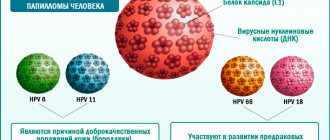
Main culprit
HPV is a dangerous infection that is transmitted from person to person
The causative agent is a virus that affects the upper layer of the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. Transmission of these viruses is possible only from person to person; infection occurs through contact with the skin or mucous membranes of a sick person. After infection, the virus remains in the skin and mucous membranes; it does not enter the blood or other organs. Human papillomavirus infection is not a disease transmitted only through sexual contact. Infection may not necessarily occur through sexual intercourse; the use of a condom, virginity, or a regular sexual partner do not guarantee the absence of HPV in the body.
Human papillomavirus infection is characterized by a hidden (latent) course, the incubation period (from infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease) is long from 3 months to several years. There are no clinical manifestations; the existence of the virus in the body can only be determined through tests. For many infected people, the virus becomes undetectable within two years, even without treatment. In others, HPV can live in the body for a long time, even from birth, and appear for the first time in the middle of life due to a decrease in immunity. In this case, the virus is activated, its increased reproduction and the disease enters the stage of clinical manifestations.
How does papillomavirus infection manifest?
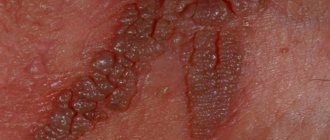
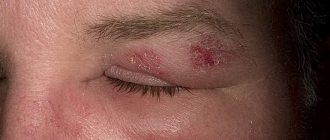
Condylomas acuminata
The most common manifestations of human papillomavirus infection are: genital warts. The development of genital warts and papillomas is often caused by HPV of low oncogenic risk. Condylomas can be single or focal, usually occurring in places that are injured during sexual intercourse. The size of the elements ranges from 1 millimeter to several centimeters, their shape resembles a “cockscomb” or “cauliflower” and is located on a narrow base (leg). Most often, women detect condylomas by touch while washing, which feels like unevenness.
With a large number or size of condylomas, they can become injured and bleed, interfere with normal sexual life and childbirth, and cause psychological discomfort.
Itching rarely accompanies manifestations of human papillomavirus infection.
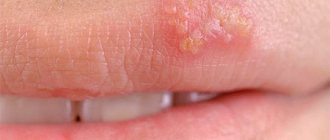
Papillomas (warts)
Papillomas (warts). Unlike papillomas of a tumor nature, viral papillomas appear, disappear and appear again, because their severity depends on the state of the body’s defenses at the moment. Viral papillomas do not differ in color from normal skin and can grow anywhere.
Flat condyloma of the cervix
Flat condyloma is a manifestation of a chronic, long-standing viral infection that causes changes in the epithelial cells of the cervix
Flat condyloma of the cervix . Flat condyloma is a manifestation of a chronic, long-standing viral infection that causes changes in the epithelial cells of the cervix. May be combined with genital warts on the external genitalia. Changes in the cervix characteristic of HPV always alert the doctor, because women who have had this virus for a long time have a 65 times greater risk of developing cervical cancer than those who do not have it. However, the presence of a high-risk virus in the body does not mean that a woman will necessarily develop cancer. Additional factors must be present for cells to become malignant. The fact that high-risk types of the virus are detected provides the patient with a significant head start in time in the fight against the disease; Here the formula “forewarned is forearmed” could not be more appropriate. Thus, the average age of women with the first signs of malignant degeneration in the cervix is 30 years, and the average age of patients with cervical cancer is 50 years.
Treatment methods
Treatment of the virus depends entirely on the clinical picture. However, it is important to understand that it is impossible to completely get rid of HPV.
Moreover, strain 56 extensively affects the brain, nervous system, and in some cases also affects the circulatory system. Therefore, it is impossible to eliminate the virus without harm to health.
The following methods are used in the treatment of HPV:
Treatment of detected HPV in the body of any person depends on how this virus manifests itself and which group of oncogenic activity it belongs to.
If there are genital warts on the genitals and papillomas on the body, one of the methods for their removal is selected. Cutting off the growths is carried out in the usual surgical way, using a laser, electric current, or under the influence of cold.
If a high concentration of oncogenic viruses is detected in tissues, antiviral treatment is prescribed. Immunomodulatory therapy is required, since only strengthening the defenses will avoid re-exacerbation and prevent the transformation of normal cells into atypical ones.
If precancerous diseases are detected, a course of therapy is selected that corresponds to the manifestations and changes. Cervical cancer, combined with viruses type 16 and 18, is treated with surgery and chemotherapy. Antiviral treatment is optional.
At the moment, there is no specific drug for the treatment of HPV; as a rule, papillomavirus is treated comprehensively, first of all, great attention is paid to strains with a highly carcinogenic type, since they can provoke a precancerous condition.
If this type of strain is present, a full examination is carried out, then an oncology specialist makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. If there are a large number of papillomas or condylomas, surgical removal of tumors or laser therapy aimed at eliminating manifestations of HPV may be prescribed.
The approach to treating this disease is determined purely individually.
Medicine knows cases of self-healing from human papillomavirus type 51. As a rule, this occurs when the carrier of the infection is young and is an indicator of the strong immune defense of his body.
If HPV is detected again 6-12 months after infection, a course of antiviral, immunostimulating and cytotoxic drugs is prescribed.
The approach to treating this disease is determined purely individually. It involves not only eliminating external manifestations, but also “switching on” the body’s defense functions.
Firstly, to treat HPV type 51, papillomas are removed. Removal is carried out in several ways:
- Physical: laser removal, cryodestruction. This includes cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
- Chemical: various chemicals are used, for example, salicylic acid, trichloroacetic acid, Solcoderm, Cantharidin.
- Surgical: surgery is performed with cutting out with a scalpel. In this case, scars form at the site of the removed papillomas. Basically, the patient himself chooses the removal method. But histology analyzes are taken into account. In the case where malignant cells are detected, exposure to radio irradiation is applied.
Treatment of human papillomavirus type 51 is carried out using cytostatic drugs:
- Podophyllin is a solution of plant origin to get rid of anogenital formations;
- Yuleomycin is an antiviral, antibacterial and antitumor drug.
Immunostimulating therapy is needed to help strengthen the body to fight infection. In such cases, immunomodulators, multivitamins and antiviral drugs are used.
Despite all the measures, experts assume a relapse of the disease or re-infection.
There are three main methods of treating HPV 58 in men: surgical, medicinal and folk. Surgery is considered the most effective treatment method. There are several operations, namely:
- Laser surgery (the most expensive and effective) involves the use of a laser that is aimed directly at the papilloma. Thus, it evaporates, leaving a small white trace in its place.
- Coagulation is used much more often and costs much less. It involves cutting off tumors using electric current.
- Radio wave surgery is almost never used today and is considered an outdated method of surgical intervention.
- The use of liquid nitrogen involves repeated freezing of tumors until there is complete necrosis of the affected tissue. Then the papillomas fall off on their own.
- Traditional removal of papillomas with a scalpel is performed when other methods cannot be used due to the individual characteristics of the body. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The only drawback of this method is the scars that remain at the site of the formations.
The stages of treatment will depend on the clinical picture of HPV development, but it is impossible to completely eliminate the virus from the brain and circulatory system without harming human health.
Such patients need to be registered with their doctor, undergo timely preventive examinations, and if the papillomavirus is reactivated, adhere to antiviral and restorative therapy.
Human papillomavirus in women
In women, human papillomavirus infection can cause genital warts (genital warts) and is also a cause of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN, cervical dysplasia or precancer), cervical erosion and cervical cancer. The insidiousness of human papillomavirus infection in women lies in the fact that, as a rule, it is asymptomatic and is detected only during a gynecological examination. There are the following main manifestations of HPV in women:
Genital warts appear on average 3 months after infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The favorite places for genital warts to appear in women are: labia minora, vagina, cervix, cervical canal, skin around the anus, oral cavity.
Genital warts look like small formations located on a wide base and having “ragged” uneven edges. A special type of human papillomavirus infection is the so-called endophytic condylomas, which grow deep into the skin and are not visible during a simple examination. The location of genital warts on the cervix or in the cervical canal indicates an unfavorable course of the disease, since in this case the risk of developing cervical cancer significantly increases.
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a precancerous condition of the lining of the cervix that is characterized by impaired cell maturation . There are 3 stages of this condition: CIN 1 and CIN 2 stages are more benign, and CIN stage 3 represents the initial stage of cervical cancer. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia is caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) types 16 and 18.
Cervical cancer is a malignant neoplasm that develops from the epithelium (surface layer) of the cervix and is caused by human papillomaviruses (HPV) types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39.
HPV type 56 in women: causes and treatment methods – Derma
-HPV
60-70% of the population of our planet are carriers of the human papillomavirus. Scientists count more than 170 types of this disease. HPV type 56 in women is a disease that increases the likelihood of cancer cells growing. If you follow doctors' recommendations, the prognosis is positive.
Features of the manifestation of HPV type 56 in women
A woman can be a carrier of papillomavirus type 56 for a long time and not realize it. The following factors can activate the disease:
- pregnancy, childbirth;
- the onset of menopause.
Human papillomavirus type 56 in women is located on the genitals. Due to its external localization, it is easier to identify the infection: during a medical examination, the surface of the cervix is examined in the speculum.
Places of manifestation of HPV strain 56:
- genitals, area near them;
- anus;
- external opening of the urethra.
A pathogenic microorganism affects the body. A change occurs in the surface cells of the mucous membrane. The virus jumps to neighboring areas, infecting them. HPV type 56 actively multiplies in women and accompanies oncogenic changes in DNA.
The first symptom indicating the presence of the disease is condyloma (pointed growth) on the female genitalia.
Causes and symptoms
| Causes | Symptoms |
|
|
During intimacy, the growths are injured, wounds appear, into which a secondary infection penetrates, aggravating the disease.
Infection with HPV type 56 in women occurs through sexual contact, regardless of the type. A condom does not protect against infection; transmission can occur through use.
Only a doctor can accurately determine the disease; self-medication increases the risk of further harm to the body.
Methods for diagnosing strain 56 in women
Need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
A gynecologist can suspect the presence of HPV in women during a routine medical examination. To study the presence of strain 56 in the body, biological material is needed. There may be a smear of the mucous membrane of the cervix, vagina, urethra, rectum.
If the result is positive, papilloma is present in the female body, you need to undergo a medical examination by an oncologist, infectious disease specialist, or dermatovenerologist.
Types of diagnostics:
- Gynecological examination. The presence of papillomas is clearly visible in the vagina.
- Colposcopy is a method that allows you to detect erosion and identify areas of dysplasia. For cytological analysis you will need biological material from the cervix.
- Digent test - a type of smear shows what type of HPV a woman has.
- A PCR test that extracts viral DNA from human cells. The analysis is carried out only in the laboratory.
- Biopsy. It is done by an oncologist if there is a suspicion of cancer.
Before diagnosing HPV type 56, you need to be tested for sexually transmitted diseases. STDs (gonorrhea, trichomoniasis) aggravate the disease.
If the result is positive, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Treatment of papillomavirus 56 in women
Treatment of HPV in women type 56:
- medicinally;
- surgically;
- combined treatment.
During drug therapy, immunomodulatory drugs containing interferon are taken. The products enhance the protective functions of the female body.
| Drug name | For what |
| Interferon | Antiviral + immunostimulating agent. Efficiency: the earlier use is started, the greater the benefits. |
| Isoprinosine | It has immunostimulating activity and has a nonspecific antiviral effect. You need to be careful with use, there are contraindications. |
| Neovir | An antiviral drug for HPV 56, which has an effect on the DNA of the virus. There are contraindications and side effects. |
| Podophyllin | Means for topical use. Has an antitumor effect. |
Surgical treatment allows you to remove all types of growths from HPV type 56.
Types of surgery
| View | Characteristic |
| Radio wave surgery | Use of high frequency electrosurgical equipment. There are no scars left after the operation; it is a painless method. |
| Electrical destruction | Diathermoelectrocoagulation removes any growths. Excision with an electric knife. Afterwards a thin crust forms and the wound heals. |
| Laser surgery | Removal of growth under the influence of laser beams. |
| Cryosurgery | During cryoagulation, a low-temperature effect occurs on HPV type 56. Liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide can be used. It is used for cervical erosions. |
| Chemodestruction | Molinoinvasive method of treating papillomavirus. Removal of growths by rapidly freezing changes in cell tissue under the influence of liquid nitrogen. Then slow thawing occurs. |
| Surgical excision | It was used at the beginning of the twentieth century if there was a high probability of HPV type 56 degenerating into cancer. |
| Traditional methods of treatment | You shouldn't prescribe it yourself. You should listen to the opinion of a specialist. |
Precautions to take if you have a virus in your body
In order to protect yourself from strain 56, get vaccinated. Cervarix will not help protect against uterine dysplasia.
General strengthening vitamins should be taken every off-season. This will help strengthen and keep the immune system against HPV 56 in order.
In any public place (swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna), take precautions and use only your own hygiene products.
What is the dangerous type and prognosis of the disease?
The appearance of itching, redness around the genital area, or rashes is a reason to immediately contact a clinic or a specialist. This is a trigger for further development of the infection.
HPV strain 56 increases the risk of cervical cancer. Timely started therapy has a positive result. Prevention should be observed and women's health will be normal.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors Link to the main publication
Didn't find suitable advice?
doctor or see all questions...
articles:
(1
Source:
HPV type 56 - DNA and genotype in women and men, how to treat
Human papillomavirus is an extremely invasive, chronic infectious disease, infection of which leads to structural changes in the epithelial layers.
To date, more than a hundred types of the virus are known, forty of which are classified as a high oncogenic risk group.
The presence of the above strains in the body leads to the appearance of external manifestations of the human papillomavirus, which include skin growths, warts, as well as the degeneration of neoplasms into cancerous tumors.
HPV type 56 provokes the appearance of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, and significantly increases the risk of developing uterine cancer in women.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: Anastasia, an ordinary girl, not even a blogger, shared her secret against moles, papillomas and warts read here...
What are the features of this type of viral agent, and what is their danger?
Let's talk about this in more detail.
What it is
HPV type 56 in women is a disease of viral etiology, characterized by a high level of oncogenic risks and rapid progression.
Pathological skin neoplasms caused by the activity of viral agents quickly increase in size, occupying local areas of the skin and mucous tissues, and can degenerate into malignant tumors.
The peculiarity of oncogenic viruses is that they exclude the possibility of complete recovery. It should be noted that cases of self-healing have been noted in the field of practical medicine, but such phenomena are extremely rare.
In the vast majority of clinical cases, HPV type 56 remains in the body throughout life.
Accordingly, the main goal of therapeutic procedures is to suppress the activity of the infection and introduce it into a state of suspended animation.
Human papillomavirus in women
Causes
The incubation period for HPV type 56 in women can range from several days to several years. Against the background of a high level of resistance of the body, pathogenic flora is in the blood in an anabiotic state, showing no signs of presence. Factors that lead to weakening of the body can trigger the activity of oncogenic HPV:
- Hormonal imbalances, for example, caused by taking medications.
- Various diseases occurring in acute and chronic forms.
- The period of gestation, breastfeeding, menopause.
- Gynecological diseases.
- Long-term use of strong medications, such as antibiotics.
- Poor nutrition, consumption of low quality food.
- Having bad habits.
- Exposure to stressful situations, nervous experiences, depressive states, and other psycho-emotional disorders.
Even minor factors can provoke a surge in virus activity, for example, colds, general hypothermia, following a strict diet, or lack of certain microelements.
What is the danger and routes of transmission
It is generally accepted that HPV type 56, as well as other forms of infection, are transmitted to a healthy person exclusively during intimate intimacy. In fact, the parenteral route of invasion, that is, infection through contact with the biological fluids of an infected person, is prevalent, but not the only one.
HOW TO CURE PAPILLOMAS, WARTS, BAD MOLES?
Here's what a simple girl who solved this problem says: Even pretty moles are dangerous: yes, my dears, it's a virus. More than 80% of the population is infected with it, not to mention warts and papillomas, the first thing you need to do is this... Read more...
Human papillomavirus type 56 can be transmitted vertically, as well as through contact or household means, for example, when visiting public swimming pools, saunas, baths, or using other people's personal hygiene items. Viral agents are extremely small in size and have a high level of resistance to negative environmental factors. Due to the combination of these aspects, everyone is at risk of invasion.
The peculiarity of HPV type 56 lies in its oncogenic danger and specific external manifestations.
Increased activity of infection leads to the formation of numerous genital warts on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, which have a tendency to transform into malignant tumors.
Infection of a woman with this type of HPV threatens the development of Bowen's disease, and subsequently uterine cancer.
Symptoms of infection
Activity in the body of an HPV type 56 infected person is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic external manifestations and symptomatic signs, the main ones of which are:
- The prevailing symptom of the disease is numerous pathological papillomas that appear on the skin and mucous tissues of the genital organs. They are not painful, but mechanical impact on them, for example, with constant friction against clothing, leads to their damage, bleeding, and secondary infections.
- Itching in the intimate area, burning, and discomfort are also possible. There is the appearance of uncharacteristic vaginal discharge, which may contain minor impurities of purulent exudate or blood, and have an unpleasant odor. There is also discomfort during sexual intercourse and when visiting the toilet.
The prognosis is especially unfavorable when the viral flora is activated during pregnancy. HPV type 56 can cause infection of the baby during natural delivery, as well as lead to premature spontaneous birth or miscarriage.
Diagnostic methods
In order to identify papillomavirus type 56, complex diagnostic procedures are required. At the initial stage, a physical examination of the patient is carried out, aimed at identifying papillomas.
Course of pregnancy
There is evidence that primary HPV infection during pregnancy can lead to the threat of miscarriage, but whether such infection causes malformations in the fetus is a controversial issue
During pregnancy, visible condylomas often recur, tend to increase significantly, become loose, and large formations can cause difficulties during childbirth. There is evidence that primary HPV infection during pregnancy can lead to the threat of miscarriage, but whether such infection causes developmental defects in the fetus is a controversial issue. The frequency of transmission of HPV from mother to fetus, according to different researchers, varies quite significantly - from 4 to 80%. How the virus is transmitted is still not known exactly. Most likely, through the cervical canal and fetal membranes in an ascending way or by contact when the baby passes through the mother’s birth canal. Recently, HPV infection during childbirth has been associated with the development of papillomatosis of the larynx, trachea and bronchi and anogenital warts in infants. This disease is quite rare, and cases of this disease have been described in children born by cesarean section, so the presence of HPV and its manifestations in a pregnant woman is not an indication for cesarean section.
The only indication for surgery is the presence of a giant condyloma, which complicates vaginal delivery. But such condylomas occur only in women with severe immunodeficiency, for example, with AIDS.
After childbirth, HPV detected during pregnancy is most often not detected, and clinical manifestations in the form of massive growths significantly decrease or disappear. I would like to note that HPV, first detected during pregnancy, as a rule, is not detected after childbirth.
Detailed description of HPV 66
So far, more than 100 types of the virus have been identified, of which about 30-40 are classified by various sources. They are related to the anogenital area. Representatives were divided into groups according to the level of participation in the morphogenesis of oncology and benign proliferative changes. Number 66 (HPV type) is a pathology with a high oncogenic potential, which leads to the likelihood of developing cancer of the female and male genitalia.
If HPV type 66 DNA is detected in women, only a doctor will tell you what it is and how to fight it during a consultation. You should not re-read the literature and make lotions with folk remedies, as this will not bring the desired result.
Stress causes the spread of HPV
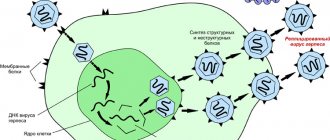
After entering the body, the virus is not immediately activated, sitting on the epithelial layer of cells for this purpose. In the presence of favorable factors (most often reduced immunity, stress or exacerbation of a chronic disease), HPV begins to penetrate the structure of cells, changing DNA and actively multiplying them. This leads to the formation of papilloma.
Clinical manifestations
Some types of HPV viruses cause the familiar “warts” (benign growths of integumentary tissue), while others cause genital warts. The latter also belong to benign tissue growths, but in some cases they can become malignant, in other words, lead to cancer.
The incubation period for genital HPV infection ranges from 3 to 8 months. In most cases, HPV infection is short-lived and resolves on its own within 12-24 months (if re-infection does not occur), which is determined by the activity of antiviral immunity.
As a rule, a woman can become infected with the papilloma virus in her youth at the beginning of sexual activity, but the virus does not immediately and relatively rarely manifest its pathogenicity, remaining for many years in a hidden (latent) state. Activation of the virus and the occurrence of a malignant neoplasm of the cervix can occur many years later - at 50-70 years of age under the influence of a wide variety of provoking factors.
Diagnostics
Cytological examination reveals not the virus itself, but changes characteristic of this infection in the epithelial cells of the cervix
HPV infection is very insidious, and the changes associated with it that precede cancer not only do not cause any concern or discomfort, but are often not detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. The human papillomavirus test (HPV test) is a reliable assistant to the doctor: identifying the virus draws the doctor’s special attention to the problem of the possible development of cancer and forces additional examinations. It should be added that at the moment, many European countries use cervical screening, which includes regular examination of women for the virus (HPV test) and/or Pap test (determines changes in cells associated with the virus). Every woman undergoes such an examination every 3-5 years. Experience in a number of countries has shown that this practice can reduce the likelihood of developing cervical cancer by more than 1,000 times.
The main method for diagnosing PVI is a routine clinical examination.
To confirm this diagnosis, colposcopy (examination of the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina using a special magnifying device) and cytological examination (for this, scrapings are taken from the cervical canal and from the surface of the cervix) are used. A cytological examination does not reveal the virus itself, but changes characteristic of this infection in the epithelial cells of the cervix. Histological examination helps to clarify the cytological diagnosis: in this case, not a scraping of surface cells is taken, as for cytology, but a piece of tissue, and not only the structure of the cells is studied, but also the correct arrangement of their layers. During pregnancy, a biopsy is not usually performed.
To determine the types of virus and their oncogenic risk, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used, which detects DNA fragments of the pathogen. It allows you to accurately determine the presence of the HPV virus in the cervix. This is important for predicting the development of cervical diseases.
HPV tests
Diagnosis of HPV begins with collecting anamnesis from the patient
Research methods used by a gynecologist to identify urogenital infections, including HPV :
- taking an anamnesis - the woman has chronic inflammation of the genital organs, infertility, miscarriage, pathological course of a previous pregnancy, inflammation of the genitourinary tract in a sexual partner
- examination of a woman’s external genitalia to determine signs of inflammation (swelling, hyperemia) of the urethral and vulvar mucosa, pathological discharge, condylomas
- examination in mirrors to determine signs of inflammation in the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, pathological discharge
- bimanual gynecological examination - presence of signs of inflammation of the uterus and appendages
Already during the examination, the gynecologist reveals the presence of a symptom of HPV - condylomas on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. However, for complete treatment of HPV, other tests will be required:
- colposcopy
- cytological examination of discharge
- histological examination of biopsy material
- detection of papilloma virus by PCR (DNA analysis)
- immunity examination
Indications for prescribing tests for HPV are:
- presence of signs of acute inflammation or chronic urogenital infections, papillomas, condylomas
- infertility
- spontaneous abortions, pregnancy pathology
- a woman has a sexual partner with urogenital infections
Tests for suspected urogenital infection, including HPV:
- general blood analysis
- general urine analysis
- bacterioscopic analysis of secretions (smear)
- PCR diagnostics
- culture with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics (to identify concomitant HPV microflora)
Diagnosis of HPV is based on the detection of HPV in smears from the affected area of the genital mucosa (PCR analysis) and antibodies to the virus in the blood of patients.
The most informative are analyzes of vaginal discharge - PCR diagnostics of HPV. Identification of the opportunistic flora accompanying the papilloma virus is helped by culturing vaginal discharge for dysbacteriosis while simultaneously determining the sensitivity of the flora to antibiotics. For a general assessment of the disease, it is also recommended to conduct tests for chlamydia, mycoplasma, HIV, hepatitis and other sexually transmitted infections, which are often detected during human papillomavirus infection.
PCR is a time-tested method for molecular diagnostics of STIs, including HPV
PCR is a time-tested method of molecular diagnosis of STIs, including HPV. The PCR method allows you to determine the presence of the HPV pathogen, even if only a few viral DNA molecules are present in the sample. The accuracy of PCR analysis when performed correctly reaches 100%. The PCR method for diagnosing STDs allows you to detect even single cells of bacteria or viruses. PCR diagnostics detects the presence of the HPV pathogen in cases where this cannot be done using other tests. PCR analysis is especially effective for diagnosing latent forms of microorganisms, including the papilloma virus, which are often encountered in asymptomatic and chronic STDs.
Using PCR analysis, the HPV pathogen is determined, and not the body’s reaction to its introduction. Thus, human papillomavirus infection can be diagnosed during the incubation period and during its latent course, when there are no clinical or laboratory symptoms of HPV.
But even PCR diagnosis of HPV is not an ideal analysis. This is a very high-tech research method that requires compliance with the strictest laboratory equipment rules. A sample of the material for any analysis must be taken by a qualified physician, strictly following the instructions given by the laboratory. The results of the PCR analysis should be assessed by the doctor who is treating a particular patient.
A positive PCR test result does not always mean the presence of the disease. False positive test results are possible if:
- the material sample was contaminated
- after a course of treatment, the dead and no longer dangerous infectious agent is eliminated from the body by the immune system
False-negative test results are possible even in the presence of obvious symptoms of a urogenital infection. Possible reasons for this analysis result:
- the material for analysis was taken or examined unsuccessfully
- the woman has recently taken medications or used suppositories, douches
- it was not taken into account that before collecting material from the urethra you should not urinate for 1 hour
- absence of a microorganism's genome in a sample of material (in secretions) when the inflammatory process is localized in the deep parts of the reproductive system (ovaries, fallopian tubes, prostate gland)
PCR analysis is a powerful and effective diagnostic tool that allows you to quickly and accurately find the causative agents of many STDs. Most often it is used to diagnose sexually transmitted infections. In any case, you cannot limit yourself to just one analysis. It is best to combine various tests and take them several times if the results are questionable. In addition to determining the HPV pathogen itself using PCR diagnostics, it is also necessary to evaluate the body’s immune response, which is determined by serological methods, for example, ELISA.
A screening test used to diagnose precancerous conditions and cervical cancer
A screening test is used to diagnose precancerous conditions and cervical cancer.
There are more than 100 genotypes of human papillomavirus. Infection with this virus is quite common. The infection is usually transmitted sexually; in rare cases, vertical transmission of the virus from mother to child during childbirth is possible.
Infection with the papilloma virus may not have clinical manifestations; natural cleansing of the virus from the body is often observed, especially at a young age. But the persistence of the virus in the epithelium of the cervix for a long time can cause its pathological changes.
Cervical cancer is one of the few types of malignant neoplasms for which the underlying cause of the disease has been established. Numerous studies have shown that human papillomavirus DNA is found in almost all cases of precancerous conditions and cervical cancer. Infection with the papilloma virus precedes subsequent squamous (scaly) intraepithelial dysplasia of the cervix. The third stage of cervical intraepithelial neoplasm occurs only in the presence of persistent infection with high oncogenic risk papillomavirus genotypes.
It has been proven that long-term persistence (5–10 years) of papillomavirus genotypes of high oncogenic risk in women over 30 years of age is associated with a significant increase in the risk of developing malignant changes in the cervix.
Infection with papillomavirus genotypes of low oncogenic risk can clinically manifest itself in the form of genital warts.
Causes and treatment of HPV type 56
HPV 56 is one of the most dangerous types of human papillomavirus, which causes the development of cancer. Cervical cancer is caused by human papillomavirus types 51, 56, 58, etc. There is only one way of transmitting the virus - sexually.
There are no other transmission options. The prevalence of oncogenic viruses is so high that a woman can become infected within 3-4 months after having an intimate relationship with a man.
According to statistics, more than 30% of women experience an infection after less than six months of sexual activity.
This infection is called transient, that is, when it enters the body, the protective function of the latter is triggered, and for a while the viruses do not manifest themselves in any way for a long period.
But under the influence of unfavorable factors that contribute to a decrease in immunity, the papillomavirus is activated and provokes the growth of cancer cells.
In order to detect the infection in time and begin its therapy, it is necessary to undergo an annual examination by a gynecologist and take tests to prevent the development of oncology.
Causes of the virus
The reasons why the virus manifests itself in the body are related to its transmission from another infected partner. In the case of HPV type 56, household transmission or infection in a public place is excluded.
If it is detected in the body, then the cause must be sought in the sexual partner. An interesting feature is that in men, any types of HPV, including oncogenic ones, may not be detected.
This happens because it is not always possible to take the necessary analysis for research.
You can become infected with viruses through any form of sexual contact - anal, vaginal, oral. Once in the body, the virus can remain in it for as long as the body’s immune functions are strong. But there comes a time when the defense system weakens, and the virus begins to actively manifest itself, damaging the tissue of the genital organs.
Human papillomavirus 56 can manifest itself against the background of:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- strong shocks;
- colds;
- flu;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
You can become infected with human papillomaviruses even by using contraception, including a condom. The thing is that it can easily live on the mucous membranes of the genital organs and around them, while any touch to the body will be fatal. The risk of infection especially increases if women have cracks on the genitals or inside the vagina.
Penetration of papillomavirus into the bloodstream, internal organs and tissues is impossible. Once in the body, it settles and multiplies deep in the skin, localizing directly in the cells themselves. When the virus matures, it comes out, where it appears in the form of irregularly shaped growths.
When a mature papillomavirus appears on the skin as papillomas or condylomas, it poses a danger to another person. If it is deep in the skin, the virus does not pose a danger to other people.
Oncogenic viruses are rarely transmitted in public places, during visits to baths, saunas, city beaches, etc. You can become infected from a sexual partner, including during the first intimate contact. This is important for all girls and women, as well as men, to remember: the choice of a sexual partner determines the future health and quality of life in general.
Many types of HPV cause genital cancer. When an infection enters the body, the degeneration of cells into a malignant form occurs after 10-12 years.
HPV constantly undermines the body's protective functions, which contributes to the development of various diseases of internal organs, penetration and activation of viral, fungal or bacterial infections.
Symptoms of infection and diagnosis
HPV types 51, 56, 69 can cause the appearance of anogenital warts. Lumps on the genitals or inside the vagina resemble cauliflower or cockscomb in appearance.
They can appear singly or grow, merging into one large formation.
Papillomas appear most often in the area of the foreskin, head of the genital organ, endural area, vaginal area, on the cervix, at the mouth of the urethra.
In men, the virus manifests itself less frequently than in women, and most often its appearance is preceded by infection with other pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the development of chlamydia, syphilis, etc.
Oncogenic HPV appears more often in women and poses a serious threat to health.
Symptoms of the disease may be absent for a long time, depending on the functioning of the immune system and the presence of other infectious diseases.
Basically, the symptoms of infection are expressed as:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bleeding not associated with menstruation;
- the appearance of blood during or after sex;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- discomfort when urinating, etc.
This symptomatology is due to the fact that when friction occurs, the growths inside the genital organs are damaged, which provokes bleeding and the development of pain symptoms. They cannot be called characteristic of HPV, because cystitis, cervical erosion, the presence of inflammation, cysts, etc. can manifest themselves in this way. Only a doctor can determine the exact cause after all the necessary studies.
Papilloma tends to quickly increase in size and progress, damaging the tissue completely.
The treatment that will be prescribed when the virus is detected can only suppress the infection, but not remove it from the body, since today there is no cure for the papilloma virus.
After careful therapy and removal of growths, they may soon return, therefore, if oncogenic type HPV is detected, regular examinations by a doctor will need to be carried out throughout life.
When cervical condylomas appear in women carrying a baby, pregnancy will be at great risk.
They are not easy to identify, and if they decay, they can provoke bleeding, which will lead to a miscarriage or will be a good help for the addition of a secondary infection.
To prevent this from happening, women and men must be tested for all possible infections during the period of planning a child and, if an infection is detected, undergo appropriate treatment, during which they must be protected with a condom.
Diagnosis of HPV 56
As for diagnosis, it is carried out on the basis of taking blood for analysis and visual examination, where men are examined by a urologist, and women by a gynecologist.
During each examination by a gynecologist, a woman undergoes smears for cytology, which can indicate the presence of precancer or cancer of the female genital organs. This examination is recommended for all women aged 28 years and above.
Women who have reached menopause will not be an exception, since during this period the virus, which has been dormant for many years, can actively manifest itself.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of oncogenic type HPV must be mandatory, since this is the only way to reduce the risk of tissue damage and prolong a person’s life. It is known that the oncogenic type of virus reduces human life expectancy by more than 20 years.
Treatment is carried out when the virus appears in an active form.
If it is in remission, it cannot be eliminated, since at this moment HPV hides where drugs do not penetrate.
Treatment consists of antiviral and restorative therapy, which helps reduce HPV activity and strengthen the immune system so that the virus does not begin to progress again.
Growths on the mucous membranes are removed surgically, radically, in order to save organs and prevent malignancy of tissues.
To do this, depending on the location of the infection, laser, cryodestruction, and chemical exposure are used. To carry out such therapy, you need to carefully choose a doctor who will carefully remove the growths without damaging healthy tissue.
Prevention of infection today is vaccination, which can and should be given to a girl before she becomes sexually active.
The vaccine can also be administered to an adult woman, but before this it is necessary to donate blood to check for the possible presence of HPV in the body.
The vaccine consists of protein compounds of certain types of viruses, which, when they enter the body, are not only destroyed by immune cells, but are also remembered by them, which subsequently develops immunity against the real virus.
The use of Gardasil or Cervarix, which helps prevent damage to the anus, cervix, genitals, and the development of precancer and uterine cancer, is effective as a vaccination.
Vaccination can only be carried out if there is no virus in the body, when the person is healthy and has no complaints of any ailments. Thanks to the vaccine, a woman will be able to protect herself from vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and oncology of the internal and external genital organs.
This vaccination is absolutely safe as it does not contain virus cells. Today it is precisely this that is a reliable prevention against a fatal disease.
As a secondary prevention, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene and not have intimate intimacy with a person before examining him in the hospital.
If a connection can still occur, you can protect the body with the help of a condom.
It is imperative to monitor your diet and lifestyle, avoiding drinking alcohol, smoking and casual relationships with the opposite sex (and members of your own sex too).
It is impossible to cure HPV, but with the help of maintenance therapy you can significantly prolong life and improve health. This will help you feel good in everyday life and make it possible to conceive and give birth to a healthy child. If treatment is not carried out, malignancy of the cells will occur sooner than in a year, and in this case it will be extremely difficult to help a person.
Traditional therapy
Among the traditional treatments for HPV, there are only drugs that will help maintain and strengthen the immune system.
For this purpose, decoctions of medicinal herbs, various tinctures and ointments are prepared. If the papillomas are located on the outer part of the genital organs, then they can be lubricated with beaten egg white.
It will help dry out the formation and slow down its growth.
To stop the growth of genital warts, you can prepare a horse chestnut bath. To do this, approximately 7 kg of fruits need to be poured with boiling water, wrapped and left for 10 hours.
After this, the prepared infusion is added to bathing water for 2 weeks, then washing and thoroughly drying the genitals.
After treatment, towels and underwear must be washed in hot water with added powder.
Treatment of infection with folk remedies is possible only if they are compatible with traditional methods. Be sure to consult a specialist before starting therapy. After undergoing therapy, at least 3-4 times a year, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination. You should also protect your body from diseases.