Reasons for the formation of papillomas
Papilloma is a soft, benign neoplasm consisting of small epithelial papillae and a large root extending deep into the skin. The appearance of such growths is caused by the action of the human papillomavirus - HPV.
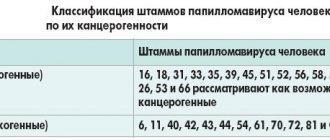
Anyone can become infected with the virus. According to statistics, more than half of people are sick/infected with HPV. There are more than a hundred different types of this virus, some of which have a potential risk of developing cervical cancer.
Malignant degeneration of papilloma cells that arise on the skin is a fairly rare occurrence. Condylomas that form on the mucous membranes of the genital organs are dangerous.
The peculiarity of HPV is the ease of infection. The virus is transmitted through sexual contact. In everyday life, you can become infected with papillomavirus due to a decrease in immunity, or when using other people's personal hygiene items.
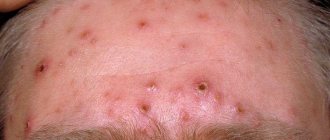
After entering the blood, the virus may not manifest itself for a long time. Then, after a few months, it is activated. The provoking factor is decreased immunity or severe stress. The presence of the virus in the active phase is indicated by the sudden growth of papillomas. They can appear on any part of the body.
In most cases, warts (popularly called papillomas) affect the feet and hands. This is due to a decrease in local immunity due to profuse sweating of the feet and contact of hands with household chemicals.
Papillomas: what is it?
Papilloma is a formation on the skin or mucous membrane. This growth has a soft structure and is located on a base of varying thickness. In rare cases, the size of the formation exceeds 10 mm. Usually papillomas are several millimeters in diameter. If the growth reaches 2 cm, it must be removed followed by an examination.
The hue of the papilloma is similar to the color of the surrounding tissues. If the formation has a rigid structure and becomes white, a yellow tint may appear. If the papilloma is located on the mucous membrane, it usually has a pink tint. After some time, the formation becomes covered with a gray coating, which occurs as a result of the proliferation of connective tissue. Papillomas are benign formations, but some of them are characterized by an increased risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
What is papilloma
On a note! If you find papillomas on your body, you need to consult a doctor to diagnose the disease and eliminate the papillomas.
Features of papillomas
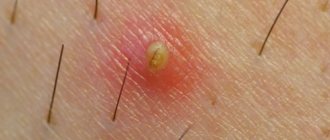
The visible part of the papilloma is just its body, a harmless accumulation of cells rising above the surface of the skin. The main part of the wart is hidden under the skin. This so-called root is fed by blood vessels, allowing warts to grow.
The rapid growth of new formations on the skin is due to decreased immunity. This is observed after recent colds and infectious diseases, against the background of severe stress, overwork, and lack of vitamins. Quite often, the causes of the sudden growth of papillomas on the body are potent drugs taken by the patient to treat infectious diseases.
Papillomas often appear during acute respiratory infections
The appearance of papillomas on the neck is observed in the hot season. This is due to profuse sweating in this area. The reason papillomas appear on the neck in men is damage to the skin during shaving. The increase in the number of neoplasms on the skin is affected not only by general immunity, but also by disruption of the local protective functions of the skin during injuries, burns or infections.
Typically, the appearance of papillomas on the neck occurs in young patients. Such neoplasms have characteristic features - the presence of a thin stalk on which rises a yellowish body of the growth.
Symptoms in women and men
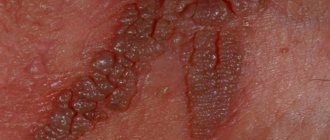
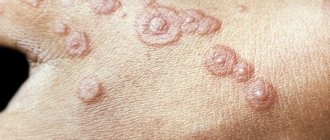
The main symptom of papillomatosis is the appearance of growths in the groin, which look like loose lobules collected in piles, reminiscent of a broccoli inflorescence or a rooster's comb.
Locations:
- in men - on the scrotum, around the head of the penis, near the urination channel, in the folds between the legs;
- in women - on the vulva (on the labia majora and minora, in the vagina, on the pubic part), in the cervix;
- independence from gender - on the skin in the perineum between the genitals and anus, around the anus and inside the anus (rarely).
The glans penis affected by papillomas
Types of papillomas in the intimate area
Inguinal growths have their own differences and types:
- Filiform papillomas. At the beginning of development, small yellowish bumps appear, which over time develop into elastic thread-like formations.
- Flat papillomas. Rounded small bumps that blend in color with the skin. They are rare, but can cause inflammation in the genitals, itching, burning, and pain.
- Condylomas (pointed). Elastic growths look like a large number of small lobules fused together.
- Papillomas of the bladder and urethra. It mainly affects men.
On the female organs, or rather inside them, genital warts most often develop. You can see them during a gynecological examination.
What types of papillomas there are in intimate places and what they look like is shown in the photo.
Flat type of papilloma
Acute condylomas
Growth of papillomas
Under the influence of a number of factors, existing papillomas can increase in size. This is observed with HPV activity. The condition itself is not dangerous if it is not preceded by damage to the body of the growth.
As a rule, by stopping the activity of the virus with the help of special drugs, it is possible to avoid an increase in the size of the papilloma and stop the appearance of new growths. However, the main feature of the papillomavirus is the inability to completely get rid of it, so with repeated episodes of immunodeficiency, new growths may appear on the skin.
Treatment during pregnancy
Papillomas in the intimate area can grow greatly during pregnancy and subsequently interfere with childbirth. To avoid this, doctors prescribe laser excision of growths and treatment with antiviral substances. During pregnancy, Viferon and Betadine are allowed to be used.
Papillomavirus detected during pregnancy must be treated without fail, as it threatens to infect the fetus (most often during the child’s passage through the birth canal) and cause the baby’s nasopharynx and larynx to be affected by condylomas.
Papillomas on the genitals are an unpleasant and very dangerous phenomenon, since if left untreated for a long time, there is a high probability of developing cancer. Therefore, it is important not to hesitate to consult a doctor if suspicious growths are found in the groin.
Risk factors
Why papillomas can increase in size depends on their location. Growths located on exposed areas of the body may become larger when exposed to ultraviolet rays. This also increases the risk of developing a malignant tumor at the site of the papilloma.
Papillomas located in the folds of the skin (groin, armpits) can increase in size due to friction with clothing. This phenomenon is caused by stimulation of blood circulation due to irritation of the body of the growth. The more blood flows to the papilloma, the faster its size increases.
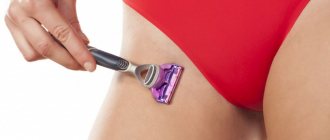
Another reason for the growth of growths is improper removal. This is observed when trying to get rid of a benign tumor on your own. In attempts to remove the growth, dubious means are used - salicylic alcohol, fresh celandine juice, garlic and onions. All this provokes blood flow to the papilloma, as it has a vasodilating effect. The result is an increase in the size of the growth.
Traditional methods of removing papillomas sometimes give the opposite result
When using alkaline or acidic agents to burn out papillomas, it is important to correctly calculate the required amount of the drug. It often happens that the papilloma disappears, but after some time it appears again, but larger than before. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the alkali burned only the body, but did not affect the root of the growth. The blood vessels feeding the papilloma continue to function, which means that over time it grows again in the same place.
What do papillomas on the body mean?
Growths on the human body can be single, grow to large sizes, or multiple small ones that are practically invisible on the surface of the skin.
Frequent places for their localization are the neck, armpits, chest, and arms. Papilloma is not particularly dangerous unless it begins to quickly change in size, shape and color.
This is usually preceded by injury to the growth with clothing, a washcloth, etc.
Injury can cause inflammation, which can lead to complications.
In another situation, a person may note that existing growths have expanded the area of their location.
The reasons that the area of neoplasms on the body has increased may be:
- infectious diseases (sore throat, flu, tonsillitis, pneumonia, intestinal infections and those that are sexually transmitted);
- chronic diseases that are transmitted genetically (eczema, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, etc.);
- HIV infection (acquired and congenital);
- inflammatory processes of organs in the pelvis (prostatitis, cystitis, etc.);
- hormonal imbalance;
- metabolic disorders, development of hypothyroidism and diabetes;
- immunodeficiency.
It is difficult to single out one single reason why papilloma grows, since the disease occurs in a latent form for a long time.
Consequently, its provocateur has long been forgotten, because from the moment of infection with HPV until the growth of growths appears, six months or several years can pass.
Therefore, the right decision would be not to look for the reasons, but to determine a way to get rid of the aesthetic problem and complications associated with papillomas.
What to do if papillomas grow?
A sudden increase in the number of growths on the skin indicates a violation of the body's immune defenses.
The first thing that needs to be done is to correct the immune system by taking immunostimulants and restoratives. For this purpose, preparations with interferon or herbal remedies, for example, echinacea extract, are recommended. Additionally, it is recommended to take sedative medications to normalize the functioning of the nervous system, since stress aggravates immunodeficiency. The doctor may also recommend taking a course of vitamins and restorative medications.
Then you should move directly to the fight against the virus. For this purpose, antiviral drugs containing acyclovir and interferon are used. Specific drugs whose activity would be aimed directly at HPV have not yet been developed.
An ointment containing an immunomodulator and an antiviral agent should be applied to each growth. Additionally, the patient is shown tablets with acyclovir. This treatment regimen allows you to quickly suppress the activity of the virus.
Removal of papillomas
When stopping the growth of new papillomas, existing ones should be removed. To do this, methods are used to get rid of not only the visible part of the growth, but also its root.
The most effective removal method is laser vaporization. Laser burning of papilloma is carried out layer by layer, which allows you to remove the root and minimize the risk of bleeding due to the effect on the blood vessels. After such a procedure, scars or scars rarely remain, and since the root is removed, re-growth of papilloma in the same place is excluded.
Laser removal of papillomas is the best option
Electrocoagulation of warts is no less effective. During this procedure, the vessels that feed the growth are cauterized. This ensures that the virus does not spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. After the papilloma stops feeding, the process of necrosis of its tissue begins. A few days after exposure to electric current, the wart turns black and falls off.
It is not advisable to use liquid nitrogen to remove growing papillomas. The repeated appearance of a wart in the same place indicates the deep location of its roots. Finding the optimal duration of nitrogen exposure is quite problematic, so the method does not guarantee the absence of relapse after some time.
At home, you can use special alkaline solutions (Super Celandine). Such drugs are sold in pharmacies, but are not medicine. They contain several types of alkalis or acids, which simply burn out the build-up. To avoid the reappearance of papilloma, you should strictly adhere to the recommendations given in the instructions for the drug. It is recommended to apply just one drop of the product exactly to the center of the growth. Repeated treatment is carried out after three days. The manipulation continues until the papilloma disappears.
Another fairly gentle means for removing papillomas on your own is a lapis pencil. Its advantage is that in addition to cauterizing papillomas, the pencil has an antiseptic effect, protecting against infection and preventing the virus from spreading through the bloodstream. The pencil should be used every other day until the growth falls off on its own.
Additionally, you can use various drugs with antiviral components to prevent the spread of the virus.
Treatment methods
Papillomavirus cannot be removed from the body, but it is quite possible to put it into a dormant state.
The following methods allow you to do this:
- removal of papilloma;
- drug treatment;
- use of folk remedies.
Therapy for papillomatosis should be comprehensive and combine several methods at once.
Removal of papilloma on the genitals
Timely detected papillomas respond well to treatment and do not have time to harm a person. You cannot try to eliminate such a problem on your own, otherwise you can provoke serious complications.