bacteriological examination. In this way, the type of causative agent of inflammation is determined. The patient is also given a blood test to make sure there are no undiagnosed diseases.
Carbuncle: causes, treatment and removal with ointment at home
A carbuncle is an acute inflammation of the skin, sebaceous glands, hair follicles and subcutaneous tissue with purulent contents. Externally, the carbuncle looks like several formations fused together. Skin infections can be caused by various bacteria, but the most common pathogens are Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus.
Without timely treatment, the skin disease can develop into sepsis, lymphadenitis, abscess or meningitis.
It has been proven that men are more likely to suffer from carbunculosis.
How to treat?
Several years ago, carbuncles were treated only with surgery. Often, even now, patients with the disease are sent to the hospital. However, when a carbuncle appears in a single instance, surgical treatment is prescribed very rarely.
Important! When the carbuncle ripens, in most cases, medical attention is necessary, since pain can accompany the patient for more than two weeks, and in the absence of proper treatment, the inflammation can spread to other parts of the body.
Carbuncles can appear on any part of the body; in rare cases, the source of inflammation is on the face
If a purulent carbuncle appears, the doctor may prescribe a course of antibacterial therapy (sulfonamides, Streptomycin, Penicillin, etc.). Patients are administered broad-spectrum drugs intramuscularly (Cefazolin, Gentamicin, etc.).
A solution of brilliant green or special ointments (Levomekol) are applied to the dressing material for chemical sanitation of the carbuncle.
When changing the dressing, the wound is washed with an antiseptic (chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide) and dead tissue is removed from the inflamed area of the skin.
If the patient is intoxicated, an isotonic sodium chloride solution and a 5% glucose solution are additionally administered intravenously.
In order for damaged skin to heal faster, wound-healing ointments “Actovegin”, “Solcoseryl”, etc. are applied. In combination with the drugs, patients are prescribed vitamins, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Fact! Previously, carbuncle was treated with salicylic acid. In modern medicine, this drug is not used for this purpose.
When diagnosing the disease, the doctor must exclude the possibility of parasitic sycosis, scrofuloderma, anthrax carbuncle
Surgical treatment
In some cases, opening the carbuncle surgically is simply necessary. During surgical treatment:
- The open wound is sanitized.
- Dead tissue is excised.
- Treat the source of inflammation with an antiseptic.
- Pain relief.
- The carbuncle is opened with a cross-shaped incision.
- A drainage is inserted into the wound cavity.
- Remove purulent, necrotic masses and the core of the formation.
- Apply anti-inflammatory ointments to the dressing material.
According to medical statistics, people with diseases of the endocrine system are more likely than others to develop carbuncles that need to be removed promptly
Treatment of boils
If you have a boil on your face, and especially in the area of the nasolabial triangle, you need to see a doctor. In other cases, inflammation can be successfully treated at home. It is better not to hesitate and start treatment at an early stage, before an abscess forms.
The inflammation is treated with an antiseptic - medical alcohol or a solution of brilliant green. During the day, dry heat should be applied to the boil - heated bags of salt, sand or rice, warm boiled eggs. This helps improve blood circulation. And along with it comes the influx of leukocytes that fight infection.
If a boil has formed on a limb, you need to provide it with rest. To relieve pain, use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (analgin, ketorol, ibuprofen) or paracetamol.
Under no circumstances should the purulent “head” be opened! When it opens on its own, thoroughly treat the wound with an antiseptic and apply a sterile bandage.
Treatment options
Since the disease has quite pronounced symptoms, it is not difficult for a doctor to make a correct diagnosis. But nevertheless, in order to prescribe the correct treatment, a specialist must determine which pathogen caused the disease .
If the disease does not cause any significant changes in the patient’s health, then hospitalization is not necessary. Treatment is carried out at home under the supervision of a doctor.
With the help of medications
A patient who has a carbuncle is prescribed the following drug treatment:
- Antibacterial drugs. They are used both internally and externally in the form of injections into the place where the purulent process occurs.
- Painkillers. Prescribed if the patient complains of severe pain.
- Antipyretic medications. It often happens that during the maturation of the carbuncle, the patient’s body temperature rises sharply.
Treatment of carbuncles
If you have a carbuncle, you need to see a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable here. In some cases, hospitalization is necessary. For example, with extensive purulent tissue damage. Since this threatens blood poisoning and all the ensuing consequences.
The treatment here is surgical. Under local anesthesia, specialists open the purulent cavity, remove all dead tissue, and clean the wound. Then the surgical site is treated with antiseptics and sterile dressings are applied. In some cases, stitches and even skin grafting are required. Additionally, antibiotics and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Boils and carbuncles are similar, but at the same time not identical inflammatory processes. They are distinguished by the scale of inflammation, treatment features, provoking factors, and locations of tissue damage.
How to cure the disease?
Carbuncle therapy is carried out under the strict supervision of doctors: either in a hospital or in a day hospital.
- Oral antibiotics: Ceftriaxone 1 g 2 times a day, Amoxicillin 1 g 2 times a day, Azithromycin, Summed 250-500 mg 1 time a day, Clarithromycin or Klacid 500 mg 1 time a day, Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 2 times a day. Duration – 10 days.
- Local antibiotics: ointments and gels for treating the skin around the wound, as well as ulcers after rejection of pus (Levomycetin, Gentamicin, Baneocin, etc.) twice a day.
- Antiseptic solutions: brilliant green, methylene blue, furatsilin, hydrogen peroxide.
- At the initial stages, you can slow down the development of the carbuncle with chlorethyl or pure ichthyol.
- Physiotherapy: UV irradiation, UHF, UT, electrophoresis with antibiotic.
- To improve tissue nutrition during wound healing: Solcoseryl ointment, Actovegin locally.
- Complex vitamin preparations containing microelements.
- Diet with restrictions on fatty, sweet, salty, spicy foods.
If the disease progresses rapidly, the carbuncle must be opened urgently. This is done by a surgeon in the operating room under local anesthesia. The doctor cleans the wound of pus, excises the affected tissue and installs drainage (special tubes through which pus comes out of the wound). An aseptic dressing is applied.
Dressings are done in the morning and evening. The surrounding skin is treated with antiseptics (listed above). The wound itself is washed through drainage with furacillin or chlorhexidine. After a few days, antibiotic ointments can be applied internally.
Only a doctor can treat a carbuncle. The disease cannot be left to chance. Also, you should not try to cope with it using traditional methods. Staphylococcus is a pathogenic microorganism; only serious antibiotics can kill it.