What you need to know about papillomas
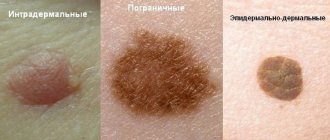
Papillomas look like single or multiple skin formations with an uneven surface, located on a stalk or broad base and rising above the skin level
Papillomas look like single or multiple skin formations with an uneven surface, located on a stalk or broad base and rising above the skin level. The color of the papilloma may match the color of the skin, or it may be dirty gray or brownish. The pedunculated formation is well mobile. The size of the papilloma varies from 3 mm to 3 cm, the surface is often uneven, with partial keratinization. Papillomas grow slowly and stop when they reach a certain size.
They are caused by the human papillomavirus. By the way, this virus causes the appearance of not only papillomas on the skin, but also warts and genital warts. It is transmitted by contact, but can also be transmitted in utero - from mother to child. Moreover, the virus tends not only to cause localized formations, but also to infect neighboring areas of the skin.
Increased attention
Often the appearance of warts on any part of the body is associated not only with poor personal hygiene, but also with increased sweating, and therefore growths appear on the surface of the feet and palms.
Tight, uncomfortable shoes and visiting a public pool or sauna can easily lead to formations on the sole of the foot.
Any scratch or the slightest cut on the hands that is not treated in time can lead to a wart appearing. Reduced immunity or imperfection of its development will contribute to the problem, which is especially important in childhood and adolescence. After all, it is during this period that this problem often manifests itself.
It is always necessary to monitor the growth if it is not possible to remove it immediately. You should not delay a visit to the doctor in cases where the formation:
- begins to grow quickly, change its shape and color;
- loses clear boundaries;
- is constantly injured or in pain;
- increases in quantity;
- starts to itch or bleed.
No one will deny that warts often go away on their own. You just need to strengthen your immune system and the problem will disappear. Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, proper food, healthy sleep and a positive attitude towards yourself and life will help you consolidate the results so that you will never remember unpleasant growths again.
On what parts of the body do papillomas most often appear?
The most common places where tumors accumulate are the eyelids, nose, and neck of a person. Often, papillomas appear on the ears, as well as on the natural folds of the human body. The area of the body where such neoplasms occur depends on the type of papillomas.
Basically, this formation is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) occurs in almost 90% of the world's population, and most papillomas are not oncogenically dangerous.
In appearance, papillomas can be the size of a tiny grain or reach a large filamentous formation. Therefore, in any case, everything is individual and it is better to consult with a clinic specialist.
Types of effects on tissue during electrocoagulation
During the electrocoagulation procedure, a high-frequency electric current is applied to the tissue of skin tumors, and the following types of effects are produced on condylomas:
- Thermal - the high temperature created by the current causes a burn. When calculating the time and depth of exposure, the size of the neoplasm is taken into account, so healthy skin tissue is not damaged. Burnt tissue is easily separated from the skin.
- Electrodynamic - heating of intercellular fluid, blood and lymph in the area of influence causes rejection of pathological tissues. The dynamics caused by electric current are a secondary effect of the burn.
- Physico-chemical - an effect that occurs at the level of biochemical connections of cells. The physical effect of the current provokes the rupture of chemical bonds between the cells of healthy and pathologically altered tissues.
- Biological - this type of effect concerns healthy tissue cells, which, when receiving a burn and subsequently separating the neoplasm, receive an irritating and at the same time coagulating effect. As a result, the vessels coagulate, eliminating the possibility of bleeding.
The effect of high-frequency current on skin tissue requires precise calculation, so the intervention is carried out with preliminary preparation in a clinical setting. Before performing electrocoagulation, it is necessary to perform an examination, assess the compliance of the indications and exclude possible contraindications.
When calculating the time and depth of exposure, it is very important to know exactly the size and volume of the neoplasm so as not to damage healthy skin tissue.
Medicine knows many types of skin tumors, among which are condylomas.
Cutaneous condyloma is a warty formation, the appearance of which is caused by the human papillomavirus. Most often, condylomas are located in the genital area and anus, on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease is chronic; relapses occur from time to time, mainly associated with a decrease in immunity and the body's defenses. The disease affects both men and women.
Due to the active reproduction of the virus in cells, the process of transformation of the epidermis into surface epithelium is disrupted. The result of this pathology is the growth of the deep skin layer. The keratinized layers of the skin areas undergo uneven thickening. These thickenings take the form of warts and are condylomas.
Among the varieties of condylomas there are:
- exophytic or pointed;
- endophytic;
- Buschke-Loewinstein tumor.
Genital condylomas are fibroepithelial formations that look like small cones and cylinders of flesh-colored or pink color, rising above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane. Structurally, condyloma is represented by a stalk and a base.
Endophytic condylomas grow in the inner layers of mucous tissue and are not always noticeable on its surface. They can be:
- flat;
- atypical;
- inverted.
Giant condyloma, or Buschke-Loewenstein tumor, is quite rare and is localized mainly in the apogenital area. Initially, the disease begins with the appearance of many closely spaced genital warts or papillomas, which then grow together, turning into a single exophytic formation.
Why do papillomas appear?
Papillomas are formed:
- in areas of friction and frequent skin trauma
- in the folds of the skin
- with hormonal changes in the body (especially during pregnancy, during premenopause)
- with decreased immunity (after sunbathing, when using chlorinated water for washing)
Papillomas are viral in nature; sampapillomavirus lives in the blood and cannot be eliminated. With various provoking factors listed above, the papillomavirus is activated and manifests itself in the form of neoplasms on the skin - papillomas. There are many types of papillomavirus (more than 20); the formation of skin papillomas is associated with the presence of a non-oncogenic virus in the body. Papillomas on the skin rarely undergo degeneration. However, skin papillomas are capable of multiplying on the surface of the skin: many daughter papillomas appear near the mother papillomas.
What are the advantages of the electrocoagulation method?
- Fast execution,
- Painless,
- No bleeding
- Safety,
- Short recovery period
- Low cost,
- Relapse prevention.
As a rule, after electrocoagulation, warts do not reappear, and cauterization of one wart prevents the spread of the virus that causes the appearance of this type of tumor.
In some cases, patients complain of itching and burning after coagulation. This may be due to individual skin sensitivity, intolerance to the local anesthetic, or a violation of the procedure itself.
Is it worth removing papillomas?
Most often, papillomas do not pose a cancer risk. If they do not become larger or increase in size, are located in places under clothing and are not injured, then they do not need to be removed.
Most patients seek removal of papillomas for aesthetic reasons. To prevent complications, removal can be performed if the papillomas are located in areas of frequent trauma (lumbar region, collar area) or cause painful discomfort.
Methods for removing papillomas
The technique allows you to remove one or even several tumors in just one session. Among them are not only moles, papillomas and warts, but also age-related keratomas, complicated acne, spider veins and much more.
To treat papillomas, an oncologist can use various techniques: surgical excision, laser removal, cryodestruction and radio wave radiation. The surgical method is now practically not used; there are enough other methods that are less traumatic.
Laser removal allows you to perform the manipulation quickly, accurately and avoid bleeding.
Cryotherapy uses the cooling effect of liquid nitrogen to destroy cells at the site of treatment. If the papilloma is located superficially, then, as a rule, one procedure is sufficient. The manipulation is atraumatic and well tolerated by patients.
The radio wave method shows good results. Here, removal of papilloma is achieved through tissue coagulation using the energy of radio waves generated by the surhydron device. The papilloma is removed at the level of the pedicle, its base is covered with a dark crust, which after a few days disappears almost without a trace. Advantages of the method: high accuracy, absence of complications, favorable recovery period, possibility of taking material for biopsy.
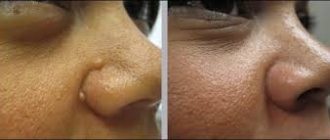
Results of electrocoagulation of papillomas
The photo shows the result of electrocoagulation of papillomas
Ideally, if the doctor did everything correctly, a dry crust should form at the site of the papilloma in a few days. When everything proceeds without pathologies, this scab disappears 7-14 days after the session. By this time, there are no longer any traces left on the skin from the effects of electric current.
Complications during care after electrocoagulation of papilloma are possible if the doctor has not received proper training in working with the device. They can also occur when the growth is exposed to current for a long time, which can lead to burns. Incorrect dosage selection, performing the procedure too often and failure to follow safety rules may also very well cause a slowdown in the recovery process.
If the doctor was unable to destroy the papilloma with electrocoagulation, then other growths may soon appear in this place or nearby. Relapse is extremely rare, and this only happens if the dosage of current was not high enough and the depth of penetration was small. Most often, such problems arise when removing thread-like formations.
- See also possible complications after wart removal
Removal of tumors using electrocoagulation
You can get rid of tumors using electrocoagulation
You can get rid of them using electrocoagulation. Other indications for the procedure are hemangiomas, fibromas and lipomas, cystic acne and rosacea, molluscum contagiosum.
This surgical procedure is based on the action of high frequency electric current. The mechanism of influence is the temperature effect on the neoplasm with direct or alternating current, leading to the destruction of proteins, that is, the destruction of neoplasm tissue.
Removal of benign formations on the skin using an electrocoagulator allows you to quickly and painlessly get rid of unsightly warts and papillomas.
As a rule, there are no strict medical indications for the removal of benign tumors, and we are talking more about aesthetic discomfort and prevention. Doctors recommend paying close attention to moles and papillomas that are subject to constant friction or trauma. For example, when playing sports, protruding formations located in the folds of the skin (axillary, inguinal areas) can become twisted “on a stalk” and become inflamed. In such cases, it is better to consult a cosmetologist-dermatologist to prevent negative consequences.
Electrocoagulation or electrodestruction is one of the most common and reliable cosmetic methods for removing pedunculated tumors protruding above the surface of the skin. It is also sometimes used to eliminate spider veins and punctate hemangiomas.
The essence of the method is the excision of tissue with an electric knife and simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels, which promotes the formation of a thin crust and rapid healing of the wound, and prevents the appearance of a rough scar. The electric knife seems to coagulate the smallest vessels that fed the neoplasm.
Electrocoyagulation can be called one of the delicate methods, because, unlike surgical intervention, after it the risk of forming a rough scar on the skin is minimal. This method is also used in cases where special care and caution is required: removal of tumors along the ciliary edge, papillomas in the corners of the eyes.
Advantages and disadvantages of the radio wave method
The main advantage of this method is the ability to remove papilloma in open areas of the body.
Removal of benign neoplasms (papillomas, warts, condylomas, etc.) using radio waves of a certain frequency is a unique method that attracts many with its speed, simplicity, painlessness and short rehabilitation period. Let's consider a few more advantages of this procedure:
- Only affected skin cells are removed, healthy skin remains unaffected.
- Basically, there is practically no direct contact of the skin with the electrode.
- The procedure is relatively painless; in some cases it is quite possible to do without anesthesia.
- The radio wave device has a sterilizing effect, which promotes faster healing.
- In the process, coagulation of blood vessels occurs, which results in the absence of bleeding.
- There is a minimum risk that scars and scars will remain after the operation.
Most medical diagnostic and treatment centers in our country offer to perform this procedure. The average price for one session varies between 450-1350 rubles. in most cases, the first session is more expensive than subsequent ones. The price will depend on the size of the tumor, as well as on the location of the papilloma removal.
Positive reviews from patients note the speed and safety of removing papillomas using a device such as Surgitron. Among the disadvantages are the following points:
- minimal, but still, the risk of scars and cicatrices;
- possible relapses;
- For some, the price of the procedure is expensive;
Is it safe from an oncological point of view?
Professional removal of ordinary, benign formations poses absolutely no threat
Professional removal of ordinary, benign formations poses absolutely no threat. What is really unsafe is to ignore large moles that have recently increased in size, become very dark or damaged.
Such moles can turn into malignant formations and require immediate removal. But any large mole can be removed without waiting for alarming symptoms - this will be the best prevention.
In our clinic, moles are removed quickly and painlessly, and the cut sections of tissue are immediately sent for histological examination. It is also necessary to get rid of warts, since they are very contagious and can spread to all family members.
How to remove papillomas using the radio wave method
As medical practice shows, the average duration of the procedure takes from 10 to 20 minutes.
The duration of the procedure depends on the number of papillomas to be removed, their size and the qualifications of the doctor. No special preparation is required before removal. Stages of the procedure:
- Anesthesia - before removing a papilloma, in order to eliminate possible pain, anesthesia (local anesthesia) is mandatory. Today, there are several methods of anesthesia - the intended area is treated with a gel-like substance; injection method of introducing an anesthetic into soft tissues; Irrigation of the required area with an aerosol.
- Removal - a specially prepared thread-electrode is directed to the papilloma, through which an electric current of the required frequency passes. Using an “electronic knife,” the tumor is instantly cut off at the very base. At the same time, tissue cauterization occurs, which helps prevent blood loss, as well as save the patient from possible complications (swelling, infection).
- Histology - after the procedure, the removed papilloma is sent for histological examination to ensure that the tissue is benign.
- Rehabilitation period – after all necessary procedures, antiviral and immunostimulating local therapy is selected individually for each patient.
Flaws
- not for use on large areas of skin
- longer healing period due to the involvement of nearby healthy tissues in the process
- very painful removal of warts, especially those located on the soles and feet, as well as prolonged and painful healing, often with scarring
- when removing large elements, healing with scar formation
- not recommended for removing large elements in cosmetically significant areas (face, open décolleté, neck)
Contraindications
- Herpetic rash on the skin is a contraindication to the procedure
intolerance to electrical procedures and drugs for local anesthesia
- blood clotting disorder
- suspicion of a malignant nature of the skin formation
- acute infectious diseases
- herpes skin rash
- presence of a pacemaker
- rapid growth of benign neoplasms
- systemic blood diseases, leukemia
- increased skin sensitivity to light (photodermatoses)
- endocrine diseases (decompensated diabetes mellitus, etc.)
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (crisis course of arterial hypertension, heart and pulmonary failure stage 3)
Contraindications for electrocoagulation of papillomas
First of all, this procedure is not recommended for people with sensitive skin, as it can cause itching, irritation, and redness. It is also performed with caution on children and elderly people, since tissue repair processes in them proceed much more slowly than in others.
Strict contraindications to electrocoagulation of papillomas are:
- Problems with blood clotting . They are mainly inherited, from mother or father to child. The most famous and dangerous disease is hemophilia. If it is present, a person may experience bruises on the body, seemingly without reason.
- Dermatological diseases . It is not recommended to carry out electrocoagulation for eczema, urticaria, cold allergies and other similar problems. Such a prohibition is relevant only in the acute stage; when symptoms disappear, the decision on the possibility of performing the procedure is made by the attending physician.
- Malignant formations . In reviews of electrocoagulation of papillomas, doctors advise those diagnosed with skin and blood cancer (leukemia) to refuse it. The current can provoke tumor growth and accelerate the course of the disease, thereby worsening the patient’s health.
- Somatic diseases . These include bronchial asthma, gastritis, colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and arterial hypertension. Separately, it is worth mentioning the danger of performing the procedure for people with stomach and duodenal ulcers.
- Tendency to form keloid scars . Usually it is congenital, but sometimes people acquire it, for example, as a result of previously incorrectly performed cosmetic procedures, taking various medications, exposure to sunlight and low temperatures. Because of this, problems may arise during care after electrocoagulation of papilloma.
Important! The presence of at least one contraindication from the list is grounds for refusing to remove papillomas using electrocoagulation. But still, the final decision about this is made by the attending physician.
- See also contraindications to cryodestruction of papilloma
Progress of the procedure for electrocoagulation of neoplasms
Before removing a tumor, you must consult with a cosmetologist-dermatologist about the possibility of carrying out the procedure and choosing the optimal method.
No preliminary preparation is required to remove tumors. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is absolutely painless for the patient. Immediately after removal, pink, delicate skin is noticeable at the site of the former neoplasm, which forms into a crust during the healing process.
After the procedure, it is recommended not to sunbathe for 3-4 weeks, it is necessary to protect the removal site with sunscreen, and the crust that has formed on the skin should not be removed ahead of time. Under the crust, which protects the wound from infection and comes off on its own within 10 days, a new epithelium is formed.
A follow-up meeting with a cosmetologist-dermatologist takes place in 7–10 days. The doctor assesses the condition of the wound surface and gives additional recommendations for care.
After electrical destruction, the doctor can provide material for histological examination to further confirm the benignity of the neoplasm. For comparison, after laser removal there is no such possibility, since the laser evaporates the tissue, thus destroying the material for analysis.
In some cases, a cosmetologist-dermatologist can supplement the electrocoagulation procedure with a small laser resurfacing to smooth the edges of the wound and even out the skin area. In this way, the most improved aesthetic effect from the procedure is achieved: after healing, the skin remains smooth and beautiful, without a hint of the procedure performed.
How is electrocoagulation of papillomas performed?
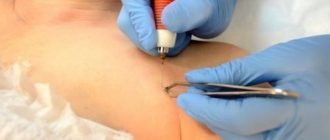
To carry out the operation, a special device with electrodes is used, which cauterize the surface of the growth. The doctor must perform all manipulations wearing sterile gloves. The patient can lie or sit at this time, depending on the location of the growth.
This procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, the patient does not need to be admitted to a hospital, after which he is allowed to go home immediately.
Here's how electrocoagulation of papilloma works:
- The cosmetologist disinfects the problem area that he will work with.
- Next, having determined in advance the size of the desired area, an anesthetic cream is applied to the skin, which allows you to minimize discomfort.
- Then the electrode with a loop is brought to the papilloma and installed at a slight angle.
- Cover healthy surrounding tissues with a napkin so as not to injure them.
- In the other, free hand, take sterile tweezers, which are used to support the formation.
- Next, the growth is heated to high temperatures, which prevents the survival of cells affected by the papilloma virus.
After electrocoagulation of papilloma, it is recommended to be observed by a dermatologist at least once every six months to exclude relapse. Doctors also advise taking a course of antiviral drugs and immunostimulants to bring the virus under control.
- See also how laser removal of papillomas is performed
Technique
Electrocoagulate
Before the procedure, local anesthesia and antiseptic treatment of the skin area with the formation that needs to be removed is performed. If it protrudes above the surface of the skin, the doctor will use a loop or knife-shaped electrode. This will take a few minutes. Non-protruding defects are cauterized layer by layer with a flat or round electrode. Accordingly, the duration of the procedure will be 5-15 minutes. Pinpoint lesions such as hemangiomas or spider veins are removed with a needle-shaped electrode. A crust forms at the site of the defect, which must be treated daily with a special solution. When the crust falls off after three or four days, a pink spot will remain, and after a while it will disappear. Scars form after electrocoagulation extremely rarely.
Simple procedure
The electrocoagulation procedure is quite simple and takes a few minutes. Usually one session is enough to remove several medium-sized warts at once. To avoid pain during the procedure, local anesthesia is used, and to prevent infection, the skin is pre-treated with an antiseptic.
After completing the preparatory stages, a heated loop of a coagulator is placed on the wart and a high-temperature electric current is applied. The tissues of the growth are damaged, followed by their death due to thermal burns. At the same time, the blood vessels are cauterized, eliminating the risk of bleeding. Usually growths less than one centimeter are removed.
The consequences of this procedure are minimal. A dense crust forms at the site of the wart. Underneath it, tissue healing begins, which will end with the crust falling off and in its place there will be a smooth, pink spot on the surface of the skin. It will disappear over time. In case of damage to the deep layers of the skin, the spot has a light shade, but also disappears over time.
Sometimes, after removal of a papilloma, patients complain to the doctor of itching or burning. They can be explained by the sensitivity of the skin. Experts recommend treating the surrounding tissue at the site of removal of the growth after the electrocoagulation procedure with an antiseptic for one week.
There is no need to touch the resulting crust. You shouldn’t get it wet, which will guarantee quick healing. Recurrence of formations after cauterization with high-frequency current usually does not occur, since the procedure eliminates the further spread of papillomavirus, which is the source of skin rashes.
To consolidate the result, the doctor may prescribe medications to enhance immunity. It will never be possible to completely get rid of the source of the disease, since the virus is constantly present in the body and simply does not manifest itself until problems with the immune system arise. Therefore, it is imperative to monitor your health and constantly improve your immunity.
A loop of an electrocoagulator is placed on the wart, through which a current is supplied.
What is the peculiarity of removing papillomas using electrocoagulation?
Often it is necessary to remove small and large papillomas, papillomas on the body, on the face, on the eyelids, even between the eyelashes. Removal of papillomas on the genitals is carried out by doctors of relevant specialties (gynecologists, urologists). The smaller the papilloma, the easier and faster it is removed! Therefore, do not wait until the papilloma becomes large, when a dozen daughter papillomas appear around it - the removal of such papillomas is longer and more difficult.
The procedure for removing papillomas by electrocoagulation is quite fast, takes about a minute, with the exception of removal of large papillomas.
Removal of papillomas using electrocoagulation may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations, so for patients with high pain sensitivity we offer preliminary anesthesia. Using the electrocoagulation method, you can remove not only papillomas, but also keratomas and adenomas of the sebaceous glands, which give an uneven appearance to the skin on the face and body.
Removal of warts by electrocoagulation: all the information
Warts and papillomas look unsightly and are constantly injured because they protrude above the skin. In addition, there is always a risk of their malignant degeneration over time. But today there are simple and effective ways to remove tumors forever. In this article, we will look at what methods of getting rid of warts modern dermatology offers us, and we will tell you in detail about one of the most common methods - electrocoagulation.
Advantages of wart removal using modern physical methods
Many people try to get rid of skin tumors at home, but this is not always justified. There are reasons why you should not remove warts and papillomas yourself:
- Often, neoplasms appear on the face, near the eyes or lips, in deep folds of the skin and other hard-to-reach and delicate places. Cauterization with chemicals available in pharmacies can cause burns, scars and deep wounds.
- Often the changed cells go deep into the skin, creating a kind of “root”. Incomplete removal will cause the wart or papilloma to grow back.
- Inside the warts are blood vessels and nerve endings. Attempts to remove the tumor yourself are painful and sometimes lead to severe bleeding. Doctors have the opportunity to use anesthesia (an injection or a special gel), although all modern physical methods destroy the formation so that it is almost not felt. A crust immediately forms at the site of exposure, and no bleeding occurs.
- The doctor uses dermoscopy and other methods for diagnosis to make sure that it is a wart (papilloma), and the formation does not have signs of malignancy.
The only disadvantage of wart removal procedures is the rather high price, which is still probably worth paying for clean and beautiful skin without scars.
Wart removal methods
Modern methods of getting rid of skin tumors include:
- Electrocoagulation or diathermocoagulation.
- Laser destruction.
- Radio wave method.
- Cryodestruction.
- Argon plasma coagulation.
It is impossible to say for sure which method is better. It all depends on individual characteristics: the age and health status of the patient, concomitant diseases, location, size and type of formation. Typically, clinics offer several methods, the choice of which is the task of a dermatologist.
Benefits of electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation of warts has many advantages, so this method remains one of the most popular. Here are some of them:
- The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, after which you can go home immediately;
- No special patient preparation is required;
- Electrocoagulation gives a good aesthetic effect; it almost never leaves scars;
- The method is suitable for any part of the body, including the face (except for the skin on the edge of the eyelids);
- The procedure goes very quickly;
- Any wart is removed in one procedure, regardless of its size, re-treatment is not required;
- You can remove several formations at the same time;
- The recovery period is short - after only 2 weeks, new, clean skin will grow at the site of the wart;
- Removal of warts by electric current is affordable (cheaper than laser and argon procedures), and there are specialists who work with electrical equipment in almost any clinic.
Disadvantages of electrocoagulation
Among the disadvantages of electrocoagulation are the following:
- Some people feel a burning sensation and pain during and after the procedure, but this is minor;
- Deep plantar warts are not always amenable to coagulation with current, since they do not protrude to the surface, but go under the skin; for them, you need to choose other methods;
- The qualifications of the doctor are of great importance. If the current frequency and duration of exposure are incorrectly selected, scars may form.
Contraindications
Electrical coagulation is not suitable for everyone. You cannot remove warts with electric shock in the following cases:
- Any blood clotting disorders (hereditary and acquired);
- Acute infectious processes, including ARVI;
- Exacerbations of chronic somatic diseases;
- Herpes in the acute stage with rashes and blisters on the skin;
- The period of bearing a child or breastfeeding;
- allergy to local anesthetics;
- Suspicion that the neoplasm may be malignant.
Diabetes mellitus is a relative contraindication, since people with this disease have poor wound healing (this does not apply to people with well-chosen therapy and stable glucose levels). In rare cases, people with a tendency to form keloid scars may have visible traces of removed warts (they remain regardless of the method of removal, and doctors can at least minimize this process).
Removal procedure
A coagulator is a small tabletop device with various tips. Used in dermatology, gynecology, ENT practice, dentistry, etc. The most common model of electrocoagulator is EHHF-50 Medsi. Warts are usually removed with a pointed tip with a small ball at the end, and pedunculated papillomas with a special loop.
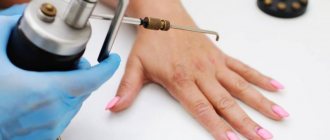
Removal of one formation using electrocoagulation with all preparation lasts only 2-5 minutes. The skin is lubricated with an antiseptic, and if necessary, local anesthesia is given (lidocaine injection under the wart or lubrication with anesthetic gel). The electrode is applied to the tumor and a shock is applied. By adjusting the shape of the tip and the frequency of the current, the doctor selects the desired degree of impact on the skin.
Under the influence of a current that heats the skin to 80 °C, the intercellular fluid evaporates, the proteins coagulate, and a dense crust-scab forms at the site of the wart. After the procedure, they are additionally treated with a solution of potassium permanganate or fucorcin.
Under the crust, which protects against infection, healthy tissue gradually forms. After 10-14 days, healing will be completed and the crust will fall off on its own.
Rules for skin care after the procedure:
- Lubricate the skin with brilliant green, a 5% solution of potassium permanganate or fucorcin for 1-2 days;
- Protect the crust from getting wet under the influence of water (do not soak it for 5 days, do not go to the sauna or swimming pool);
- Do not bandage or tape for free ventilation;
- Protect wounds from excess UV rays (do not sunbathe) to avoid the appearance of age spots.
- Do not apply any cosmetics to the scab until it has healed.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend using ointments and creams for scars and scars (Contractubex, Dermatix, Mederma and others). Whether you need to do this or not, he will tell you during the consultation.
Cost of the procedure
The price of electrocoagulation varies greatly; it depends on many reasons, including the region. In large cities and the capital, prices are traditionally higher.
The cheapest way to remove formations is on smooth skin of the body, arms and legs - from 250 rubles. for one wart (papilloma). If the formation is located on the face, the price will be higher - from 600 rubles. Local anesthesia in the form of an injection – from 200 rubles.
Personal reviews about diathermocoagulation
Anna B.:
Medicines for papillomas do not help! I applied oxolinic ointment on the advice of a friend every day for a month - no reaction. She spat and went to the clinic to have it removed by electric shock. There were a lot of papillomas, so at first they counted me almost 5,000, but then they gave me a discount (at this clinic there is a discount of 5 pcs. and also for pensioners). So it turned out moderately. The papillomas have disappeared, no problems.
Anastasia K:
I had two moles (nevi) removed. I was very tired of them: they clung to my clothes, once I even tore one off, there was a lot of blood. When everything healed, the skin in this place was much lighter for a very long time - just two round spots. I thought it would stay that way, but a year later I couldn’t even remember where my moles were.
Ekaterina N.:
Two warts were removed from a child's finger. They were afraid that he would cry, but everyone there entertained and distracted him. Then he even said that it didn’t hurt. The wounds healed very quickly. The only negative is the strong smell of burnt meat; it would be necessary to make a hood for such things.
Sources used: bezgribka.com
How to prevent recurrence of papillomas
After the procedure, the doctor will invite you for a re-examination in 2 weeks to evaluate the results of the procedure and give further recommendations on lifestyle to prevent the appearance of skin tumors in the near future.
- The procedure for removing papillomas should be carried out by an experienced dermatologist trained in oncodermatology, so as not to mistake malignant neoplasms on the skin for papilloma, requiring radical removal and subsequent treatment to prevent metastases.
- In addition, excessively deep removal of papillomas can lead to the formation of scars or white spots on the skin after the scab comes off.
- Papillomas should not be removed if the skin is tanned, since the risk of discolored spots on the skin in this case is greater.
Sources:
- https://medi.spb.ru/esteticheskaya-meditsina/uslugi/apparatnaya-kosmetologiya/elektrokoagulyatsiya/
- https://astartamed.by/onkologiya/udalenie-papillom/
- https://vokkvd.ru/patients/
- https://petrovka-beauty.ru/abc/electrocoagulation/
- https://primaks.ru/ehlektrokoagulyaciya.html
- https://edit.ua/udalenie-papillom.html
After care
After electrocoagulation, a small wound remains on the skin. Over time it will heal. In order for the regeneration process to go faster, proper skin care after the procedure is necessary.
After a few days, the wound heals and a dry crust forms in its place. There is no need to remove it - it will go away on its own in about 2 weeks.
If the crust is damaged, skin restoration will be disrupted, and a pigment spot will form in this area. In particularly severe cases, bleeding may develop.
On this topic
- Skin covering
Why does the wen itch?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 5, 2020
A healing wound should be treated with an antiseptic every day. This will prevent infection. This treatment must be carried out until the crust peels off.
During the recovery period, you should not use cosmetics or aggressive detergents. Exposure to the sun should be limited and you should not visit the solarium.
After the skin has recovered, the area should be protected from adverse effects with moisturizers or sunscreens. Frequent use of decorative cosmetics is undesirable. To boost immunity, you should take vitamin complexes.