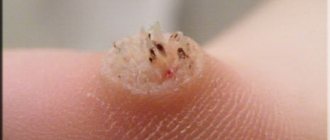
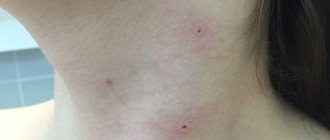
Unfortunately, absolutely no one is immune from the appearance of papillomas on the body - small growths that resemble simple warts with a wide flat base or a thin stalk. They can suddenly appear on any area of the skin:
- on the face;
- on the legs or arms;
- in the genital area;
- in the groin.
The occurrence of anal papillomas is deservedly considered one of the most unpleasant manifestations of the disease. Photos of these neoplasms will help you identify the problem in time and distinguish it from other similar pathologies. Why do these growths appear and how to get rid of them? All this and more will be discussed further.
Human papillomavirus
Viral infection
The papilloma virus from the Papovaviridea family has a tendency to infect epithelial cells and mucous membranes, transforming into an oncogenic nature. It happens that it settles in the vagina in women, in the urogenital tract in men.
Papilloma at the anus is a viral infectious disease with the formation of warts of a papillomatous nature on the mucous membrane and skin. Usually the virus lies dormant in the body, waiting for a special occasion. It begins to progress with a weakened immune system, if a person is experiencing severe psychological, physical stress or has undergone a course of chemotherapy or been treated with hormonal medications.
Condylomas in the anus are a chronic, recurrent form of HPV when the virus is activated. Usually it is benign in nature and does not have an oncogenic nature. But it causes particular discomfort to patients. If you ignore and do not remove papilloma in the anal area, then over time it can transform into a malignant form, highly oncogenic cancer of type 16, 18.
Preventive actions
Currently, vaccination is used against the most oncogenic types of HPV. The use of the vaccine causes the formation of lifelong immunity from these types of viruses. It is advisable to vaccinate before the start of sexual activity. Young women are screened for HPV before vaccination.
Currently, two HPV vaccines are used:
- Gardasil;
- Cervarix.
The first vaccine is effective against HPV viruses No. 11, 16, 18. It has some effectiveness against viruses No. 31, 35, 39. The second vaccine is effective against HPV viruses 16 and 18. Vaccination is carried out three times. The second vaccination is given 1 month after the first. The third - 6 months after the first vaccination.
There are several types of papillomaviruses
Anal neoplasms are divided into several types, taking into account the degree of carcinogenic danger and appearance:
Viral diseases
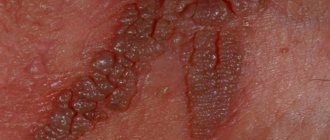
- Pointed in the form of growths with a thin base resembling ridges. Single or multiple settle, gradually merging with each other in a complex manner. At an early stage, when localized in the rectum, they are hidden, invisible to the naked eye, which poses difficulties for doctors when conducting diagnostics.
- Keratotic ones are similar in appearance to dense growths with a hard surface. They resemble tubercles or form a ring around the circumference of the anus, located in the form of single papules.
- Papules of a dark pink color, similar to warts in the anus. More often they form on the genitals and genitals in the form of a tumor-like swelling.
Treatment with folk remedies
If the disease is mild and single small papillomas are located in an accessible place, then treatment with folk remedies is possible.
- Fresh celandine juice or its concentrate. It needs to be applied to the formation several times a day. To enhance the effect, the affected area is steamed before the procedure.
- An alcoholic iodine solution, which is applied pointwise to the growth without affecting healthy tissue. This helps dry out the formation and cleanse the skin.
- Potato juice, decoctions and tinctures. For the preparation of which, rose hips, horsetail, nettle or plantain are used.
- A decoction of chaga, which is frozen in ice trays and further influences the formation. Ice is applied to the growth and left for three minutes. The procedure is repeated several times during the day.
Due to the fact that the cause of the disease is a virus transmitted through contact with a carrier, there is a possibility of secondary infection, and a complete cure does not occur. But by following a number of recommendations, you can contain the disease and allow it to come out.
Chaga mushroom in the form of a frozen decoction alleviates the disease
The causative agent is human papillomavirus
New growth on the body
Anal papillomavirus is a microbial body with a microscopic form of life, but can only exist inside the cells of the human body. The causative agent of the virus is Papovaviridea. It settles in the cells of the mucous membranes or skin, causing papillomavirus infection.
Medicine knows over 91 varieties of this microorganism and several strains with low, medium, and high oncogenicity. Non-oncogenic strains – 12.41, settling on the soles in the form of warts. Weakly oncogenic - 6, 11, 30 strains, appearing as condylomas on the mucous membranes. Highly oncogenic strains - 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 68 - are the most dangerous, developing on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of dysplastic changes, causing cancerous lesions.
The note! The most highly oncogenic is virus type 16, 18. It is often detected in women as cervical cancer.
Causes of genital warts
The main reason for the settlement of genital warts in the anus is infection with a viral infection if the pathogen penetrates deep into the body through cracks or microtraumas on the body.
Condylomas are benign growths. They can settle in almost any area, even in the anus. Then they begin to penetrate soft tissues and grow, increasing cancer rates. It happens that they merge and grow together, forming lumpy formations in the form of islands.
At first, benign neoplasms remain dormant. Only after a certain time they begin to flare up in the form of painful rashes in the anus, the reasons for which are:
Provoking factors
- promiscuity, when HPV is often detected in an infected person along with chlamydia, herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages, narcotic drugs (cytostatics, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids) that undermine the immune system;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- use of household items of an infected person;
- cold;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking) that provoke activation of the virus;
- chronic internal diseases during exacerbations;
- prolonged stress;
- pregnancy;
- emotional stress with the appearance of characteristic rashes on the skin.
Anal genital warts can be located in the anus or rectum. If localization occurs in the walls of the colon in the form of a large growth, then constipation and fecal obstruction may occur. It is important to promptly identify and remove even minor changes in the epithelium in the anal area, otherwise the virus may spread to the genital organs: the vagina and uterus in women with the formation of a malignant tumor up to complete closure of the anus.
Reasons for development
Causes of anal papillomas
A strange type of neoplasm is caused by the human papillomavirus. There are many varieties of the virus - scientists have identified more than 8 dozen subtypes. It is quite possible that not all viruses have been discovered yet, and in the future the “collection” will be replenished.
Anal papillomas can form due to the presence of HPV in the body:
- low oncogenic risk;
- high oncogenic risk.
The first include 6, 11, 42, 43, 55, 54 and other subtypes. The second ones include 16, 18, 31 and several more strains.
A patient who is bothered by papilloma near the anus cannot independently determine which strain caused it. It is necessary to undergo a study, during which the doctor will determine which HPV gave impetus to the development of anal papilloma and prescribe treatment.
The appearance of papillomas between the buttocks is associated with the presence in the body of certain types of papillomavirus, the transmission of which could occur through sexual contact. Less commonly, such an illness can be transmitted through touch, when using other people's household items or when visiting public places.
There are several types of pathology depending on the severity and quantity. For example, large and multiple papillomas can be easily seen in the photo, while papillomas located in the anus, but small, will not be visible in the photo.
The reason behind the development of this pathology is the human papillomavirus or, for short, HPV. It is worth noting that a large number of people on our planet are carriers of the virus. So why do papillomas appear if the virus is constantly in the body?
The fact is that if a person is healthy and full of strength, then HPV is dormant and does not actively reproduce.
If a person gets sick and his immunity has decreased significantly, the virus is activated and begins active reproduction, which leads to the person developing papillomas.
There are many forms of the disease, which are characterized by different positions of the tumors and their shape. In some cases, the difference between one or another tumor can be seen even from a photo.
Neoplasms are provoked by the human papillomavirus, of which there are about a hundred strains.
Each of them causes different deformations of the skin. HPV enters the skin and penetrates into the cells of the basal layer of the skin. In this case, the viral cell removes its protein shell before infecting a healthy human cell.
Papillomas form on the anus due to human infection with human papillomavirus. As a rule, the virus “sleeps” in most cases and begins to work actively during the period of decreased immunity.
It is worth noting that the disease can develop in different ways: quite quickly, in just a few days, reaching large sizes, or not making itself known for a long time.
Today it has been precisely established that the basis of the disease is made up of pathogenic viruses of the group of human papillomaviruses types 11 and 6. Infection occurs more often through sexual contact, and condoms are not reliable protection, therefore, currently, according to various sources, from 50 to 80% of the population are carriers of the virus.
The virus begins to manifest itself under the influence of certain factors, which invariably lead to a decrease in immunity, general or local.
Factors for the development of the clinical picture:
- Fatigue and lack of sleep;
- Frequent stress;
- Somatic and infectious diseases that greatly affect the level of immunity;
- Having bad habits;
- Poor nutrition, refusal of vegetables and herbs, addiction to meat dishes.
A common location of anal condyloma (see photo) is the anal area, the rectal mucosa. Accordingly, complaints will mainly depend on the location of the growths and their size.
Route of transmission and conditions of infection
A common route of transmission of papillomavirus is sexual intercourse. The longer it is and the less protected it is, the more significantly the degree of HPV infection increases.
The skin in the anus is delicate and thin, easily injured. The virus begins to penetrate tissue through cracks and cuts.
The main routes of transmission of the virus:
Unprotected sexual contact
- sexual intercourse against the background of unprotected sexual intercourse;
- household in case of infection in public places with high humidity, transmission of the pathogen through non-sterile instruments during manipulation, because the microbe can live for some time in a humid environment;
- vertical from mother to newborn as the microbe moves through the placenta or during breastfeeding through milk;
- contact, when a child at birth becomes infected with HPV during passage through the birth canal.
Reference! People who are promiscuous, neglect personal protective equipment, and do not maintain personal hygiene of the external genitalia are at risk of contracting the HPV virus. Even modern methods of contraception do not guarantee complete protection against such infection. Infection can occur through direct contact, for example through household items and children's toys.
Condylomas in the anus
Condylomas around the anus
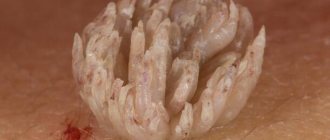
At first, condylomas in the anus look like pinkish papillae, then they can increase in size and merge with each other, forming a cauliflower. If they settle at the entrance to the anus, they can partially (completely) block the anus.
A special feature of condylomas located on the anus is the presence of legs and flesh-colored lobules. They are prone to rapid growth, proliferation, and increase in size. If they are localized in the perianal area, they begin to hurt.
Patients are considered carriers of HPV if the virus spreads to the groin, perineum, or anus.
Condylomas in the anal area symptoms
As the condyloma virus penetrates the outer layers of the epidermis, it first remains in an incubation period and does not manifest itself in any way.
If a shock occurs, the papillomavirus begins to rapidly multiply and become activated. Mature cells increase in size and move throughout the human body.
Signs in infected people completely depend on the location and size of the tumor:
- pain, difficulty defecating;
- burning, itching, pain, swelling in the anus;
- bleeding in case of injury to growths;
- the appearance of sexual and psychological discomfort;
- constant presence of a foreign body in the rectum;
- discharge of feces from the anus with an unpleasant odor;
- intoxication of the body;
- the formation of fistulas in the event of a secondary bacterial infection or suppuration of papillomas.
Reference!
Often condylomas in the anus affect the rectum. If caused by HIV infection or homosexual sexual intercourse, they can provoke blockage of the anus with the manifestation of recurrent symptoms. It happens that condylomas go away on their own for a while. They begin to assert themselves again as soon as the immune system fails. You can see what papillomas in the anus look like in a medical reference book or in a photo.
Externally, condyloma is similar to a common wart. It settles as a single small species or large (multiple), uniting and merging with each other. The main difference between condyloma and warts is the presence of a thin stalk and a rough top layer. As a rule, patients turn to doctors when growths in the anal area are already obvious and easily palpable.
Worth knowing! Signs of the virus on the body largely depend on the state of the immune system. The virus can decrease or increase in size and quantity at different periods of life. However, this infectious agent can only live inside the human body. It cannot live outside cells, although it retains its properties for some time, staying in the atmosphere in the fresh excretions of the patient’s feces.
What do papillomas in the anus look like in women?
Photos of papillomas in the anus in women
In the first months or even years after the appearance of papilloma, there is usually no concern. Since it is out of sight, it is discovered either by accident during an examination by a proctologist, or after the onset of painful sensations, which are one of the important symptoms of such a pathology.
Here are the signs that indicate papilloma in the anus in women:
- Burning in the anus . It can bother you either constantly or periodically. Its intensification usually occurs after anal sexual contact with a male carrier, in case of ignoring the rules of personal hygiene, after examination by a proctologist. Sometimes these sensations become aggravated as a result of the act of defecation, due to tension in the intestinal walls and pressure on the formation.
- Increased moisture in the tissues between the buttocks . This symptom is not necessary for papilloma in the anus in women; it mainly appears if it has already been here for a long time. Liquid can accumulate in the growth cavity, and if the integrity is damaged, it can leak out. As a result, the underwear becomes damp, which indicates possible problems.
- Itching . This phenomenon is a strong, sometimes uncontrollable urge to scratch the area near the anus. This is dangerous due to the fact that when such a need is satisfied, the mucous membrane and the papilloma itself in the anus in women can be injured, as a result of which blood will appear, and with a high degree of probability any infection will penetrate inside. As a result, these areas may become red, inflamed, and irritated. Especially often, such problems arise after anal intercourse and when anal hygiene is ignored while taking a shower.
- Discharge from the rectum . In this case, the woman may see mucus in the excrement that is white, pale yellow or black. Usually there is not a lot of it here, so such a symptom in itself is not a basis for making a diagnosis of “papilloma in the anus.” Because of this problem, underwear can get dirty faster than usual.
- Constipation . They are associated with a violation of intestinal patency, when papilloma in the anus in women, reaching large sizes, blocks the path for the exit of waste products. Because of this, the act of defecation occurs less frequently and with great difficulty, pain and bleeding occur, and the abdomen swells. If such a problem is not solved for a long time, then in addition to this, symptoms of intoxication of the body appear - weakness, nausea, dizziness, loss of appetite.
- Sensation of a foreign body in the anus . It resembles a feeling as if the act of defecation was not completed fully. As a result, the woman wants to repeat the procedure, but this is not possible. It is aggravated by walking, prolonged sedentary lifestyle, pressure on the formation of tight underwear and anal intercourse.
In addition to the listed symptoms of papilloma in the anus, women may experience a slight fever. Sometimes there is also a false urge to defecate, and hemorrhoids, if such problems exist, worsen.
Speaking about what papillomas on the anus look like in women in photos or in real life, it must be said that growths of any type can appear here - flat, hanging, vulgar, pointed. They look like bumps or lumps on a stalk, depending on the type. Their color is usually flesh-colored, pale red or pink. If present for a long time on the mucous membrane, the color may turn black due to infection of the formation.
Papillomas in a woman’s anus can be single or multiple. If they are in the rectum, they also appear around the anus, between the buttocks. Their size is on average 0.3-0.7 cm, their surface is almost always non-smooth.
Anal condylomas diagnostics
First of all, when contacting a proctologist:
Carrying out the procedure
- conduct a visual inspection of the perianal area;
- examine the medical history;
- visually examine the growths around the circumference of the anus;
- determines the shade, shape (usually in the form of cauliflower);
- will redirect you to undergo a proctological examination to assess the condition of the muscles of the anus, epithelium of the anus and rectum.
Other diagnostic methods for recognizing condylomas in the anus:
- anoscopy with examination of the anus under a microscope to obtain a general assessment;
- sigmoidoscopy to examine the inside of the rectum up to 25 cm, starting from the anus;
- ELISA (PCR) to detect even minor changes in the epithelium of the anus.
To clarify the diagnosis, differential methods are prescribed to distinguish papillomas (condylomas) from squamous cell carcinoma, gonorrhea, syphilis:
- biopsy;
- Ultrasound;
- irrigography;
- Video rectoscopy of the anus.
Reference! In case of condyloma infection caused by sex, it is recommended that both sexual partners undergo diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnostics
A proctologist diagnoses HPV (human papillomavirus). Based on the patient’s complaints, the specialist will conduct a series of diagnostic measures. All procedures are painless and will help in establishing the correct diagnosis. Here they are:
- interviewing the patient, collecting anamnesis.
- Visual inspection of the anal area, checking for growths.
- Examination of the rectum using sigmoidoscopy. This technique allows using a microscope to identify tissue injuries to the epithelium of the anus. The data obtained will provide the doctor with a complete picture of the patient’s intestinal condition.
- Collection of blood or tissue sample that will be required to carry out the necessary tests in the laboratory (cytology, biopsy).
Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor will be able to confirm or refute the patient’s anal papillomatosis.
Please note: timely contact with a specialist will help prevent serious complications of the disease. Self-medication is unacceptable.
Genital warts in the anal area
Growth in the anus
Genital warts look like small genital warts with jagged, cauliflower-like edges. More often these are oncogenic strains of the virus type 16-18.
They are localized in women on the genitals, labia, causing damage to the cervix and vagina. In men - on the skin of the foreskin, glans penis, leading to damage to the urethra, bladder, and skin around the anus.
Reference! The virus becomes extremely dangerous and can develop into cancer if it stays in the body for more than 1 year. Usually invisible, it begins to appear at the last stage of infection, when treatment becomes difficult and sometimes pointless.
In men, genital warts settle extremely rarely in the anus, on the head or frenulum of the penis. Although they are no less dangerous, they require urgent removal, and it is impossible for patients with them to have a normal sex life or observe normal personal hygiene measures.
Reasons for appearance
The main cause of anal papillomas is the activation of the papillomavirus. HPV can be present in the body in latent form for a long time and manifest itself after infection months or years later. Most often, the causative agents of these growths are the 6th and 11th strains of the virus. In this case, neoplasms can be simultaneously observed on the genitals: in the vagina, on the labia, shaft of the penis or foreskin.
Papillomas appear when natural immunity weakens and HPV begins to actively multiply. This may be caused by:
- experienced stress;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- pregnancy period;
- frequent overwork;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- bad habits.
All these factors reduce the body’s defense reactions, as a result of which the virus is activated. At the same time, several types of HPV may be present in the body at once, which complicates the treatment process.
Course of the disease
The HPV virus is resistant to heat treatment. Can live in the external environment for some time. It multiplies quite slowly and is not detected in the blood. This is an etiotropic pathogen that can lead to layer-by-layer damage to the epithelium of the mucous membrane or skin.
Several types of papillomavirus can be detected in one patient. The main route of transmission of the virus is an infectious agent that transforms the basal cells of the epidermis, which begin to divide, forming condylomas or papillary polyps on any part of the body. In advanced cases, condylomas occupy significant areas of the anal area and spread to nearby healthy areas. It happens that the condyloma virus subsides and even disappears for a certain time. However, it remains in the body and can be quickly activated if the immune system is weakened.
If condylomas are not removed in a timely manner, they will gradually begin to increase in number and occupy large areas. The risk of infecting a sexual partner will increase significantly.
Important! Medical help from doctors should be sought urgently if condylomas bleed, lead to difficulties in anal hygiene and psychological discomfort.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment after diagnosing papillomas around the anus is always prescribed in a comprehensive manner. It is important to understand that it is impossible to completely get rid of the papilloma virus; it can only be controlled and the uncomfortable symptoms eliminated. But treating papillomas is important, since they tend to quickly increase in number and size, and also cause a number of serious side effects.
Among the drugs that can be used to treat papillomavirus it is worth noting:
- Viferon is a drug in the form of anal suppositories or gel that has an immunomodulatory effect.
- Genferon - rectal suppositories with interferon.
- Allokin-alpha - used for papillomas that are likely to transform into malignant ones.
- Immunomax is an injection-type drug for intramuscular use, the action of which is aimed at stimulating the immune system.
- Epigen spray - helps suppress discomfort such as itching, pain, and spotting. Usually the drug is prescribed after surgery.
- A variety of ointments for papillomas - which have antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects (for example, oxolinic ointment).
Complications of perianal condylomas
Perianal condylomas, if they grow, can block the lumen of the anus, since they are prone to recurrence and re-development even after initial successful removal.
Some types of condylomas degenerate into cancerous tumors, although usually they do not have high oncogenicity when they settle in the anus. The main thing is to remove it in a timely manner or treat it with medications so that it does not form into a malignant tumor, subsequently spread to the genitals, acquire a purulent infection, or develop sepsis.
Treatment of condylomas in the anal area
Treatment measures
If condylomas are detected in the anus, doctors usually resort to surgery or cauterization. The method of cryotherapy and electrocoagulation with excision of a piece of affected tissue, followed by histological examination, is widely used to exclude (confirm) degeneration into oncology. Condylomas are excised together with adjacent healthy tissue.
If flat condylomas are detected in women on the mucous membrane of the vagina or cervix, then an additional biopsy is performed with a piece of tissue taken for analysis. If the degeneration of cells into a cancerous tumor is confirmed, then radical surgery is performed. Sometimes, in case of dysplasia of the affected tissue, extirpation is performed.
Surgical methods for removing papilloma:
- laser - a bloodless, non-contact option for removing anal condylomas with a laser, leaving a crust at the site of condyloma removal, although the likelihood of scarring and relapse remains high;
- radio wave by applying a radio wave electrode to the tumor for cutting, followed by coagulation of blood vessels, applying an antiseptic bandage;
- surgical performed under local anesthesia.
If cell dysplasia is not observed, then drug therapy is prescribed according to a specific regimen including antiviral agents:
Medicine
- Viferon (suppositories, gel) - a modulator of the immune response for condylomas in the anus;
- Genferon from the group of interferons with the introduction of rectal suppositories into the anus;
- Allokin-alpha for suspected transformation of condyloma into a malignant tumor;
- Lykopid is an immunomodulator to stimulate the functions of the immune system;
- Epigen intimate with local use to relieve swelling and itching, heal wounds, strengthen local immunity.
Treating papillomas with folk remedies (especially when found on the genitals of women) is strictly prohibited. Although many patients try to resort to folk remedies when they see a wart on the body.
Important! It is folk remedies that, instead of the expected benefits, can provoke an outbreak and progression of the papilloma virus. Removal of the genitals in women should be carried out only in a hospital setting and with subsequent collection of material for testing for dysplasia.
An effective method of getting rid of genital warts is cryocoagulation (cauterization with liquid nitrogen), a painful procedure. In 80% of patients, after 2-3 sessions, complete elimination of condylomas is observed. With the permission of a doctor, it is possible to use celandine juice in acceptable doses with application to genital warts after preliminary steaming of the skin and subsequent smearing of the affected area with a greasy cream. You can also use plantain juice, treating the growths 2-3 times a day.
Treatment
Treatment of neoplasms is carried out in different ways.
The first thing the doctor will do is refer the patient for removal of anal papillomas. This is necessary to prevent malignancy of the process.
After this, immunotherapy is mandatory, the purpose of which is to “awaken” the body’s defenses and force them to attack the virus so that it falls into a latent state. Then the disease will not threaten the person.
Papillomas are destroyed in different ways.
If papilloma is confirmed in the rectum and anal area, mandatory treatment is carried out. It can be conservative or surgical. It all depends on the scale of the lesion and the area where the growths are localized. But any approach should be carried out comprehensively and consist of:
- Removal of formations involving affected adjacent tissues through physical or chemical action.
- Immunotherapy, consisting of a course of immunomodulators: “Immunal”, “Cycloferon”, “Imunnolmax” and their analogues, as well as vitamin complexes and adaptogens.
- Antiviral therapy, which consists of taking medications aimed at suppressing the virus inside the body.
If the formations are single, located in an accessible place and are not complicated by pathologies such as hemorrhoids and fissures, then conservative therapy is prescribed.
In case of multiple growths, when localized on the walls of the rectum and if there are hemorrhoids, it is recommended to use surgical tactics, the meaning of which is to excise or burn out the papillomas.
Papilloma or condylomas that are located around the anus and in the rectum can be removed with a scalpel, electric current, radio wave knife, laser or special ointments and creams.
Modern medicine also offers cryopharm as a treatment. The method consists of using a special patch soaked in a medicinal solution, which is applied directly to the growth and destroys its tissue.
This method allows you to get rid of growths within three to four hours at home. But when using this product, you must ensure that the patch does not come into contact with healthy skin, so it is recommended to lubricate healthy adjacent tissues with a fatty cream.
If the disease is mild and single small papillomas are located in an accessible place, then treatment with folk remedies is possible.
photo of anal warts
Once an accurate diagnosis is made, treatment can begin. Doctors use the following therapeutic methods for getting rid of anal warts:
- laser therapy, in which the affected area is irradiated with laser light that destroys tumor tissue (absolutely safe for health);
- cryodestruction is the process of freezing condylomas using liquid nitrogen, as a result of which tissue necrosis occurs and anal papillomas disappear on their own;
- electrocoagulation or cauterization of tumors using electric current;
- radio wave surgery, which uses a knife that emits radio waves to cut tissue without causing bleeding.
These are the most effective physiotherapeutic procedures with which you can quickly get rid of condylomas. However, in addition to the above methods, you can resort to medications and traditional medicine methods to remove anal papillomas.
To get rid of anal warts, you can use the following drugs: Solcoderm, Papilux, Verrumal, Papilight. You can also lubricate the affected areas with salicylic or oxalic ointment, Vartek cream, Aldara, Viferon ointment.
However, before using these remedies, you should consult your doctor.
Traditional medicine can also come to the rescue. To remove condylomas of the anal canal and the area around the outlet, you can use an alcohol tincture of propolis.
You need to moisten a cotton swab in this solution and apply it pointwise to the anal warts. At first, you may feel a slight burning sensation, but it goes away after a minute.
It is best to carry out such procedures before bedtime. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks.
A more gentle remedy can be prepared from propolis. To do this, you need to dilute 80g of propolis with 300g of rendered pork fat.
This ointment should be applied to the affected areas. Aloe or Kalanchoe juice is also good for treatment; you can use it to wipe the anal warts or apply the juicy part of the plant leaf to the growths.
The main thing during the treatment period is to adhere to the following rules:
- eat healthy foods enriched with vitamins;
- regularly, several times a day, carry out water procedures for intimate places;
- control sex life;
- adhere to the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor and see him regularly.
These tips and information from the article will help you properly deal with emerging anal warts and get rid of them in a short time. Good health!
There are plenty of ways to treat the external manifestation of HPV – condylomas on the butt.
But none of the mechanical, thermal or chemical removal methods guarantees one hundred percent destruction of virus cells.
About a third of patients cannot be cured of this disease, but if papillomas appear, they still need to be urgently removed.
- Complex treatment is carried out using medications used both externally and internally. The principle of therapy is an antiviral and immunostimulating effect. Isoprinosine is most often used as an antivirus, and Genferon or Panavir is used to stimulate the immune response.
- Single and small growths are cauterized with solutions of the drugs “Condilin” or “Solcoderm”, or the growth is prevented with the help of “Podophyllin”.
- If papillomas appear on the butt, modern medicine offers not only conservative methods of combating them, but also removal.
Gay syndrome
Gay syndrome is observed in homosexuals in cases of condylomas affecting the walls of the colon. Gay and bisexual men are recommended to receive the vaccine, since sexually active people are more likely to become infected with HIV infection or HPV types 16, 18. A sexually active person can become infected with the virus even after only having sex with an infected partner. Treatment is carried out taking into account the individual characteristics of patients.
The main thing is to undergo a course of therapy in a timely manner to prevent the development of anal fissure and gonorrhea.
Possible complications
The main feature of the virus is its long stay in the body, and therefore a high frequency of relapses. Renewal of the disease was observed in patients both after conservative and after surgical treatment.
A rare, but most dangerous complication is malignancy of formations. A tendency of perianal condylomatosis to degenerate into squamous cell carcinoma has been noted.
Forecast
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure the papilloma virus. If primary infection occurs, the person remains a carrier for his entire life. The prognosis is favorable if papillomas are removed in time and their activity is significantly reduced. Doctors often manage to suppress the activation of condylomas in the anus in one session.
To achieve treatment effect, it is important for patients to:
What does official medicine say?
- treat concomitant sexually transmitted diseases;
- use condoms;
- have a permanent partner;
- keep a healthy sex life under control;
- take courses of strengthening tonics;
- harden the body;
- take Interferon against many surrounding viral invaders.
HPV infection - latent begins to progress only with reduced immunity, outbreaks of chronic diseases, alcohol and tobacco abuse. Unfortunately, the virus remains in the human body even after removal of condylomas from the body.
Even after the initial removal of condylomas, patients are under constant medical supervision for another 1 year. Women are tested and examined by a gynecologist, men by a urologist. It is the provoking factors that allow the virus to activate. Preventing its development means avoiding stress, treating acute and chronic diseases in a timely manner, eliminating stress on the body and prolonged exposure to alcohol.