What is HPV, symptoms
Papillomaviruses are known for their variety of strains, of which there are more than a hundred. About seven dozen of them have been well studied. The main manifestations of infection are expressed in the form of neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes:
- In the form of dense growths with a keratinized surface on the hands and feet;
- Flat warts on the face, neck;
- Rod-shaped neoplasms rising above the surface of the epithelium, soft to the touch, pink in color;
- Genital warts in the genital area, anus, and larynx;
- Pathological changes in the cells of the cervical mucosa.
Types of human papillomavirus
Let's consider the viral strains that pose the greatest danger to women - HPV with high oncogenicity. All of them are combined into group “A-9” (these are strains of types 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59).
Warts are the result of the widespread human papillomavirus (HPV). Medical statistics state that 90% of the population on the planet are carriers of various human papillomaviruses. Let's learn about this classification in detail.
Today, doctors describe more than 70 different types of papillomavirus that cause diseases of the mucous membranes and skin. An experienced dermatologist will be able to determine the genotype of the virus by its external manifestations. They have their own numbering.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is an infectious disease that is transmitted from person to person by direct contact (through unprotected sexual intercourse, to a child from a mother during childbirth). The localization of the virus can be on the skin or mucous membranes; this disease has various types and manifestations, but in any case it must be subjected to professional treatment.
There are several methods for diagnosing the human papillomavirus - they are all equally used in medicine, but differ in their characteristics, the principle of “work” and the level of accuracy of the results. The HPV vaccine can prevent infection with the disease.
HPV - types of human papillomavirus; in most cases, HPV exists in human blood asymptomatically and manifests itself when immunity decreases
Human papillomavirus (HPV, human papillomavirus, HPV) is a very common virus that causes changes in the growth of body tissues. Papillomas and warts appear on the skin precisely under its influence. Some types of HPV are extremely dangerous because they can cause cancer.
According to various estimates, from 60% to 90% of the population are carriers of this virus. It is transmitted only from person to person. The main routes of HPV infection are: sexual contact (including oral and anal sex); in 0.1% of cases, it is possible for a child to become infected from the mother during the passage of the birth canal (but not during pregnancy); infection through household means through minor lesions on the skin.
Common symptoms of human papillomavirus
In most cases, HPV exists in a person’s blood asymptomatically and manifests itself when immunity decreases. Characteristic features are neoplasms:
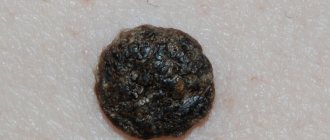
- Warts are small benign formations with a diameter of 2-10 mm. They have a round or irregular shape, clear boundaries and an uneven surface. The color can be very different: flesh-colored, yellow, red, brown, gray and so on. Warts usually appear in places that are often subject to injury, such as fingers and knees.
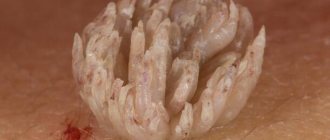
- Papillomas are soft formations, flesh-colored or darker, attached to a stalk or thick base. Most often they appear on the neck, face, armpits and genitals. Papillomas grow rapidly and occupy more and more new areas.
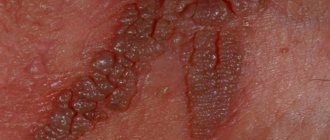
- Genital warts are soft, moist formations on a stalk. They have a pink color and an uneven surface, like a wart. Affects the genital and anus areas. A characteristic feature is very rapid growth and spread. Sometimes an entire “colony” can grow in a few hours.
- Bowenoid papulosis, in which rashes appear on the skin of the genitals. They look like pink, yellow or white plaques. In some cases, bowenoid papulosis can develop into skin cancer.
In addition to the general symptoms, the human papillomavirus has different manifestations in men and women.
Features of HPV in women
As mentioned above, the most common way of contracting the virus is sexual contact with an infected person. Therefore, if you suspect HPV, you need to take measures to avoid infecting your partner.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7HQqiDmJ-lw
Usually, HPV occurs almost unnoticed against the background of inflammatory processes of the genital organs: vulvovaginitis, endocervicitis, pseudo-erosion of the cervix. Almost always combined with other sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, trichomoniasis, herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis.
The phrase human papillomavirus or HPV occurs quite often and some people believe that infection with this microorganism causes only papillomas to appear on the body.
But not everything is so rosy; infection with HPV sometimes leads to the development of a rather serious disease - cancer. It is possible to guess how the infection will behave in the body, but only by knowing the type of papillomavirus.
Research conducted over the past decades has made it possible to establish that HPV is transmitted only from one person to another, and this can be either a carrier of the infection or a patient with pronounced clinical signs of papillomatosis.
It has been established that papillomavirus is divided into types; there are more than one hundred of them. Depending on the type of virus that has entered the body, all external and internal changes will occur in the future.
The division of HPV into types has made it possible to develop treatment tactics for patients with microorganisms detected through testing.
Photos of different types of papillomas
Features of the clinical picture
Most often, the process of infection of men and women does not reveal any specific symptoms. Among the patients suffering from vivid manifestations of the disease, representatives of the weaker sex are often found. When a human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk settles and successfully develops in the “host” body, a person observes the following symptoms:
- formation of warts on the mucous surface and skin;
- vaginal bleeding or unusual discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen, in the vagina during and after sex;
- bad feeling;
- transformation of the tissue structure of the cervix, inflammation (identified during a visual examination by a gynecologist).
Subject to the presence of provoking conditions (weakened immune system, injuries, promiscuity), the process of degeneration of benign cells is observed. A malignant wart begins to form. Over time, warning signs may appear:
- dark color of papilloma;
- uneven base, inflammation in the affected area;
- visualization of hardened crusts on formations;
- rapid tumor growth.
Sometimes the indirect presence of oncogenic HPV strains in the body is caused by diseases transmitted through unprotected sexual contact. These types of infections are significantly larger in size than the virus being described, so it can attach to various sexually transmitted infections and together with them achieve its intended goal.
Other signs of pathology in both sexes
Highly oncogenic types of HPV, present in a woman’s body, have a huge impact on the condition of the patient’s reproductive system. The following are specific symptoms:
- heavy periods, accompanied by an unpleasant clinical picture (pain in the lower abdomen, chest, lower back, etc.);
- unscheduled appearance of blood from the vagina in the middle of the menstrual cycle;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes, ectopic development of the fetus;
- disturbances in the functioning of the ovaries;
- infertility.
Against the background of the mentioned symptoms, cervical dysplasia develops.
As a reaction of the male body to the invasion of viral particles, multiple papillomas on the penis, pain and a burning sensation appear. Characteristic symptoms manifest themselves more clearly during intimacy and during hygiene procedures.
HPV type 52 in women - what kind of infection is it?
The formation of warts on the body of people is caused by HPV or human papillomavirus entering the body. These diseases have been known to mankind since ancient times, however, doctors began studying them relatively recently, after it became known that some of them can cause cancer.
What is this
HPV, or human papillomavirus, is a common type of infection. It is transmitted mainly during sex. The main danger of this infection is the high probability of its mutation into cancer.
There are about 120 different types of virus. Less than half have been studied. In total, there are three groups of viruses, depending on how often they are capable of causing cancer:
- HPV with a high risk of cancer;
- HPV with low risk of cancer;
- non-oncogenic HPV.
The first type includes HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68. The second type includes HPV 6, 11, 42, 43, 44. The third type HPV includes types 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 27, 53, 54, 55, 62, 67.
The virus itself does not have a large or serious impact on a woman’s health, since it manifests itself differently from other viral infections.
Sometimes there is a chance of getting an infection during a kiss, along with saliva. Thus, the disease manifests itself in the form of various types of rashes and condylomas in the mouth or throat.
There is a high probability of transmission of infection from mother to child. This happens during natural childbirth. This type of infection is not transmitted through household means.
HPV type 52 belongs to a large group of human papillomaviruses. There are more than 100 species in total, among which doctors separately distinguish the oncogenic category. These viruses are dangerous because they can cause cancer, primarily in women. It is with their activity that the World Health Organization associates 70% of cases of cervical cancer.
Routes of infection
Human papillomavirus type 52 is anogenital - it is activated on the genitals and in the anus. The main route of infection is unprotected sexual contact with a carrier of the infection.
A girl can become infected already during her first sexual contact. This happens especially often if sexual activity begins at an early age (before 16 years).
It is extremely rare that the virus can be transmitted through household items, personal hygiene products, etc.
The peculiarity of HPV type 52, like other papillomaviruses, is that most infected people are carriers of the infection, and the disease itself does not manifest itself in them. This is associated with the rapid spread of the virus - the infected person does not know that he poses a threat to his sexual partner.
Infection occurs in 60% of cases. In almost 90-95% of men, the virus does not manifest itself, but for women it poses a threat because it can cause dysplasia and cervical cancer.
Development of the disease
The virus affects the epithelium of the cervix and cervical canal, gradually leading to cell degeneration. At this stage, dysplasia is diagnosed, depending on the extent of the process, stage 1, 2 or 3.
HPV 52 DNA invades healthy cells, integrates into the genome and modifies them, turning them into cancer cells. At this stage, a woman is diagnosed with oncology, often the process covers large areas of the internal genital organs, and metastases appear throughout the body.
The entire process from the onset of dysplasia to cancer takes 10-20 years. In 32% of women diagnosed with stage 1 cervical dysplasia, the process of spreading the pathology stops and does not develop further.
The disease progresses under favorable conditions – weakening of the immune defense. The virus often becomes active after the age of 35, and during menopause the active growth of the tumor begins. This is due to hormonal changes and the aging process. Other provoking factors include:
- Chronic diseases of the genitourinary system, inflammation, candidiasis.
- STD.
- Abortions and miscarriages.
- Poor nutrition.
- Bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs).
- Congenital and acquired immunodeficiencies.
- Prolonged illnesses with a long (2-4 months) rehabilitation period.
Symptoms of the disease
What is the danger of strain types 16 and 18
When serotype 16 or 18 of the papilloma virus is detected in a woman’s body, the doctor is obliged to warn the patient that she has an increased risk of developing dysplastic processes in the uterus, vagina and other organs of the pelvic area.
That is, there is a risk of developing cancer. Strains 16 and 18 settle and multiply in the cervical canal and penetrate into the deep layers of the mucous membranes of the woman’s genital organs.
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of virus development:
- First stage . Incubation stage. HPV is in a woman’s body, but is not activated. Depending on the strength of the immune system, the virus remains in this dormant state for anywhere from two weeks to 10 or more years. Aging of the body, the presence of various diseases and other provoking factors reduce the body’s resistance, and the virus enters the second stage.
- Second stage . Stage of clinical manifestation. The virus begins to actively multiply, which leads to visible skin changes. Round, pointed, flat, pedunculated, rough, smooth, and so on new growths appear. They can be localized on the eyelids, lips, mucous membranes.
- Third stage . Stage of tissue dysplasia. The DNA of the virus is integrated into the cellular genome and destroys a healthy cell. This process is irreversible, which means that the tissue structure changes irrevocably.
- Fourth stage . Stage of appearance of cancer cells. Under the influence of HPV, DNA mutates, and an invasive form of oncology develops.
Types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and methods of its diagnosis
In order to diagnose human papillomavirus in the patient’s body, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Examination of the patient reveals the presence of warts on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Women undergo colposcopy, histological and cytological analysis of a smear from the cervix, which makes it possible to isolate the virus in the cells of the genital organs.
- Histological analysis of papilloma or condyloma tissue.
- PCR is a polymerase chain reaction that allows for the most accurate typing and determination of the oncological danger of the virus.
Colposcopy with histological analysis of the smear is prescribed for women with dysplasia or erosion of the cervix (detected during a gynecological examination).
Histological examination reveals the presence of specific cells, larger than the cells of healthy cervical epithelium.
Cytological examination reveals the number of changed cells, but does not specify the cause of the changes. Smears are classified according to their purity:
- Class 1-2 - practically no modified cells were found;
- Class 3 - there are modified cells, additional studies are required to clarify the diagnosis;
- Class 4-5 - many modified cells, with a high degree of probability a malignant tumor can be assumed.
Virus typing is best done using PCR - this is the most accurate technique. It allows you to identify all known forms of the virus, so its positive result can indicate not only the risk of developing cancer, but also the presence of relatively harmless infections that can heal themselves. For greater reliability, experts recommend testing for 15 types of the virus.
Treatment
Once infected with the papilloma virus, a woman will have to live with it for the rest of her life. The fact is that it is impossible to eliminate the papilloma virus; treatment of the pathology is aimed only at suppressing its activity.
Conservative therapy:
- Panavir is an antiviral drug that helps inactivate HPV.
- Viferon is a remedy that understands immunity.
- Isoprinosine - eliminates the symptoms of HPV and helps reduce the activity of the virus.
- Genferon – prevents the spread of the virus throughout the body.
In addition, the following are assigned:
- Epigen intimate is a spray to relieve inflammation, itching and burning in the genital area.
- Verrukacid is a means for cauterizing papillomas, used only by a doctor.
- Solcoderm is an acid that removes growths.
- Cryopharma - freezes the growth, as a result of which it falls off on its own and leaves no traces behind.
- Super celandine is a harmless product used to cauterize papillomas, but it must be used very carefully so as not to damage healthy tissue.
Surgical removal of papillomas can be carried out in the following ways:
- Cryotherapy is a painless and reliable removal of papillomas using liquid nitrogen.
- Laser therapy – does not leave scars, the laser action limit is well controlled, the procedure is painless.
- Electrocoagulation does not affect healthy tissue areas, so it can be used for small tumors.
- The radio wave method is a quick procedure that completely eliminates the possibility of infection.
- Surgical intervention - removal with a scalpel. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
How is the analysis for papillomavirus performed?
The human papillomavirus (HPV) can exist in the body for a long time, manifesting itself only when the immune defense is weakened. To detect infection, various types of tests are used to detect the disease at an early stage and provide effective treatment.
Decoding the HPV analysis allows you to confirm or refute the presence of infection. The papilloma virus is one of the most common pathogens on the planet.
There are more than a hundred varieties of the virus, most of which provoke the appearance of condylomas on the genitals. The mucous membranes are often affected.
Some types are completely harmless to the body, others are highly oncogenic and provoke the development of cancer.
Medical indications
There are several ways to detect infection in the body. A referral for quantitative HPV analysis is issued by a gynecologist, urologist, or dermatologist if there is any suspicion during the examination. The specialist himself chooses the examination method.
Modern techniques make it possible not only to confirm the very fact of the presence of papilloma in the blood, but also to determine the concentration of the virus, the type and danger to the body.
According to recent studies, more than 80% of the young population of the entire Earth are carriers of human papillomavirus infection (PVI). At the moment, several diagnostic methods have been developed that make it possible to determine HPV indicators with maximum accuracy.
What types of HPV tests are there?
The most common types of examination for papillomavirus today are PCR (polymerase chain reaction) analysis and Digene test. The efficiency of HPV detection is 100%. The material for these studies is urogenital scraping.
These techniques allow not only to differentiate the type of virus present in the body, but also to determine the stage of development of the disease and formulate predictions for its course. Normally, the amount of HPV is not determined during these laboratory tests.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics will help identify the progressing virus in the body
In order to accurately determine the type of papilloma virus and prescribe effective treatment, the patient must undergo procedures such as:
- Colposcopy. It is carried out if there is a suspicion of the formation of papillomas on the female genital organs. The technology allows you to examine the mucous membranes, magnifying the picture several times, and notice the smallest defects in the tissues.
- Cytological method. Based on examination of a smear using a microscope.
- Histological examination. Involves taking a small sample of tissue to examine it using a microscope.
- HPV tests. At the moment, there are several highly accurate tests that can accurately determine the presence of HPV in the human body. We are talking about tests such as PCR, Digene test, as well as laboratory tests aimed at detecting antibodies to papillomavirus.
How is the human papilloma virus (causative agent) transmitted?
Hello. We are glad to see you on our website. Today we will tell you how the human papillomavirus is transmitted and how you can become infected with it.
The largest number of human diseases are viral in nature. More than a thousand viruses are known, of which the human papillomavirus occupies a special place.
Next, we will look at how the pathogen is transmitted, its characteristics, and the spread of the human papillomavirus in the population.
But let’s move a little away from the topic and I want to advise you to definitely read one book from which you will learn about ways to combat the disease using effective folk recipes. Details on this page.
What is a virus?
This is a very common pathogen that is easily transmitted and therefore can be found in almost every person. Most of the total number of virus types (more than 100) are causative agents of skin diseases.
Preventive measures and prognosis
Since medical science knows what an oncogenic virus is and what consequences the development of pathology in the body can lead to, scientists have developed a vaccine that provides protection against the virus. This drug is called Gardasil. The vaccine is used against viruses of types 16, 18, 11 and 6. The medicine helps the body develop immunity to diseases of this type. There are currently no alternative preventive measures against such viral particles.
Experts can only give some recommendations that will reduce the risk of being infected with any infection (even non-oncogenic). These tips include:
- observe the rules of genital hygiene, do not neglect appropriate measures in public places;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle to support your immune system;
- include fresh vegetables and fruits in your menu;
- have a measured sex life, be selective about your partners, protect yourself with a condom;
- Get vaccinated on time and visit a specialist regularly.
In conclusion, we formulate the main conclusions arising from the above information.
The human papillomavirus lives in the body of almost every person. HPV of low oncogenic risk and high risk are distinguished. In the first case, the virus provokes the formation of papillomas on the patient’s body and mucous membranes, which happily “live” in tandem with the “host” without causing cancer. In the second, we are talking about the likelihood of transforming a benign growth into a malignant tumor, which can lead to the patient’s death.
Most often women suffer from HPV ; the clinical picture in the fair sex is also more pronounced. When a person contacts a specialist, a number of diagnostic measures are carried out to determine the type of virus, its oncogenicity and viral load. Depending on these indicators, the doctor chooses a specific therapeutic direction. Possible methods of treating papillomas include: drug therapy, traditional medicine, radical treatment of warts on the body and mucous membranes.