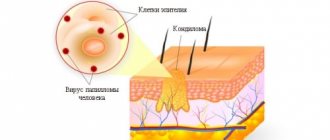
What is athlete's foot?
Athlete's foot is a skin lesion caused by a fungus that appears on large areas of the skin. It appears as large pink spots that peel off and become covered with vesicles. Most often spread in the groin area. They can also occur on the chest and under the arms.
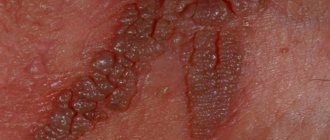
What does the disease look like, photo
You can see what the disease looks like in the photo. As a rule, these are large inflamed pink symmetrical spots with rounded outlines. As they grow, they acquire a red-brown color and reach 10 cm in length.
The stain is smooth, with small bubbles, scales and crusts. As it develops, it shifts from the center and moves to the whole body. As it grows, it separates from healthy skin using a scalloped border and becomes inflamed, causing itching and pain.
Symptoms of the disease, stages
A symptom of the disease in both males and females is increased sensitivity of the skin in the area affected by the fungus.
Actively observed in patients:
- Itching and burning;
- Painful sensations when touched (pain even from clothes);
- The appearance of symmetrically located fungal rashes called epidermophytis;
- Circular growing spots.
At the first initial stage, the pathogen penetrates under the top layer of skin and actively multiplies. At this stage, small tender spots on the skin are observed.
During the acute stage, new fungal colonies appear and grow in different areas of the skin that are most susceptible to moisture. The center of the spots becomes pale, the circular spots acquire red outlines at the edges.
At the chronic stage, the disease becomes protracted, flares up in other areas, and constantly worsens every month. The spots become smaller, but do not disappear completely. Repeated exacerbations are also painful, but pass quickly.
At an advanced stage, large blisters appear that burst and turn into eczema. Its presence leads to skin damage and the person needs medical attention.
Causes
Athlete's foot is a fungal disease or dermatomycosis in other words. The causative agents are the fungi Epidermophyton floccosum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, which a person becomes infected with through household contacts.
These could be dirty towels, linen, washcloths. The disease also arises from failure to maintain personal hygiene or the use of other people's personal hygiene items.
Factors that aggravate the situation and bring the disease include:
- high temperature;
- high humidity.
Also, the most common cause of athlete's foot is obesity, which makes proper hygiene difficult and increased sweat production. Often, untreated lesions on the skin cause the infection to spread and localize near the groin.
Causes and mechanism of formation
Despite the fact that the fungus can affect any person on whose skin it gets on, there is still some pattern in the susceptibility to this disease. In particular, athlete's foot in the groin occurs more often in men than in women and in women more often than in children. Conditions conducive to the development of fungal activity include the following factors:
- increased humidity, sweating;
- overweight;
- maceration of the skin;
- metabolic disease;
- violation of personal hygiene rules.
Once in the warm, moist environment of a large skin fold, the fungus begins to actively multiply, forming a lesion. Therefore, the disease is often localized in the groin. In this area the most favorable conditions for his active work. The groin area is often subject to friction, profuse sweating, and is deprived of access to air and light. An insufficient number of hygiene procedures only increases the risk of developing various diseases, including fungal infections. Moreover, in men, due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure, the likelihood of being affected by inguinal fungus only increases.
A warm, hot climate should also be considered as a conditioning factor. Despite the fact that fungal infections, in particular athlete's foot, are quite widespread in any country, they are most often found in places with high humidity and a warm climate. If there are two or more predisposing factors, the likelihood of infection with epidermophytosis increases.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease includes a visual examination by a dermatologist or mycologist, taking an anamnesis and taking the necessary scrapings.
To confirm the etiology of the disease, a scraping is taken for fungi, cultured on their medium, and the affected areas are examined with a Wood's lamp. The scraping is taken directly from the affected area or nails. Typically, small peeling areas of skin are removed for examination under a microscope.
Using a lamp, damaged areas of the skin are illuminated, which, if green, indicate the presence of inguinal athlete's foot.
It allows you to distinguish this disease from erythrasma (it has a red glow). The lamp also allows you to distinguish it from diaper rash with candidiasis, psoriasis, dermatitis, trichophytosis and rubromycosis.
Symptoms and signs of the disorder
Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot in men should be carried out soon after the appearance of a fungal infection on the skin. The main signs of mycosis are the appearance of a round-shaped spot, the diameter of which is approximately 10 mm. It can be single (often at the initial signs) or grow in the form of several characteristic spots that will constantly cause itching, peel and increase in size.
Soon, bubbles will appear on the affected skin along the perimeter of the spots, in which purulent exudate may be present, and crusts will appear. Unpleasant symptoms of infection will intensify while walking or bathing.
When the inflammatory process subsides a little, clear skin, pale and slightly sunken, will appear in the central part of the spots. In appearance, the spots of a subsiding infection will look like rings, which will confirm the cause of the skin changes. In addition to discomfort, during any movement, the spots in the groin will hurt when you touch them. As the infection develops, pustules may open, followed by the formation of ulcers and erosions. If another infection occurs during this period, the consequences can be extremely severe.
If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, it will become chronic and will periodically recur. The chronic form of infection is extremely dangerous, since in the future, even after complete recovery, it will worsen each time the body’s defense system is weakened.
Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot
In order to get rid of this disease, it is quite effective to organize local treatment with a resorcinol solution and silver nitrate, an ointment based on betamethasone and clotrimazole.
A good effect is obtained from the use of modern antifungal drugs, for example, terbinafine, undecylenic acid and clotrimazole.
Local anticomitant therapy is carried out for 4-6 weeks under the supervision of a doctor until the spots completely disappear. The lesion sites are also treated with iodine tincture or fucarcin.
You should consult your doctor about the use of all substances! Possible side effects.
Oral medications
Currently, oral antibiotic drugs are actively used for the treatment of athlete's foot in the form of:
- Griseofulvin;
- Amphoglucamine;
- Levorina (Levoridon);
- Nystatin;
- Pimafutsina.
- Fluconazole (Diflazol, Diflucan, Medoflucan, Mikomax, Mikosist, Fluconazole, Flucostat, Ciscan and others);
- Itraconazole (Irunin, Itrazole, Itraconazole, Canditral, Orungal, Orunita, Rumikoz, Teknazole);
- Ketoconazole (Mycozoral, Nizoral, Oronazole, Funginok, Fungistab, Fungavis);
- Terbinafina (Atifina, Binafin, Bramisil, Lamisil, Terbizil, Terbinafina, Terbinox, Terbifin, Tigal-Sanovel, Fungoterbin, Exitera, Exifina).
When treating with antibiotics and anti-infective drugs, treatment should not be interrupted mid-course. You should take the course of antibiotics to the end so as not to cause negative consequences.
Local treatment
Local treatment is carried out with external antifungal agents. When it comes to a severe form of the disease, the patient additionally takes antifungal drugs.
Basically, drugs are prescribed as antifungal ointments and gels for local treatment in the form of:
- Isoconazole (Travogen);
- Clotrimazole (Amiclon, Imidil, Candibena, Candida, Candizol, Canesten, Kanizon, Clotrimazole, Funginal, Fungicipa);
- Miconazole (Dactarina, Mycozone);
- Oxiconazole (Mifungara);
- Econazole (Ifeneca);
- Naftifina (Mycoderil, Exoderil);
- Sertaconazole (Zalaina, Sertaconazole, Sertaconazole);
- Ketoconazole (Ketoconazole, Mycozoral, Nizoral, Oronazole, Funginok, Fungistab, Fungavis);
- Terbinafina (Atifina, Binafina, Bramisil, Lamisil, Terbizil, Terbinafina, Terbinox, Terbifin, Tigal-Sanovel, Fungoterbin, Exitera, Exifina);
- Lotserila;
- Batrafen;
- Undecylenic acid (Undecine, Zincundan);
- Octicyla;
- Anmarina;
- Decamina;
- Nitrofungin;
- Fukortsina.
Antifungal drugs are often prescribed in combination. Such complex substances include Mycozolon with Mycospor, Travocort, Triderm, Pimafucort.
To strengthen the immune system
When fungi are actively multiplying, it is important to maintain your immune system and try to eat right in order to help you take medications and heal faster. Echinacea or Eleutherococcus are suitable as means to strengthen the immune system for this disease. You should also eat non-allergenic fruits.
Folk remedies
To alleviate the effects of the disease, you should take medicinal baths with washings using decoctions of chamomile and oak bark.
You can also make gauze dressings with herbal decoctions and apply them to the affected areas for 30 minutes daily.
Consequences and complications
If a lot of time has passed after the appearance of inguinal athlete's foot, and there is no treatment, then the severity of symptoms may increase. Severe consequences in the presence of cutaneous mycosis are rare, but they are possible if the immune system is weak. First of all, the danger comes from constant scratching of the affected areas. In this case, complications may arise in the form of a staphylococcal infection.
The symptoms in this case become pronounced: purulent foci appear, which are often painful at the slightest touch. The infectious process can affect the deep layers of the skin, which requires immediate medical intervention.
Long-term mycosis and constant trauma to the affected areas provoke the appearance of unaesthetic marks on the skin, which may not heal for a long time. In place of the papules, crusts often remain, after which bleeding wounds appear. The constant presence of fungal infection and damage to the epidermis reduce the protective functions of the skin, which can no longer resist dangerous pathogens.
If a woman is faced with inguinal epidermophytosis, then she needs to patiently and carefully study the causes of the phenomenon.
Feedback from patients suggests that well-chosen therapeutic measures that use medications and traditional medicine recipes can permanently cure the disease. According to ICD 10, the pathology has a number of 35.6.
Prevention measures
To ensure that the disease never makes itself felt, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene and try to keep the body in good shape, preventing the immune system from weakening.
You should also adhere to the following recommendations:
- Do not use other people's personal hygiene items;
- Do not wear synthetics and wear things made from natural materials that absorb sweat;
- Dry the skin with a towel;
- Fight sweating by applying powder to the skin;
- Eat right and give up alcohol and smoking.
Epiderma in the groin is a complex and serious disease that requires immediate treatment due to its negative consequences.
Who is at risk: causes of the disease
The optimal conditions for spore development are warmth and humidity. Male professions (driver, military man) oblige a person to wear warm, unventilated clothes for long hours, day after day creating an optimal habitat for the causative agent of the disease.
A weakened body, the presence of mycosis on other areas of the skin, contact with people who are carriers of mycoses, metabolic disorders are factors that increase the risk of epidermophytosis.
Knowing the causes of the disease, we can identify the main categories of men who are at risk:
- elderly people;
- patients with diabetes and (or) obesity (treated and advised by an endocrinologist);
- men with hyperhidrosis (this means profuse, uncontrollable sweating);
- people with immunodeficiency;
- drivers, military, police, rescuers, etc.
What are the causes?
The causative agent of epidermophytosis is fungi of the genus Epidermophyton, there are several types of them. For example, the fungus Epidermophyton inguinale (groin) and rubrum (red) “prefer” to multiply in the groin area. Epidermophyton intertriginoides and interdigitales parasitize the interdigital folds of the feet. There are several varieties of such mushrooms.
The filamentous fungus Epidermophyton, which causes the development of epidermophytosis
The main source of infection is a sick person. The pathogen can enter the skin through direct contact, as well as indirectly, that is, through common objects (towels, clothes, shoes, pool water, the surface of a sports equipment, floor mats, bed linen). Fungal spores can also come from the external environment - soil, puddles, and so on.
Fortunately, not everyone develops the disease when exposed to the pathogen. Healthy, dry and intact skin is resistant to fungal penetration. The spread of the disease is facilitated by a number of provoking factors, such as:
- Prolonged stay in conditions of high humidity.
- Work with elevated ambient temperatures (hot shops, food factories).
- Excessive sweating.
- Violation of skin hygiene rules.
- Exposure to production factors (chemical agents, skin trauma, cracks).
- Obesity.
- Decreased immunity.
- Weakening of the body after radiation therapy, chemotherapy in cancer patients.
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes, thyroid deficiency).
Remember. Infection with the athlete's foot fungus can be completely avoided if the reasons why the infection develops are eliminated.
We recommend studying this topic:
Darier's disease: a chronic illness you can live with
6610
0
3
reading information
Steps
Treatment of inguinal athlete's foot at home
- Identify the symptoms of athlete's foot.
Most often, the infection affects the skin in the groin, buttocks and inner thighs due to humidity, which promotes the growth of fungi and bacteria. Although in most cases, athlete's foot can be treated at home, you should visit a doctor who will make an accurate diagnosis and also determine what caused the infection (fungus or bacteria), since the treatment method will depend on this. The following symptoms indicate athlete's foot:
- Itching, redness and rash on the skin in the form of crusty patches shaped like a circle or crescent
- Burning
- Pain (usually due to a bacterial infection)
- Blisters around the edges of the rash
- Wash your groin area two to three times a day with an antifungal shampoo.
Keeping the infected area clean will help prevent further spread of fungus or bacteria. Throughout treatment, wash your skin two to three times a day with an antifungal shampoo.
Keep infected skin areas dry.
Excess moisture promotes the growth of fungus and bacteria that cause athlete's foot. Dry your groin area completely after showering and be careful not to allow sweat to accumulate there. Change clothes immediately after exercising and wash them.
Apply an antifungal cream to the infected area.
There are various over-the-counter antifungal creams that help with athlete's foot. Apply the cream every time after bathing and drying the skin, being careful not to miss the edges of the rash.
Be careful not to expose the contaminated area to aggressive substances.
Strong detergents, bleach, and even fabric softener residue on clothing can cause additional irritation to your skin, making it worse. Avoid contact of these and other harsh substances with the skin in the groin area throughout the course of treatment.
Use an aluminum salt solution.
A ten percent solution of aluminum chloride or aluminum acetate blocks the sweat glands and is therefore an effective antiperspirant. To prepare the solution, do the following: :
- Dissolve one part aluminum salt in 20 parts water. Apply the prepared solution to the infected area and leave it for 6-8 hours. It is better to apply the solution before bed, since the sweat glands are less active at night. When you notice that the lubricated skin begins to sweat again, wash off the solution. Repeat the procedure until the rash dries and begins to shrink.
In most cases, the fungal infection that causes athlete's foot causes blisters to form over fairly large areas of the skin. These blisters can also be treated at home by applying medicinal compresses to them, moistened, for example, with Burov's liquid. This will dry out the blisters and reduce discomfort, allowing you to continue treatment with antifungal creams.
Cure athlete's foot.
If athlete's foot is accompanied by a fungal infection (mycosis) of the feet, you may re-infect the groin area when you put on underwear. Treat both fungal diseases to avoid becoming infected with athlete's foot again.
Try general remedies.
If you prefer to treat yourself with home remedies, you can try the following options:
Health care
- If your condition does not improve after two weeks, contact your doctor.
If treatment with home remedies for two weeks does not bring results, this means that you need stronger antifungal drugs, or the disease is not fungal, but bacterial in nature. In this case, your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics.
If your doctor determines that the illness is caused by a fungus and over-the-counter medications have not worked well after two or more weeks, he or she will likely prescribe you a stronger antifungal cream. These may be the following drugs:
- Oxiconazole 1% cream (Oxistat)
Cream with 1% econazole (Spectazol)
Inguinal epidermophytosis is a fungal pathology characterized by the appearance of specific spots in the area of large folds, which cause discomfort to a person because they itch and grow up to 10 cm in diameter. Men are more often affected by the disease, and this disease practically does not occur in children and adolescents. Women can also experience the disease, but much less frequently than men, and in them the spots characteristic of athlete's inguinal athlete can be located in the labia, on the inside of the thighs, and also in the folds under the breasts.