Discharge from the nipple, pain, discomfort, an unknown lump in the mammary gland - if you notice such symptoms, you need to visit a mammologist, but there is no need to sound the alarm and panic ahead of time. It is quite possible that this is not cancer, but a benign neoplasm, for example, intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland. It does not grow into neighboring tissues, does not metastasize and is not life-threatening. Although, sometimes it increases the risk of cancer in the future.
Our expert in this field:
Alimardonov Murad Bekmurotovich
Gynecologist-oncologist, Ph.D.
Call the doctor
What do modern scientists know about intraductal papilloma? This is a benign neoplasm on the wall of the mammary duct. Why it occurs is not known. There are considerations that hormonal imbalances in the body are to blame. Most often, the disease occurs in women aged 35–55 years.
Intraductal papillomas can be single or multiple. Papillomatosis is often included in the same group with papillomas, a condition in which pathological proliferation of cells occurs in the milk ducts.
Reasons for the formation of the disease
The formation of intraductal papilloma may be associated with obesity.
The causes of papilloma in the thoracic duct are usually associated with changes in hormonal levels, which can be triggered by:
- frequent abortions;
- obesity and other endocrine disorders;
- consumption of alcohol and nicotine;
- inflammatory diseases of the ovaries, infertility;
- stress and frequent emotional tension;
- treatment with hormonal drugs and frequent use of contraceptives;
- surgical interventions in the breast area;
- refusal to breastfeed after the birth of a child.
The main symptom of papillomas is discharge from the nipple
The first symptoms of intraductal papilloma of the mammary glands are observed at the second stage of the disease. Gradually they intensify. The characteristic signs of Mintz disease are:
- copious discharge when squeezing the mammary gland, which has a transparent or yellowish tint;
- breast swelling develops, which intensifies as the tumor grows;
- the pain increases if you touch the mammary gland;
- the skin of the breast becomes red due to changes in blood vessels.
At first, the symptoms of Mintz disease occur occasionally, may intensify during menstruation and completely disappear after them. However, as the disease progresses, they become more frequent. Patients often complain of malaise and high temperature that occurs out of the blue.
Clinical manifestations
The main clinical symptom of a woman having intraductal papilloma is the presence of bloody discharge from the nipples. This process occurs in the midst of complete well-being and intensifies during the premenstrual period.
Experts explain this condition by the fact that intraductal papilloma has a fairly loose consistency and is easily damaged even with a slight mechanical impact on the female breast. The papillary bundles are separated from the base of the tumor, the vessels begin to bleed, and bloody discharge flows through the milk sinuses into the nipple of the affected mammary gland. Among other things, constant local hemorrhages can lead to inflammatory processes in the mammary gland, and treatment of non-lactation mastitis is usually protracted.
The severity of bleeding from the nipples can vary, but most often the blood is released on its own in the form of a few drops or even a stream. In some cases, to obtain discharge, it is necessary to squeeze or massage the mammary gland. Combat syndrome during bleeding is weakly expressed; women complain of pain in the chest or in the area of the areola in the presence of crusts from coagulated blood in the nipple area. Another cause of pain with ductal papilloma is the accumulation of secretory fluid and blood clots in the altered ducts under the influence of fibrocystic mastopathy.
We recommend reading the article about breast ductectasia. From it you will learn why pathological dilatation of the milk ducts occurs, how ductectasia manifests itself, what complications can arise, and how this disease has been treated in recent years.
Signs of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland and methods of its treatment
One of the characteristic symptoms of the disease is the appearance of discharge from the nipples, the intensity of which increases with compression of the breast. Transparent discharge can be colorless or have different shades. Reddish discharge appears due to disruption of the structure of blood vessels in the area of the tumor.
Intraductal papilloma resembles a soft, pedunculated wart. Its twisting leads to damage, blood entering the ducts, as well as tissue necrosis. The size of papillomas ranges from 2 mm to 2 cm. Large papillomas can sometimes be felt. There is a slight enlargement of the breast due to swelling that occurs when the tissue in the area of the papilloma becomes inflamed.
Benign breast formations should not be considered not dangerous to health. Some of them, for example intraductal papilloma, under certain circumstances degenerate into cancer, so treatment of such formations must be carried out in a timely manner.
Intraductal papilloma is a growth formed from the epithelial cells of the milk ducts of the mammary gland. This benign neoplasm has other names - cystadenopapilloma, papillary cystadenoma.
Visually, the papilloma located inside the duct is similar to a cystic growth; in advanced cases, areas of necrosis and areas with hemorrhages are detected around the tumor. Inside the papilloma there is a secretion with blood; the walls of this formation are quite fragile and therefore any, even the most minor injury can lead to damage.
Injury to the tumor ends with the release of ichor or even a large amount of blood from the nipple.
Intraductal papilloma can be single (solitary) or a woman develops multiple cystic growths in the milk ducts. A large number of papillomas increases the risk of their degeneration into a malignant tumor.
The size of intraductal papilloma varies greatly; in some patients, during examination, a formation of several millimeters is found, in others, the papilloma grows to several centimeters.
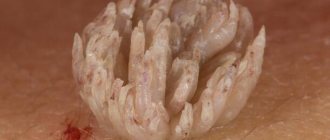
The photo shows a removed intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland
Papillomas located deep in the mammary gland do not change the external shape of the breast; it is possible to understand that atypical changes are occurring in the mammary gland only by the appearance of various discharges from the nipple itself.
There are no age restrictions on the possible formation of papillomas in the ducts of the mammary glands. Often this pathology is detected in teenage girls and women who have entered the postmenopausal period.
But still, most women with intraductal papillomas are identified after 40 years of age; after this age, natural changes occur in the breasts, increasing the risk of any neoplasms.
Reasons for development
The primary reason leading to the appearance of papillomas in the ducts of the mammary gland is a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body.
A similar shift in the body occurs in a number of diseases and under the influence of provoking factors; this group of hormonal disorders includes:
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases in the appendages - oophoritis, adnexitis.
- A history of multiple abortions and surgical procedures on the appendages and uterus.
- Obesity.
- The influence of long-term negative stress.
- Ovarian dysfunction.
Examination of patients with cystadenopapillomas made it possible to establish a risk group, which includes:
- Women with a hereditary predisposition to benign and malignant breast tumors.
- Smoking patients.
- Nulliparous women.
The disease is least often diagnosed in those women who have given birth repeatedly, breastfed their children and were protected by hormonal medications. In some women, papillomas inside the ducts form during mastopathy, since this disease increases the expansion of the ducts and thus creates suitable conditions for cystic neoplasms.
Classification
Intraductal papillomas are usually classified according to several parameters. Depending on the location of this neoplasm, the following are distinguished:
- Central papillomas, they occupy a place next to the areola of the breast.
- Peripheral papillomas can grow anywhere else in the breast.
Depending on the amount of papillomas formed inside the breast ducts, they are divided into:
- Single or solitary. A single papilloma most often occupies the subareolar zone.
- Multiple papillomas. A large number of cystic papillomas are detected in the peripheral areas of the breast. It is multiple papillomas that most often undergo malignant degeneration.
We suggest you read Why get tested for human papillomavirus
Symptoms
Often intraductal papilloma becomes an accidental finding during a routine examination of the mammary glands. This is typical for neoplasms located in the accessory ducts.
Papilloma can be determined by two signs, these are:
- Discharge. A clear or reddish secretion may be released from the nipple; such a change is noted both constantly and periodically.
- Pain. Painful sensations are more disturbing when you feel the node. On palpation, the neoplasm resembles a round, elastic knot in consistency. Pressure leads to the fact that the amount of discharge from the nipple increases, and the nodule itself then decreases somewhat in size.
Often, intraductal papilloma becomes infected and this causes severe pain, the skin over the formation becomes inflamed, swollen, the nature of the discharge changes, it becomes yellowish with an admixture of pus.
Diagnostics
A mammologist examines women with breast tumors. Already upon examination and palpation, the doctor, based on the characteristic signs and nature of the discharge from the nipple, can assume the presence of papilloma inside the ducts.
A smear of the discharge is immediately taken for cytology. If the analysis shows the presence of atypical cells, then an in-depth examination is required to rule out a cancer process.
To confirm the diagnosis of intraductal papilloma, the mammologist prescribes:
- Ductography. This is a method of X-ray contrast examination of all mammary gland ducts, which makes it possible to identify the size of the tumor and its location. It is on the basis of this examination that a decision is made on the choice of method for removing papilloma.
- Ultrasound, mammography and MRI are prescribed to rule out other benign or malignant tumors in the breast.
The detection of intraductal papilloma is regarded by doctors as a precancerous change in the mammary gland, therefore, in any case, removal of such a tumor is indicated.
The operation is called sectoral resection. First, a surgical incision is made around the nipple, this allows the surgeon to view all the ducts. If defective tissues are identified, they are removed along with the papillomas, and the incision is closed with a cosmetic suture.
If the formation is located near the nipple, then patients are prescribed local anesthesia. When detecting tumors deep in the chest, general anesthesia is used. The operation is carried out in such a way that the shape of the woman’s breasts remains virtually unchanged and, therefore, there is no need for subsequent plastic surgery.
Tissues removed during surgery are sent for histological examination. If cancer cells are detected, the patient is additionally prescribed chemotherapy or radiation therapy sessions.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of the disease. Women should understand that most breast tumors occur due to hormonal imbalance and therefore it is necessary to treat all diseases on time.
Regular preventive examinations and examinations required by age allow us to catch any formation in the breast at the stage at which treatment is most effective.
Prerequisites for the occurrence of the disease ↑
The main causes of papillomas in the ducts lie in hormonal disorders. For example, obesity can lead to cystadenopapillomas. In addition, in women who have undergone an abortion, tumors (papillary cystadenomas) may be detected in the milk ducts. Ovarian dysfunction leads to papillomas inside the breast; another cause of the disease is adnexitis.
Girls who have not given birth are at greater risk than women who have given birth and breastfeeding. Another factor detrimental to women's health is smoking. It also provokes the occurrence of intraductal papillomas.
The disease usually occurs together with mastopathy, as a result of which the milk ducts expand, and papillary cystadenomas grow in them.
Heredity plays a major role in the occurrence of intraductal papilloma. Relatives usually have a history of malignant or benign breast formations.
Prevention of pathology
The main preventive measure to prevent the appearance of intraductal papillomas is careful attention to the condition of the breast. To do this, you need to visit a mammologist at least once a year to check the mammary glands and do palpation yourself.
It is important to maintain a balanced diet and exercise to support your immune system. And also monitor the discharge - if this sign is present, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Self-examination is done no earlier than 7-8 days of the cycle and involves a certain sequence of actions:
- With arms down and straight posture, visually assess the condition of the mammary glands.
- Raise your arms up, analyze the shape of the chest and its appearance in this position.
- Using your index, middle, and ring fingers, move clockwise across your chest with light pressure. This palpation should begin from the top, from the outer quarter of the mammary gland.
- Pinch your nipple with your fingers to check for discharge.
- Palpate the chest while lying on your back.
- Assess the size and sensitivity of the lymph nodes in the armpit area.
Central intraductal papilloma
There are several forms of breast cystadenopapilloma, which depend on the location of the tumor:
- Central form. The neoplasm is located directly in the duct and is large in size. Most often it is alone and has no tendency to develop into a cancerous tumor. However, with prolonged absence of treatment, benign formations can provoke the development of adjacent tumors and atypical cells. Central intraductal papilloma is usually observed in women after 40 years of age. During diagnosis, various harmful bacteria are often found in the ducts of the gland.
- Peripheral form. Papillomas develop in groups and often affect both mammary glands. Their shape and diameter may vary. This form can be found even in younger women.
- Atypical form. A separate group of diseases in which atypical cells are found that can develop into invasive cancer. If this type of disease is detected, immediate surgery is required. If the cells degenerate, they can block blood flow, causing necrosis in dense areas of the breast.
Understanding the form of intraductal breast papilloma gives doctors a chance to react quickly and remove the sources of the tumor, which is potentially dangerous to health.
Classification
Based on their structure, there are solitary papillary tumors (single), usually located closer to the nipples, and multiple, often located in the peripheral region of the gland. Such formations often degenerate and become malignant.
Atypical cells with an unusual structure, size and shape can be found in papillomas. The presence of such cells increases the likelihood of tumor degeneration.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Papilloma on the lip: causes and treatment methods
Cystadenomas or cystadenopapilloma are divided into groups, depending on the place of their formation, as follows:
- central - in the area of the nipple;
- peripheral - in the deep tissues of the lobules;
- areolar - in the area of the areola of the gland;
- atypical - outside the ducts and lobules of the gland.
There are certain statistics that confirm that the central type is less likely to develop into malignant formations. Peripheral - more often, papillomas with this type are numerous and affect a large area of tissue.
The atypical type of disease is characterized by growths of unusual shape and structure.
Papillomas are also divided into:
- single or solitary - most often located in the alveolar zone (near the nipple);
- multiple or papillomatosis are the most dangerous growths in the peripheral zone.
How to prevent the occurrence of papillomas in the mammary glands?
There is no special prevention for the disease. In order to protect yourself and your body, and prevent the appearance of intraductal papillomas, it is necessary to undergo systematic examinations by a specialist.
- If necessary, treat mastopathy and other disorders and inflammatory processes in the body.
- You should pay attention to your usual lifestyle.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Protect yourself from various stressful situations, be less nervous.
It should also be remembered that many formations in the female body arise due to hormonal imbalance. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to changes in the body in a timely manner and treat all diseases.
In order to detect a tumor in the early stages of its inception, you should undergo systematic examinations, which include the pulp examination method. In the early stages of formation, treatment is most effective.
Having studied what intraductal papilloma is, having become familiar with all the intricacies of this disease, issues and methods of treatment, you must remember that a healthy lifestyle, regular examinations and attentive attitude to your body are the key to your health.
Stages of neoplasm development
The development of benign intraductal papilloma is characterized by classical processes that provoke tumor growth. Under the influence of certain factors, the DNA of the cell is destroyed, which is why it begins to functionally differ from a healthy element.
At the first stage of tumor development, the process affects only the cellular level and does not manifest itself externally. This stage is called the beginning of breast tissue hyperplasia. Pathology can be detected only through cellular analysis - a biopsy or studying the composition of the blood for tumor markers.
Then the second stage begins, at which the tumor takes on one or another character. Here you can already make a diagnosis - intraductal papilloma. At this stage, the first symptoms appear, the neoplasm constantly increases in size.
Symptoms
The formation of intraductal papillomas of the mammary glands in the initial stage is difficult to notice; there are simply no clinical signs.
Only at the stage of growth of the “body” of the cyst the following symptoms appear:
- Discharge of liquid masses from the mammary gland. The nature of the fluid depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the stage of the disease, the color ranges from transparent to pink, discharge can be infrequent or, conversely, constant
- If the papilloma is located in the central duct, during manual examination you can feel it; when pressing on it, the woman experiences pain. If you squeeze hard, a liquid mass is released from the nipple opening, the neoplasm becomes smaller in size
If the neoplasm is damaged, an inflammatory process immediately occurs, the temperature increases, and weakness appears. The skin in the area of damage swells and changes color. If the inflammation is not treated, the papilloma becomes denser, and purulent masses begin to form, which are released from the breast nipple.
Methods of treatment and removal of formation
Treatment of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland requires an integrated approach. It begins with conservative therapy, but it is not possible to avoid surgical intervention in every case.
Intraductal papilloma is highly dependent on hormonal levels and immunity, so the doctor prescribes hormonal drugs, including herbal remedies based on phytoestrogens. Additionally, immunomodulatory vitamin complexes are recommended.
Sectoral breast resection
There are several ways to surgically eliminate the disease. Most often, cystadenomatous papilloma is treated by partial removal of breast tissue:
- Sectoral resection. The surgeon removes the area with the affected ducts. Stitches are then applied. An incision is made along the lower edge of the nipple. The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia.
- Complete removal of the mammary gland. Mastectomy is used in the presence of cancer cells, since it requires removal of not only the lesion, but also accompanying tissues to stop the malignant process. Mastectomy may be incomplete if the lesion is small in size.
- Coagulation by electric current. A gentle procedure aimed at the external elimination of papilloma located in the nipple area.
- Laser elimination. Like the coagulation method, it is used mainly on external tumors.
The method of eliminating a tumor completely depends on the characteristics of the tumor and the stage of its development.
Red beet compresses are used as a folk remedy.
Herbal ingredients are used mainly during the rehabilitation period and while waiting for surgery. They cannot be prescribed as an independent method of treatment. The effective components include the following products:
- calendula, celandine, mint, string, St. John's wort;
- red beets in the form of compresses;
- beetroot and honey recipes;
- garlic, apple cider vinegar, red wine, lemon juice.
Herbs can be brewed either separately or in combination, after discussing the recipe with your doctor.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Treatment of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland includes several removal methods. Ductal formations are precancerous conditions. Depending on the size of the formations, the intervention can be partial (excision of gland lobes) or total (complete removal of the breast). Against the background of surgical intervention, conservative drug therapy is carried out in order to normalize hormonal levels and prevent the development of a secondary infection. Immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed to prevent relapse of papillomatosis.
The conservative method as the only form of treatment is permissible only in the presence of a single small formation without signs of growth.
The operation to remove papillomas in the area of the delicate tissue of the glands is carried out only under general anesthesia. For small growths, gentle surgical methods are used - resection along the periphery in sectors (incomplete excision with the application of a cosmetic suture). It is possible to preserve your own gland without losing the shape and size of the breast, without deforming the areola of the nipple, and an incision is made in the area around the nipple.
In the presence of voluminous growths with atypical growth of cancer cells, removal of the entire gland is used - mastectomy with excision of nearby tissue.
Among the methods of minimally invasive intervention for small growths of papillomatosis, laser destruction is used (rapid coagulation with a recovery period of up to 14 days). Hardware methods and surgery are aimed at preserving the functionality of the pectoral muscles responsible for the movement of the upper limbs.
The effect of various drugs, homeopathic medicines, including those for papillomas, is aimed at restoring the immune system in the body. Traditional methods of treatment are not used due to the high risk of malignancy and the lack of data on the clinical effects of home therapy. They use immunomodulators, antiviral drugs in the form of tablets, drops, ointments (Viferon, Ganaferon, Proteflazid, Immunoflazid).
Homeopathy and enzyme therapy in combination with traditional remedies for papillomas have a good effect. The effect of using a natural homeopathic enzyme is short-lived and the accumulation dose is not constant.
They take groups of vitamin-mineral complexes, antioxidants to strengthen the immune system and normalize metabolic processes.
In specialized medical institutions, diagnosis of breast papilloma is carried out using:
- palpation examination;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood tests for tumor markers;
- cytology of smears of nipple discharge;
- mammography (breast x-ray);
- ultrasound echography (ultrasound) of the mammary glands;
- X-ray examination of the ducts with a contrast agent (ductography or galactography);
- aspiration biopsy and histological examination of papilloma tissue.
A fiber optic microendoscope with an outer diameter of 0.55-1.2 mm is inserted under local anesthesia through the ductal opening on the surface of the nipple, which allows direct visualization of the ductal epithelium and intraductal biopsy.
There is also the possibility of therapeutic intervention (insufflation, irrigation, lavage).
We suggest you read How to remove redness from your face quickly and easily
Diagnosis of intraductal papillomas requires clear differentiation of this disease from fibroadenoma, ductal carcinoma and papillary breast cancer, which is very similar to papilloma.
During an external examination of the mammary gland, it is very difficult to detect the presence of intraductal papilloma. Most often, a benign tumor is located in the lumen of a large milk duct.
If this duct is located in close proximity to the areola, then upon palpation of the nipple and areola, an oblong painless compaction can be detected. If you press on this seal, ichor or blood may be released from a single milk duct.
In more rare cases, ductal papilloma is located deep in the mammary gland. With such a localization, it will not be possible to identify a benign tumor of the milk ducts with your fingers, and the only signal about the presence of papilloma in the lumen of the milk duct will be bloody discharge from the nipples.
In this case, it is necessary to examine the entire mammary gland and experimentally determine the point upon palpation of which the discharge of blood from the nipple increases.
However, in most cases, even the most thorough palpation and mammography do not allow one to clearly localize the location of intraductal papilloma. In such a development of events, specialists resort to ductography and cytological analysis of the fluid released from the nipples.
Diagnosis of intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland begins with an examination by a doctor: an external assessment of the mammary glands and a digital examination, during which the specialist detects a small-diameter nodule.
An exclusively external examination by a mammologist does not allow a diagnosis to be made, so additional diagnostic procedures are carried out to clarify it. A blood test is prescribed to identify tumor markers.
Various breast diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the breast. Visual examination helps to examine the deep tissue areas of the breast and detect papillomas, the characteristic shape of which allows them to be differentiated from other neoplasms.
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is one of the safest ways to assess the type and size of growths.
- Mammography. X-ray examination is prescribed for women after the age of forty, since the mammary glands are no longer as dense.
- Ductography. The study involves the injection of a contrast agent into the ducts. The diagnostic measure has the highest information content; it reveals duct breaks, narrowing, and expansion.
- Cytological examination of discharge. Cytology analysis makes it possible to detect changes in the level of red blood cells, which indicates the presence of an intraductal neoplasm.
- Histology. Histological examination of tissues allows us to identify oncological tissue damage, necrosis and other pathologies.
Therefore, treatment without surgery is not carried out due to its ineffectiveness. When a diagnosis of intraductal papilloma is made (ICD code 10 - 24), the woman is scheduled to see a surgeon.
If the size of the papilloma is several millimeters, there is no inflammation, the operation does not have to be immediate.
Intraductal papillomas detected during pregnancy are removed after the birth of the child. In case of a high probability of developing cancer, it is advisable to treat papillomas during pregnancy. Conservative treatment is prescribed along with surgical intervention.
This allows you to access the ducts that are located in the mammary glands. Surgery for intraductal papilloma involves the removal of papillary tumors and blood clots that are caused by tissue injuries and are located near them.
Treatment
For this type of disease, home treatment is not indicated. Since papilloma is a precancerous formation, its treatment is carried out by surgical intervention.
An important task of the doctor is to convince the patient that this operation is safe and to give a positive attitude. Often women are extremely upset by this course of events; they are afraid that their breasts will be disfigured with a scalpel.
After a conversation with the patient and an attitude towards a positive result, the doctor performs a sectoral resection, this is the removal of formations using an incision. The papilloma is removed, including the surrounding tissue. This is done to ensure that the growths do not recur. An incision is made along the areola, this helps open the ducts for examination. If there are indications for removal, they are removed.
After the operation, the removed tissue is analyzed for the presence of cancer cells. If the tests are normal, the patient can undergo further rehabilitation at home. In this case, rest, proper nutrition, taking vitamins and (if necessary) certain medications are indicated.
Important! After the time prescribed by the doctor, you need to undergo a series of examinations and tests to determine the further course of the disease.
You may ask how to get rid of this potentially very dangerous tumor. Unfortunately, the treatment is surgical. “Grandma’s poultices” are powerless in this case.
For cystadenopapilloma, the following is carried out:
- Sectoral resection - with the removal of part of the gland with pathologically modified flows. This operation is performed through the perialeolar approach. Thanks to this, the size of the bust and its shape are preserved. After such an operation, reconstructive mammoplasty is not required.
- If the lesion is multiple and the papilloma becomes malignant, a radical mastectomy is recommended. Most likely, in this case, you will have to use a T-shaped incision ending under the mammary glands in the intramammary fold.
The removal operation is performed under anesthesia. Modern medical technologies make it possible to carry out treatment in gentle ways:
- papilloma is removed with a laser;
- pathological modified ducts are cauterized using electrocoagulation.
After removal of the papilloma, the resection site hurts for an average of 2 weeks. The duration of rehabilitation depends on the volume of intervention. It is believed that pain after treatment of papillary intraductal formation is insignificant.
With this we say goodbye to you. Invite your friends to our site via social networks and you will want to yourself. We are preparing new articles for you with answers to the most pressing questions.
Treatment of cystadenopapilloma is surgical. The operation consists of removing all the ducts of the mammary gland (Koenig operation). The patient will not be able to breastfeed after this operation.
For nulliparous women, or in cases where our patient plans to give birth and breastfeeding in the future, we offer Babcock surgery - this is when we find, isolate and remove only the duct with papilloma. In this way, it is possible to preserve the possibility of lactation in a woman through other (unremoved) ducts of this mammary gland.
Unfortunately, cases where intraductal papilloma on the breast resolves spontaneously are rare in mammological practice.
In 99.9% of cases, the doctor prescribes removal of the growth using one of the surgical methods.
Removal is the only correct treatment, given that the risk of injuring the papilloma, which contributes to its degeneration into a malignant formation, is quite high.
The seriousness of papillomas that appear in the intraductal glands should not be underestimated. After all, their appearance is considered to be precancerous conditions, so they are subject to mandatory treatment.
But first, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out to exclude a malignant tumor. If the result confirmed that the intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is benign, then conservative treatment is possible.
It consists of taking antiviral, immunostimulating and even homeopathic remedies. It is also recommended to take vitamins E, C and A. In case of inflammation of papilloma, it is necessary to take antibacterial drugs to neutralize the source of infection.
But in most cases, doctors recommend surgery. It is called sectoral resection. After the procedure, the recovery period lasts about a week. In this case, neither the shape nor the size of the breasts, as a rule, change.
But don’t think that surgery is a panacea. Even after it is carried out, relapses are possible. Thus, intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland may reappear after surgery if the hormonal balance in the woman’s body has not been restored. Antiviral therapy is also important, since the appearance of papillomas is caused by the activation of the corresponding viral infection.
If you previously neglected the advice that you need to visit a mammologist regularly, now you cannot forget about these preventive examinations. This is the only way to detect the appearance of new papillomas in time.
In addition to regular visits to the doctor, it is important to learn how to independently examine your breasts and closely monitor your condition. If you follow all these recommendations, then even newly appearing breast papilloma will be detected on time.