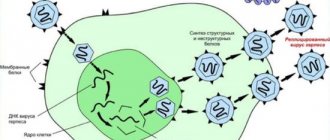
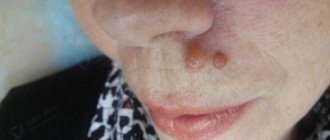
Symptoms
Some genital papillomas (look like thin, tall papillae) are characterized by respiratory manifestations.
The temperature rises and your health worsens. Duration of illness: phenomena are rarely observed longer than 1-2 weeks. Then the symptoms go away on their own until the next relapse. This type of disease is called recurrent papillomatosis of the genital area. Flat condylomas (low, wide formations), with rare exceptions, do not bother women and do not manifest themselves in any way. They only bleed and hurt when their integrity is broken. Because of this, patients complain of discomfort during urination (urine gets on the labia, on which there is a wound from the growth) and sex (due to friction, the formation is damaged even more).
When infected with HPV and an STI at the same time, a woman notices itching and burning in the groin area. Symptoms of an inflammatory process are often present.
Swelling and itching can be observed in the absence of other sexually transmitted diseases. Against the background of intensive growth of pathology, periodic damage to growths, the labia swell and slightly change color.
Diagnosis of the disease
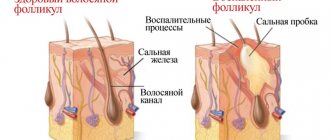
Papillomas can occur on both the labia majora and minora. As a rule, a woman discovers them on her own. You can see what papillomas on the labia look like in the photo. Genital papillomatous formations can be in the form of tubercles, flat plaques (most often these are papillomas on the small lips), cockscomb, and also papillary growth (condyloma acuminata).
You won’t be able to carry out other diagnostic tests on your own; to do this, you need to see a doctor. Laboratory tests are very important to determine the type of virus, since different types have different degrees of oncogenicity. For laboratory testing you will need:
- smear for STDs;
- smear for oncocytology;
- biopsy of the formation.
Causes
The causative agent is human papillomavirus. The infection enters the body in different ways, but the main and most likely route of infection is sexual. Type of sex: anal, oral, regular. Localization largely depends on the species. If papillomas are located on the labia minora, then it is highly likely that they were infected during intimacy.
Not every sex with a carrier ends in infection. 4 out of 10 women manage to stay healthy after just one sexual intercourse. Of those who have an infection in their body, not all will find a growth or other symptom. In some patients, spontaneous self-healing will occur, in other patients the virus will go into a latent form, in others the incubation period will drag on for many years (in most patients it ends in the first six months).

The papillomavirus can come out of dormancy due to:
- pregnancy, childbirth;
- hormonal changes;
- contracting another infection;
- endometriosis;
- unfavorable working and living conditions;
- taking strong medications (hormonal, antibiotics, contraceptives, cancer);
- irradiation;
- psycho-emotional stress, disorder;
- surgery of the pelvic organs.
Alternative route of infection: household. This option is unlikely, since outside the body the human papillomavirus does not live long and only at a certain temperature. Conditions for infection:
- violation of the integrity of the skin (the virus is not able to overcome the skin barrier, but scratches and cuts allow it access to the body);
- using someone else's towel or underwear (the infection lives longer on cotton fabric);
- using someone else's razor (it is especially dangerous to shave the groin area, since the skin of a woman's external genitalia is much thinner than that located in other parts of the body, and therefore it is easier for microorganisms to penetrate through it even during careful shaving).
Treating the wound with an antiseptic and using an adhesive plaster reduces the likelihood of contracting HPV through household contact.
Folk remedies
Treatment of papillomas in intimate places is not recommended. Firstly, folk remedies in this case are ineffective. Secondly, drugs offered by alternative medicine often contain aggressive components that can lead to burns of the delicate mucous membrane of the external genitalia. And thirdly, all recipes are aimed at eliminating the visible symptoms of the disease, while they do not have any inhibitory effect on the virus itself.
The only thing you can use are products that will relieve the unpleasant sensations of itching and burning. In this case, it is recommended to take sitz baths with decoctions of plantain, sage, lemon balm, and St. John's wort. These remedies do not cure, but only help relieve the intensity of unpleasant symptoms.
Also, using traditional medicine recipes, you can increase immunity by taking decoctions of the following herbs: echinacea, Rhodiola rosea, chamomile, aloe, rose hips, licorice, ginger, eleutherococcus, etc.
Complications and consequences
To determine the level of danger, tests should be taken to determine the type of strain. The diversity of species is divided into 4 categories according to the degree of threat.
| Threat level | Strain |
| Low | 40-44, 72-73, 61, 51, 11, 3, 13, 6, 32, 34 |
| Average | 52-53, 35, 45, 68, 56, 30 |
| High | 50, 70, 33, 31, 59, 64, 68, 64 |
| Very tall | 18, 16 |
HPV type 16 is the most dangerous for women. It is found in 54% of cases of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. 46% of patients have other types of papillomavirus.
All patients with cervical cancer have one or another HPV. However, not all women infected with the papilloma virus develop cancer.
In addition to malignant degeneration, warts in the intimate area cause pathological changes in the epithelium lining the internal genital organs. Hence the erosion. This gynecological problem has serious consequences. Among them:
- ban on natural childbirth;
- problems with conception;
- increased likelihood of ectopic pregnancy;
- difficult birth.
An additional threat comes from papillomas located on the walls of the vagina, intestines, and larynx. They can grow, blocking passages.
Reason for spread: constant violation of the integrity of warts. Being in the intimate area, in the mouth, these growths are systematically damaged during eating, sex, defecation, and urination. Self-infection occurs. Small papillomas unite, a large association is formed.
Overgrowth is fraught with infertility: it is more difficult for sperm to penetrate through the layering. Large formations negatively affect the microflora, causing the outflow of urine to be disrupted. Untimely removal of decay products provokes inflammation of the urinary tract and genital organs.
The papillomavirus itself does not cause problems with conception and pregnancy, but accompanying diseases and complications can affect reproductive function.
You should not assume that growths on the labia are not dangerous. With this localization, there is an extremely high probability of the presence of “hidden” papillomas - formations on the mucous membranes of internal organs. Most patients have both of these types simultaneously (approximately 85%). Therefore, all women with genital warts are required to undergo colposcopy.
Diagnostics

Growths in intimate places are the responsibility of a gynecologist. Having learned about the reason for the request, the doctor must examine the patient in a gynecological chair. During the procedure, in addition to standard instruments, a microscope that magnifies the image is used. The manipulation is called colposcopy.
Additional measures:
- treatment of mucous membranes with a drug that allows you to identify hidden papillomas (healthy areas will remain the same color, and the affected areas will turn white);
- collection of material (epithelial smear) for histology, cytology - methods for diagnosing HPV;
- collection of secretions (smear for flora) for examination for the presence of certain STDs (trichomoniasis, gonorrhea).
Testing for sexually transmitted diseases is an optional but desirable measure. Reason for this: with anogenital warts, 9 out of 10 women are diagnosed with other infections that attack the organs of the genitourinary system.
Deadlines for receiving results:
- during colposcopy - immediately;
- after treatment with the drug, wait 10-15 minutes (the medication takes time);
- when performing cytology – from 1 to 3 days (it is possible to conduct an express test);
- for histology – up to 5 days.
The patient is also given a referral for a PCR or digene test. Using the first one, you can find out the DNA of the virus. The method is highly accurate. Diagnosis test allows you to identify the type of strain. The method is accurate and affordable (costs less than PCR).
Important! Express tests for papillomavirus are sold through pharmacy chains. The results obtained in this way should not be trusted. The probability of error reaches 80%.
Treatment
Key points:
- It is impossible to completely get rid of HPV. You can only strengthen your immune system so much that it suppresses the activity of the virus.
- The growth itself is removed. Exception: there is no need to remove papillomas during pregnancy. You need to wait until birth. Drastic measures are taken only after them.
- During therapy they do not enter into intimate relationships. Some experts suggest replacing abstinence with condom-protected sex. However, the contraceptive may tear or move. And its protection is limited: the virus can be transmitted through uncovered parts of the genitals.
- You should not quit treatment because of a one-time violation of the sex taboo.
- Regular partners undergo examination and treatment of papillomas together.
Removal methods
Chemical burning for papillomas on the small lips is practically not used.
Exposing sensitive skin and one of the key erogenous zones, in the thickness of which arteries, nerves, and blood vessels lie, to aggressive influence is an unwise step. Even if it is possible to avoid deep-seated damage, the wound will take a long time to heal due to its localization. Long-term recovery is a prerequisite for the re-formation of the growth. The outer side of the labia majora is sometimes treated with agents for chemical removal of papillomas. Here the skin is thicker and more difficult to damage (compared to the small lips). It is not recommended to apply medications yourself. There is a high risk of the product spreading, getting onto the legs of the labia minora, the clitoris, and the vestibule of the vagina.
Recommended techniques:
- Radio wave method. Painless and most expensive method. It is used for the location of papillomas on both the labia minora and labia majora.
- Laser removal. Requires anesthesia and lasts only 10 minutes. The skin recovers very quickly.
Less popular techniques for this localization of growths:
- Surgery . It is used for very large flat papillomas on the upper labia. The wound takes a long time to heal (more than a month). A scar remains. The operation is inexpensive (cheaper than analogues).
- Treatment with liquid nitrogen . A bloodless procedure is used for dysplasia and cervical erosion. It is effective against old formations.
- Electrocoagulation (electric knife). The measure is contraindicated for inflamed genital growths. Removal is bloodless, but the wound takes longer to heal than after liquid nitrogen.
To speed up the healing of the wound after excision of the papilloma, Bepanten cream or gel should be applied to the problem area 2-3 times a day. It is absolutely safe when treating intimate areas.
Immunomodulators and antivirals
They are used before and after removal. Group representatives:
- Viferon . A safe drug based on interferon. Reduces the toxic effect of antibacterial agents, stimulates immunity and regeneration of healthy tissues. For papillomas on the small lips, vaginal suppositories are placed, gel is applied (directly to the affected area, or a tampon is soaked in the product and inserted into the vagina). When treating the intimate area with topical preparations, you should first remove discharge from the labia and vaginal opening (using a cotton ball). There may be a burning sensation after application.
- Isoprinosine . Sold in tablet form. Used together with Acyclovir, it enhances its effectiveness. Take three times after meals for 5-14 days. The dosage is determined based on body weight (usually 2-3 tablets at a time). In severe cases, the number of doses is increased. At the end of the first course, they take a two-week break, then start taking medication again. Total number of courses: 3. Often causes headaches, itching, joint pain. The drug does not treat papillomas in girls (under 3 years of age).
- Acyclovir . An antiviral drug based on the active substance of the same name. Promotes the rapid formation and drying of crusts on wounds. It is taken in the form of tablets (take only 1 course, as insensitivity may develop). Dosage regimen: every 4 hours, 1 tablet for 5 days. In case of pronounced immunodeficiency, the single dosage is increased to 0.4 g. The medication can provoke undesirable reactions from the urinary, respiratory, and nervous systems. Contraindicated in case of lactose deficiency or renal failure. Breastfeeding women should switch their baby to formula.
Immunosin (persistent antiviral, immunomodulatory effect) and Genferon (these suppositories can also be used during menstruation) will also help get rid of papillomas;
Attention! To cure the disease faster, you need to take sources of vitamins E, A and C.
Ointments and gels
You can apply to the intimate area:
- Aldaru . Effective against genital papillomas on the labia.
- Imiqvod (or Imiqwad). Incomplete analogue of Aldara. Suitable for external and perinatal warts in women.
- Veregen . Do not apply ointment to the labia minora. It is used only on the outer walls of large ones.
- Epigen Intim . Hygiene product. It not only cleanses the skin, but also has immunostimulating and antiviral properties.
What is the danger of the disease?
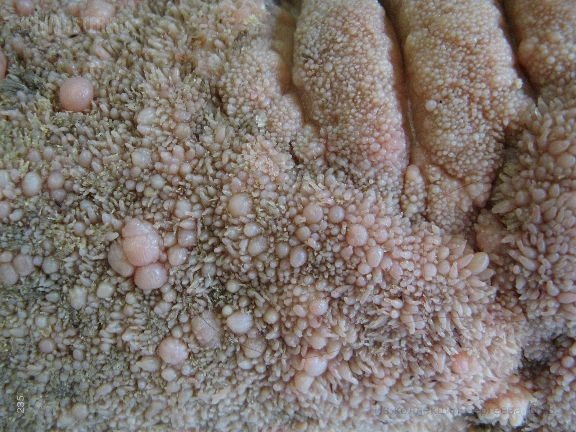
However, if they are treated promptly and correctly, this danger will not arise. In addition, papillomas on the labia are vulnerable to injury, which results in a source of infection that can spread into the body. Doctors testify to cases where multiple papillomas on the mucous membrane of the small lips completely closed the entrance to the vagina. This uncontrolled cell division is considered a precancerous condition.
A woman should be wary and concerned if pain occurs after intimacy, or if itching, bleeding and an unpleasant odor appear. Such symptoms indicate that the formation has been injured. In this case, you should definitely visit a gynecologist.
Forecast
It is impossible to exclude the possibility of re-formation of growths using any removal method. However, following your doctor's instructions reduces the chances of relapse.
Sometimes the body copes with the virus on its own (the papilloma on the lips remains, and you still need to get rid of it early). This is possible in the first 2 years after infection and in people under 30 years of age (juvenile warts disappear more easily). There is no cure for advanced forms of HPV, but there are ways to slow down the activity of the pathogenic microorganism.
The disease causes minimal inconvenience to patients in good health. Often their illness does not manifest itself at all and does not affect their quality of life. Therefore, strengthening the immune system is one of the main tasks facing infected women. The second global goal of treating papillomas is to prevent complications.
To do this, you need to systematically undergo examinations by a gynecologist. It is mandatory to examine the cervix every six months. If the schedule is followed, any pathological change in the epithelium will be diagnosed in a timely manner. The pathology will not have time to develop to a condition requiring drastic measures.
In general, complications should be feared by people who have been diagnosed with a highly oncogenic strain or the wart has managed to degenerate into cancer. The remaining categories of women are relatively safe (provided they have gotten rid of the formations). A carrier of papillomavirus needs to understand that HPV in the absence of layers of STDs and autoimmune diseases is not so dangerous. You can live your life to the fullest with the virus.
Lip papillomas and pregnancy

With this localization of growths, there are no reasons for abortion or cesarean section. Natural childbirth is excluded only if there are a large number of warts on the walls of the vagina, or the presence of sexually transmitted infections.
There is a risk of infection to the fetus, but it is protected in the womb. Infection is possible only if the integrity of the bladder or childbirth is violated. After delivery, it is necessary to check the child for HPV. The microorganism can cause high sensitivity and pain in the genital organs of a newborn, eye damage such as conjunctivitis, and breathing problems (if located in the mouth).
If a woman has warts, she should inform her doctor about this when registering for pregnancy.
Papillomas of the small lips require examination. Reason: with this localization, there is a high probability of detecting growths on the walls of the vagina (located in 8 cases out of 10). The latter type of formations is dangerous due to complications (erosions, cancer, ectopic pregnancy).
With timely removal of the formation, the risks are reduced. The chances of maintaining health are even higher for patients who take immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs. They are available in the form of tablets (Acyclovir), suppositories (Viferon), gels (Epigen) and ointments (Vergen). Many drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy (Immunosin).
Causes of papillomas on the labia
The causes of papillomas are associated with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The human papillomavirus can be transmitted both sexually and domestically. There is a risk of infection of the baby from the mother during childbirth.
Since HPV can remain viable for a long time in the air, it can be infected in baths, saunas, public swimming pools, solariums, if you sit on benches with your genitals uncovered and use other people’s personal hygiene products.
As for sexual transmission of the virus, a condom cannot protect against infection; this should definitely be taken into account when entering into casual intimacy with an untested partner.

For a long time, the human papillomavirus can remain in the body in a latent state and not manifest itself until favorable conditions for its development occur. However, despite the fact that there are no visible manifestations of the virus, a person is already a carrier of it and can transmit it to his sexual partner.
The impetus for the formation of papilloma can be:
- weak immunity;
- stress;
- poisoning;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- hormonal imbalances;
- avitaminosis;
- chronic diseases;
- poor environmental situation.