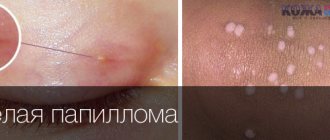
In terms of prevalence among the population, the human papillomavirus (HPV) is second only to the herpes virus. Its danger lies in the fact that more than 35 strains are oncogenic and provoke carcinogenesis. A feature of the pathology is the absence of clinical manifestations in the first stages of the disease, so donating blood for HPV is often the only way to determine the presence of infection and take timely measures for treatment.
General information about HPV
People learn about the human papillomavirus (HPV) what it is when it has already manifested itself.
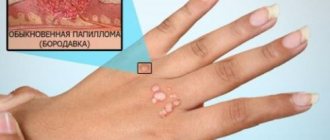
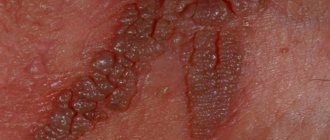
On the mucous surface of the genitals in men and women, pointed growths appear - condylomas. More serious consequences - pathological degeneration of the cervix - become known at an appointment with a gynecologist. The danger of this virus is expressed in latent inflammation
Doctors have known this virus for a long time: it causes the formation of papillomas and warts. Doctors and scientists began to sound the alarm when they traced a direct connection between the presence of the virus in the body and the development of a cervical tumor. Infection is found in almost every biopsy material.
HPV is widespread. Only about 20% of the planet's population manages to avoid meeting him. The main route of transmission is contact, during intimacy. Condoms do not protect, but they slightly reduce the risk of transmission of infection. The more actively a person searches for new sexual partners, the higher the risk of infection. Now condylomas are spreading in the anal area, on the surface of the rectum.
This is due to the increasing popularity of anal sex. Infection and development of the virus can occur from an infected mother to an infant during childbirth. The baby develops growths on the larynx and genital warts. Such clinical cases are rare, but they do exist. A contact and household method of infection with warts is possible if the skin has microdamages.
When to donate blood for HPV infections?
If a person notices the appearance or change of a tumor, the best solution would be to consult a dermatologist. He will refer the patient for examination. In addition, you can also take a blood test for HPV yourself. Women have more reasons for such examination. Doctors have identified a connection between the papilloma virus and genital cancer. The time interval between infection and the clinical manifestation of oncology is sometimes 10 years. Dermatologists recommend being diagnosed with HPV every 2-3 years if a previous test for the virus gave a positive result. Men also have good reasons to consult a specialist, especially if they detect condylomas on the genitals.
There are two methods of testing blood for HPV - enzyme immunoassay and polymerase chain reaction.
What is papillomavirus?
Papillomavirus is a heat-stable pathogen that multiplies slowly without causing any symptoms. Therefore, people may not suspect they are infected for many years.
The virus is transmitted from person to person. Once in the body, the virus is neutralized with stable protection. But with an inadequate immune response, it affects cells, leading to a change in the nature of epithelial growth - causing the formation of warts and papillomas on the skin, condylomas on the mucous membranes. The reasons for their appearance are contact with the affected areas of an infected person.
Test for human papillomavirus in women: how to take it, preparation
To ensure the quality of life of the body, health care should be a priority. Moreover, modern science allows us to diagnose hidden potential dangers at an early stage.
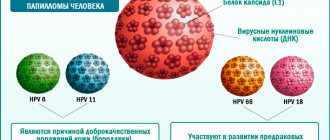
For example, an analysis for papillomavirus allows you to identify a dangerous agent even before it begins to destroy the human body. The papilloma virus family includes about 70 strains, and each of them carries one or another danger to certain organs.
It must be said that the most favorable environment for the development of this virus is the vaginal microflora, therefore this infection is most often diagnosed in the fair sex.
Of course, not all strains of papillomavirus are deadly, but their oncogenicity can only be determined through laboratory tests.
If an HPV test is prescribed to a patient in the presence of its external manifestations on the body, the purpose of diagnosis is to determine the type of virus for
selection of the optimal treatment regimen. If there are no visual manifestations of the virus yet, an examination is carried out to identify the virus after contact with the carrier. This study is also necessary during pregnancy or if a woman wishes to become a donor.
The strain of the virus is determined in order to understand the danger that this infection poses.
Important!
Some strains of HPV have a high oncogenic index, so if a doctor has prescribed a test, it is not advisable to refuse it.
The following methods are currently used and are considered most effective:
- blood sampling;
- urine test;
- histological examination;
- colposcopy;
- cytological method;
- Digene test.
Next, each method will be discussed in more detail.
Blood collection
Using a blood test, human papillomavirus can be determined in two ways:
- PCR is a polymer chain reaction method.
- ELISA – enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Deciphering the PCR results allows you to assess the stage of the disease, the amount of virus and its life cycle. In the blood, the virus reveals itself by the presence of antibodies or its own genetic code.
According to the enzyme immunoassay, it is impossible to determine the degree of oncogenicity of the virus, since this study is based only on the detection of antibodies to the virus, therefore, it cannot be considered definitive.
Reference! After 30 years, all women, without exception, need to donate blood for the presence of the papilloma virus; in the future, such an analysis should be carried out every 3–5 years.
Urine examination
No less reliable results can be obtained by analyzing a woman’s urine. These tests are also carried out using PCR and ELISA. How to properly renew the collection of biological fluids will be discussed below.
Histological examination is the processing and analysis of tissue under a microscope; it includes 7 stages:
- fixation - the material is treated with a special substance to prevent the process of decay;
- wiring - creating a solid block, dehydration;
- pouring - the material under study is poured with paraffin;
- cutting to obtain thin sheets of fabric;
- coloring - the material is filled with a special dye;
- conclusion - placing the material under a glass slide;
- research - examination of sections under a microscope.
To conduct this analysis, you need to obtain a piece of the tumor from the patient, that is, perform a biopsy. Most often, a removed papilloma is fused for analysis.
Reference! Histology is an integral stage in refuting or confirming the fact of the development of an oncological process.
Colposcopy
Colposcopy is the most accessible diagnostic method that is performed on women to determine the papilloma virus. The cervix is treated with Lugol's solution or acetic acid, and the following is observed:
- the epithelium turns white;
- mosaic or dotted appearance appears;
- an atypical zone is revealed.
The modified HPV area becomes similar to semolina.
Reference! According to ongoing research, in 99% of cases, cervical cancer is associated with the presence of highly oncogenic strains of HPV.
To conduct a cytological analysis, the doctor uses a special flat brush to take a smear from the cervix and apply it to a glass slide. This study allows you to determine the presence of the virus, but in this case it will not be possible to judge the quantitative characteristics.
In this regard, so-called liquid cytology is currently used, during which cells are captured from the entire surface of the cervix, as well as from the cervical canal. The resulting material is completely applied to a glass slide, and after staining it is examined by a cytologist.
A special analytical analyzer identifies suspicious and questionable areas, which allows the doctor to pay closer attention to them. Such a study allows you to most accurately analyze the cells of the cervical uterus and choose the right therapy.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Removal of intimate papillomas in Moscow. Price
Digene test
The Digene test is a screening study that also allows you to determine the presence of the papilloma virus in the body even before the onset of pathological changes in the epithelium.
The benefits of this study are as follows:
- high accuracy;
- the ability to determine the presence of 18 strains of the virus, of which 13 are highly oncogenic and 5 are moderate;
- painlessness - a regular smear;
- relative speed of obtaining results;
- the ability to determine the exact concentration of the virus in the body;
- samples can also be used for cytological examination;
- simplicity and objectivity.
The disadvantage of this study is its high cost.
Currently, a test for human papillomavirus can be taken in almost any clinic. The main thing is that it is equipped with modern equipment.
A smear to determine the human papillomavirus is prescribed in the following cases:
- pregnancy planning;
- frequent miscarriages and infertility;
- inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- the presence of warts and condylomas on the external genitalia;
- discharge, the cause of which cannot be determined;
- having a partner with sexually transmitted infections;
- itching in the genital area;
- uncomfortable and painful urination;
- prevention.
The study can be done both before and after menstruation.
Preparing for the HPV smear:
- For 2 days you should avoid sexual intercourse, do not use cosmetics for intimate hygiene and do not douche.
- Before the procedure, you must take a shower without using hygiene products.
- If a woman is taking any medications, she must inform the doctor in advance.
- A smear is not taken during menstruation; it is better to take this test in the first days after the end of menstruation.
A blood test for HPV also requires preparation. To get the most reliable result, doctors recommend:
- the day before the upcoming test, do not drink alcohol or smoke;
- ELISA is given on an empty stomach;
- 3 days before donating blood, it is advisable to avoid intimacy;
- 2 weeks before the analysis it is recommended to stop antiviral therapy;
- on the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude stress factors.
How to take it
Colposcopy is a visual examination method in which the doctor examines the structure of the cervix and evaluates the condition of the tissues. During colposcopy, tissue samples may be taken for other research methods. For a cytological examination, a smear is taken from the woman, which is then examined under a microscope.
Histology is also a study under a microscope, the material for which is a piece of neoplasm tissue. This may be a distant papilloma. A blood test is taken from a vein.
To carry out the Digene test, you will need material that was obtained using one of the methods listed above. Most often, a biopsy is performed as part of a colposcopy.
For PCR analysis, different biomaterials can be used - blood, urine, amniotic fluid, smear from the genital mucosa.
Only a doctor can take material for research. In some cases, the analysis may be false positive, the reasons for this may be the following factors:
- failure to comply with training requirements;
- incorrectly taken sample;
- using vaginal suppositories or douching (if a smear test is taken);
- taking medications;
- the virus is localized deep in the genitals.
The biomaterial is collected using a soft brush; this is an absolutely painless procedure that does not cause any discomfort to the patient. After receiving the biomaterial, the brush must be packaged in a sterile tube and sent to the laboratory for analysis.
The result of the PCR analysis needs to wait 2 days, the Digene test will be ready in 7–14 days.
The results of the PCR analysis are as follows:
- PCR is negative, cytology is negative - the patient does not need special observation and should visit a gynecologist for preventive purposes once a year.
- PCR is positive, cytology is negative - it is recommended to repeat the cytology test in six months.
- PCR is negative, cytology - initial signs of epithelial dysplasia - observation and repeat cytological analysis after six months is necessary.
- PCR is positive, atypical cells were found in the smear - colposcopy is recommended.
Due to the fact that new methods of analysis for human papillomavirus have now appeared, their cost remains quite high. Of course, it depends on the research method and the medical institution where the analysis will be carried out.
The average prices are:
- colposcopy – 700–1500 rubles;
- cytological analysis – 1100–2500 rubles;
- smear collection – 300 rubles;
- histological examination – 2000–3000 rubles;
- PCR analysis – 700–1900 rubles.
Therapy for human papillomavirus infection involves the use of special drugs, the action of which is aimed at stopping the progress of the pathology. It is impossible to completely remove the virus from the body.
If the immune system works well, then the virus is suppressed by the body on its own without additional therapy. Prevention of the disease consists of timely vaccination.
- Have the best day everyone!
- Today I want to share my experience about a test for HPV (human papillomavirus), which I had to undergo on a referral from a gynecologist.
- Very often, many gynecologists associate the presence of HPV (human papillomavirus) with cervical cancer, so they try to send every second woman for examination after examination.
- During a routine examination, and based on the ultrasound report, I was no exception.
- A little official information to understand the essence and importance of this study.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the common name for a group of viruses that are extremely common throughout the world.
- More than 100 types of HPV are known, of which at least 14 are oncogenic (the so-called high-oncogenic risk viruses).
- HPV is transmitted primarily through sexual contact, and most people become infected with HPV soon after becoming sexually active.
- Cervical cancer develops as a result of certain types of sexually transmitted HPV infection.
- In 70% of cases, the cause of cervical cancer is two types of HPV (16 and 18).
Who needs research
Sexually active people, especially those with non-regular partners, are recommended to be tested for human papillomavirus once every 2-3 years.
For women under 30 years of age, who may have the virus transiently, if HPV is detected, the test must be repeated after 9-10 months. There is a high probability that the immune system will independently eliminate the human papillomavirus from the body.
In women over 30 years of age, the risk of cancer increases, in particular cervical cancer, caused in 90% of cases by high-risk HPV. Most often these are genotypes 16 and 18.
For early diagnosis, it is recommended to donate blood to detect papillomavirus, which will reveal antibodies to the virus, in the presence of clinical symptoms - PCR or Digen-test.
A positive test does not indicate the presence of cancer. If a woman has HPV types 16, 18, it is necessary to examine the cervix for pathogenic changes. In the absence of clinical manifestations, it is necessary to pay close attention to your lifestyle, strengthen your immune system, and treat chronic diseases.
These simple methods will help the body cope with HPV and prevent a woman from developing cervical cancer. Your doctor may prescribe antiviral therapy. However, the effectiveness of this treatment method has not been proven. The course of the disease must be monitored every 3 months.
For men, if symptoms appear in the form of warts, papillomas or warts, or pain during sexual intercourse, it is recommended to visit a doctor who will refer you to a laboratory for tests. You can also take the test yourself, but to read the results and prescribe treatment you will need to consult a specialist.
Preparation for the procedure
The first screening is recommended for women aged 25–30 years. If sexual activity began early, then 3 years after the first contact. If the result is negative, the examination is recommended to be repeated every 3 years. For patients with weakened immune systems - every year.
Men are carriers in most cases. Their risk of developing cancer is much lower than that of women, so examinations are prescribed to them only for differential diagnosis if the partner has a manifestation of the virus in the form of condylomas.
To obtain the most reliable result, proper preparation for the analysis is important, which depends on the methodology.
Before cytological, extended studies:
- 3 days before the procedure, it is prohibited to use topical medications or antibacterial hygiene products;
- do not empty your bladder for 2–3 hours;
- For 2 days before the procedure, you must refrain from contact with your sexual partner.
A diagnostic procedure is prescribed before the start of any specific treatment in order to exclude drug influence on the results. A few days before the examination, it is recommended to review your usual diet (exclude fatty, smoked, salty foods). It is also necessary to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.
If the study is carried out using the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method, then there is no need for preparation. The test will be accurate in any case.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Papillux papillux remedy for warts and papillomas: reviews
For any diagnostic method, biomaterial is not collected during menstruation, which is explained by possible distortion of the results.
The danger of papillomatosis is the risk of developing malignant neoplasms; it must be diagnosed in a timely manner.
An HPV test in women helps to quickly determine the presence of a specific strain of viral infection and select the optimal treatment regimen.
An analysis for the presence of papillomavirus in a woman is done in specialized laboratories, after the appointment of a specialist doctor (gynecologist, dermatovenerologist).
The doctor first conducts an examination and diagnoses papillomatous formations.
For preventive purposes and to prevent infection of the child during natural delivery, blood tests for HPV for pregnant women and women who are planning a pregnancy are mandatory.
Blood collection
Venous blood is taken for the purpose of performing an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Hemotest is used to establish the activity of the immune system, study disorders of the immune response and determine the causes of disorders in the body’s immune system.
ELISA is an auxiliary diagnostic method that determines the presence of antibodies to HPV in a woman.
Often, when using such an analysis for research, the result may be false negative; the virus is in a latent phase, the immune system simply did not have time to produce them.
In gynecology, ELISA is used for women after the age of 30, during menopause, the susceptibility to infection increases.
A young body can independently fight a viral attack and produce protective antibodies that help eliminate residual foci of papillomatous proliferation; with age, this ability is lost. Monitoring of the study should be carried out once every 4-5 years to prevent activation of the virus and the development of complications.
Do you need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
For the polymerase chain reaction method, epithelial scrapings from the cervix are used. PCR allows you to determine the DNA of the virus.
PCR diagnostics allows you to determine the presence of HPV in small quantities and in the latent phase; the analysis determines the pathogen itself, and not the penetration reaction of the viral agent as a consequence of transmission from the carrier of the disease.
An important condition is that the rules for collecting material are strictly followed, the woman is prepared before taking the test; only a qualified medical professional can take a sample for testing. When conducting a PCR test, there may be a false positive result due to contamination of the sample; after a course of therapy, the pathogen is not active and is in the stage of residual elimination from the body.
Taking a smear
The cytological method is a classic study involving taking a smear of discharge from the cervical canal.
The method is simple to perform and safe, but the risk of incorrectly taking diagnostic material and the level of false negative results (5-35%) do not allow us to focus on the final result.
Biological material is taken from the patient using a long, soft, flexible brush (previously a Volkmann stemmed spoon was used).
PCR analysis is carried out in two ways:
- With typing. An advanced research method that allows you to determine the presence of a specific HPV strain and determine the level of oncogenicity.
- No typing. This reaction allows you to determine only the presence of HPV in the body.
When taking a smear, it is important to follow the rules for collecting material in order to avoid false research results (contamination of the material, after a course of therapy, before the analysis, the woman performed douching or vaginal suppositories).
Scraping
The Digine-test is a quick and convenient method for determining 8 oncogenic strains of papillomavirus.
The essence of the method is to take a scraping of epithelial cells from the vaginal area, from the cervix or from the urethral canal.
The method is widely used as a rapid diagnosis of human papillomavirus and is the method of choice for preventive annual examination of women.
Before taking the test, a woman needs to take certain preparation measures for an accurate result:
- Hygiene procedures (showering, personal intimate hygiene) on the day of taking a smear are carried out without the use of soap and the use of intimate hygiene wipes before collecting the material;
- absence of menstruation at the time of the smear test;
- temporarily do not use tampons, antibacterial vaginal ointments and gels, do not douche, do not use vaginal suppositories before preparing for analysis (3-5 days);
- When testing blood, you must appear on an empty stomach or if more than 6 hours have passed since eating.
If the preparation rules are violated, it is better to contact a doctor or laboratory and reschedule the diagnosis date.
Consultation after receiving test results accurately and in full, with diagnosis and determination of further treatment tactics, can only be provided by the attending physician.
There are gradations of research results:
- Cytology (smear with a brush or stem spoon) is assessed according to classification levels from 1 to 5, as the oncogenicity of the pathogen increases: class 1 - negative test for HPV, 5 - positive response.
- The Dijin test is deciphered according to the amount of DNA of the virus. An increase above the norm is a sign of infection with papillomavirus; high numbers are evidence of massive dissemination of the virus in the body.
- When carrying out PCR in women, the results are interpreted as follows: indicator up to 3 - low concentration of the virus, indicator within 3-5 - sufficient amount of HPV to activate clinical manifestations (precancerous condition), indicator 5 - quantitative indicator at the highest level with a large load on organism with a high risk of malignancy. The number indicates the amount of papilloma DNA per 100 thousand healthy cells.
Carrying out tests to determine HPV in women is a mandatory measure in the treatment of papillomas or warts in order to prevent infection (age factor, pregnancy). The examination should be carried out when the fact of infection with papillomavirus is established, and after a full course of therapy, even if there are no symptoms for a long period.
Only a specialist has the right to decipher the results of examinations and give recommendations for the treatment of papillomatous manifestations. To avoid negative consequences and dangerous complications, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. Timely measures taken to eliminate HPV will help quickly and effectively eliminate all manifestations in the early stages of the disease.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
How to prepare for the test
Venous blood is taken for analysis and given in the morning on an empty stomach. No special preliminary preparation is required, there are only general recommendations:
- do not drink alcohol, do not overeat and do not abuse fatty foods the day before;
- take care of yourself by limiting physical and emotional stress;
- stop antiviral treatment at least two weeks in advance (this issue is discussed with your doctor).
So, when diagnosing HPV, the main thing is to take a smear, and a blood test can be used as an additional research method.
Cytological screening
A method of early prevention of HPV VCR (high carcinogenic risk) of pathological processes of the cervix. Allows you to identify atypical epithelial cells. A smear is taken every time you visit a gynecologist.
The collection of cellular material is an unpleasant but painless procedure. The doctor cleans the cervix with a cotton swab. The biomaterial is taken using a special brush and applied to a glass slide. In the laboratory, the material is examined under a microscope. To obtain reliable information before visiting a doctor, you do not need to use vaginal suppositories, tampons, or douches. It is also necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse for two days.
Liquid-based cytology (LBC) is recognized by WHO as the “gold standard” as the most informative method for screening for cervical diseases. Samples can be stored for a long time for subsequent testing for the presence of HPV and other urogenital infections, as well as repeated cytological studies.
If the examination result is positive, an additional colposcopy is performed.
We suggest you read: A guy has papillomas on his penis
How is it carried out?
Testing is prescribed for patients who have not previously had an infection. The manipulation is simple - during a gynecological examination, a smear is taken from the inner surface of the cervix using a special cytological brush. If a man is examined, a smear is taken from the urethra. After collection, the biomaterial is placed in a special environment and subject to examination.
When using the PCR method, saliva, blood, and skin cells can act as biological material.
Screening detects the presence of HPV in the body. After receiving a positive result, upon referral from a doctor, extensive screening is carried out to determine the genotype of the pathogen and the number of infected cells. If a malignant tumor of the cervix is suspected, cervical screening is performed, which is more sensitive.
Colposcopy
The colposcopic method has a fairly high percentage of effectiveness
A diagnostic method for examining the vagina using binocular optics - a colposcope. It is also used to perform vulvoscopy – examination of the genital mucosa. The study identifies and determines the nature of pathological changes in the cervix. Modern colposcopes magnify the image by 7.5 - 30 times.
There are no contraindications; no special preparation is required. Colposcopy is performed on any day of the menstrual cycle (except for menstruation). The study is carried out on a gynecological chair. Due to the non-contact and painless method, anesthesia during the procedure is not indicated.
The effectiveness of the colposcopic method is over 80%. Based on the research results, the doctor decides on the need for a histological examination using a biopsy.
How to test for HPV in women: features of the procedure and results
A positive test result indicates a high risk of cancer. The doctor will prescribe an additional examination - examination of the biomaterial using various diagnostic methods: colposcopy or urethroscopy, biopsy.
If a positive test result is obtained, a quantitative study is carried out. The PCR method allows you to accurately determine the amount of each strain of the virus in biological material, which allows you to diagnose the severity of the current disease and predict further development. Calculated in genomic equivalents (GE).
Interpretation of results:
- less than 103 - does not pose a threat to health;
- more than 103 - high risk of developing cancer;
- more than 105 - the beginning of the development of cancer.
Analysis transcript
The result of a blood test for HPV can be obtained within 24 hours.
If the patient underwent a PCR examination, then the result of the analysis will be the word “positive” if the papilloma virus was detected, or “negative” if the person is healthy. If virus strains are identified, the number of its titers is also indicated:
- titers are less than the threshold (when deciphering the analysis, this value is taken as a variant of the norm or evidence of a previous infection);
- titles beyond threshold;
- high titers.
Diagnosis of HPV by ELISA provides information about the body’s immune response to the virus. Before the examination, do not take immunomodulatory drugs. The enzyme immunoassay form contains the types and quantities of immunoglobulins that the body produces in response to a viral attack. Depending on the type of antibodies that the examination revealed, a conclusion is made about the presence and stage of infection.
| Antibodies | Stage of disease development |
| IgM | Acute |
| IgG | Chronic illness or convalescence |
| IgA | Exacerbation of a chronic disease |
The examination results will be ready in 1-3 days. It depends on the type of analysis. The forms are deciphered, a final diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed by a dermatologist. Under no circumstances should you prescribe medications or self-medicate. You should not be afraid to undergo examination, since a disease identified in time is much more amenable to treatment.