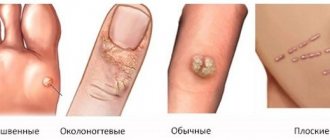
Types of warts on the hands and what they look like (photo): viral, small filamentous on the fingers, dry
One of the most common skin diseases are benign formations, warts.
They are a type of viral infection that affects any part of the body, but most often the face, arms, legs, and nails. Today we will talk about what they are and what types of warts on the hands are, photos, how to diagnose them and how to treat them.
There are several types of warts, each of which has its own causes and methods of treatment.
- Just touching someone else's viral wart is enough to become infected with HPV.
- The patient may unintentionally promote the spread of benign lesions by successively touching the growths and other (wart-free) areas of the body.
- If the integrity of the skin surface is compromised, the risk of infection increases significantly.
Should I see a doctor and when?
You should definitely consult a doctor . When? Better earlier. Any neoplasm can turn out to be a malignant tumor. And in this case, delay is dangerous for your life.
You also need to see a doctor urgently if:
If you decide to treat HPV yourself with folk remedies, be sure to consult a doctor who treats warts. Different types of warts require different treatments. And what helps with flat papillomas may be contraindicated for filamentous papillomas.
See below: filamentous warts photo.
You can see other photos of what a wart looks like here. We also recommend that you read the material “What is the difference between a wart and a papilloma?”
It is worth remembering that warts can appear anywhere:
And it is not necessary that you will have exactly a thread-like one. There are also:
Filiform papillomas of the acrochord. Their signs and treatment
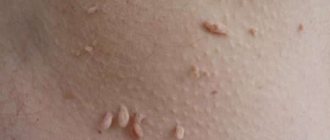
Threaded papillomas usually appear in the armpits, in the neck and face, mammary glands, groin, that is, wherever there is increased skin moisture. Threaded papillomas are characterized by the following features:
- initially a small yellow bump appears, which increases in size over time;
- the tubercle transforms into an elongated growth, the stem of which can reach 5-10 mm;
- the neoplasm has an elastic nature to the touch, usually the color of the acrochord does not differ significantly from the color of the skin, but in some cases the wart may have a brown tint;
- when several acrochords appear in one place, they can be observed merging into one new formation.
Threaded papillomas are prone to inflammatory processes if they are injured. Severance of the acrochord leads to the appearance of a new wart in its place.
Any trauma to the growth, as a rule, leads to the appearance of new warts on healthy areas of the skin. This type of wart usually does not transform into an oncological form, but acrochords do not show a tendency to self-destruct, so treatment of this disease is mandatory.
In everyday life, these neoplasms bring a lot of everyday inconvenience. All accessories worn around the neck can easily injure them.
Tight underwear can also cause injury to the acrochords.
These warts do not appear in children; signs of their appearance can only be noticed after 40 years. But after 80 years, their presence is almost mandatory. The reason for the appearance of filamentous warts is quite trivial - the human papillomavirus with its subsequent development in the body.
For the active manifestation of the disease there are a number of mandatory factors:
- Infection with papilloma virus.
- The factor of changes in hormonal levels during menopause, puberty, and pregnancy is also significant. Hormonal changes in thyroid diseases and diabetes are also dangerous.
- The possibility of the appearance of acrochords increases during frequent states of severe stress and any serious deviations in the psycho-emotional state.
- A decrease in the protective capacity of the immune system is the most common factor that accompanies the onset of activation of the virus.
If neoplasms appear during pregnancy, this may indicate more serious diseases of the female body. It is possible that acrochords may appear on the mucous membrane of the larynx; in this case, their manifestation may be loss of voice.
It should also be noted that the incubation period can be very long. And if you constantly maintain the state of the immune system, there is a high probability that the virus will not leave the latent state at all and warts will not appear.
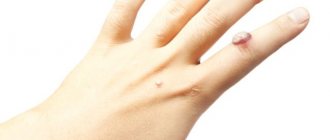
Wart on finger
The main reason for the appearance of filamentous and any other warts is infection with the human papillomavirus and its activation in the body.
At certain periods of life, a person is at greatest risk of developing warts of various types, so every person has encountered filiform warts at least once.
But why are they so common and how to effectively deal with them so as not to encounter this problem again in the future?
What is this
Filiform papillomas or acrochords are warty formations that can appear on any part of the skin, but are more often localized in skin folds or where the skin is very thin.
They are of a viral nature, as their appearance is caused by the activation of the human papillomavirus.
Acrochordons can grow after infection with HPV types 3, 5, 8 and 9.
Thread-like papillomas or acrochords visually represent thread-like outgrowths located on the human body. They can take the shape of an elongated oval, but sometimes an acrochord (see photo) is a round wart with a thin stem-base.
The main and, perhaps, the only reason for the growth of filamentous warts is the introduction of papillomavirus into the body (another name is human papillomavirus). The causative agent of the disease is HPV of four types - the third, fifth, eighth and ninth.
Infection occurs through contact. Most often, pathology is detected in people over 35 years of age. In childhood, adolescence and adolescence, filamentous warts of the acrochord are not found. Approximately half of the cases of detection of papillomas in patients aged fifty years and older are caused by acrochords. In elderly people, this type of wart is common.
Thread-like papillomas can be detected over the entire surface of the skin, but their “favorite” places are:
- area around the eyes;
- wings of the nose and adjacent skin;
- the entire surface of the neck;
- groin area (most often acrochords are formed in the area of the folds);
- under the breasts in women;
- in the area of the skin of the armpits.
If we analyze the main locations of warts, they “select” areas with delicate skin (the area around the eyes), as well as skin folds where there is increased humidity (groin and armpit cavities).
The type of HPV that causes filamentous papillomas (photos presented here) may not make itself known for a long period of time. Doctors identify several factors that can activate HPV. These include:
- Severe stress. A state of habitual stress can trigger the awakening of the virus.
- Hormonal imbalances. The reasons may be diagnosed diabetes mellitus, excess weight (very often accompanied by metabolic disorders), pregnancy and menopausal changes in the body.
- Deviations in the functioning of the ovaries. In this case, acrochords may begin to form in fairly young women.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the appearance of papilloma on the penis
If a person’s immune system is normal, then there is no reason to worry. Filiform warts, papillomas or acrochordas can appear only if the immune system is weakened.
At the first stage of their development, acrochord papillomas look like miniature growths, somewhat reminiscent of moles. As viral activity increases, warts transform into papillary-like formations. The length of the papilloma can reach 6 mm. Sometimes acrochords form a complete formation.
The basis of diagnosis is examination of the patient, followed by dermatoscopy. PCR analysis is mandatory. It is this study that makes it possible to determine the current concentration of the virus and diagnose the type of HPV.
Studies help distinguish filamentous warts from nevi and fibroid formations.
Threaded papillomas (the treatment and technique are chosen by the patient’s leading specialist) do not disappear from the skin on their own and require forced removal. Especially if the formation itches or worsens the quality of life. Acrochords - black or flesh-colored - located in an area that is often subject to trauma should be removed first.
The most common treatments are:
- laser removal;
- use of a radio wave scalpel;
- cryotherapy (freezing with liquid nitrogen);
- electrocoagulation technique (cauterization with electric current discharges).
Removed acrochords - treatment by surgical excision is practically not used - heal in a short time and do not relapse.
Removal with modern devices
If filiform warts do not respond to any other treatment method, the doctor will prescribe their removal with a laser. This method is characterized by high cost and increased risk of scarring.
Filiform papillomas do not disappear on their own, as happens with juvenile warts. Moreover, if nothing is done about them, they will begin to grow and spread throughout the skin. In some patients, a scattering of hanging warts can be observed. Treatment consists of cutting off the skin growth or removing it in another similar way.
There are several ways to get rid of filamentous warts:
- laser removal;
- removal with an electrocoagulator;
- cutting with a radio wave knife;
- cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
If there is a choice in your locality, then you can choose laser or radio wave surgery. These two methods are performed under local anesthesia and are quick and painless. This removal does not leave any scars, which is especially important for the face area.
Its cost is low, but it may leave small scars or dimples. In addition, the pedunculated wart does not disappear immediately, but within 4 days, and all this time a black spot is visible on the skin.
If the cosmetic center has an electrocoagulator in its arsenal, then you will be offered to remove acrochords with its help. Under the influence of a pulsed electric current, skin tissue is destroyed, and coagulation (soldering) of blood vessels occurs. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, there is no bleeding. Healing takes about seven days.
It should be noted that removal does not guarantee the disappearance of the acrochord forever. To prevent it from appearing again, you need to monitor the general condition of your body. He must receive all the necessary vitamins and microelements. Do not overwork, try to rest in a timely manner, practice hardening. Only in this case the likelihood of warts will decrease, and your skin will be healthy and clean.
How to distinguish a mole from a papilloma
The main cause of skin rashes is infection with papillomavirus. Once in the bloodstream, HPV is integrated into the DNA of epithelial cells, leading to their proliferation. As a result, papillary-like soft nodules (10-20 millimeters in diameter) appear on the skin or mucous membranes, attached with a thin stalk.
Acrochords resemble a piece of thread, their size ranges from small (half a millimeter) to large (about twenty millimeters). A characteristic feature of filamentous neoplasms is the presence of a stalk, with the help of which the papilloma is attached to the skin. Middle-aged and elderly people are at risk.
Although acrochords have a characteristic appearance, you should not make the diagnosis yourself. It is better to contact a specialist who can even visually distinguish such a wart from other manifestations of HPV viruses, as well as from moles and other skin growths.
But in order to detect HPV, you need to do a blood test, in this case it is called PCR. This study makes it possible to determine the type of papillomavirus that occurs in a particular situation, which is important for its subsequent therapy.
You can determine what exactly has appeared on the skin, a mole or a papilloma, by the appearance of the neoplasm: they differ in borders, color and size.
These two pathologies have different causes and have different treatment methods.
Recently, cases of melanoma, squamous cell and basal skin cancer have become more frequent.
Often, a seemingly harmless mole can cause the development of cancer; in the presence of papilloma, the risk increases several times.
The similarity between a mole and a papilloma lies in the fact that they are benign neoplasms, can appear on any part of the skin or mucous membranes, and have a tendency to malignancy (degeneration into a cancerous tumor).
The main difference between these formations is the nature of origin; the development of the process, appearance and treatment methods are also different for these pathologies.
The following types of moles can be distinguished:
- borderline - looks like a spot slightly raised above the skin;
- intradermal - has the appearance of a tubercle;
- intradermal - a neoplasm on a stalk, very similar to a hanging papilloma (how to distinguish a hanging papilloma from a flat papilloma and a nevus is described below);
- papillomatous - looks like broccoli, located on any part of the body;
- basal - has a flesh color due to low melanin content;
- linear – congenital nevi arranged in a chain;
- blue – has a blue or bluish tint, has a high tendency to malignancy;
- Seton's nevus - a hypopigmented (white) spot around the colored mole;
- Ota moles are spots of a dirty-brown hue localized on the face.
Depending on the appearance and location, we can talk about the following types of papillomas:
- wart. A neoplasm with a dense surface, located on various parts of the skin, warts can be pointed, flat, simple (vulgar) and plantar;
- condyloma. Pointed papilloma, developing in the area of the external genitalia and anus;
- acrochordon (senile papilloma). Papilloma, in appearance resembling a thin thread, is localized in the face and neck;
- cutaneous horn. A dense keratinous neoplasm, in appearance resembling a small horn.
Papilloma can be flat or hanging (in the form of a dense rounded neoplasm on a thin stalk) and have a size from 2 to 20 mm in diameter.
- Often, after an injury (thermal, chemical or mechanical), the neoplasm begins to rapidly increase in size, in which case its immediate removal is required.
- A large papilloma, often injured by the edge of clothing, must also be removed during hygiene procedures or during work.
Many people remove warts at home, using traditional methods or using cryodestruction devices.
This is quite dangerous, because after such removal the deep part of the tumor may remain untouched and the further development of the process will become unpredictable.
Many people believe that any growth on the skin is a mole.
Why did a mole appear on the head under the hair?
To prevent the development of cancer, you need to figure out how to distinguish a mole from a papilloma yourself.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what papilloma is in women, how it is dangerous and how to treat it
Locations
Our skin has protective properties (immunity).
In places of friction and high humidity (armpits, groin folds), the immune system is weak. This is a favorable condition for the formation of filamentous warts, which grow from a tiny nodule. The nodule has a thin stalk. Gradually it takes on an elongated shape or becomes like a ball on a leg. Such nodules often occur in areas of the body that are most delicate and subject to friction from contact with clothing:
- on the neck;
- in the folds of the groin;
- under the mammary glands;
- armpit.
Filiform warts also often appear on the skin of the face: in the area of the nose and eyes.
When choosing a location, growths are quite selective: they appear where the skin is thinner, in the folds of the skin and in places of high humidity.
Often filamentous warts appear:
- in the facial area (affect the eyelids, frontal part, near the nose),
- in the groin area,
- cervical region,
- in the armpits,
- in women under the mammary glands.
In places with a thicker layer of skin, neoplasms are not observed.
Risk factors
There are known circumstances that significantly increase the risk of contracting the infection responsible for filiform warts. Papillomas appear in a short time in those who are exposed to the following risk factors:
- damage to the skin (cuts, abrasions);
- weakened immune system;
- prolonged exposure to HPV;
- close contact with a carrier of the human papillomavirus;
- warm and moist skin.
Thread-shaped warts can occur at any age, but over time their number increases significantly. Especially after 50 years, their appearance is observed in every second person.
What it is?
A filamentous wart (papilloma) is one of the types of viral growths on human skin.
How to identify a wart? Unlike other warts (round and flat, which often appear in children), it has an oblong shape. If you look closely, you will notice that this species looks like a peculiar flower.
Many elongated petals are collected on one leg. There is also an opinion that a filamentous wart looks like torn threads.
But no matter how she looks, in reality she is not a pleasant and not a welcome guest. New growths of this species are usually called acrochords . Acrochords appear in the most delicate areas with thin skin. Most often these are the eyelids, neck, corners of the lips. Other favorite places are under the breasts of women, in the groin folds, and in the armpits.
Diagnostics
Filiform papillomas have a number of characteristics that make it easy to distinguish them from other formations of this type. Despite the fact that the upper part has a slight thickening, the stem of these growths is always thin.
The appearance of such neoplasms is preceded by the formation of a small spot on the skin, reminiscent of a small mole. Thread-like variants of papillomas are flesh-colored or dark brown.
Their consistency is always dense, but the wart itself remains elastic.
Sometimes the doctor uses dermatoscopy - studying the skin under a microscope. This procedure allows you to understand whether the vessels are affected and whether blood clots are present in them. These are signs of a viral infection.
In some cases, PCR diagnostics are performed, which makes it possible to establish the fact of infection with the human papillomavirus. It can be supplemented by a biopsy of acrochord tissue and their histological examination.
Treatment of filamentous papillomas should be comprehensive. Since their appearance is a consequence of the activation of the virus, therapy should be aimed primarily at the pathogenic agent. In parallel, a set of measures should be developed to strengthen the human immune system. And only then is a method of physically eliminating the tumors chosen.
Papilloma must be diagnosed by a specialist. A person who finds it on his body can only guess about the type of growth, comparing it with the neoplasms in the photo depicting different types of viral rashes.
An experienced doctor will be able to recognize acrochords during a standard examination. To study the structure of the tumor, you will need to examine it under a microscope.
Additionally, the following tests are prescribed:
- PRC;
- Blood analysis;
- Biopsy of affected tissue.
The test results will help the specialist understand what virus the patient is infected with and whether the detected papilloma has a tendency to become malignant.
Differential diagnosis in the case of acrochords is not particularly difficult: at the initial appointment, a dermatologist can determine the type of neoplasm based on a visual examination and the procedure of dermatoscopy - magnification and examination of the skin formation under a microscope.
Dermatoscopic examination makes it possible to examine thrombosed vessels and angiopathy in thread-like formations - direct signs of the viral origin of the neoplasm.
Sometimes additional examinations are needed to clarify some data:
- PCR diagnostics to establish the fact of infection with the human papillomavirus;
- biopsy of wart tissue;
- their histological examination.
All these activities are carried out to differentiate acrochords from fibromas, moles, genital, flat, plantar and other types of papillomas.
Clinical signs ↑
At the end of the incubation period, the virus becomes active. Before the appearance of the acrochord, there are no signs on the skin that could precede this.
A long, yellow formation forms, attached to the skin at one end. Then it grows to a length of about 0.5 cm, but sometimes it can increase to 1 cm.
It happens that warts are located in clusters. They can then form one formation. Papillomas are usually skin-colored, but there are also darker colors.
Most often, acrochords can be seen on the face. They are localized in the following places:
- forehead;
- chin;
- nose area;
- eyelids;
- around the mouth.
- in the areas of the mammary glands and armpits.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a procedure in which fleshy skin lesions are exposed to liquid nitrogen. After treatment ends, small blisters may appear on the affected area.
Doctors recommend that their patients wear bandages on areas where filiform warts were previously located. The treatment is considered complete once the dead skin is removed.
If the growth has reached a large size, you will need to undergo several sessions of treatment with liquid nitrogen before the wart completely disappears. Depending on the exact number, size and location of the formations, doctors prescribe up to six cryotherapy sessions at intervals of 2-4 weeks.
Some people react very painfully to treating the skin surface with liquid nitrogen, so the freezing process is slowed down as much as possible and the effect on the growth is carried out gradually.
Cryotherapy may have side effects such as pain, tendon damage, superficial nerve damage, skin discoloration, scarring, or recurrence of viral warts.
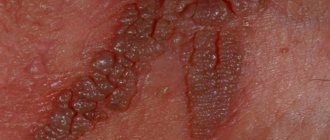
Condylomas acuminata
Such neoplasms are usually located in the groin area or in the mucous membranes. They are caused only by strains of HPV that occur during unprotected sex. Most often they affect:
The growths look like thin papillae and are small in size - 2-3 mm. Usually the virus is not limited to the appearance of one neoplasm. Condylomas are characterized by the appearance of several growths at once, gradually merging with each other. Neoplasms quickly increase in size and proliferate. At this time, their shape begins to resemble cauliflower inflorescences.
Genital warts are considered one of the most dangerous types of papillomas. In addition to the fact that these growths can degenerate into a malignant tumor, they are often associated with infection. Also, neoplasms are prone to recurrence after removal, so patients will have to undergo regular examinations to monitor the concentration of HPV.
In rare cases, condylomas can form on internal organs, for example, on the walls of the stomach or in the rectal area. In this case, it is impossible to diagnose the presence of a tumor on your own. The lack of specific symptoms can become a problem in diagnosing and treating the disease.
Types of warts: photo, description
Depending on the location, the following types of external manifestations of HPV are distinguished:
- Vulgar (simple) warts, which account for up to 70% of all skin warts and are more common in school-age children. They are elevations above the surface of the skin with an uneven, keratinized surface. They most often appear on the hands, but can be on the edges of the lips, on the face and, extremely rarely, on the oral mucosa.
- Flat (juvenile) warts are less common (4%). They are found in children and young people on the back of the hands and feet, face, and oral mucosa. These are warts of different shapes; they have a smooth surface and slightly rise above the skin level.
- Palmoplantar warts are very common (34% of cutaneous warts). They are dense formations with horny layers.
- Filiform warts are soft, flesh-colored to dark brown papillomas, often pedunculated. They are located on the neck, skin of the eyelids, armpits, groin, under the mammary glands.
- Genital condylomas are multiple, less often single, soft papillomas located on the mucous membranes of the genital organs, around and inside the rectum, sometimes in the urethra. They have the appearance of simple (pyramid, ball) or complex (cauliflower) growths with a keratinizing surface on the stalk.
What types of warts (photos below) are dangerous? How do benign formations differ from each other? Let's figure it out together with the famous psychotherapist Louise Hay.
Peculiarities
One of the most common skin diseases are benign formations, warts. They are a type of viral infection that affects any part of the body, but most often the face, arms, legs, and nails.
Today we will talk about what they are and what types of warts on the hands are, photos, how to diagnose them and how to treat them.
Wart on finger
Many people have warts during their lifetime. Most warts are harmless and go away on their own. This infection occurs most often in children, less often in adults. Warts are a skin infection caused by a type of human papillomavirus. Warts can affect any area of the body, but they typically enter the body through small cuts or scrapes on the fingers, hands, or feet.
Children can become infected with warts from touching an infected person (direct route of infection), or indirectly by using things of an infected person (towels, etc.). Children who bite their nails or pick hangnails tend to get warts more often than children who don't. They create an unprotected wound into which the virus can easily enter.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what they inject in the face for wrinkles
Risk of malignancy of filiform warts
Filiform warts are usually not characterized by degeneration into a malignant formation, however, under certain factors, their inflammation and dissemination over the human skin is possible.
Thus, the spread of acrochords is facilitated by their traumatization. For example, when a wart is localized on a man’s chin, it is often injured during shaving. Even if a person carefully “bypasses” additional education, at some point the acrochord may still suffer. As a result, new warts may be located close to the site of injury.
This happens more often when using a razor than with an electric razor, since the latter does not fit as tightly to the skin as the machine. Thus, traumatization of warts is observed much less frequently.
In addition, inflammation of filamentous warts is observed when they are frequently rubbed by clothing, for example, when localized on the neck - with a shirt collar, wrist - with cuffs, lower back - with a belt, and also in the bra area.
In such cases, it is recommended to remove acrochords to prevent their spread to the skin. Also, if a red rim appears around the wart and its color changes, you should contact a dermatologist to decide on the removal of the filamentous wart.
Filiform papillomas of the acrochord. Their signs and treatment
Such warts are easy to distinguish from other varieties. At an early stage of development, filamentous papilloma looks like a small flesh-colored bump, sometimes it is even mistaken for a mole.
But gradually it begins to grow and soon takes on a characteristic shape. Although such a growth is called a pedunculated wart, a pedunculated wart is not always present.
The main and, perhaps, the only reason for the growth of filamentous warts is the introduction of papillomavirus into the body (another name is human papillomavirus). The causative agent of the disease is HPV of four types - the third, fifth, eighth and ninth.
Infection occurs through contact. Most often, pathology is detected in people over 35 years of age.
In childhood, adolescence and adolescence, filamentous warts of the acrochord are not found. Approximately half of the cases of detection of papillomas in patients aged fifty years and older are caused by acrochords.
In elderly people, this type of wart is common.
If we analyze the main locations of warts, they “select” areas with delicate skin (the area around the eyes), as well as skin folds where there is increased humidity (groin and armpit cavities).
Appearance and localization
Not everyone knows what acrochords look like and what they are. They can be distinguished from other types of warts by their characteristic features. The main feature of filiform papilloma is its long and thin stalk. The head may be thicker and harder. To study these tumors in more detail, you should look at the photo of filamentous papilloma.
It is a dense but elastic wart that is dark brown or pink in color. The shape of the head can be oval or spherical. The length of such skin growths is usually 3–5 mm, but in some cases the acrochords grow up to 10 mm.
Initially, a small bumpy bump appears on the skin, which can easily be confused with a mole. But then it stretches out and takes on a characteristic shape. Often these warts grow in groups.
In this case, they often grow together, resembling a cockscomb. Solitary acrochords most often appear in adolescents and young adults.
Filiform warts prefer areas of the body where the skin is thin and delicate, as well as various folds and depressions with high humidity. Acrochords are rarely found on the soles, legs, thighs, arms, back, and buttocks. The skin in these places is too dense and rough for them.
On the face, filamentous warts usually appear on the eyelids, near the nose, and on wrinkles in the forehead. Their favorite place is the neck, especially its lateral surface. They often grow in the armpits and groin. Women may find acrochords under the mammary glands.
Minor surgery
- The operation is performed using a scalpel or an electric needle.
- Before surgery, the affected area of the body is subjected to local anesthesia.
- Considering that filiform warts are small formations on the surface of the skin, surgical intervention is carried out quickly and guarantees complete removal of the growth in one single procedure. Repeating the operation is not required.
- Scarring may occur in the affected area after surgery.
- Electrosurgery involves two procedures: curettage (curettage) and cauterization.
- The base of the wart is burned off using diathermocoagulation, or cauterization.
- The surgical wound heals within two weeks.
- Secondary spread of formations is possible.
Treatment approaches for filamentous warts
Cryodestruction is carried out using low temperatures to freeze the wart
Treatment of filiform warts is necessary when they are localized in places with constant exposure to a damaging factor, as well as when they are inflamed. The main directions of treatment are:
- removal of acrochord;
- increasing the body's immune forces;
- use of antiviral drugs;
- treatment of chronic infectious and inflammatory foci.
The process of removing filamentous warts can occur in various ways. Among them, surgical intervention is considered the most effective method in terms of low likelihood of relapse. However, its use is limited due to the presence of a scar after excision of the formation.
Cryodestruction is carried out using low temperatures to freeze the wart. The advantages of this method are the absence of pain and scarring on the skin. The disadvantages include a long healing period - approximately six months.
The use of a modern laser ensures rapid tissue regeneration, absence of scars and disinfection of the wound surface. The disadvantage of the method is the high cost of the procedure and the lack of possibility of further histological examination.
Electrocoagulation involves the use of high-frequency current, which ensures the safety of the removed material for histological diagnosis. The disadvantage is the presence of scars after the procedure and the high probability of relapse.
Other traditional medicine methods
At home, unwanted growths can be covered with a band-aid or tape to prevent them from becoming oxygenated and to prevent the infection from spreading throughout the body and spreading to other people. Some doctors recommend treating tumors with cytotoxic substances. In the presence of multiple warts, somatic retinoids are used.
It is advisable to get vaccinated against the human papillomavirus. Although the vaccine is not a cure, it will protect you from infection.
Diagnosis begins at the first meeting with a dermatologist by visually examining the wart. Next, it is necessary to use dermatoscopy, which is carried out using a special microscope to enlarge the acrochord. During the examination, blood clots and angiopathy are detected in the blood vessels.
This information confirms the presence of viral genesis in the appearance of warts. In addition, to confirm infection, PCR should be used, which can detect the papilloma virus in human blood. If these methods could not confirm the diagnosis, then you need to resort to a biopsy with a histological review of the acrochord.
Prevention of infection and relapse
It is recommended to touch less handrails, handles, railings and other objects in public places that are often touched by other people. In addition, you must use only your own gloves, shoes, household and personal hygiene items to reduce the risk of contracting the papilloma virus, warts and other skin diseases.
To reduce the risk of infection with the human papillomavirus, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the skin, avoiding cracks due to drying out. It is imperative to carry out antiseptic treatment of existing wounds and microcracks.
Questions and answers
There are still a few important questions remaining regarding filiform warts.
How not to get infected
- To do this, you need to take care of the skin of the whole body, in particular the hands, so that it is moisturized and there are no wounds or even microcracks.
- In public places, you should try to touch less handrails, railings, handles and other things that are touched by a large number of people.
- You only need to use personal shoes, gloves, a towel, a machine and other things.
- And it is imperative to maintain your immunity at a high level.
Can it be removed with thread?
This is absolutely not worth doing, as you can provoke inflammation of the wart, which will entail more serious consequences.
What to do if a wart appears on the pubic area in men? Find out here
How to remove chicken wart on toe? Read on.
In particular, the acrochords will begin to spread further throughout the body.
Is liquid nitrogen removal effective?
Yes, this technique is often used to remove various tumors.
- Pharmaceutical products for self-use are very popular, after which the papilloma disappears approximately on the 10th day.
- Hardware removal of acrochords with liquid nitrogen is also practiced, but this may require several procedures.
Contagiousness
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V2wLOuvxuoM
Filiform warts are extremely contagious. Avoid touching similar growths on other people's bodies. In addition, it is not advisable to share clothes, shoes and personal hygiene items with infected people. The human papillomavirus can be caught in any public place, so be sure to wear rubber slippers in places designated for water procedures (showers, swimming pools).
For any, even minor, damage to the skin (cuts, scratches, abrasions), cover the wounded area with a band-aid. By following these simple preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of the virus entering your body, and therefore reduce the likelihood of filamentous warts.
Where do acrochords come from?
The cause of hanging warts is the papilloma virus. It enters the human body through cuts, cracks and other microtraumas on the skin. The papilloma virus loves damp and warm places, so it most often affects people suffering from excessive sweating.
You are unlikely to encounter filamentous warts on the body of a young person, because they appear in people over 35 years of age.
The older a person is, the more likely he is to find a hanging wart on a stalk. This is due to weakening of the immune system, as it becomes difficult for the body to fight viruses.
Once in the blood, the virus is not immediately activated. The impetus for its reproduction can be stress, disease of internal organs or hormonal imbalance. As soon as your internal forces, which resist all negative external factors, weaken, the virus will begin to manifest itself. As a result, a wart will appear on the skin.
Even the complete removal of one acrochord does not guarantee getting rid of it forever. Therefore, it is important to take care of your health and visit a doctor promptly. Treatment of chronic diseases helps prevent the growth of hanging warts.
Potato
Many women know that raw potato pieces do an excellent job of eliminating dark circles under the eyes. However, few people know that an ordinary inexpensive vegetable can literally erase unwanted formations from the skin quickly and without a single side effect. To carry out a home procedure, peel a potato, cut a round slice from it and rub it on the wart for five minutes. These steps must be repeated three times a day. Use the potato until the wart is completely gone.
Apple vinegar
Ordinary food apple cider vinegar can relieve a wide variety of skin and hair problems. It is considered one of the most powerful remedies for combating skin rashes and growths. The acid in the base of this liquid attacks the overgrown epidermis and literally removes excess layers from the surface. Moreover, apple cider vinegar also eliminates the virus living in the wart.
To effectively remove tumors, take two tablespoons of vinegar, pour them into a cup and soak a cotton ball generously in the liquid. Place the ball on the wart and secure it with a clean cloth or bandage. Leave the bandage on all day. The wart will go away after a few weeks of regular use of apple cider vinegar.
Pineapple juice
Pineapples are considered an exotic dessert, rich in vitamins and promoting healthy digestion. Who would have thought that the juice of amazing fruits can not only saturate the body with essential nutrients, but also eliminate filamentous warts, the treatment, removal and prevention of which are not always possible using traditional medicine? Its acidity, along with the presence of special enzymes in the liquid, makes it possible to effectively and quickly remove tumors.
Cut and peel a piece of pineapple, then squeeze out the fresh juice. Soak the wart in the juice for 5-10 minutes, then wipe it with a clean cloth. Repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day. It will take several days for the growth to completely disappear from the surface of the skin.
Treatment
If other types of warts themselves can disappear without a trace, then the acrochord that has settled in you will not disappear on its own. Even if it accidentally comes off, a new one will definitely appear in this place. There are many remedies and methods for treating hanging warts. Dermatologists will suggest the most productive ones.
Pharmacy products
Various types of medications
Drugs in this direction help the body cope with the virus, activate its own powers and increase immunity.
They affect tumors at low temperatures.
- Necrotizing drugs (Ferezol, Condilin, Verrukacid, Vartek, Solcoderm).
With their help, the neoplasm is cauterized, which leads to subsequent destruction. They have an anti-inflammatory effect, which helps speed up wound healing.
- Keratolics (Collomac, Salipod) are used externally only.
They soften the top layer, destroy the wart cells, which leads to their destruction. They have an anti-inflammatory effect.
The main difference between the methods of traditional medicine and folk medicine is an integrated approach to the problem of treating HPV.
When prescribing treatment, a dermatologist will competently select an immunomodulator to protect your immunity, antiviral drugs to fight the virus that has settled in your body and advise how best to remove tumors on the finger and other parts of the body, what techniques to use to remove the growth on the finger.
When using medications, you must strictly follow the instructions for use . Take precautions. Using necrotic preparations, treat the healthy part of the skin with medical Vaseline and, if necessary, cover with a band-aid. When applying bandages, use only sterile material.
Among the pharmaceutical remedies for warts, the following are also considered effective:
Traditional methods
Almost every family has some secret for fighting warts. These are conspiracies for the waning moon, threads against warts, tying a certain number of knots, followed by burying this thread in the ground.
By the way, they buried both apples and raw potatoes in the ground. The most interesting thing is that for many, the warts disappeared once and for all. The most effective recipes are:
Using celandine juice. Celandine juice should be applied to the entire surface of the wart once or twice a day. It is better to take juice from the old part of the plant. Treatment is carried out for two weeks; if the result is not achieved, repeat the course after 10 days.
Using garlic juice. Crush a clove of fresh garlic into a paste. Make a hole in a piece of wide plaster and put it on the papilloma. Apply garlic paste and bandage everything well. Leave overnight. Do this until there is no result. Instead of garlic, you can use potatoes for warts.
Using a bow. There are many recipes. One of them (checked personally). Cut the onion into small pieces 1-2 cm, pour 9% vinegar for 12 hours. Prepare the wart, spread Vaseline on all sides of healthy skin, stick the patch so that only the wart is above its surface.
Cover the entire surface of the papilloma with a piece of onion and secure with a band-aid. Leave for 10 – 12 hours. After the time has passed, remove the bandage. The wart will be translucent and fluid will begin to ooze from it. After 2-3 hours, the wart will turn into a hard crust. There is no need to tear anything off, everything will fall away on its own.
Juice of fruits and berries. Use lemons, apples, rowan berries. You need to put one drop on the acrochords every day.
Acetic acid. It is used in various recipes, as one of the components and in its pure form.
All these methods are aimed only at direct home wart removal. But getting rid of it does not get rid of the cause of the disease on your fingers and other parts of the body. There is no guarantee that these uninvited guests will not visit you again. Therefore, it is worthwhile to comprehensively remove growths using pharmaceutical and folk remedies for warts.
Hardware removal
Laser. The most favorite method of treatment by many. Not expensive, does not require multiple visits. The procedure is painless, as anesthesia occurs first and is safe; the patient wears dark glasses throughout the entire procedure. The principle of this method is burning. The papilloma seems to evaporate, leaving a thin crust in its place, which will disappear in 5-6 days.