Home / Impotence
Back
Published: 04/24/2020
Reading time: 9 min
0
7
- 1 Is boil contagious?
- 2 Why you shouldn’t be afraid of transmitting infection to another person through ordinary contact
- 3 Therapy for boils
- 4 Forecast
- 5 Is furunculosis contagious and in what cases can the disease be transmitted?
- 6 Origin of the disease
- 7 Mechanism of appearance and causative agent of boils
- 8 Is it possible to become infected with furunculosis: the mechanism of the disease
- 9 Routes of transmission of the disease furunculosis and stages of its development
- 10 How Staphylococcus aureus enters the body
Is furunculosis contagious and in what cases can the disease be transmitted?
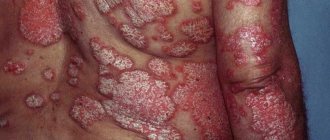
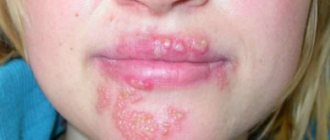
Boil is a purulent-necrotic skin formation of bacterial etiology.
Whether a boil is contagious depends on the form of the disease and the individual characteristics of the person. There is a risk of contracting the disease. Content
Doctors associate the mechanism of occurrence of the disease with reduced immunity and hypothermia. Opportunistic microflora begins to actively attack the body. Staphylococcus aureus is the main pathogen.
The microorganism lives on clothing, skin, in poorly ventilated areas, and dust. Penetrates into the papillary layer of the skin through traumatic injuries and microcracks.
The bacterium provokes inflammatory changes in the hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and surrounding tissue.
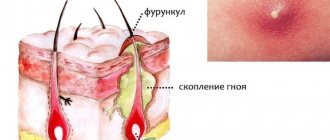
Over time, an abscess forms - a purulent pustule with a necrotic core. The stage of abscess formation begins. The boil opens independently or with surgical help. Lack of treatment, severe course ends in hospital. The disease is complicated by abscess, phlegmon, lymphangitis, lymphadenitis, and septic shock.
There is no clear answer to the question of whether chiria and boils are contagious to other people. Numerous medical studies have shown that the likelihood of infection increases with close contact with a patient, a tendency to pathology, or the presence of provoking factors in a healthy person.
Some types of staphylococci can survive in an open environment for several weeks. The disease does not occur in people with strong immunity. The skin performs a protective function. Prevents the entry and penetration of staphylococci. Bacteria and skin have the same positive charge. It is difficult for microorganisms to gain a foothold on the skin.
The strength and constant renewal of the stratum corneum of the skin prevents the internal penetration of staphylococci.
The disease develops in healthy people with predisposing factors:
- Working in a workplace with hazardous working conditions causes another person to become ill. Dust particles get on the skin and cause microcracks. If there is close contact with a sick person, the potential victim has a chance of becoming infected. A similar situation is with people who have scratches and microtraumas on their bodies.
- Constant stress and poor nutrition negatively affect the immune system. A person becomes infected with furunculosis and other bacterial infections from the carrier of the disease.
- People with dermatological skin problems (eczema, dermatitis) are recommended to avoid contact with a patient with furunculosis for 2 weeks. Skin diseases are often accompanied by itching. The patient constantly scratches the pathological areas of the body. Creates a gate for the penetration of staphylococcus. The same applies to patients with diabetes and various metabolic disorders.
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency negatively affect the immune system. First strengthen the body's own defenses, then help patients with boils.
Pathology poses a danger even to the sickest. Pus flows from the boil and enters neighboring areas of the body. Furunculosis develops. New chiryaks complicate the course of the disease. In the absence of antibacterial therapy, chirias unite into fused lesions. A carbuncle or abscess appears. Both diseases require immediate surgery and long-term antibiotic therapy.
Are boils and styes contagious to another person? Infectious diseases are dangerous. Furunculosis is transmitted in various ways:
- a healthy child cannot become infected from a sick mother. Breastfeeding provides the baby with a strong immune system. The risk of infection is present in premature, weakened children;
- A decent number of diseases are transmitted through sexual contact. If the boil is localized in the groin or genital area, a healthy sexual partner cannot become infected. In the presence of predisposing factors, the boil becomes contagious;
- staphylococci inhabit public places (baths, swimming pools, clinics). Many people think that infectious agents attack from the air. The disease is never transmitted by airborne droplets (through kissing, talking);
- heredity does not affect the risk of boils;
- contact transmission is possible when working with contaminated instruments, catheters, and dressings.
A boil is an unpleasant, painful formation on the skin. With proper and timely treatment, the pathology goes away in a couple of weeks. Often the boil is complicated by abscesses, phlegmon, and sepsis. Simple measures will help you avoid infection and complications of the disease:
- Hand hygiene after processing chiria is the main measure to prevent the disease. Along with hygiene procedures, you need to disinfect your hands with antiseptic agents.
- To prevent the spread of infection, it is necessary to apply a gauze bandage to the inflamed area.
- You cannot use the patient’s bath items and hygiene products.
- It is advisable to do daily cleaning.
- During the period of illness, it is necessary to maintain a balanced diet. Include animal proteins, fiber, fruits, and vegetables in the patient’s diet. You can’t eat sweets, chocolate, citrus fruits, fish, eggs.
- People with reduced immunity need to drink a complex of vitamins and minerals every six months.
- A healthy lifestyle, absence of bad habits, walks in the fresh air, gymnastics are the main prevention of inflammatory and chronic diseases.
- You cannot self-medicate. Timely diagnosis and treatment of a boil will help avoid unpleasant consequences.
- If you have diabetes or obesity, do not start the pathological process, visit your doctor annually.
There are many ways to prevent the occurrence of a boil. Avoid stress, maintain your immunity and illnesses will not bother you!
The article has been verified by the editorsLink to the main publication(1
The cause of furunculosis is Staphylococcus aureus, but in some cases the disease can be provoked by bacteria of another type of Staphylococcus - epidermal. Both bacteria are present in the environment. 70% of people on the planet are their carriers.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JlPJeIqrxms
Microorganisms can pass from an infected person to other people, but in a completely healthy person the disease does not develop, since this requires additional factors favorable to bacteria. Simply put, for infection with furunculosis, the pathogenic microorganism is not as important as the factors that contribute to its reproduction. Such factors can be external and internal.
Most often, the main cause of the disease is weakened immunity in humans. External causes can be: trauma to the epidermis, dermatological pathologies, and internal factors (internal causes) are:
- decreased immunity;
- chronic diseases;
- vitamin deficiency;
- autoimmune disorders (diabetes);
- overweight;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- anemia;
- pathologies of the nervous system.
Causes
- Furunculosis can manifest itself as the primary form of the disease, developing on completely healthy (before the disease) skin.
- As a secondary form, due to complicated processes currently present in deep or superficial staphyloderma.
Various factors influence the development of the disease - first of all, the pathogenic properties of bacteria and their virulence (degree of infectiousness), predisposing causes - internal and external.
The main exogenous cause of furunculosis (external) is due to the creation of a “gate” for the introduction of infection, in the form of small wound skin lesions caused by scratching, friction of clothing, or traumatic injury. Internal factors play an important role in the development of large foci of furunculosis:
- pathologies of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders (DM, obesity);
- diseases of the nervous system and gastrointestinal tract;
- anemia and hypovitaminosis;
- constant exposure to cold or overheating, leading to a decrease in immune reactivity;
- chronic alcoholism;
- long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs, cytostatics or hormones.
The reasons for the development of pathological purulent furunculosis can be supplemented by many more factors, so that both preventive measures and treatment of furunculosis, the causes of which are not clear, will not bring the desired effect and the disease will take a chronic form.
The development of this disease is facilitated by skin contamination and friction against clothing, various injuries and abrasions. Even simple scratching can cause boils to appear.
Increased activity of the sebaceous and sweat glands, especially with seborrhea and acne and other similar diseases, also causes acute purulent inflammation.
Weakening of the immune system, hypovitaminosis, endocrine disorders, especially diabetes.
Puberty in adolescents is a factor contributing to the development of furunculosis.
Symptoms of a boil
The causes of boils depend on the following factors:
- avitaminosis;
- poor personal hygiene (skin contamination, scratching);
- chronic diseases of staphylo- or streptococcal etiology (tonsillitis, sinusitis);
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease);
- reduced immunity;
- anemia;
- other dermatological problems;
- adolescence;
- nervous disorders;
- frequent hypothermia or overheating.
Stages of development
Furunculosis is one of the pustular skin diseases, or pyodermatitis. It belongs to the group of deep staphylodermas, along with deep folliculitis, hidradenitis (inflammation of the sweat gland) and carbuncle. The fact that the disease is classified as a group of deep lesions indicates the possibility of scar formation after it.
Furunculosis is an inflammation of the hair follicle with the formation of a purulent core, accompanied by the spread of infection to the surrounding connective tissue of the middle layer of the skin. The causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus, less commonly the cause of infection is Staphylococcus epidermidis.
These microorganisms are common in the environment: street dust, industrial premises, clothing, living rooms. They quite often live on the surface of human skin and the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx without causing any diseases. According to some reports, up to 75% of people are carriers of staphylococci.
Is it possible to become infected with furunculosis from another person? Transmission of staphylococcus itself is possible, but for the development of the disease, the presence of exogenous and endogenous factors is necessary, which we will discuss below.
A furuncle can occur both on healthy skin and on skin affected by other forms of staphyloderma when the process spreads to the hair follicle.
Like any infectious disease, furunculosis occurs as a result of the interaction of a pathogen and a macroorganism.
For its development, not only a source (staphylococcus), but also internal (endogenous) predisposing factors, as well as certain environmental conditions (exogenous factors) are required.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Black mask made of charcoal and pva glue
Exogenous factors contributing to the development of furunculosis:
- minor injuries caused by solid particles of coal or metal suspended in the air in production, creating an entry gate for bacteria;
- friction of clothing on the lower back, neck, buttocks, which contributes to the transition of saprophytic (safe for humans) forms into pathogenic ones and their penetration deep into the skin;
- scratching the skin of patients with other pathologies - eczema, neurodermatitis, scabies.
Endogenous factors that increase the risk of developing furunculosis:
- exhaustion of the body and hypovitaminosis;
- diseases of the endocrine glands (diabetes mellitus, obesity), anemia, intestinal diseases, nervous system diseases;
- alcoholism;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body, especially repeated.
Endogenous factors cause a decrease in the body's reactivity, in particular, inhibition of local immune reactions. The pathogen penetrates the skin through damage caused by external factors. There it finds itself in a favorable environment and begins to actively multiply, causing inflammation.
Among the many substances secreted by this microbe, coagulase is of particular importance. Under the influence of this enzyme, coagulation (clotting) of blood plasma and blockade of surrounding lymphatic vessels occurs.
This leads to the limitation of infection with the formation of infiltrates with the subsequent formation of purulent-necrotic rods. Staphylococcus aureus also secretes hyaluronidase, which dissolves the base of connective tissue and promotes the penetration of microorganisms into the deep layers of the skin.
Thus, staphylococcal infection is characterized by spread not laterally, but in depth.
There is an opinion that many diseases are based on psychological causes. The psychosomatics of furunculosis is based on the assertion that emotions such as anger and constant irritation are favorable for its appearance.
It can be assumed that negative emotions cause a prolonged release of stress hormones and subsequent exhaustion of the adrenal glands, which, in turn, leads to suppression of the immune system and the development of chronic furunculosis.
There are single boils, recurrent boils that appear after some time, and furunculosis, in which pustules appear continuously one after another.
Clinical picture
The development of the boil occurs sequentially and has three stages:
- development of infiltration;
- suppuration and necrosis;
- healing.
As such, the incubation period of furunculosis is difficult to determine, since in most cases the disease is caused by its own microorganisms that have long settled on the skin. Initially, a raised compaction (infiltrate) appears around the hair follicle. It is bright red in color, has unclear boundaries, is slightly painful, or is accompanied by a tingling sensation.
After one or two days, the infiltrate thickens and expands, taking on the shape of a tumor and becoming painful. Nearby tissues swell, especially if a boil develops on the face.
After three to four days, the next stage develops. The infiltrate increases to 1-3 cm, in the middle of it a core is formed, consisting of dead and disintegrated tissue. A pustule forms at the top of the boil, which looks like a white head.
Pus consists of remnants of leukocytes, destroyed microorganisms, and decayed tissue of the hair follicle.
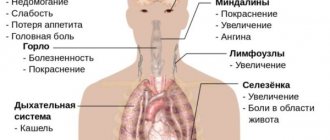
At this stage, the boil resembles a cone covered with smooth, stretched skin. The formation is painful, especially when located in the external auditory canal, scalp, fingers, or shins. If there are multiple ulcers, the patient’s body temperature may rise to 37-38 degrees. Symptoms of intoxication (poisoning) appear: weakness, headache.
This stage lasts about 3 days. Then the pustule opens, pus is released through the top of the follicle, sometimes with blood, and then a yellow-green purulent “plug” comes out - a necrotic core. In place of the abscess, an ulcer forms, which has uneven edges and a “undermined” bottom. It is filled with necrotic masses.
Recurrent furunculosis is accompanied by the formation of a new abscess after the previous one has healed. This condition most often occurs in adolescents, young men, and young adults with an allergic predisposition (sensitization) to staphylococci, as well as in patients with diabetes, alcoholism, and diseases of the stomach and intestines. Often a recurrence of the boil occurs with pediculosis (lice) and scabies.
When the course of the disease is erased, the infiltrate does not suppurate, and a necrotic core does not form.
Acute furunculosis lasts from several weeks to two months. It is accompanied by the appearance of numerous boils. Chronic furunculosis is characterized by a few follicles that appear constantly or with short breaks over several months.
Complications
The consequences of furunculosis are a cosmetic defect caused by scarring.
In some people prone to the formation of keloid scars, traces of furunculosis may be significant, with tightening of the surrounding tissue.
The formation of boils is especially dangerous in exhausted, weakened patients. In such patients, the disease is often complicated by an abscess or phlegmon (purulent melting) of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
The appearance of boils on the upper lip is very dangerous. From here, infection through the venous and lymphatic vessels can easily spread to the vessels of the brain and even cause sepsis - a general blood infection.
Infection of the veins with a facial boil causes progressive inflammation, that is, thrombophlebitis. From there, the pathogens enter the sinuses (extensions) of the dura mater, causing a serious complication - purulent basal meningitis.
It is accompanied by the rapid development of facial edema. Condensed veins are palpable and may be painful. Body temperature rises sharply to 40 degrees and above.
If the formation occurs on the neck, thigh, shoulder, it can be complicated by lymphadenitis - inflammation of nearby lymph nodes.
If staphylococcus gets into the blood, purulent foci may form in the internal organs - liver, kidneys and others.
Factors contributing to the development of complications:
- attempted squeezing, piercing or other impact;
- injury while shaving;
- irrational treatment with only ointments and other topical agents;
- location of the boil in the nasolabial triangle, on the nose.
Treatment
Which specialist should I contact for furunculosis? A dermatologist will help you choose the right therapy and help get rid of risk factors. If necessary, he refers the patient to a surgeon to open the abscess.
The dermatologist prescribes routine tests to show the general condition of the body.
In case of recurrent and chronic course of the disease, it is useful to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics, as well as to assess the person’s immune status (immunogram, diagnosis of HIV infection).
Treatment of furunculosis should be comprehensive. It includes:
- proper nutrition;
- systemic antimicrobial therapy;
- local impact;
- surgical methods;
- immunotherapy.
Nutrition
Nutrition for long-term furunculosis should be rich in proteins, including those of animal origin, as well as plant fiber. Fats and refined carbohydrates (sweets) should be limited.
Is boil contagious?
Boils are a common problem. That is why many people are concerned about the question: can you get infected with boils? It is impossible to become infected in cases where there are no certain prerequisites for this, from which every person is not insured. The factors that contribute to the appearance of furunculosis need to be understood in more detail.
Boils that affect one person do not pose a threat to people around him.
The causative agent of furunculosis
Furunculosis is an inflammatory process in the hair follicles, during which a rod with pus is formed. The causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. However, sometimes Staphylococcus epidermidis can also contribute to the appearance of the disease. Both types of bacteria are widely distributed in the external environment. Excessive amounts of them are found in dust on the street, in rooms with poor ventilation, in clothing and even in residential apartments. Staphylococci often exist on people’s skin and mucous membranes, without causing the development of diseases. According to research, about 70% of people are carriers of these microorganisms.
Return to contents
How is it transmitted person to person?
Is there a chance of catching furunculosis from an infected person? Transmission of the microorganism is not excluded, but the development of furunculosis requires a number of internal and external factors. The disease, like other infectious diseases, involves interaction between the pathogen and the macroorganism. For infection with furunculosis, it is not so much the microorganism itself that is important, but the factors that contribute to its progression. Based on this, we can conclude that furunculosis is transmitted from person to person only in the form of microorganisms, which in most cases are not infectious and do not provoke the development of boils.
Return to contents
External reasons
External factors that provoke the onset of furunculosis:
- minor injuries caused by particles of fine graphite or metal dust, for example, emitted in industrial conditions;
- the process of rubbing items of clothing on certain places of the human body, for example, on the buttocks, due to which staphylococci from a form that is not dangerous to humans turns into a dangerous one and is rubbed into the deep layers of the skin;
- scratching the skin when other skin diseases (scabies or eczema) are present.
Return to contents
Internal factors
Internal reasons due to which furunculosis manifests itself:
- decreased immunity;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diabetes;
- excess body weight;
- anemia;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- alcohol abuse;
- frequent overheating and then hypothermia.
Internal causes contribute to the deterioration of immunity, and external causes cause damage to the skin. It is into these lesions that staphylococcus penetrates. Finding itself in a favorable habitat, it begins vigorous life activity and reproduction, which ultimately becomes the cause of inflammatory processes. Furunculosis is not contagious. Infestation by neem is impossible even through sexual contact when another person has boils on the genitals (one of the most common places where boils appear), if the person does not have prerequisites for this in the form of the above factors.
Return to contents
Therapy for boils
When a person becomes infected with furunculosis, it is important not to engage in treatment and consult a dermatologist as soon as possible. To begin with, the patient will have to undergo a series of specific tests that show his general health. After the patient undergoes the required studies, the specialist prescribes complex therapy, which includes special nutrition, systematic antimicrobial treatment and immunotherapy. In some cases, the patient will need to see a surgeon who will open the boil through surgery.
Return to contents
Prevention of infection with furunculosis
To avoid becoming infected with staphylococcus, doctors recommend following personal hygiene rules and proper nutrition. A person should include as much protein food (mainly of animal origin) in their diet as possible. You need to enrich your menu with fiber by consuming enough fresh fruits and vegetables. You will need to limit your intake of fats and sweet foods. It is also recommended to exclude allergenic foods from the diet, for example, chocolate, eggs, citrus fruits and seafood. It is not recommended to consume salty and spicy foods. It would be useful to systematically take special vitamin and mineral complexes that will improve immunity and prevent the development of boils.
In addition, a healthy lifestyle and frequent walks in the fresh air will protect against infection. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that if a small boil appears, it should under no circumstances be squeezed out. In such a situation, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible. Only he will be able to diagnose and prescribe the required treatment. Another important rule is disinfection of the skin after cosmetic procedures, for example, hair removal. It is important to resort to them not only at home, but also in beauty salons.
stoprodinkam.ru
Stages of development
- At the initial stage, a small knot forms at the base of the hair follicle.
- After a few days, a cone-shaped boil with a necrotic formation in the central part grows at the site of the node.
- Along with the follicle, the sebaceous glands and adjacent layers of skin are affected. A mature formation causes severe tissue swelling and may be accompanied by pain.
- Then the purulent focus is opened, purulent masses come out of it in copious amounts, and an ulcer with a greenish tint forms in the cleaned wound.
- As a result, the rod comes out along with the remains of pus and blood, after which the painful sensations subside.
This process is quite lengthy and causes a lot of discomfort. In particularly severe forms of furunculosis, carbuncles are formed - accumulations of purulent foci. It is advisable to treat the disease with medications after consultation with a dermatologist, but you can also practice treatment with folk remedies.
Many people are carriers of this type of bacteria, because it can remain on the mucous tissues of the nasopharynx and also settle on the skin.
- Staphylococcus in its latent form is not dangerous to the body, but under favorable development conditions the bacterium takes on a threatening and infectious form.
- Furunculosis can be transmitted from a carrier to another person in the usual household way (within the family, among athletes, in the workplace).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Non-surgical blepharoplasty Plasma BT – Virsheba
Most often, primary infectious diseases are named among the main factors in the progression of staphylococcus, among which are:
- intestinal flora disorders;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the skin;
- dysfunction of the endocrine and genitourinary systems;
- various lesions of the nasopharynx.
Furunculosis differs from other skin diseases in that it can recur on the integument for a very long time, appearing on different parts of the body many times. Therefore, furunculosis is usually divided into main types:
- localized (abundant damaging elements are concentrated on one specific area of the body);
acute (the stage of progression of many boils in one period of time);
- chronic (a long process of development, during which some foci of inflammation subside, while others appear and progress);
- disseminated (inflammation populates the surface of the entire body).
Localized furunculosis can be eliminated with an active course of therapeutic antibacterial procedures. As for the chronic stage of the disease, it will take a lot of effort to bring furunculosis to a state of regression. During the period of temporary retreat of the infection, it is best to carry out additional diagnostic methods for internal processes and use immunomodulatory drugs.
Inflammation causes the development of bacterial flora, mainly represented by staphylococci and streptococci. In the chronic course of the disease, some microorganisms remain in the hair follicles and do not manifest themselves for a long time. But under certain conditions, activation of pathogenic (disease-causing) microorganisms occurs, an increase in their number and re-development of the inflammatory process with necrotic phenomena, the formation of pus (relapse or exacerbation of furunculosis).
Origin of the disease
The cause of furunculosis is Staphylococcus aureus, but in some cases the disease can be provoked by bacteria of another type of Staphylococcus - epidermal. Both bacteria are present in the environment. 70% of people on the planet are their carriers.
Microorganisms can pass from an infected person to other people, but in a completely healthy person the disease does not develop, since this requires additional factors favorable to bacteria. Simply put, for infection with furunculosis, the pathogenic microorganism is not as important as the factors that contribute to its reproduction. Such factors can be external and internal.
Most often, the main cause of the disease is weakened immunity in humans. External causes can be: trauma to the epidermis, dermatological pathologies, and internal factors (internal causes) are:
- decreased immunity;
- chronic diseases;
- vitamin deficiency;
- autoimmune disorders (diabetes);
- overweight;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- anemia;
- pathologies of the nervous system.
The main pathogenic factor in the formation of such a disease is bacterial infection of the skin with staphylococcal infection. Pathogenic pathogens under the influence of exogenous and endogenous factors contribute to the manifestation of furunculosis. The disease itself has a fairly long process of development, progression and extinction.
At the initial stage, a small node forms and matures in the cup of the hair follicle.
- After a few days, a sensitive cone-shaped boil with a necrotic formation in the center forms on the skin.
- Along with the follicle, the sebaceous gland and adjacent areas of the epidermis are damaged.
- A mature formation causes severe tissue swelling and an increase in throbbing pain.
When the focus of inflammation is opened, abundant discharge of purulent masses is observed. In the cleared cavity, an ulcer with a necrotic core of a greenish tint forms. The presence of such a basis indicates that the presumed diagnosis is confirmed by furunculosis, the inflammatory course of which decreases only in the case of rejection of necrotic tissue.
- if the components of furunculosis are single in nature, then the patient’s condition can be diagnosed within normal limits;
if the nasolabial triangle, nasal area and external tissues of the auditory organ are affected, symptoms of general intoxication, increased body temperature and severe headaches are observed;
- in case of injury to the affected components of furunculosis or independent non-sterile removal of the lesion, there may be a risk of thrombophlebitis of the facial veins and deep damage to internal tissues;
- When boils form on the face, inflammation may progress and transform into meningitis.
The most dangerous consequence of the disease can be considered sepsis, characterized by numerous abscesses in the internal organs and leading to death.
Danger of infection
Some types of staphylococcus are able to maintain their vital activity in the external environment for several weeks. The infection is transmitted from a sick person to the skin of a healthy person and causes not only the appearance of boils, but also provokes other diseases.
In addition, the danger of the disease lies in the fact that it becomes potential for others and can spread to the body of an already sick person. The pus that flows from the boil can end up on a healthy area of skin, and this is enough for further infection. The emergence of new boils complicates treatment and progresses to the stage of development of furunculosis.
In addition, if the infection enters the bloodstream, blood poisoning and the appearance of a carbuncle may develop.
Therapy for boils
The first thing you need to do is go to the hospital to see a dermatologist and find the exact cause of furunculosis. It is not recommended to treat boils on your own, since without eliminating the cause, the disease will not disappear and will soon relapse. It is also impossible to open boils at home, since pus and necrotic tissue will remain in the wound and cause complications.
The doctor will order tests to fully assess your health status. He will then select treatment, which usually consists of the following procedures:
- taking antibiotics;
- eliminating the cause of inflammation;
- diet;
- immunotherapy.
Antibiotics for furunculosis are used to destroy bacteria (staphylococcus); drugs with a wide spectrum of effectiveness are most often prescribed, namely Amoxicillin, Methicillin, Oxacillin.
If the boil cannot open on its own or there are multiple boils, then you should go to a surgeon who will properly open and thoroughly clean the abscess.
Therapeutic furunculosis, antibiotics and drugs
The entire treatment process for furunculosis is carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. Self-treatment of furunculosis at home using the antiseptic liniment "Vishnevsky" is often complicated by the spread of purulent processes, damage to deep layers of tissue and rapid damage to muscles and tendons.
The use of liniment is possible only at the stage of breakthrough of the capsule with pus, during the period of granulation of the cavity. Independent removal of the core of boils is unacceptable.
Early opening of the abscess and removal of pus threatens the contamination of adjacent healthy tissues with a pathogenic microorganism, and not completely removing the core can contribute to the development of chronic processes.
- During the treatment of furunculosis, it is necessary to limit the ingress of water onto the affected areas. In the stage of extensive damage, it is recommended to disinfect the skin with a slightly colored, fresh solution of manganese.
- To prevent the bacteria from contaminating healthy tissues, it is wiped with antiseptic solutions - furatsilin, salicylic alcohol. The slightest wounds should be treated with brilliant green or iodine.
- Bed and underwear should be changed regularly.
- The diet should be enriched with vitamin and protein products, this helps improve tissue regeneration.
- In case of abundant localization of furunculosis elements, in order to disinfect them, during the ripening period, the suppuration is wiped with antiseptics, or the inflammation zone is injected with an antibiotic with a novocaine solution.
- Treatment of furunculosis with antimicrobial drugs using electrophoresis is prescribed to prevent possible complications - abscess or phlegmon.
- During the period of noticeable fluctuation (appearance of pus), application dressings with sodium salicylate are used, which has a softening and dissolving effect that helps accelerate the resorption of the infiltrate and the rapid rejection of the necrotic core.
- Phlegmonous, abscissing course of purulent pathology requires surgical intervention to open the formation. Under local anesthesia, the cavity is cleaned of pus and necrotic tissue, followed by aniseptic treatment and application of antibiotic ointment - Erythromycin and Syntomycin or Levomikol. The wound treatment procedure is carried out every two days. At the stage of the granulation process of the wound, products with an ichthyol base are applied.
- Ultrahigh-frequency and ultraviolet therapy are used in doses at any stage of the disease.
- Antibiotics for furunculosis are prescribed for abscessed processes - “Erythromycin” or “Clarithromycin”. Their intravenous administration is indicated in the presence of underlying diseases, exhaustion of the body and to increase immune defense.
- Increases the body's resistance - ozone therapy, restorative drug therapy, ultraviolet irradiation of the blood and the introduction of a fraction of whey proteins (gamma globulin) into the body.
How to prevent infection
In 90% of cases, infection can be avoided, despite the high statistics and doubts of people. It is enough to follow certain recommendations of specialists.
- adhere to simple hygiene rules; avoid contamination of the skin;
- properly plan your diet;
- maintain a healthy and active lifestyle;
- walk more often in the fresh air;
- treat all diseases until the patient recovers completely;
- do not take medications for a long time;
- avoid nervous stress and tense situations;
- take good care of yourself and your health.
The last point is especially important to observe. As a rule, the patient does not take into account the advice of doctors, especially when the boil develops at the initial stage.
It is not recommended to take measures on your own if you are infected with furunculosis; you should go to the hospital for medical help. First of all, it is important to undergo effective treatment and not squeeze out the chiryak. Otherwise, blood poisoning may occur, resulting in furunculosis spreading throughout the body.
We are talking about shaving or hair removal; you should treat microtraumas yourself using special antiseptics.
Patients' nutrition should be dietary and balanced, containing a complex of essential substances, vitamins and microelements, amino acids. This is one of the components of a strong immune system, which helps prevent infection with staphylococcal infection.
Boils: is there a risk of infection?
Staphylococcal disease is a common problem. Many people are interested in whether it is possible to become infected with furunculosis or not. Especially on the street or in other public places. Boils are popularly called boils, but to understand whether there is a risk of infection, you need to find out about this disease p{amp}gt;
Most often, furunculosis affects people who have chronic pathologies or hormonal disorders due to diabetes mellitus or excessive functioning of the adrenal glands. In addition, boil infection occurs due to increased sweating. As a result of these disorders, the structure and protective properties of the skin change.
The main causative agents of such a pathology as boils are purulent bacteria - Staphylococcus aureus. When these cells enter the hair follicle, an inflammatory process begins to develop. Infection of others and the development of furunculosis does not occur on its own; a person is surrounded by numerous provocative factors.
These include:
- weak immunity;
- certain diseases;
- skin injuries (burns or open wounds);
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- metabolic disease.
It is difficult to protect yourself from staphylococcal infection; the risk of infection is high. But, if you follow the rules of contact with a sick person, a completely healthy person will not catch furunculosis, even after close contact. It should be remembered that boils can be infected by airborne droplets if hygiene rules are not followed.
Transmission routes
Staphylococcus bacteria are transmitted between people, but they cannot develop independently. This requires suitable conditions and factors.
Is the boil contagious or not: is it passed on in the family, is it inherited?
.
A boil or boil is a purulent inflammation that affects the sebaceous glands, fatty tissue or hair follicles.
Furuncle - purulent inflammation
Causes
The disease can be caused by simple trauma to the skin or scratching it. Boils are often the result of failure to comply with basic personal hygiene standards. The most likely cause of boils is weakened immunity, which occurs against the background of diseases such as:
- diabetes;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- alcoholism;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- anemia;
- frequent hypothermia and overheating;
- hypovitaminosis.
Usually the disease occurs in the spring, when the body lacks vitamins and microelements.
This disease is also dangerous because it can be contracted from another person. Knowing the main symptoms of illness will help you avoid this. A timely detected disease and timely prescribed treatment will guarantee the health of other family members and everyone around.
Nervous system disorders can lead to boils
Symptoms
Boils appear most often on the lower back, back of the head, buttocks and abdomen. Although there is no guarantee that the exception will be the face, neck, arms and legs. The only places where boils cannot form are the palms of the hands and soles. This fact is explained by the fact that there are no hair follicles there. The formation of a boil occurs as follows:
- A small lump appears near the hair follicle. It is painful, pain is felt, and the color is dark red with a bluish tint.
- The tumor becomes pronounced and its size increases.
- If the boil is on the face, then swelling of the cheeks, lips or eyelids is possible.
- After 4 days, the boil becomes cone-shaped, and the purulent core is clearly visible. Its top is a yellow dot called a pustule.
- There is an increase in temperature, general malaise and headache.
- The top of the boil opens, this can happen without treatment. Sometimes there is a discharge of pus with blood.
- The rod is rejected, the pain goes away, and the remaining crater heals over the course of several days.
The duration of treatment is up to 10 days.
Sometimes the disease proceeds almost unnoticed, which is especially dangerous. A person, unaware of his illness, can become a source of infection for others.
In this case, there is no suppuration, the core of the boil is almost invisible. This situation is typical for people with weakened immune systems.
High temperature often accompanies the maturation of a boil
Prevention
If it is not possible to avoid contact with an infected person, then certain precautions should be strictly observed:
- Mandatory hand washing after treating the boil and the skin around the sore spot. It is useful to use disinfectants for treatment.
- You can prevent the spread of germs by applying a gauze bandage to the sore spot.
- The patient must use separate hygiene products, bed linen and towels. After recovery, everything must be thoroughly disinfected.
- The room where the patient is located must be constantly cleaned using disinfectants.
- It is recommended to pay special attention to those places where friction is most frequent. These are the cervical and lumbar regions, as well as the buttocks. Dust getting on the skin in these places can cause infection.
You should know that other diseases have symptoms similar to boils. Therefore, self-medication is dangerous. It threatens complications and loss of time. H
It may take a long time for a person to get a true diagnosis. The disease is serious. Some boils are so dangerous that, due to untimely treatment, they cause infection to enter the brain. The resulting inflammation can be fatal.
Source: https://kozhmed.ru/furunkul/zarazen-ili-net-dlya-okruzhayushchih-kak-peredaetsya.html
Diagnostic methods
A furuncle (boil) is a neoplasm that occurs as a result of suppuration of the sebaceous glands, fatty tissue or hair follicle. Such growths appear against the background of skin infection by pathogenic microorganisms. Because of this, boils can be dangerous to others.
- Pathogen
- How is furunculosis transmitted?
- Is it contagious?
Pathogen
Boils occur due to infection of the subcutaneous tissue or hair follicles by Staphylococcus aureus. Less commonly, inflammatory processes in the skin are triggered by the epidermal type of this bacterium. Both microorganisms are constantly present on the human body and in the environment.
Infection of the skin glands or tissue occurs when there are open wounds on the surface of the body.
In addition, a weakened immune system caused by:
- diabetes mellitus;
- endocrine pathologies;
- anemia;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- pathology of the central nervous system;
- poor diet and alcohol abuse, smoking.
We suggest you read: How many days can urticaria last in adults?
The impact of these factors inhibits general immunity. Due to the weakening of protective mechanisms, the colony of Staphylococcus aureus begins to actively expand.
The impact of pathogenic microorganisms on skin tissue provokes the development of inflammatory and purulent processes.
In fact, furunculosis is not transmitted. Boils occur due to infection of the body with Staphylococcus aureus. The most common method of infection with this bacterium is transmission of the pathogenic microorganism through mother's milk to the child.
In this case, infection occurs if the child’s body is weakened. Strong immunity suppresses the activity of staphylococcus.
The risk of infection remains through sexual intercourse. Staphylococcus often affects skin areas located in the groin area. However, you need to understand that this type of infection does not apply to sexually transmitted pathologies.
Staphylococcus aureus spreads through the air, and therefore people often become infected while in public places:
- baths;
- swimming pools;
- saunas and more.
In addition, the cause of boils in rare cases is non-compliance with the rules for placing a catheter, dressing open wounds or using medical instruments.
Is it contagious?
Staphylococcus aureus is a contagious infection that is transmitted by air, through household objects or food. Some bacteria of this type remain viable outside the body for several weeks.
Infection with staphylococcal infection is possible if a person has a weakened immune system. The likelihood of boils appearing on the body in people with a strong body is extremely low.
To avoid infection with Staphylococcus aureus, it is recommended:
- regularly wash your hands and observe other hygiene rules;
- Healthy food;
- lead an active lifestyle, giving up smoking and alcoholic beverages;
- timely cure diseases of internal organs;
- do not exceed the dosage of medications;
- avoid severe stress.
If the immune system is weakened by external factors, it is recommended to temporarily limit contact with the environment.
Boils are inflammatory growths on the skin resulting from tissue infection by Staphylococcus aureus. Furunculosis is not a contagious disease. An infection that causes suppuration of skin tissue poses a danger to others.
In order to diagnose furunculosis, it is necessary to carefully study its symptoms. Often, inflammation of this type can be externally similar to diseases that have a different bacterial nature:
- if the resulting inflammation has a spherical surface without a purulent head and is localized in the groin area, in the armpit or in the chest area, these are most likely signs of hidradenitis suppurativa;
in cases of inflamed areas appearing on the gums or tongue, it would be best to consult a dentist;
- an abscess localized on the mucous membrane of the throat can be a harbinger of purulent tonsillitis, pharyngeal candidiasis, diphtheria and other ENT diseases.
In cases of self-examination, the patient should see a purulent-necrotic core in the center of the resulting inflammation, which is the main sign of furunculosis. If inflammation appears on the neck, skin under the hair, temples, the area behind the auricle, in the external auditory canal, on the forehead, in the eyelid area, on the temples, cheeks, wings of the nose, lips, and is accompanied by severe pain, you should immediately seek advice to the surgeon. An experienced specialist should use the following diagnostic methods:
- Initial examination and identification of the depth of the inflammation.
- Palpation of regional lymph nodes.
- Laboratory tests of blood, urine, feces (clinical, general, biochemical).
- Culture of inflammatory secretions for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Ultrasound examination of the genital organs, abdominal cavity and thyroid gland.
- X-ray of the sinuses and chest organs.
In addition to the above procedures, research methods such as gastroscopy and electrocardiogram are possible, as well as consultations with a dermatologist, urologist, endocrinologist and otolaryngologist.
Otherwise, there is a huge risk of infection of healthy skin areas. In addition, the bacterial pathogen remains inside the ulcer and poses a risk of the disease degenerating into a chronic form and causing complications.
How is furunculosis transmitted?
In fact, furunculosis is not transmitted. Boils occur due to infection of the body with Staphylococcus aureus. The most common method of infection with this bacterium is transmission of the pathogenic microorganism through mother's milk to the child.
In this case, infection occurs if the child’s body is weakened. Strong immunity suppresses the activity of staphylococcus.
The risk of infection remains through sexual intercourse. Staphylococcus often affects skin areas located in the groin area. However, you need to understand that this type of infection does not apply to sexually transmitted pathologies.
Therefore, skin infection occurs in the presence of predisposing factors: open wounds and weakened immunity.
On this topic
All about the difference between a carbuncle and a boil
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 17, 2020
Staphylococcus aureus spreads through the air, and therefore people often become infected while in public places:
In addition, the cause of boils in rare cases is non-compliance with the rules for placing a catheter, dressing open wounds or using medical instruments.
Should you take boils on your head seriously?
The formation of abscesses is an extremely unpleasant phenomenon, causing a lot of discomfort and pain. They can appear anywhere on the body. No less common is a boil on the tailbone. This is where the accumulation of...
A boil can appear on various parts of the body where hair is present. The infection can penetrate the hair follicle, causing inflammation and other discomfort inside it. Contents PathogenHow is furunculosis transmittedIs it contagious...
In what cases can furunculosis be contagious?
The reason for the development of furunculosis is infection or unhindered reproduction of opportunistic flora. After all, it is a typical inhabitant of the skin.
It is impossible to become infected with furunculosis from another person. But with close contact, transmission of staphylococcus is possible. With normal immune defense, the alien will be neutralized.
Cases when a patient with boils will infect others:
- He is infected with anthrax. But the disease occurs with clear symptoms, it is extremely contagious, the patient and his entourage will be immediately hospitalized in the infectious diseases department of the hospital.
- With reduced immunity in surrounding people. A patient with boils poses a danger to cancer patients, organ transplant recipients, and those taking immunosuppressive drugs. Patients at risk include patients after any surgical intervention, treatment with aggressive drugs, or relapse of a chronic disease.
- Special categories. Staphylococcus and a patient with boils are contagious for pregnant women, newborns, small children, and elderly people with various chronic diseases and dementia. Representatives of these groups have reduced immunity for physiological reasons. Although a woman’s fetus is protected by the placental barrier, during the passage of the birth canal there is a high probability of infection of the child.
- Professional risk. Medical workers treating purulent wounds, surgeons, employees of purulent-septic, infectious diseases departments, ENT doctors, dentists, dermatologists are at high risk of infection.
Content
Prevention
Preventive measures:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- adhere to proper nutrition;
- cure chronic diseases;
- make sure that clothes and shoes do not rub the skin;
- increase immunity;
- do physical education;
- in case of endocrine disorders, do tests and monitor biochemical blood parameters;
- Avoid hypothermia, overheating and skin injury.
An important role in the prevention of furunculosis is played by timely identification of symptoms and periodic blood tests by persons who are at risk for this disease.
Prevention of boils is aimed at eliminating the causes of the rash. Therefore, following these simple rules makes it possible to cure the disease and prevent the occurrence of furunculosis.
Post Views: 879