Human papillomavirus infection is a fairly common problem that many people face, regardless of gender and age. It is worth saying that human papillomavirus is a term that combines more than 70 types of virus (each of them has its own specific characteristics). HPV 16 is considered one of the most dangerous today. That is why many people are interested in additional information about this type of disease. How is the infection transmitted? How does the virus affect the body? What signs can be used to determine the presence of papilloma virus? Are there effective treatments? The answers to these questions will be useful to every reader.
What is HPV?
Human papillomavirus is a large group of viruses that belong to the papillomavirus family. Modern medicine knows a huge number of different strains of this virus, each of which has its own unique DNA. HPV type 16 is just one of many types.
This infection is extremely common. Recent studies have shown that more than 60% of the world's population are carriers of one or another strain of papilloma.
This infection usually affects skin tissue and mucous membranes. But it is worth noting that any external manifestations are rarely present. Moreover, most strains do not pose a real threat to human life. However, among them there are species with increased oncogenicity - it is this group that HPV 16 belongs to. The presence of this virus in the body increases the likelihood of developing cancer.
By the way, the group of viruses with a high degree of oncogenicity also includes other strains, including 18 and 31. But, according to research, HPV type 16 in women most often leads to cancer of the genital organs.
HPV types 16 and 18, what is it?
The peculiarity of papillomatous infection is the ability to form epithelial neoplasms growing in the tumor. Tissue damage and the type of changes in the epidermal layers are multiple in nature: from papillomatous lesions on the skin to dysplasia of the mucous membranes.
Neoplasms in themselves are not dangerous to life and health, however, with a burdened heredity or with a persistent decrease in immunity, the risk of malignancy of cells and destructive processes in the mucous membranes of the organs of the reproductive system increases.
Viral human papilloma in women type 16
Viral strains of type 16 are dominated by proteins with oncoprotein compounds E9 and E6. Such microparticles, under the influence of contributing factors, inactivate intracellular immunity and increase the risk of cancerous transformation of cells.
Under the influence of genetic instability, oncoproteins in type 16 strains promote mutations and cause cancer of the uterine cavity and cervical canal.
Dysplasia or neoplasia in the mucous membranes of the uterine cavity and cervical canal are caused by a disruption of the structure of the epithelial layers and proliferative changes in cellular structures at the DNA level.
Viral strain type 18
Human papillomavirus type 18 is more common in women and contributes to the development of genitourinary infections. The pathogenic activity of viral strains is usually observed in a combination of 18 and 16 types of virions. Virions penetrate the mucous membranes and surface of the skin, gradually changing the structure of epidermal cells. Find out what papillomas look like in women here.
Viral infections of types 18 and 16 are oncogenic and enter the body through the blood or seminal fluid. Unprotected sexual contact is the main and common route of transmission.
Note ! The infection is transmitted from man to woman as a result of unprotected sexual contact. Unfortunately, even the use of barrier contraception does not protect against infection.
Routes of transmission of the virus
Many people are interested in questions about how exactly one can catch such an infection. In fact, there are several ways of transmission of HPV type 16 (as well as any other strain):
- The most common method of transmission is sexual transmission, which occurs during sexual intercourse without using a condom. By the way, anal and oral contacts are also dangerous.
- Household transmission of infection is also possible, although this is much less common. From the damaged skin and mucous membranes of an infected person, viral particles fall onto household items, in particular, bed linen, towels, clothes, etc. When used together, the infection can enter a healthy body through skin lesions, including scratches, sores, etc. d.
- The placental route of infection is quite often observed. If the mother is a carrier of the virus, then the likelihood of transmitting it to the child during childbirth is very high. This is why HPV 16 is considered a serious problem among pregnant women.
- Self-infection is also possible when the virus enters the human body again and again during shaving, hair removal, etc.
Are there risk factors?
As mentioned earlier, the human papillomavirus is extremely common. However, some people are more susceptible to this infection than others, especially when it comes to household infection. So what can be considered risk factors?
- The risk group primarily includes people who began sexual activity too early.
- HPV 16 is most often diagnosed in people who are promiscuous, as well as in those who have several sexual partners at the same time and do not use condoms.
- Risk factors also include anal intercourse, during which the likelihood of damage to the mucous membranes and skin is much higher.
- The presence of sexually transmitted diseases, including trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, also increases the risk of contracting the virus, since the person’s immune system is weakened.
- However, any diseases accompanied by weakened immunity are considered risk factors (HIV infection, diabetes, chronic inflammatory diseases).
- This list also includes people with cancer who are undergoing radiotherapy or chemotherapy, or taking medications that suppress the immune system.
- HPV 16 is also diagnosed more often in women who have undergone any serious gynecological procedures, including abortion.
It is worth noting that the presence of all the risk factors described above not only increases the likelihood of infection of the body, but also increases the likelihood of developing an infection. The papilloma virus can live in the host’s body for many years without causing any harm, since its activity is strictly controlled by the immune system. Against the backdrop of weakening protective forces, the possibility of developing a disease with the manifestation of external symptoms cannot be ruled out.
Stages of the disease
HPV 16, like any other type of human papillomavirus infection, occurs in several stages. Modern medicine identifies four main stages in the development of the disease:
- The first stage is called latent. It can last from several weeks to several years without causing any external signs. The presence of the virus in the body can only be determined using PCR diagnostics.
- At the second stage, symptoms can already be seen with the naked eye. This stage is accompanied by active reproduction of the virus and accelerated division of epidermal cells. The result of such processes is the formation of various growths on the skin and mucous membranes, including warts, papillomas, condylomas, etc.
- The third stage is characterized by dysplasia processes. During this period, HPV type 16 DNA interacts with the genetic material of human cells, resulting in the introduction of the viral genome into the normal DNA of the cell. Thus, a change in cellular structure occurs.
- Integration of viral DNA increases the likelihood of further development of various mutations. The fourth stage is considered to be the period of malignant degeneration of cells and the formation of cancer.
Symptomatic manifestations
Human papillomavirus infection often occurs in a long-term latent form and does not manifest itself for years. From time to time, some rashes are possible, which are also capable of self-amputation and destruction.
Clinicians identify the main 4 stages of development of the infectious process:
- Compensatory stage or incubation . The virus is already present in the body, but immune forces stop its pathogenic activity. Within a year, the human body is able to defeat any infectious environment.
- The appearance of the first symptoms . The most sensitive areas of the skin to the pathogenic activity of viral microflora are the delicate areas of the skin, therefore papilloma is localized in the intimate area of women, on the eyelids, in the oral cavity and on the organs of the woman’s reproductive system.
- Dysplastic changes . Mucosal dysplasia occurs due to the deep penetration of viruses into the DNA of healthy cells, which gradually atrophies the normal function of the epidermal layers. Against this background, pathological growths develop in the form of papillomas, condylomas, and wart structures.
- Oncogenic transformations . Oncological diseases arise against the background of irreversible changes in the skin. Cancerous changes in the skin inhibit the functionality of healthy tissues, and an invasive form of oncology develops.
With papillomatosis of the vagina, cervical canal and uterus, the functions of the genitourinary system are disrupted, pain occurs during sexual intercourse, and discomfort occurs when urinating. Women feel bad breath and observe atypical discharge.
What are the symptoms of the virus?
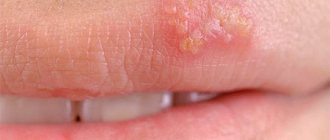
As mentioned earlier, active reproduction of the virus and accelerated cell division leads to the formation of various skin growths, popularly called warts. These skin growths can have different shapes, sizes and even colors. In modern medicine, it is customary to distinguish several main types:
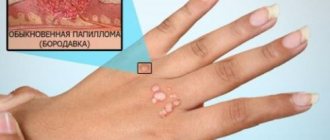
- Flat (vulgar) warts are dense skin formations, most often round in shape. They do not cause pain or any other discomfort other than aesthetic ones. Typically, these growths form on the skin of the arms, legs, face, palms and soles. The color of warts matches the skin tone. Quite often, such neoplasms appear and disappear on their own.
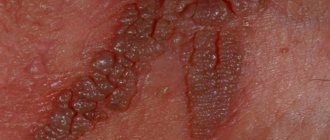
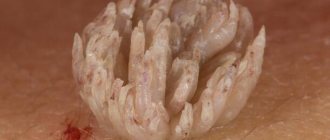
- Condylomas acuminata, more commonly known as genital warts, are raised skin growths with jagged edges - shaped like a cauliflower. They may have a pinkish color or match your natural skin tone. As a rule, condylomas appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, for example, on the foreskin or around the head of the penis, on the labia. Sometimes such neoplasms appear in the urethra, vagina, and bladder.
What is the danger of the virus?
Sometimes HPV type 16 leads to the development of a disease known as bowenoid papulosis. This disease is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic rashes that look like compacted plaques, slightly rising above the surface of the skin. Such formations may be pink, yellowish or even white. As a rule, rashes appear on the skin of the thighs, in the area of the external genitalia, and less often around the anus.
Bowenoid papulosis indicates the process of dysplasia and the appearance of cellular mutations, which, accordingly, increases the risk of developing cancer. This is why type 16 papillomavirus is considered so dangerous.
Also, this strain of the virus in men can trigger the development of Bowen's disease, which most often ends in penile skin cancer. In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, the disease can metastasize to other organs.
Human Papillomavirus 16/18 (HPV 16/18), DNA [real-time PCR]
A study to identify the causative agent of papillomavirus infection types 16 and 18 (Human Papillomavirus 16/18), during which the genetic material (DNA) of the papillomavirus is determined using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method in a sample obtained from the urogenital tract or in a biopsy.
Synonyms Russian
Human papilloma viruses types 16 and 18, human papilloma viruses types 16 and 18, HPV 16, 18.
English synonyms
Papillomavirus hominis 16, 18, DNA.
Research method
Real-time polymerase chain reaction.
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Urogenital smear (with prostate secretions), rectal smear, oropharyngeal smear.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Women are advised to take a urogenital smear or urine test before menstruation or 2 days after it ends.
- Men should not urinate for 3 hours before submitting a urogenital smear or urine test.
General information about the study
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a collection of about 100 related viruses. Some types cause skin warts, while others can cause sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and genital warts. It is most common in young women and men, with the main route of spread being oral, anal or vaginal sex. Although most viruses from this group are not very dangerous to human health, there are, however, several types of papilloma (for example, HPV-16, -18, -31, -33, -35, -39) that can be dangerous to health. Usually they are not accompanied by visible changes, but, being in the epithelium, they can cause cervical cancer, as well as other, less common tumors, such as cancer of the vagina, mouth, throat, penis and anus. The HPV test detects the DNA of specific viruses associated with a high risk of cancer. In addition, there are low-risk viruses that cause warts.
Genital HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases in the world.
What is the research used for?
DNA testing for HPV has become widespread as an additional tool in determining the risk of cervical cancer. A cytological examination (smear with Papanicolaou staining) is used directly to diagnose cervical cancer, when atypical epithelial cells are detected, which may be a herald of tumor development.
This is interesting: How to cure HPV type 16 forever
When is the study scheduled?
The test is prescribed to women over the age of 30 years who are at risk of HPV infection, as well as women over 21 years of age who are at risk for HPV infection and have cytologically detected atypical squamous cells of unknown significance.
Men who are at risk of contracting HPV can also be tested.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: negative.
- The presence of genetic material of HPV types 16 and 18 in the test sample.
- The absence of genetic material of HPV types 16 and 18 in the test sample means HPV infection is unlikely.
If the Pap smear shows cytological changes and the PCR test is negative, further monitoring is required, as is the case with a negative cytological examination and a positive PCR test.
Important Notes
A positive PCR result does not indicate the presence of cervical cancer or its inevitable appearance, it only allows one to assess the risk of developing the disease.
Also recommended
- Human Papillomavirus 31/33 (HPV 31/33), DNA [real-time PCR]
- Human Papillomavirus 6/11 (HPV 6/11), DNA [real-time PCR]
- Human Papillomavirus, DNA quantitative [real-time PCR]
Who orders the study?
Therapist, general practitioner, gynecologist, urologist, infectious disease specialist.
HPV type 16 in women and its features
This virus is dangerous for both sexes. However, according to statistics, HPV type 16 is found much more often in women. Treatment, signs, prevention - all these questions are extremely interesting. But first, you should find out exactly what risks this infection is associated with.
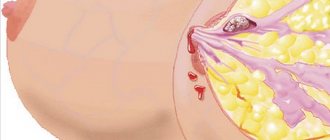
Note that condylomas in women often appear on the inner walls of the vagina or the mucous membrane of the cervix, so the patient simply cannot notice them on her own.
HPV 16 and 18 in women often leads to the development of so-called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, which is accompanied by accelerated cell division of the cervix. This condition is regarded as precancerous. In the absence of timely treatment, and sometimes even with therapy, the infection can lead to the development of cervical cancer.
How HPV infection leads to cervical cancer
In women with a normal immune system, cervical cancer develops within 15-20 years
Although most HPV infections and precancerous conditions go away on their own, all women are at risk for HPV infection to become chronic and for precancerous conditions to develop into invasive cervical cancer.
In women with a normal immune system, cervical cancer develops within 15-20 years. In women with weakened immune systems, such as those with untreated HIV infection, it may take only 5-10 years to develop.
Modern diagnostic methods
The presence of skin growths or formations on the genitals should suggest the possibility of infection with HPV type 16. What to do in such cases? Of course, you need to go to the doctor. What diagnostic methods are used in modern medicine? There are several basic procedures that will help determine the presence of the papilloma virus.
- A basic examination, during which the doctor examines skin tumors, collects anamnesis, etc.
- Colposcopy is prescribed to women for a more thorough examination of the cervix for the presence of viral lesions.
- Cytological studies, which consist of laboratory examination of tissue taken during scraping (for example, from the cervical canal). This test helps determine the presence of abnormal cells.
- PCR diagnostics are quite accurate, which makes it possible to detect the genetic material of the papilloma virus in almost any material, including scrapings from mucous membranes, tissue of warts and condylomas.
Diagnostics and tests for HVP 16
A visual examination by a gynecologist does not allow detection of HPV strain 16 in the latent stage; even symptoms in the subclinical period may be mild. In order to see new formations, you will have to use special equipment - a colonoscope, as well as take a tissue biopsy to determine their nature.
There are other effective methods for diagnosing human papillomavirus genotype 16. The materials for analysis are vaginal smears or scrapings selected by a specialist. The smear may undergo one of several types of examination:
- Polymerase chain reaction . Confirms the presence of DNA of a given type of virus in the body. Such an analysis will show the presence of even “conserved” structures. If the test is negative, it is recommended to re-screen after 3 years.
- Hybrid capture method and Digen test . It allows not only to detect the presence of infection, but also to find out the degree of its concentration in the body, and this in turn provides information about the likelihood of developing cancer.
- Papanicolaou test . Detailed examination of a smear from the cervix using stained prints. The test helps determine the current state of the reproductive organ, the degree of development of dysplasia or carcinoma.
On average, examination and laboratory tests will take up to a week. Only after an accurate diagnosis of “papilloma virus 16 in a man or woman” is treatment prescribed.
- Read about treating papillomas with folk remedies at home
HPV 16: treatment
After making a diagnosis, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen. Under no circumstances should you try to cope with the problem on your own, especially if we are talking about HPV 16. Treatment is extremely important and can only be entrusted to an experienced specialist.
This infection is quite difficult to treat. However, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing cancer. So what does the treatment process look like after being diagnosed with HPV 16? Treatment includes several important points - strengthening the immune defense, reducing the activity of the virus and removing existing growths.
So, patients with a similar diagnosis are primarily prescribed antiviral drugs. Inosiplex is considered to be quite effective, as it suppresses the proliferation of viral particles. Interferons, in turn, have antiviral, immunostimulating and antitumor properties. Patients are often prescribed drugs such as Amiksin and Cycloferon, which activate the body’s production of its own interferons. Also, the treatment cycle may include drugs that suppress the division of cells already affected by HPV. Podophyllin and Condilin are considered effective.
Treatment of HPV 16 in women also includes regular gynecological examinations and repeated tests until the activity of the virus is suppressed. Naturally, sick people are advised to have proper nutrition, sleep and rest patterns, and physical activity, since all this strengthens the immune system and, accordingly, accelerates the healing process.
What to do if you have been diagnosed with HPV 16? How to live further? With proper therapy, the risk of developing cancer is minimal. And if you undergo regular examinations, cancer can be diagnosed at an early stage, which gives a good chance of a favorable outcome. By the way, carriers of the virus should not have unprotected sex - using a condom is mandatory.
Methods for removing warts and other skin growths
Quite often in modern diagnostic practice, HPV type 16 is diagnosed in women. Treatment often includes not only antiviral therapy, but also removal of existing skin lesions. The fact is that condylomas on the genitals (in both men and women) are often injured during sexual intercourse. This creates a lot of inconvenience and increases the likelihood of secondary infection of tissues by fungi and bacteria. There are several ways to remove genital warts:
- Exposure to chemically aggressive substances (an effective and accessible technique, but when treating the delicate skin of the genital organs, damage to healthy tissues is possible).
- Surgical removal of tumors.
- Electrocoagulation (exposure to condylomas with electric current).
- Radio wave coagulation (excision of growth using a radio wave knife).
- Cryodestruction (exposure to liquid nitrogen).
- Laser therapy (removal of condylomas using a laser beam; today it is considered one of the fastest, most effective and safest methods).
The decision to remove condylomas and the choice of the appropriate technique is the task of the doctor. You should not try to get rid of growths on your own, as this can only worsen the situation.
Features of papillomavirus
Photo of the manifestation of human papillomavirus
- Human papillomavirus type 16 is more dangerous for women, although in men it can cause serious complications, including cancer of the penis or bladder;
- The worst consequence of human papillomavirus type 16 in women is cervical cancer;
- Any type of HPV, including genotype 16, remains in the body forever. Therefore, symptoms can appear throughout your life;
- Each type of virus remains in a latent state for some time - the so-called incubation period;
- Initially, strain 16 viruses do not infect the DNA of epithelial tissues. Negative and dangerous processes begin only when the body is exposed to provoking factors;
- Human papillomavirus infection or HPV can penetrate the genetic structure of cells and change their functioning. This causes disturbances in the division and growth of pathogenic cells, which ultimately form a cancerous tumor;
- The fact of detection of papillomavirus type 16 does not mean a death sentence for cancer. This strain of HPV only increases the likelihood of cancer cells forming;
- Transmitted HPV 16 during pregnancy is dangerous for the fetus, since it can infect the baby in the womb or directly during childbirth;
- To a greater extent, strain 16 is transmitted sexually, although other routes of transmission of the virus are also possible;
- The main danger of this human papillomavirus is reproductive dysfunction or its complete loss. In advanced stages, the cervix has to be removed, which makes pregnancy impossible. Pregnancy may also be impossible in advanced stages of the disease in men who lose the ability to procreate.
Considering the degree of danger that this type entails, the virus needs timely and most effective treatment. Otherwise, not only your pregnancy will be at risk, but also your life.
Routes of infection with HPV
Photo of what manifestations of the human papillomavirus look like
Currently, it is impossible to get rid of any type of papillomavirus forever. But many people manage to suppress the activity of the disease by constantly monitoring their own health. This does not mean that you will now have to spend your entire life on medications or diets. It is quite possible to maintain a good immune system by leading a normal lifestyle.
What is HPV or HPV? This is the human papillomavirus or papillomavirus, the main form of which is warts. Sometimes HPV is accompanied solely by cosmetic defects. A number of papillomas are completely safe from the point of view of the risk of developing cancer cells. Others, such as strain 16, are dangerous precisely because of their high level of oncogenicity.
It is difficult to protect yourself from papillomavirus entering the body, since there are several ways HPV can enter the body:
- Sexual. Most often, the 16th strain of the virus penetrates precisely due to sexual contact. Frequently changing partners and ignoring protective equipment only increases the likelihood of infection;
- Contact and household. Microorganisms are transmitted through various contacts with people or objects that have the virus. The human papillomavirus can penetrate even through microcracks in the skin;
- Vertical. Pregnancy with HPV is also dangerous because the papillomavirus can be transmitted from mother to child. Infection of a baby during childbirth is called vertical;
- Autoinfection. A person can infect himself. This usually occurs when basic hygiene standards are not observed.
Are there effective methods of prevention?
Surely today many people have heard about HPV type 16. Treatment and diagnosis of such a disease, its first manifestations and routes of transmission are, of course, extremely important issues. But it is no less useful to learn about means of prevention, because sometimes it is much easier to protect yourself from infection than to then worry about treatment and possible consequences.
To begin with, it is worth noting that there is a specific prevention of human papillomavirus infections, which consists of vaccination. Such vaccines (the most well-known and tested to date are Gardasil and Cervarix) contain fragments of viral DNA. Upon entry into the body, the formation of stable immunity to this infection is observed. Vaccination protects against the most dangerous strains, including types 16 and 18.
In addition, there are nonspecific methods of prevention. You must undergo a medical examination at least once every six months. It is worth giving up promiscuity and be sure to use a condom as protection. And, of course, proper nutrition, physical activity, timely treatment of sexually transmitted infections and inflammatory diseases will strengthen the immune defense, thereby reducing the risk of infection and activation of the virus.