Human papillomavirus genotype 66 in women
Papillomavirus is a chronic disease caused by the pathogen Human papilloma virus. The targets of this disease are the skin and mucous membranes. There are approximately 160 varieties of the virus. Some of them are harmless and do not interfere with a person at all, while others pose a threat to life.
HPV type 66 in women - what is it: a peaceful neighbor or a dangerous enemy? Genotype 66 is classified as a virus with a highly oncogenic risk that can cause cervical cancer. Most HPV carriers are not aware of its presence, since the infection does not manifest itself for quite a long time. To identify it, a diagnosis is carried out, and then treatment is prescribed.
Methods of transmission
HPV type 66 is transmitted through contact. The most common infection is through sexual intercourse without a condom. The probability of infection is about 60%. But even the use of a contraceptive does not guarantee 100% protection, since the virus is very small in size and is able to pass through the pores of latex products.
It is important to know! Papillomavirus affects the outcome of pregnancy. Infection of a child can occur during natural childbirth from a sick mother.
Less commonly, the disease occurs in domestic conditions (using shared towels, personal hygiene products) and when visiting crowded places (swimming pool, sauna).
Typical manifestations
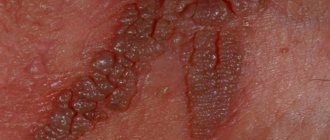
Like many other diseases, this virus has an incubation period of 4-8 months. At this stage, it does not show itself in any way, does not interfere with the life of the carrier, and can only be diagnosed through laboratory testing. When the immune system is functioning normally, it is almost impossible to detect the virus. It begins to actively manifest itself when the body’s protective function decreases. The main symptoms in women are:
- inflammatory processes;
- the presence of pathogenic vaginal flora;
- foul-smelling whitish and yellowish discharge;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- itching inside the genitals;
- discharge mixed with blood not associated with menstruation.
The same symptoms can be caused by other diseases of the reproductive system acquired as a result of a virus.
Factors provoking the development of the virus
Papillomavirus is one of the genus of diseases that never arise out of nowhere. The passive state of the disease lasts until favorable conditions for its development are activated. These are created when the immune system is weakened. Few people think that a normal deterioration in general health can lead to more serious illnesses. The causes of immunosuppression are considered:
- regular stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- hormonal disorders;
- bad habits;
- chronic diseases.
These factors stimulate the progression of HPV. The culture of sexual relations is also important. Normally, it is desirable to have one permanent and trusted partner.
The risk of developing cancer in women
HPV type 66 is dangerous because it is integrated into the DNA of cells and, if detected untimely, the development of a precancerous and cancerous condition begins. According to statistics, 65%-75% of cervical cancer occurs precisely because of this virus. Particular attention should be paid to women who have already been diagnosed with erosion or dysplasia. People with papillomas, as well as those whose close relatives have been diagnosed with this, are also at risk.
It is important to know! Cervical cancer is not the only disease that can be caused by a virus. Complications when it is present in the human body are also oncological changes in the area of cells of the vagina and anus.
Features of papillomatosis in men
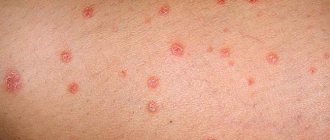
This disease can be transmitted either from man to woman or vice versa during sexual intercourse. In men, according to reviews, the scrotum, head and shaft of the penis are most often affected. Less commonly - the urethra and groin area. Due to the appearance on the surface of the genitals, particular discomfort is caused during sex, since the formations are susceptible to constant contact. These areas become inflamed, which can lead to the development of additional infection. And then you will need treatment for several diseases at once. If growths appear at the entrance of the urethra, problems with urination are possible.
How does the disease manifest itself?
After infection, the virus remains in the incubation stage in the body. This lasts for an average of six months. At this time, the HPV 66 genotype is detected only during a medical examination of the patient.
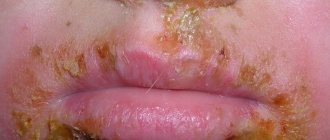
The first changes occur in the cervix, cervical canal and vagina. Initially, the woman does not experience any symptoms. But over time, the microflora of the mucous membrane changes. Fungal or bacterial infections develop. Dysbacteriosis and inflammatory process in the vagina develop.
A woman notices a white or yellowish-green discharge. After this, pain occurs, which occurs at the moment of intimacy and during urination. In some cases, bloody discharge appears after sexual intercourse.
A woman feels itching and burning in the genitals. Very often, HPV type 66 is accompanied by other sexually transmitted infections, such as:
- chlamydia;
- trichomoniasis;
- gonorrhea.
Diagnostic procedures
For timely detection of the disease, women are recommended to undergo regular examination by a gynecologist at least every six months. If any primary signs of the presence of HPV are detected, the doctor must carry out a series of procedures to determine the exact type.
Main research methods:
- Smear. It is taken to conduct a cytological analysis to search for altered cells in a state of cancerous degeneration.
- Colposcopy. Examination of the cervix under a microscope in the presence of visual changes.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The main method for identifying small concentrations of the virus and its type. The most accurate result is when conducting 2-3 tests.
- Blood test from a vein.
If the disease is detected, both partners must undergo a full examination and it is advisable to abstain from sexual intercourse during this period.
Diagnostics
The first step in diagnosing cancer is an examination by a gynecologist. For this purpose, special gynecological speculums are used. Next, a smear is taken from the cervical canal to identify the development of dysplasia. The results of a smear can tell you for sure whether there is cancer, although the gynecologist usually advises other diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis.
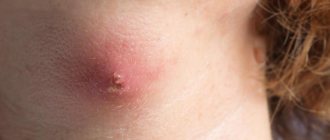
Papillomas are small in size at the initial stage, so the doctor treats the damaged area with a special solution that changes color when there is an infection.
To definitively confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy is performed. To study the DNA of papillomas, the PCR method is used, and the Digene test is used to determine the type of virus.
Treatment method
After accurately determining the strain of the virus, it is very important to prescribe the most effective treatment. But it’s also worth remembering that you won’t be able to completely get rid of the infection. You can remove unpleasant symptoms and maintain the general condition of the body to prevent subsequent relapses.
Drug therapy is considered the simplest. Drugs are prescribed for both oral and external use.
The first group includes:
- antiviral - “Isoprinosine”, “Viferon”, “Novirin”;
- immunomodulators – “Immunomax”, “Cycloferon”, “Wobenzym”, “Anaferon”.
They are used to suppress the spread of the virus and destroy its DNA.
External preparations:
- "Superclean";
- "Wartner Cryo";
- "Ferezol";
- Candles "Polyoxidonium".
They remove skin formations, thereby reducing the number of infected cells.
All other methods are intended for the destruction of tumors:
- Laser coagulation is a virtually painless one-time procedure that is performed with a neodymium or carbon dioxide laser.
- Cryotherapy is the removal of papilloma by freezing it with liquid nitrogen, nitric oxide or carbon dioxide.
- Diathermocoagulation - after local anesthesia, the growth is burned out with high-frequency alternating current. The disadvantage of this procedure is the possible occurrence of scars.
- Radio wave therapy - destruction of formations occurs due to the drying of intracellular fluid under the influence of radio waves.
- The chemical method is the removal of papillomas by applying substances to their surface, such as bismuth, mercury, hydrogen peroxide. The longest procedure, as 3-5 sessions are required.
- Surgical intervention is used mainly for excision of malignant tumors, as it is a highly traumatic method.
After any type of treatment, you should follow simple recommendations:
- normalize sleep;
- balance nutrition;
- reduce physical and emotional stress.
The doctor determines which method of treatment to use, depending on the patient’s condition.
Relevance of prevention
Prevention of infection includes timely and proper personal hygiene and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The following actions are necessary: control of bad habits, exclusion of untested sexual partners, use of contraceptive methods, regular visits to a gynecologist, periodic use of immunostimulants.
It is important for all family members to have personal bathroom amenities. If you have frequent contact with strangers, you should disinfect your hands, especially if there are skin lesions, since the virus is very insidious and easily transmitted.
Attention! The most effective method of prevention is vaccination, which is carried out before the onset of sexual activity.
Probable causes of infection with HPV type 66 virus
Viral infection type 66 is localized on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, and causes significant discomfort due to its symptoms. Do not delay your visit to the doctor, as in the early stages you can get by with more humane methods of removing papilloma. The mucous membranes where genital warts appear cannot be treated with medications and solutions that cause burns. And this extremely narrows the list of applicable medications.
It is undesirable to ignore growths in the genital area. Although there are cases in medical practice where patients experienced self-healing, you should not tempt fate and hope for chance.
To begin with, you need to figure out what can accompany the penetration of the virus into the body, what reasons are most often the founders of the infection? Many people ask these questions. That is why, the task of a qualified specialist during a routine examination of a patient is to highlight them.
Comprehensive advice can warn a person and maintain health. The patient should not hesitate to ask questions to the doctor. Thus, every examination of a woman by a gynecologist is accompanied by a smear. Find out for yourself why this is being done and what should be avoided in everyday life so that the infectious disease, even if it penetrates the body, does not continue to develop. Progression is what is really dangerous.
Possible causes of infection in the body, which include:
- weakened immune system (the main reason for penetration into the body):
- poor diet (food with preservatives, large amounts of fried food);
- immoral lifestyle (frequent change of sexual partners);
- presence of bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drug addiction);
- failure to maintain personal hygiene (using other people's utensils).
All the reasons mentioned lead to the possible appearance of HPV. Therefore, be more vigilant about your health and what you do in your daily life.