The papilloma virus is quite common and is most often transmitted sexually. HPV type 59 is one of the most dangerous, capable of causing cancer - this is why oncologists and gynecologists pay special attention to it. If it is detected in the body, immediate treatment is required.
The main source of this papilloma virus is the affected cells and mucous membrane of an already infected person. The growths do not have to be visually noticeable. They may still be in the early stages of formation. But already at this stage the virus is transmitted unhindered.
Features of the course of the disease
There are several stages in the course of papillomavirus genotype 59:
- Latent. The presence of the virus can only be determined in the laboratory using DNA tests of the human papillomavirus. He hasn't shown himself yet.
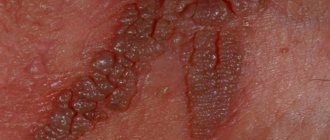
- Condylomas with sharp ends appear.
- Stage of dysplasia. Changes occur at the cellular level.
- Carcinoma. Cells begin to mutate into malignant ones.
In women, the genital organs (labia minora and majora), perineum, urethra, vagina and even the cervix, as well as the anus area, can be affected - just like men.
The peculiarity of this type of infection is the rapid growth of tumors. In a few hours, the papilloma can significantly increase in size.
Features of strain 59 species in women
If the immune system is weakened, the infection can develop rapidly. It should be noted that HPV type 59 in women is the main issue, so it should be noted that it is marked by a high risk of oncogenic disease. Settling inside the mucous membranes of the genitals (genital organs), the virus rapidly changes the healthy epidermis.
We recommend reading:
- HPV type 33 in women
- HPV type 68 in women
- Immunomax for HPV
The system of influence is as follows: the bacterium penetrates the cell and, by changing the chromosomal composition, changes it. Thus, the damaged cells begin to rapidly divide, and a warty growth appears at the site of reproduction, which in medicine is called genital warts.
Oncology, mutation symptoms
Papilloma 59 is a virus that infects human epithelial cells in the rectum or genitals. As tumors grow and change, they mutate into cancer cells. How does the virus manifest itself?
Symptoms indicating possible cancer:
- bowel disorders (constipation and diarrhea);
- discomfort during defecation;
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- bloating, pain in the intestines and increased gas formation;
- presence of blood in feces.
Common symptoms include:
- significant weight loss:
- chronic fatigue and malaise;
- anemia.
If women or men have at least one of these symptoms and have condyloma acuminata, it is highly likely that they are infected with HPV 59. It is necessary to be examined using HPV DNA testing and undergo treatment now.
Symptoms of HPV 59
Once in a woman’s body, the human papillomavirus may not show itself for quite a long time until factors favorable for this appear, for example:
- hormonal changes, including pregnancy;
- intrauterine devices;
- drug suppression of immunity.
The main symptoms of this type of HPV in women are:
- the presence of pointed papillomas in the area of the labia minora and majora, urethra, cervical canal, cervix;
- anemia – iron deficiency;
- constant fatigue;
- weight deficiency.
Symptoms of possible oncology in the presence of this type of virus are:
- a feeling of heaviness in the lower intestines that does not disappear after bowel movements;
- unstable stool;
- abdominal pain, flatulence;
- discomfort during defecation;
- the presence of blood in the stool.
Diagnostic methods
There are only 2 research methods that can detect HPV type 59 in both men and women, which use blood or DNA as a basis:
- PCR to detect human papillomavirus.
- Pathogen DNA analysis.
Using PCR, only the presence of type 59 virus in the human body is determined. This method does not provide quantitative indicators, and therefore nothing is known about the viral load. The material for analysis is blood. In some cases, a swab is taken from the affected area.
Human papillomavirus DNA analysis is a relatively new method that is more accurate than the previous one. Based on the study of scrapings from the affected area in both women and men, not only the type of virus, but also its concentration is determined. The DNA of a virus is detailed information about its genetic nature.
Additional methods for diagnosing women for this type of HPV:
- colposcopy;
- biopsy;
- cytological smear;
- urethroscopy;
- acetic acid test;
- histological examination.
The use of acetic acid followed by Lugol's treatment indicates infection with HPV, but does not provide information about the type of virus. The appearance of a characteristic mosaic pattern when materials are absorbed is a clear sign that the body already has this pathogen.
Based on this study, the HPV class is identified.
- 1-2 – tissues are not modified;
- 3 – additional histological examination is necessary;
- 4-5 – presence of malignant tumors.
Histological analysis reveals particularly large epithelial cells. For this, the chain reaction method is used.
HPV treatment depending on type
HPV type (in women 16, 18 and some others can cause pathologies of the genital organs, as well as the bladder) provoke diseases depending on which group they belong to. Each type has its own treatment methods; therapy is especially necessary for the second and third groups.
HPV in these groups does not always mean oncology, but other serious health problems may arise. Even the slightest deterioration in health or the appearance of neoplasms should be a reason to visit the hospital for examination.
14 type
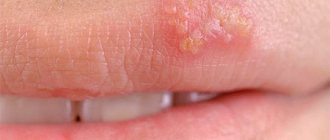
Type 14 (for women and men) belongs to the group with a low oncogenic risk. The danger arises in people with malignancy, and in this case the doctor prohibits self-medication. Otherwise, type 14 causes the formation of warts, which can be removed both at an appointment with a specialist and at home. The doctor also prescribes antiviral drugs (for example, Isoprinosine).
To prevent further growth of formations on the skin, cryotherapy or its analogues are used. Some remove growths using caustic alkaline preparations. Type 14 is not dangerous and provokes cancer in quite rare cases (a combination of factors, severe weakening of the immune system).
16 type
HPV type 16 in women is considered one of the most dangerous. It increases the risk of malignant pathologies several times. Type 16 can cause cervical cancer - this type was found in approximately half of women with this disease.
Actively dividing, pathogenic cells cause the formation of papillomas and genital warts on the mucous membranes and skin. During the development of type 16 virus, cervical dysplasia appears - a sure sign of oncology of the reproductive organs.
18 type
Papillomas and condylomas grow most rarely with type 18 of the virus. However, with this type they also manifest themselves and can grow together into one large growth. Formation on the external genitalia, thighs, and oral mucosa leads to discomfort and other inflammations.
In men, type 18 can cause Bowen's disease (the formation of warts on the penis), which is also a prerequisite for the occurrence of cancer.
Typically, type 18 is not as common as type 16, but its development occurs much faster. Detection of this type means immediate therapy, the prescription of immunomodulators, vitamins and subsequent removal of unpleasant tumors.
31 and 33
Most often, these types of HPV cause diseases such as bowenoid papulosis and cervical neoplasia. Women's disease can be mild or severe.
The latter is already oncology. When combined with other types, women may develop neoplasms (condylomas). Bowenoid papulosis is most characteristic of the male body and occurs against the background of promiscuity.
51, 52 and 56
These strains also belong to the high-risk group and are transmitted mainly through sexual contact. These types provoke the occurrence of genital warts, including around the anus and rectum. In women, these HPV types cause cervical erosion and dysplasia. Types 51, 52 and 56 are the causes of oncology of external and internal diseases of the genital organs.
The effect of laser on condylomas
Scientists have not yet developed a drug that would destroy the structure of the virus. Doctors use some therapies that inhibit the growth and development of HPV and prevent its reproduction, so that the population does not provoke intraepithelial pathological growths.
To suppress papillomavirus strain 39, treatment must be combined and include the following types of therapies:
- Destructive;
- Immunocorrective;
- Antiviral;
- General strengthening.
First, the growths must be removed by chemical methods (caustic substances) or physical methods (laser, radio wave, electrical excision, cryogenic).
Growths caused by HPV strain 39 are most often removed with a laser device, since it leaves virtually no traces or scar tissue, which is so undesirable for the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Large malignant growths are excised with a scalpel, trying to cover as large an area as possible.
For example, to increase local immunity, a specialist may prescribe interferon inducers in the form of ointments and creams (Cycloferon, Viferon), as well as antiviral drugs for parenteral (Panavir) and oral use (Groprinosin).
After entering the body, the virus can take root, or it can be eliminated on its own after some time - it all depends on the state of the immune system.
Causes of infection
The most common case of acquiring this disease in both women and men is infection through intimate intimacy. But not everyone develops and transforms the virus. This is influenced by a number of factors that contribute to the further development of the disease:
- addiction to smoking or alcohol;
- lack of a regular regime of rest, sleep and nutrition;
- hard physical labor;
- failure to comply with basic hygiene rules in public places;
- in rare cases, communication with an infected person.
Weakness of the immune system is the main impetus for the development of HPV 59. Any actions that reduce the body’s defense response can lead to an exacerbation of the disease in men and especially women.
And with regard to oncological consequences, it is the weaker sex who are at increased risk.
Treatment methods
The presence of genital warts is not only a cosmetic problem. They cause some discomfort when moving, and bleed during or after sexual intercourse. The main danger is the risk of acquiring a disease such as cervical cancer. Doctors have long proven that this terrible disease very often occurs in women with HPV type 59.
This infection is treated using several methods:
- removal of growths;
- use of antiviral drugs;
- strengthening a weakened immune system.
Removal of tumors can be carried out in several ways:
- Destruction under the influence of trichloroacetic acid. Removal is safe and effective; a few sessions are enough to completely get rid of numerous condylomas.
- Laser removal. The method requires equipment capable of destroying the structure of formations with a laser.
- Cauterization under the influence of liquid nitrogen. High temperature destroys the structure of growths. The disadvantage is the possibility of getting burned.
- Radiosurgery. New growths are destroyed by radio waves, not a trace remains in their place, and healing occurs in the shortest possible time. At the moment this is the best of all known methods.
But even in its entirety, this virus is almost impossible to destroy. However, the infection may subside and no longer progress. The main thing is to avoid relapse, follow basic hygiene rules, a healthy lifestyle, daily routine, give up bad habits, avoid hypothermia and negative emotions, and treatment will not be pointless.
How is HPV type 39 transmitted and manifested?
Modern medical science has identified more than 150 types of virus. Depending on its type, it affects the functioning of all organs and systems of the human body. For example, infected people notice various new growths on their skin and mucous membranes in the form of condylomas and wart-like growths.
The main route of transmission is physical contact with a carrier, including sexual intercourse without a condom. But household infection is also quite common.
Usually, after entering the body, the infection does not manifest itself in any way, so people do not even know that they are carriers.
The cause of HPV can be not only unprotected sexual intercourse, but also:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced immunity;
- disrupted eating patterns;
- consumption of low quality products.
It is worth noting that with frequent stressful conditions, the risk of suffering from HPV increases significantly.
Pregnancy with this infection
HPV 59 can be detected in women during routine screening during pregnancy. In this case, constant monitoring by a doctor is necessary throughout the entire period of pregnancy until birth. Treatment in this case directly depends on how the disease progresses.
While the fetus is in the womb, the virus does not affect it; it is protected by amniotic fluid and the placenta. There is only a small risk of infection during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal. If there are pronounced manifestations of infection on the cervix of the uterus, and treatment has not given the desired results, a caesarean section is prescribed. In case of their absence, childbirth proceeds naturally.
Regularity of examinations to detect the virus
To prevent the virus from spreading, regular testing is necessary for men and women. A DNA test for HPV and PCR are considered mandatory. Their frequency directly depends on age:
- Up to 30 years – once a year.
- 30 – 65 years – once every 5 years.
- 65 years old - if the analysis is normal, further examination is no longer required.
This schedule is quite arbitrary, largely depending on lifestyle and other indicators. You can rely on it only if there is no HPV as such in the body of the women and men being examined.
Prevention
Among the methods of preventing infection with human papillomavirus type 59 in men and women, the most effective is avoidance of promiscuity.
A set of actions that reduces the risk of acquiring this disease:
- Minimum number of sexual partners. Ideal if he is alone.
- Using condoms. This method cannot guarantee safety, since the affected areas may not be covered. This reduces the risk of infection to a minimum.
- Confidence in your partner's health.
- The beginning of sexual activity only after reaching adulthood. By this point, the cervix in women has fully matured, and its mucous membrane already has a higher protective function.
- Rough sex and artificial abortion are excluded. These actions can worsen the condition of the genital organs and reduce immunity against viruses.
- Treatment of any viral infections must be carried out promptly and under the supervision of a doctor.
- Physical activity, giving up bad habits, following a daily routine and healthy eating.
- Pay special attention to your own health if one of the women or men in the house is already infected with HPV, at least until the end of therapy.
- Vaccination against human papillomavirus.
What to do?
If human papillomavirus type 39 occurs, drug therapy is prescribed to help eliminate the resulting condylomas. The patient will never be able to completely get rid of the papillomavirus, so drug therapy should be resorted to from time to time. It is indicated to treat the disease with the following drugs:
- antitumor agents that can partially eliminate the virus and strengthen the immune system;
- taking medications that prevent the papillomavirus from spreading throughout the body (“Isoprinosine”);
- the use of local ointments, gels and solutions that help eliminate growths on the skin and mucous membranes;
- taking a complex of vitamins and minerals to improve immunity;
- the use of radiation or chemotherapy (for malignant pathology).
Features of vaccination
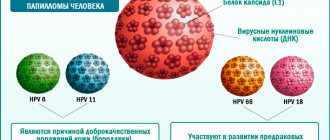
Currently, there is a vaccine against human papillomavirus types 6, 11, 16 and 18. Such prevention is considered absolutely harmless. These viruses cause cancer of the cervix and vagina in women, and cancer of the penis and anus in men. Recent data indicate the effectiveness of this vaccine against other types of viruses that cause cancer.
Vaccination is available to men and women in adolescence and to girls up to age 26. This does not require special examinations. This is not a cure, but a method of prevention. Vaccine treatment is not possible.
Vaccination is carried out in 3 stages. In total, the process takes a year. After this it can be considered successful.
Vaccination during pregnancy is unacceptable, as well as with poor DNA levels of the human papillomavirus.
Virus type 59 is dangerous for both men and women. The danger of cancer from this virus is incredibly high. Treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a doctor with systematic DNA tests and other necessary studies. Only if the DNA levels of the human papillomavirus are excellent, treatment can be suspended.