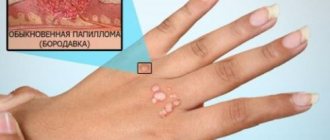
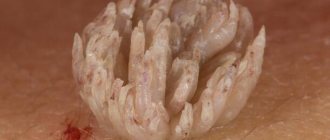
This disease is being diagnosed more and more often these days. Its greatest danger is that it increases the risk of developing cancer in the person infected with it.
READERS RECOMMEND!!!
To treat papillomas, our readers actively use the remedy... Read more
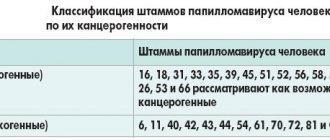
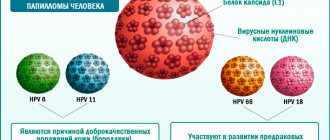
The abbreviation HPV 35 stands for human papillomavirus of the oncogenic type. In women, it can cause cervical cancer, and in men, various tumor processes of the skin and internal organs. Therefore, at the first suspicion of the development of an infection, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The essence of human papillomavirus type 35
In total, there are at least seventy varieties of the causative agent of the disease. The ways it enters the body are extremely numerous.
You need to know that the infection is transmitted through:
- sexual contact;
- using items belonging to a sick person;
- direct contact with him.
The risk of infection with HPV 35 increases when the body's defenses are weakened. Long-term smoking, alcohol abuse, metabolic disorders, disorderly life, and sexually transmitted infections can significantly affect resistance.
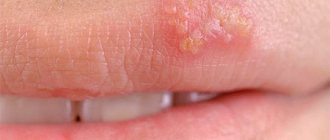
HPV 35 can provoke changes at the cellular and tissue level of the body, causing irreversible consequences. Visually they appear as various pathological skin formations.
Not all of them carry a risk of developing cancer, but some are quite capable of causing a malignant tumor in humans.
Therefore, if even the smallest warts appear on the genitals, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is required to undergo a full examination and tests for an accurate diagnosis. Timely implementation of therapeutic measures will help to slow down the development of the disease.
Diagnostics
Despite the practically absent symptoms of the disease, the virus can still be detected. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a series of tests that will help determine the DNA of the virus, as well as the HPV 35 genotype, which will help doctors determine the type of virus and understand how dangerous the infection is for human health in a particular case.
- A visual examination in a doctor’s office using a colposcope will reveal visible changes in the epithelium of the genital organs, after which additional examination methods will be required to help confirm the diagnosis. A routine blood test can also determine whether a person has an inflammatory process that accompanies the development of the virus in the body.
- At the medical institution, the patient will be prescribed to undergo PCR diagnostics. This research method helps determine how severely the body is affected by papillomavirus, which is necessary in order to prescribe effective, effective treatment. PCR diagnostics is a fairly accurate research method, however, there are errors in it.
- In addition, the doctor may order a culture, which will help diagnose the virus with almost one hundred percent certainty. For this study, a piece of biomaterial is taken from the patient, which is placed for a certain time in a special environment. Cultures also determine which medications the infection is resistant to.
- Doctors may also resort to performing a biopsy. This diagnostic method is prescribed only if the patient is diagnosed with a neoplasm. This is done in order to determine whether the tumor is malignant.
Sample PCR diagnostic results
Symptoms of the disease
There are many genotypes of the virus and methods of combating it have their own characteristics. Not all types of pathogens threaten the development of malignant neoplasms. More often, dermatitis, stomatitis or benign tumors occur on the genitals. In women they are more severe and often cause complications.
Even when a virus of increased oncogenicity enters the body, symptoms sometimes do not show themselves for quite a long time. On average, the latent period lasts about seven to ten months. The entry points for infection most often are the genitals, skin surface, mucous membranes, oral cavity, anus, wounds and cracks.
Important!
Not every person who comes into contact with papillomavirus immediately becomes ill. Most often, a healthy immune system immediately suppresses its development in the body. But with a decrease in protective forces, its activation is possible.
The manifestation of the disease varies somewhat among different sexes. Therefore, it is worth knowing the types of its signs.
The main symptoms of HPV in women:
- Genital warts;
- flat condylomas;
- papillomas;
- genital herpes;
- multiple warts;
- various skin rashes;
- itching;
- abrasions;
- redness;
- hyperthermia;
- chills;
- fever;
- diseases of the cervix, etc.
Signs of infection in men:
- The appearance of condylomas;
- warts on the frenulum of the penis;
- inflammation of the foreskin;
- polyps in the perineum;
- uncharacteristic discharge from the urethra;
- severe itching in the penis area;
- severe discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- burning when urinating;
- irritation in the anus;
- small cracks and wounds.
The table shows that, despite the fact that some symptoms are different in women and men, an experienced doctor will be able to understand that he is dealing with human papillomavirus type 35.
How does infection occur?
Oncogenic viruses from the HPV group, as a rule, enter the body during sexual contact through the mucous membranes of the genitals, rectum, and oral cavity. There are very rare cases of household infection, when there are defects and damage to the skin and mucous membranes, and the human papillomavirus penetrates through them through direct contact with the patient’s body, his underwear, and toiletries. Not everyone develops the disease. With a sufficiently strong immune system, the body immediately sends antibodies to the site of entry of the virus, which neutralize it.
There is another option for infection: the virus still penetrates the body, but is suppressed by the immune system and is in an inactive state.
The so-called carriage of the virus develops, which, with a decrease in immunity, can develop into a disease.
The third option when a virus hits is the worst. When a woman’s defense system is weakened, and this happens in the case of chronic diseases, intoxication, infections, pregnancy, and in women who smoke, the disease develops. The human papillomavirus begins its development cycle unhindered when, upon completion, symptoms of the disease appear.
In physically healthy women who lead a healthy lifestyle, including intimate ones, diseases caused by HPV occur extremely rarely.
Treatment of the disease
Typically, specific measures are prescribed to address the manifestations of the disease. As a rule, it all starts with excision of tumors on the skin. Full recovery after such measures does not occur; they are only symptomatic.
Papillomas and condylomas are removed using surgical methods. They are actively affected by liquid nitrogen, laser, magnetic induction or high-frequency currents. Radio waves and chemical reagents have a good effect. Large doses of interferon are also often administered.
Only an experienced specialist should carry out treatment, since if the technology is violated, it can provoke the spread of HPV to neighboring areas.
In addition, the use of antiviral and immunostimulating drugs is mandatory.
These include:
- Amiksin;
- Viferon;
- Genferon;
- Groprinosin;
- Isoprinosine;
- Immunal;
- Panavir;
- Polyoxidonium;
- Reaferon;
- Cycloferon;
- vitamins.
These drugs are available in a variety of dosage forms and allow you to cover the manifestations of the disease as much as possible.
Oncogenic type HPV recedes somewhat under the influence of medications. They strengthen the body's defenses and prevent the virus from spreading further. In addition, they negatively affect its DNA, which has a cytostatic effect.
Methods for diagnosing the virus
The diagnostic complex consists of a number of studies and tests to determine the HPV 35 strain. The examination regimen is prescribed by the doctor after examining the skin lesion:
- genotyping of the virus with determination of DNA identity using polymerase chain reaction (taking biomaterial from the papilloma for analysis),
- a general blood test to determine disorders in the body (anemia, bacterial or viral infection, the presence of inflammatory reactions, the norm of leukocytes, lymphocytes is determined to determine the functioning of the immune system),
- examination of the genital organs, mucous membranes of the mouth (frequent localization) and the skin of the body,
- cytological scraping from the cervix, smear from the urethral canal,
- positive digest test,
- histological examination of papilloma biopsy to identify cancer cells.
Preventing infection when living with a sick person
Many people do not know what to do to avoid becoming infected with the human papillomavirus.
Measures to prevent infection of his family and friends have a great influence on the continued existence of a sick person.
The most effective methods of prevention for both the carrier of the virus and his partner are:
- constant use of condoms during sexual intercourse;
- regular examination by a gynecologist or urologist;
- careful adherence to all principles of intimate hygiene;
- own bath accessories for each family member separately;
- fully balanced diet;
- maintaining a correct lifestyle.
Important!
In addition to strictly following preventive measures, there is also a method of specific protection. This includes vaccinations against HPV. They are intended for women to protect them from developing cervical cancer.
Vaccination takes place in three stages. First, the first injection is given, after two months it is repeated, and after four months the final stage is carried out. The patient will not be able to get rid of the threat of HPV type 35 infection forever, but the vaccination will significantly increase her body’s resistance and create a fairly powerful barrier against infection.
Causes and symptoms of HPV 35
The main etiological factors of occurrence, triggers of the disease:
- Transmission of HPV from a sexual partner in the presence of warts on the skin of the anogenital area in a carrier partner and microtraumas on the mucous membranes and skin in a healthy partner, even during protected sexual intercourse.
- Skin injuries in adults and children during everyday contact with a carrier of the disease. There may be sharing of towels, razors, bed or underwear, visiting public bathing places (baths, showers, swimming pool).
- Transmission of HPV when a child passes through the birth canal from a carrier mother, during breastfeeding. The first signs of the development of papillomatosis appear by the age of 1-2 years of the baby’s life.
- HPV type 35 in women: what is it and how to treat
- HPV type 66 in women and men, what is it: how is it transmitted and manifested
- HPV smear: features of the procedure and preparation
There are a number of factors in the presence of which HPV is activated and the body’s immune defense is suppressed:
- hormonal imbalances (puberty, pregnancy, lactation, menopause, taking oral contraceptives, treatment with corticosteroid drugs, pathological disorders of the endocrine glands),
- infectious diseases of a protracted nature with massive antibiotic therapy (pneumonia, bronchitis, influenza), autoimmune pathologies (scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout) with the use of hormonal drugs to suppress the symptoms of the disease,
- smoking, drug addiction and alcohol abuse,
- having promiscuous sex life,
- frequent exposure to stress, depressive disorders,
- lack of normal nutrition, vitamin deficiency, exhaustion of the body.
The clinical picture of the consequences of activation of the HPV 35 strain in the body includes the following symptoms:
- development of warts in children and adults. They can have different localizations (face, neck, torso, limbs, intimate area), be from light pink to black in color, differ in a convex shape or voluminous growths in the anogenital area,
- genital warts are typical for adults and older people and develop on the genitals. They can be punctate or, when several cutaneous elements merge, they form into a pedunculated condyloma fungoides,
- flat condylomas rarely develop when type 35 is activated. The danger of such formations is that the roots grow into the deep dermal layers; this type of papillomas is oncogenic.
Common manifestations of papillomatosis, regardless of location, include: itching when rubbing with clothing, pain, swelling, hyperthermia of surrounding tissues during the growth of papillomas.
Life prognosis and prevention of degeneration
There is no specific prevention for strain 35. To prevent infection and prevent the activation of the virus, you must follow the following rules:
- avoid casual sexual contacts,
- observe personal hygiene rules, do not use public items,
- support the body's defenses,
- carry out sanitation of chronic foci of infection,
- undergo preventive examinations with a therapist once a year.
With timely diagnosis and the appointment of an adequate treatment regimen, the prognosis is favorable, cure occurs in most cases. With the development of an oncogenic process, degeneration into a malignant formation, treatment is carried out by an oncologist with chemotherapy drugs that suppress the body’s immune forces.
Treatment methods for HPV type 35
Need advice from an experienced doctor? Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
If HPV strain 35 is detected, treatment should include complex treatment with antiviral drugs and surgical removal of external manifestations using hardware techniques. Elimination with folk remedies or cauterization with pharmaceutical preparations (supercelandine, condiline, verrucacid) is unacceptable due to the high risk of injury to the formation.
Taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs helps the body cope with the aggression of strain 35 and prevent relapses.
Oral administration and intravenous administration of drugs are used: interferon, viferon, genaferon, proteflazid, immunoflazid.
Removal of condylomas using surgical intervention includes the following techniques:
- surgical excision of growths and affected tissues, used for large papillomas, combined with antiviral medications,
- laser coagulation allows you to quickly and painlessly eliminate all condylomas; inconvenience is caused by hard-to-reach condylomas on the genitals and the risk of burns to the genital mucosa,
- cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen (freezing apparatus) allows you to get rid of warts most effectively in several sessions, even with deep localization,
- radiosurgical method with the creation of a radioactive field for the destruction of papilloma. A new, effective method for removing formations.
The selection of an elimination method and further therapy to suppress the activity of HPV 35 in the body is prescribed by the attending physician based on the individual characteristics of the patient.