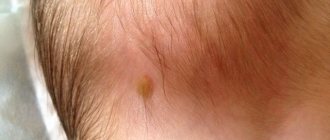
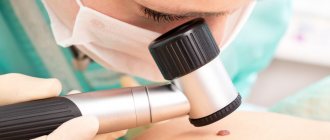
Statistics show that 80% of people with benign tumors on the dermis may have a complaint from time to time - itchy papillomas. Such skin formations should in themselves become a cause for alarm, because they demonstrate that the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is responsible for the development of cancer, has entered the body. If papillomas, which have never bothered you before, suddenly begin to itch and change in appearance, then this should prompt a person to take a closer look at the problem that has arisen.
Causes of itching papillomas
Among the reasons that cause itching, there are both completely harmless ones, which do not entail any health risks, and unsafe ones, signaling that you need to act urgently. Let's look at the most common factors that explain why papilloma may itch:
- Lack of hygiene. In this case, profuse sweat acts as an irritant.
- Injury due to uncomfortable clothing. At the same time, convex formations on the skin can not only itch, but also burn and tingle.
- Stress. It has been noticed that high psycho-emotional stress in a negative way often affects the general condition and can also provoke skin itching.
- Getting rid of warts on your own. Often they try to remove them with the help of various substances with an acidic or alkaline base, glue them, tie them with thread, etc.
- Excessive sun exposure. If you spend a long time under the scorching sun or in a solarium, you may complain that the papilloma is itchy and the skin is red.
Among the causes of endogenous origin, in which it is extremely unsafe to leave the process to chance and not seek help from doctors, there are:
- Infection. Penetration of bacteria can occur as a result of scratching, microcracks, injuries that violate the integrity of the skin.
- Activation of papillomavirus. At the cellular level, there is a rapid growth of viruses, the release of toxins into the blood, and degenerative processes in the layers of the skin.
- Malignization. Even the most common trauma can provoke malignant degeneration.
How to get rid of itching yourself
Recommendation - before starting any manipulations, coordinate your actions with your doctor.
- Those with sensitive, irritation-prone skin should choose clothes made from natural fabrics that are well ventilated and loose. Synthetic materials do not allow air to pass through well, resulting in sweat accumulation, increased friction of clothing on the skin, resulting in irritation and itching.
- Lotions and compresses made from infusions of medicinal herbs have a soothing and antipruritic effect. As a rule, take 1 tbsp. l. plants, pour 250 ml of boiling water and leave until cool. Chamomile, calendula, mint, and string are well suited for such purposes.
- Alcohol infusion of calendula relieves itching and has a bactericidal effect. You can make it yourself - pour 10 grams of raw materials into a bottle with 70% alcohol. Let it steep for 14 days, then strain. Use several times a day (wipe affected areas).
- Propolis ointment or tincture will also help relieve itching and irritation. Apply a cloth soaked in the product to the affected area, after 10 minutes the unpleasant symptoms will disappear.
- Treat irritated skin with a decoction of bay leaves. Pour 250 ml of boiling water over 3 large bay leaves, simmer over low heat until the amount of water is reduced to a widow. After removing the broth, add boiled water to it (exactly as much as has boiled away) and use three times a day (more often).
Signs of tumor degeneration
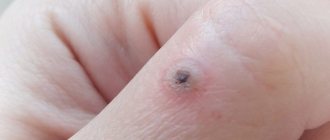
The combination of two signs, when the papilloma grows and itches, gives reason to be examined by a doctor. He will suspect an oncological process if, in addition to these 2 symptoms, there is also a change in the color of the skin formation. The usual beige color changes to black, at the same time redness appears around the papilloma, swelling and bleeding occur. The affected tissues hurt and there is a burning sensation. The growth may separate from the surface of the skin on its own, but this will not change the situation, because its internal part will continue to disturb, being located deep in the tissues.
What happens to the wound after papilloma removal
When removing small papillomas, there are usually no special changes and the wound heals quite quickly. After removal, medium and large papillomas form a wound that can heal for a month and a half. In the first 24 hours it will be inflamed, and swelling around it often occurs.
After a couple of days, the damaged area changes, inflammation decreases, and a crust appears at the site of the papilloma. It plays a very important role, because due to this barrier, bacteria cannot enter the wound, and new epithelial tissue forms under the crust. In order for healing to occur faster and with minimal consequences in the form of a scar, you need to follow the recommendations of your doctor, and also treat the wound with special means.
What not to do
In conditions when 70% of the population are called carriers of HPV, it is really difficult not to become infected with it. When a virus is detected, it is best to determine its type so as not to worry about whether papilloma can become a real threat to life. There is a high probability that a non-oncogenic type will be discovered and then all worries can be forgotten. In all other cases, if the papilloma itches, try not to make the following mistakes:
- Do not disturb the tumor with clothing, jewelry or your own hands, trying to relieve itching. If its integument is damaged, there is a high probability that bleeding will begin, and the infection will not be long in coming and will penetrate into the layers of the skin.
- Don't be in the sun without UV filters. Apply creams to those areas of the skin where there are papillomas even if you go for a tanning session in a solarium.
- Do not avoid medical examinations. Particular vigilance should be exercised by those who have been diagnosed with genital warts.
- Do not use products that can remove tumors at home if the growths are localized in intimate places. If the papilloma begins to itch after using this drug, then consult a doctor immediately - this is an unsafe symptom.
Why does a wart itch?
The question of why a wart hurts can only be answered most competently by a doctor, whom you should contact in this case. A wart is a rather unpleasant disease caused by the papilloma virus in the human body. But it’s even more difficult when a growth that appears on the body begins to cause a lot of unpleasant sensations in the form of severe itching or pain.
Why do people's warts itch?
When this formation appears on the human body at first, it does not cause pain. If initial signs of pathological changes occur, for example, the growth begins to itch or hurt, this is a signal to visit a dermatologist as soon as possible. Typically, a wart at rest does not cause such symptoms, and this may indicate possible complications.
What to do if the wart itches? Patients often complain to the doctor that a formation located on the body has begun to cause discomfort. There are several reasons why warts itch.
First of all, if a wart itches, this is a signal that a neoplasm is growing on the human body. The second reason leading to severe itching is the development of a benign form of growth into a malignant one.
If the first signs appear (itching, burning, pain), you should immediately seek help from a specialist. It is important to remember that it is not recommended to remove or cauterize a large tumor yourself, since such a rash act can lead to serious health problems.
Why do warts hurt?
Why does a wart hurt? Mostly these growths appear on the arms or legs. These are the places that are most susceptible to injury. For this reason, warts often hurt.
If a growth appears on the hands, then a person may accidentally damage it during the work process. And you can understand what’s wrong only by examining the injured area. It is worth adding separately that upon contact with harmful substances that may be present in a person’s workplace, the growth can cause complications for the body.
If such an injury occurs, the formation should be immediately treated with hydrogen peroxide and consult a doctor. You should not try to get rid of a damaged wart on your own. It is important to remember that a wart is a benign neoplasm that can develop into a malignant tumor at any time, and the main factor can be a common injury to this area of the body. If a growth injury occurs, this is a much more serious problem. There is no point in postponing its treatment, and the defect cannot be eliminated at home. The most ideal option is to quickly remove the growth immediately after it is discovered on the human body.
If a wart appears on your toe or its location is the foot, you need to understand that this can lead to injury with all the ensuing consequences.
The second option is to enlarge the affected area of the body. It is no secret that the growth may begin to increase, as a result of which a person will soon be unable to stand on his leg. The growth may become inflamed, causing severe pain and making it impossible to wear shoes.
It is worth adding separately that when growths appear in places such as limbs, they should be disposed of immediately, since wearing ordinary clothes very often causes injury to the tumor. As a result, it begins to bleed and may become inflamed, which will lead to serious consequences.
What to do if the wart becomes inflamed?
The first sign that a wart is inflamed is the appearance of dark spots on its body. In addition, it may darken and swell. In this case, a visit to a dermatologist cannot be postponed. The doctor will do a visual examination and take part of the tumor for examination, since this is most often the first sign of the development of melanoma or a cancerous tumor.
If inflammation occurs, it is not recommended to solve this problem yourself at home. It is worth understanding that in the near future there is a chance of new skin lesions developing around the damaged area. Then they will begin to grow and enlarge the painful area. When active dispersal of growths occurs, it will be possible to get rid of this problem only through surgery.
What happens after a wart is removed? Sometimes the damaged area begins to hurt. As a rule, after the operation, doctors make prescriptions and recommend how to care for the injured area.
For example, if the formation was destroyed by cauterization with liquid nitrogen, then after this procedure the ichor may appear for several days. The same can happen if the patient touches the site where the growth is removed. In addition, in addition to the occurrence of ichor, severe pain will be felt. And to avoid such troubles, you need to treat the wound with a strong solution of potassium permanganate several times a day. In a week the person will forget about this problem.
It is also important that after removal of the tumor, a person needs to undergo a course of treatment with antiviral drugs, because the disease itself does not go away, the pathogen remains in the body and can cause a relapse.
When a wart appears on the body, it does not cause discomfort and does not bother the person in any way. Do warts itch during normal development? No. If this happens, there are likely two reasons for the condition, and each requires the patient to seek help from a specialist.
You always need to remember 3 rules:
- First, at home you can get rid of this defect only if it has just appeared on the body and has not had time to grow.
- Secondly, if a wart on your finger hurts, this is the first sign of damage. In this case, it is prohibited to treat this place yourself.
- Third, if a wart on your leg itches or becomes inflamed, do not put off going to the doctor. This is the first sign that the growth may degenerate into a malignant tumor. As for treatment at home, this is now a big taboo.
Today, modern medicine offers people a wide range of services. And when it comes to such a problem as a formation on the body, the best thing to do is get rid of it with the help of professionals.
Warts or papillomas are a fairly common disease at the moment. Papillomas on the body occur due to infection of the skin with the human papillomavirus (HPV). According to the World Health Organization, every third person on Earth is a carrier of this infection. There are about 80 known variations of HPV, 20 of which are oncogenic, that is, they have a high risk of degeneration into a tumor. As a rule, by the age of 25, 80% of humanity comes into contact with 2–3 types of human papillomavirus.
Papillomas are benign neoplasms that arise as a result of HPV damage to the surface epithelium or mucous membrane of the skin. As a rule, this pathology can exist on the body for a very long time, however, if the papilloma itches, then this is a clear sign of the progression of the disease.
In this article we will look at the etiology of growths, pathogenesis and basic treatment methods.
The main symptoms of papillomas on the body
Papillomas are not uncommon and can occur even at a very young age. Typically, benign neoplasms do not bother patients for a long period of time. The incubation period of the pathology is at least 2-3 and no more than 9 months. Most often, people immediately remove the cosmetic defect, while some accept the growth and move on with their lives. But regardless of the presence or absence of papilloma, the following symptoms may appear and must be responded to immediately, since they indicate the risk or immediate possibility of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. Here is a basic list of symptoms important for diagnosis:
- The appearance on any part of the body, including the intimate part, of various reddened, keratinized tubercles, inflamed papillary or genital warts.
- Some warts can form colonies - this is papillomatosis. This feature is determined by the type of human papillomavirus. The clinical symptom will be the active growth of papillomas and the formation of groups.
- Itching of the papilloma itself or in its area. The reason why papilloma itches is constant contact with clothing, jewelry or malignancy. This symptom is considered the most important from the point of view of diagnosing pathology!
- The high temperature of the wart itself or its “burning” will indicate its malignancy.
- Burning and increased pain upon contact with papilloma.
- Changes in the surface of the papilloma. For example, changing a smooth plane to a keratinized one or vice versa.
- Swelling at the location of the growth.
- Bleeding from a wart. On the first day of appearance, consult a doctor!
If at least one sign from this list appears, consult a doctor immediately. Timely treatment will increase the chance of recovery several times. Often, in the presence of a provocateur of the pathology, symptoms of burning and itching may appear. First of all, you need to identify the reasons why papillomas itch. And then determine the chance of developing skin cancer - melanoma.
Why do papillomas itch?
In order to answer the question of why papillomas itch, you first need to understand the reason for the human papillomavirus entering the body and the pathogenesis of the disease itself. The main cause of infection is the presence of wounds, scratches, or cuts on the skin of the hands or the body itself. Upon contact with an HPV carrier (a handshake is enough), the infection will penetrate into areas where there is impaired tissue integrity (wounds) and settle in the superficial areas of the dermis of the skin. HPV can also be transmitted sexually and from mother to child. There, in the reticular layer of the dermis, the human papillomavirus can exist for a very long time and not make itself felt. And when conditions are “favorable” for infection, they appear as benign neoplasms on the epithelium or mucosa.
We recommend reading:
- Wart after cauterization with nitrogen
- Polyps and papillomas are the same thing
- Dermavit from papillomas
Do papillomas just itch? No, basically itching on or near the papilloma occurs either due to co-infection with another virus, or due to the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the body. Microorganisms easily penetrate the body through the skin, since the human papillomavirus disrupts the barrier and protective function of the epithelium. You need to understand that the symptoms that arise: itching, burning and pain are three factors that indicate the progression of the disease. Therefore, it is very important to promptly determine the cause of HPV activation.
If the wart is subject to constant friction, pressure from clothing (underwear for women) or does not receive the necessary hygiene standards, then spontaneous degeneration of the papilloma is possible. And itching in this case will only accompany the process, and not be the main symptom.
What can be the consequences of itching papilloma?
Remember! It is absolutely forbidden to scratch such areas! Since at this moment the virus begins to actively divide and in case of mechanical damage with fingers or devices, there is a high risk of degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one.
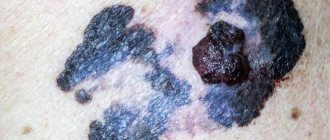
Skin cancer that arises from a wart is called melanoma. This pathology spreads very quickly throughout the body, since the skin covers the entire exogenous surface of the skin. And often it metastasizes within 3 months. Skin cancer causes sores all over the flesh. Melanoma is a quick and painful death.
What to do if the papilloma itches, hurts and increases in size?
If you begin to notice three main enemies: active wart growth, constant itching and pain over a short period of time, it means that the human papillomavirus has become more active and affects neighboring epidermal cells. What to do when the papilloma hurts or may itch? It is necessary to urgently visit a dermatologist and oncologist. Self-medication in this case may be “suicide”. If it is not possible to see a doctor in the near future, you can only temporarily reduce the discomfort. Here are some tips:
- Wear loose, non-restrictive clothing made from natural fabrics. Avoid synthetics and woolen items - they will only irritate the tumor.
- Do not touch the papilloma again - you will injure it.
- Do not scratch the wart, but use a decoction of chamomile, celandine and string to relieve itching. Apply lotions carefully to previously cleansed skin (daily morning and evening). This decoction will help relieve inflammation and disinfect the skin.
- Lubricate the wart with iodine and then castor oil to reduce pain and itching.
- Take antihistamines to help reduce the size of the wart.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
When is a visit to the doctor necessary?
Not all viral skin neoplasms are capable of malignancy. However, you should never lose vigilance, even if the growths have been formed for a long time and the only thing that worries you is why papillomas sometimes itch. Inspect these areas of skin every time you use the toilet and notice any changes. Do not neglect consulting an oncologist if:
- inflammation appeared, micro-wounds opened, the surface began to peel off;
- color has changed;
- the edges of the skin formation have become uneven;
- there are compacted areas;
- intensive growth has been recorded.
Author of the article: Shibanov Timur Aleksandrovich
Practitioner Specialization: Infectious diseases
Publications on the site: 31 (All publications by the author)
How to care for a wound
Large wounds take a long time to heal, and some patients simply cannot stand it until this process is completed naturally. Less care is taken when treating the wound, which leads to additional damage. After removing a papilloma, you should not do the following:
- remove the crust that has formed (after each removal, healing begins all over again, and this also leads to an increase in connective tissue, that is, the appearance of a large scar);
- apply cosmetics, this includes foundations, moisturizers, various scrubs and other skin care products;
- expose to ultraviolet radiation;
- cover the damaged area with a plaster;
- provide additional moisture, hold the wound over steam, wet it with water, etc.
If you are cleaning the house, make sure that various chemicals do not get into the area where the papilloma is removed.
Complications
The process of removing unwanted growth itself does not pose a danger to human health. However, such consequences may arise that the patient will regret the choice made. Negative consequences arise if the patient does not properly treat the wound or does not protect it from negative effects.
Wound after papilloma removal
People who are not used to waiting will probably try to tear off the scab ahead of time; various infections can get into the open wound, which will lead to infection. Also, stripping off the roughness will lead to a longer recovery process. Lack of treatment with antiseptics and improper care lead to the fact that the wound takes much longer to heal, and it takes longer for the crust to separate.
What should not be used to treat a wound?
To avoid problems with wound healing, you need to care for it in accordance with the doctor’s instructions, and not invent your own miracle methods. Quite often, women go to the hospital to remove growths on their faces. After removing the papilloma, under no circumstances should you smear it with creams, apply foundation or other cosmetics. The wound may fester, and the consequences will be unpredictable.
Other patients try to speed up the healing process using traditional methods, but this is not always beneficial. By using decoctions to moisten the affected area, the patient violates one of the rules of care, which is not to wet the wound. Antiseptic traditional medicines can also be highly concentrated, which will lead to new damage to healthy skin. Treatment with such means should be avoided even when the rough skin has come off and a pink spot has appeared. It will be possible to use those products that allow you to speed up regeneration.
Etiology and types of papillomas
A neoplasm papilloma is a nipple-like growth on the skin, often of benign origin. These warts appear due to the human papillomavirus (HPV). It accelerates cell division and active growth.
Types of virus
In medicine, there are about 130 types of virus, of which only 80 have been studied. Different strains of the pathogen provoke different diseases. For example, more than 25 types of viruses can cause infections of the female genital organs.
There are also papillomas that are dangerous to health. They can cause cervical cancer and other cancer pathologies. Such aggressive pathogens include HPV strains 16, 18, 31, 35, 45, 51 and 52.
Types of papillomas
In medicine, there are several types of neoplasms:
- ordinary (simple);
- plantar;
- threadlike;
- flat;
- pointed.
Simple papillomas are hemispheres with a keratinized surface. Most often they are localized on the hands. The growths do not manifest themselves in any way, but itching may occur when touched.
Plantar papillomas appear on the soles of the feet. They are often confused with calluses and corns. But such a wart does not have a characteristic calloused pattern, is flat and surrounded by a dark rim.
Filiform - in the form of thin short threads, appear in adulthood after 35 years. They occur on the neck, eyelids, groin or armpits. The reason for their appearance is skin trauma (cut, scratch).
Flat – papillomas of thin irregular shape. They may become red and itchy.
Pointed - they are called condylomas, these are sexual manifestations of the virus. They appear in the groin area, anus and inside the genitals. The growths cause discomfort when walking and during sexual intercourse.
Is it dangerous
The danger of itching is considered depending on what caused it. Elimination of external influence factors brings the condition of papilloma to normal, the discomfort disappears. This may indicate serious problems in the body or provoke their occurrence.
Due to itching, the formation is damaged. A person can scratch off a papilloma intentionally to stop the discomfort or do it accidentally, in a dream. You need to understand that the existing problem will be joined by related ones.
In addition to itching, the following signs are observed in the intimate area:
- redness around the growth;
- occurrence of cracks;
- bleeding formation;
- pain;
- change in shape;
- the growth begins to increase, grow intensively;
- color change, up to black;
- peeling of tissues.
Signs of HPV infection
The papillomavirus does not cause any acute symptoms; it often goes away without symptoms. A persistent infection remains, develops in the body, and over time can develop into cancer. This can be prevented by consulting a doctor in time.
When infected with a virus, only external signs appear - neoplasms, which can be seen with your own eyes or during a routine examination by a specialist. Itching or redness of the papilloma also often occurs.
How the disease is transmitted
The disease is transmitted only by contact from person to person:
- through microcracks in the mucous membrane during sexual intercourse or during a kiss;
- when shaking hands;
- from mother to child during pregnancy.
It is possible to reduce the risk of intrauterine infection or transmission of the virus during childbirth. To do this, before pregnancy, it is better for girls to undergo a test for the presence of a viral infection.
Locations of growths
Warts form all over the body. They usually affect:
- hands;
- legs;
- neck;
- back;
- tongue and other mucous membranes;
- genitals.
New growths can appear from the first month of infection. The location of the growths depends on the characteristics of the human immune system and associated pathologies. In medicine, multiple occurrences of viral rashes are called papillomatosis.
What do papillomas look like?
Papillomas are papillary neoplasms on a thin stalk that appear on the skin and mucous membranes. This is an unpleasant looking growth. They spoil the appearance if they appear on the face, neck or hands. Warts can vary in color (light or black), shape (elongated or flat) and size (from 1 mm to 2 cm).
Symptoms of tumor degeneration
Viruses that infect the mucous membranes are dangerous to humans. When they multiply, warts form. During development, neoplasms can change their appearance. They grow, the surface changes from rough to smooth and vice versa, it bleeds and becomes inflamed. When warts begin to itch, patients often do not pay attention to the itching, but it can be a sign of the growths becoming malignant.
There are additional signs that make it possible to recognize degeneration:
- color change to black;
- the tumor hurts when touched;
- drying of the papilloma, after which it may fall off;
- the papilloma turned red;
- inflammation of the skin at the site of the formation;
- the appearance of ulcers with bleeding.
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. Only he will be able to make the correct diagnosis, determine the degeneration of the wart and prescribe effective treatment. Doing anything on your own without a doctor's permission is dangerous!
Treatment
One of the main questions patients have is how to treat the wound after papilloma removal? In fact, all products that have an antiseptic effect are suitable for this procedure. But not all of them can be used; some are too aggressive for the skin, which leads to unnecessary peeling. Treatment is a mandatory item when treating a wound after papilloma removal. Each case of removal of a growth should be considered individually, and a specific antiseptic is prescribed by the attending physician.
Before the top crust falls off on its own, the skin around it must be treated with special products. This is done in order to prevent infection from entering the damaged area of the skin. Typically, the following antiseptics are used for such procedures: brilliant green, iodine, ethyl alcohol. In some cases, it is permissible to treat the skin around the wound with a solution of potassium permanganate. But, you need to remember that a strong concentration of potassium permanganate solution can lead to burns. Use a weak solution of potassium permanganate for treatment.
In some cases, it is possible to treat the skin around the wound with a solution of potassium permanganate
Should I delete
Do you need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
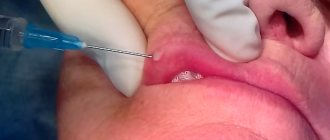
Removal of papilloma is the main component of complex treatment of viral infection, which includes taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs. The growths contain the highest concentration of pathogen cells. If you leave a papilloma on the body, the risk of spreading foci of infection increases; the person will always be potentially infectious. Permanent damage to growths due to their inconvenient location is a direct indication for disposal.
In modern medicine, papillomas are removed using hardware techniques. They allow you to achieve effective results in a short period of time, without special training or long rehabilitation.
Laser excision allows you to get rid of growths on the body. The formations are burned out under the influence of the high temperature of the laser beam. This type of treatment is quite painful and requires the use of local anesthesia. The risk of reappearance of papillomas is practically absent.
Cryodestruction or removal with liquid nitrogen. The scope of application of this technique is quite wide. Under the influence of low nitrogen temperatures, neoplasm tissues are destroyed and die. This treatment method is not recommended if the growths are located on the face, as there is a risk of residual scarring.
Diathermoelectrocoagulation allows you to get rid of warts without bleeding and the spread of viral cells. An electric current burns out the papilloma and coagulates small vessels.
Radio wave excision is considered gentle. The method is distinguished by its accuracy, bloodlessness, and painlessness. Scars and cicatrices do not remain after this procedure.
If further histological examination is necessary, the formations are removed in the usual surgical way.