Why does psoriasis occur in the groin in men?
Scaly lichen has been known to people since ancient times.
To date, the factors that provoke the pathology remain not fully understood. It is believed that psoriasis on the head of the penis develops for the same reasons as the disease on other parts of the body. The most likely reasons include:
- metabolic disorders of the body;
- penile injuries;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent stress, emotional overstrain;
- endocrine system disorders;
- transmission of infectious diseases;
- bad habits;
- taking certain medications.
Genetic predisposition plays a major role in the occurrence of genital psoriasis. In children whose parents suffer from lichen planus, the risk of the disease is 25–50%.
How does psoriasis appear on the head?
Psoriasis on the glans in men (see photo in the article) has quite specific symptoms. With this type, peeling is often absent, plaques are localized mainly on the head of the organ. The appearance of plaques is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- redness;
- itching or burning sensation;
- papules rise above the skin by 1-2 mm;
- characteristic scales are formed.
Less commonly, the rash spreads to the inside of the foreskin. In this case, an inflammatory process, swelling, and pain often occur. In addition to psoriasis on the penis, the rash spreads to the folds of the groin and buttocks. The rashes are autoimmune in nature, the disease is not transmitted sexually or by any other means.
Psoriasis on the glans in men is also characterized by the psoriatic triad:
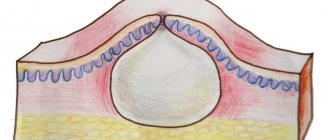
- Stearine stain - this stage is characterized by the appearance of an area with the presence of peeling. When you try to scrape off the scales, the peeling intensifies.
- Terminal film - appears if plaques are cleared of scales. At the same time, the surface of the dermis is thin and easily damaged.
- Bloody dew - due to damage to the terminal film, drops of blood appear on the surface of the skin.
If the above-described signs are detected, every man needs to seek qualified medical help as soon as possible; timely treatment of the pathology will help to avoid serious complications.
Features of the course of the disease
Psoriasis on the glans penis, like
other forms of the disease have several stages of progression. These include:
- The progress stage is characterized by the formation and rapid increase in the number of psoriatic rashes. At this stage, a feeling of burning, discomfort, and itching occurs. Not only a man’s physical health suffers, but also his emotional state. Shyness appears and the quality of sexual life decreases.
- Stationary – characterized by a decrease in the growth of plaques, but the rashes that have already appeared do not go away.
- Regression stage – there is a gradual cleansing of the dermis from plaques, a decrease in the intensity of symptoms.
Often, under the influence of various exogenous and endogenous factors, a transition from the stationary stage to the progress stage occurs. To prevent this phenomenon, it is necessary to carefully consider the treatment of the disease.
Drug treatment
Therapy for the disease must be comprehensive and complete. Both systemic and local drugs are used. The main thing is to stop the progression of the disease and accelerate the transition of the disease into remission. Treatment begins with lifestyle correction and giving up bad habits.
Systemic therapy
For internal use for psoriasis on the glans penis or other part of it, the following groups of medications are used:
- Cytostatics (Methotrexate, monoclonal antibodies). They inhibit the division of pathological keratinocytes and help reduce the severity of plaques. Used for the common form of the disease in difficult situations.
- Retinoids (Acitretin). They regulate the processes of proliferation and death of epidermal cells. They are used for a complex effect on the pathological process.
- Immunomodulators. Affect the activity of the body's defenses. Effective in case of autoimmune process. Regulate the work of T- and B-lymphocytes.
- Enterosorbents. They are necessary for binding toxins and waste throughout the body. Increases the effectiveness of other drugs.
Psoriasis on the penis, when isolated, rarely requires the use of the above remedies in the early stages of its development. However, the worsening of the patient's condition and the lack of effectiveness of simpler medications dictate the need to use appropriate medications.
Such treatment is carried out only after consultation with a doctor. He sets the exact doses and duration of the therapeutic course.
Local therapy
Psoriasis can be treated using the following groups:
- hormonal ointments (Elocom and others);
- combination creams (Triderm, Skin-cap, etc.);
- auxiliary medications (zinc and salicylic ointment).
The selection of a specific remedy depends on the individual characteristics of each case.
Diagnosis of pathology
Treatment of chronic psoriasis on the head of the genital organ begins with diagnosing the disease. Since the symptoms of scaly lichen on the penis are often nonspecific, it can be quite difficult to identify the pathology. To make a diagnosis, an integrated approach is used, including the following measures:
- Visual examination of the penis by a specialist.
- Taking an anamnesis, studying the history of the disease.
- The patient must inform the doctor about the chronology of the development of signs of the disease and the accompanying factors that could influence the occurrence of plaques.
- Laboratory tests of blood and urine analysis.
- Fungus analysis.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with diseases such as eczema, allergic rashes, lupus erythematosus, pityriasis rosea, scabies and others.
Diagnostic methods
Psoriatic manifestations can be confused with symptoms of other diseases.
To determine an accurate diagnosis, the following steps will be required:
- Medical examination, collection of anamnesis of the disease.
- Study of genetic predisposition.
- Laboratory blood tests.
- Additional measures in the form of a biopsy of the affected areas of the skin or dermoscopic analysis.
To treat and diagnose psoriasis, consult a dermatologist. The diagnostic technique is as follows:
- medical examination.
- Anamnesis collection.
- Scrapings for laboratory analysis.
- Detailed blood test.
A smear for sexually transmitted diseases is an additional examination for any diseases in the genital area.
Differential diagnosis is carried out to exclude infectious and fungal diseases of the genital organs:
- syphilis;
- microbial eczema;
- vulvitis;
- balanoplasticitis;
- T-cell lymphoma;
- Reiter's disease.
A dermatologist is involved in diagnosis and treatment. You should contact a specialist after detecting the first symptoms. But in most cases, diagnosis is complicated by the fact that patients put off going to the doctor for a long time. It is also necessary to carry out differential diagnosis, since some clinical symptoms are similar to other diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, scabies, allergies, eczema).
To make a diagnosis, the following set of measures is carried out:
- history taking and examination. At this stage, the circumstances under which the symptoms appeared, their duration and course are clarified, and heredity is studied. The doctor also conducts a visual examination of not only the affected area, but also all skin in order to rule out other forms of skin diseases;
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- tests for fungal diseases;
- skin biopsy from the affected area.
In addition to the dermatologist, a consultation with a gynecologist and urologist is prescribed in accordance with the gender of the patient. This is necessary to exclude other diseases.
Also, based on the systemic nature of psoriasis, parallel diagnostics are carried out for diseases such as arterial hypertension, diabetes, vascular diseases and vascular disorders.
Due to the speculative and scientifically unproven nature of the causes and the pathological course of the disease, when starting the treatment of psoriasis in intimate areas, the specialist develops a complex comprehensive treatment plan, including several ways to combat the disease.
Basic treatment methods Initial stage therapy consists of the external use of topical ointments and creams that can reduce the severity of rashes and cleanse the skin of peeling and plaques. In the acute period of the disease, systemic oral medications, ointments and various physical procedures are used.
The treatment complex practiced by doctors is used for various types of illness; it is also effective for genital psoriasis:
- Corticosteroid ointments (Avecort, Betazon, Silcaren, Diprospan, Flucinar, Ultralan) containing antibiotics. The action of the ointments is aimed at restoring normal metabolism, stopping the activity of prostaglandins, which increase inflammatory processes.
- Preparations containing vitamin D (Psorcutan, Daivonex). For psoriasis, taking vitamin D is a mandatory treatment item to prevent the lesions from spreading to the joints. The largest amount of vitamin is contained in regular fish oil.
- Irradiation of affected skin with ultraviolet light. The purpose of the procedure is strictly individual.
- Ointments based on tar (Antipsorin, Berestin, Alfozil, Colloidin). They stop inflammation, improve skin condition, and eliminate itching.
- Herbal (walnut, sage, valerian, pine) and turpentine salt baths.
Constant observation by a doctor and regular tests provide a clear picture of the dynamics of treatment. However, 70% of success depends on how seriously and attentively the patient takes the doctor’s recommendations.
If suspicious symptoms appear on the labia, a woman should definitely consult a doctor. Visual examination and laboratory tests will help establish an accurate diagnosis. To determine pathology, the following must be carried out:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- scraping of skin scales;
- dermoscopy.
To make a diagnosis, doctors use measures that include:
- Examination of the skin on the patient's genitals.
- Questioning the patient about the chronology of the development of symptoms and factors that could provoke the pathology.
- Collection and study of anamnesis.
- Blood and urine tests.
- Analysis for microsporia (fungus). Diagnosis of psoriasis in men
Any form of the disease, including genital psoriasis, is diagnosed using a specific triad.
- Stearic stain. When the doctor scrapes the affected areas of the skin, the scales peel off, resembling stearin.
- Terminal film. After removing the scales, the doctor sees the remaining layers of skin that shine, resembling polyethylene.
- Pinpoint bleeding. Further scraping of the affected area results in the appearance of droplets of blood (blood dew).
It should be noted that diagnostic methods are the same for men and women.
They provide:
- visual inspection of affected skin areas;
- collection of anamnestic information;
- collection of material for laboratory diagnostics;
- conducting a detailed blood examination.
In addition, a smear is often taken to identify a sexually transmitted infection, which is transmitted directly through sexual contact.
As already mentioned, diagnosing penile psoriasis is difficult because the symptoms of the disease are varied. When making a diagnosis, it is necessary:
- Conduct a general examination and collect an anamnesis of the disease.
- Collect the patient’s life history, as well as family history, since the disease can be inherited.
- In some cases, it is necessary to conduct laboratory tests - a skin biopsy or dermoscopic examination. As a rule, a laboratory blood test is also prescribed.
Treatment of psoriasis on the glans in men
Faced with the disease, patients are concerned about how to treat psoriasis on the penis? Today, the following methods are used to treat pathology:
- Use of ointments.
- The use of medications for internal use.
- Injections.
- Physiotherapy.
- Dieting.
- Traditional treatment.
Each method of therapy is prescribed by the attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease and the individual qualities of the patient.
Effective ointments
When considering how to treat psoriasis on the penis, special attention should be paid to
means for external use. Ointments for the treatment of pathology have the following qualities:
- wound healing;
- antipruritic;
- disinfectant;
- decongestant;
- regenerating;
- keratolic;
- calming.
Medicines normalize cellular metabolism, strengthen local immunity, and prevent infection of resulting wounds. To treat rashes on the penis, the following groups of medications are used:
- Hormonal drugs (corticosteroids) are used under the strict supervision of a doctor, as they have a lot of side effects. Hormones are prescribed in short courses with strict adherence to doses. Popular hormonal ointments include Cortisone, Prednisolone, Flucinar.
- Non-hormonal agents are safer, but the effect of their application does not occur as quickly as when using corticosteroids. Among non-hormonal ointments, salicylic ointment, zinc paste, and preparations with grease, tar, and vitamins are often prescribed.
- Immunomodulators are aimed at suppressing cellular immunity, which helps relieve the inflammatory process and other manifestations of the disease. The main disadvantage of these drugs is the risk of wound infection due to a decrease in the body's local defenses. Immunomodulators include Pimecrolimus, Tacrolimus.
- Products including vitamin D are often prescribed for the treatment of glans psoriasis. They help normalize cellular mitosis, promote regeneration and healing of the skin. Daivonex, Zorka, Akriderm will be used here.
Despite the relative safety of some drugs, self-medication is not recommended. This may make the situation worse.
We will take internal medications
In case of exacerbation of the disease, therapy is not complete without the use of
medications for internal use. According to the study, it turned out that the majority of patients suffering from pathology have a disturbed metabolism of the body and a deficiency of certain vitamins. To normalize this balance, vitamin preparations are prescribed. These include Undevit, Revit, Decamevit.
Treatment options
Treatment will depend on the form of the disease and the stage at which it is. Psoriasis is considered an incurable disease, but the use of medications for external and internal use can increase the duration of the remission stage.
Penile psoriasis requires a comprehensive approach:
- the use of ointments, creams with corticosteroids, a drying, healing or moisturizing effect;
- medications for internal use (including sedatives, since excessive nervousness not only complicates the general condition of a person, but also aggravates the course of the disease);
- physiotherapy;
- dietary food.
Drugs
In the first place in complex treatment are means for external use. Creams and ointments alternate with each other.
If the use of drugs for local treatment of psoriasis of the head of the penis is not enough, systemic drugs of general action are prescribed. However, the use of ointments is not canceled.
External remedies for psoriasis have different effects:
- Hormonal medications help relieve severe itching, redness of the penis, and swelling of the glans. The downside to hormones is that they are addictive.
- For cracked skin, moisturizing creams are recommended.
- If weeping areas of the skin are observed, reverse-acting drugs are prescribed - drying ones, which accelerate the healing of the affected skin areas on the penis.
- Healing ointments will speed up the process of restoration of damaged tissue.
Tablets are used for increased excitability: sedatives and sleeping pills help restore the patient’s emotional state, vitamin A actively dissolves fats.
In the presence of secondary infections, therapy is supplemented by eliminating the infectious agent, taking antibiotics or antifungal agents. The use of various methods of physiotherapy is effective. Psoriasis on the penis is treated on an outpatient basis: creams and ointments are applied several times a day after taking a bath or shower, medications are taken as prescribed by the doctor. In particularly difficult cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
How to treat at home
Traditional methods of treating psoriasis on the scrotum and penis can only be used in consultation with a doctor. Popular recipes:
- psoriasis on the scrotum is treated with a decoction of bay leaves;
- take tincture of golden mustache internally;
- the head of the penis is lubricated with propolis and sea buckthorn ointment.
Before starting any manipulations or any remedies for psoriasis, it is important to undergo diagnostics and obtain doctor’s recommendations.
Diet
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of psoriasis. It is recommended to increase the content of dairy products, cereals, fruits and vegetables in the diet. Freshly squeezed juices, herbal infusions, and green tea are useful.
The diet for psoriasis includes the exclusion of the following foods:
- fatty, fried foods:
- salted, smoked, spicy foods;
- coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- sparkling water;
- citrus fruits and tomatoes;
- legumes: peas, lentils, beans;
- flour and sweet products;
- alcohol.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic treatment for psoriasis on the penis and balls does not differ fundamentally from the treatment of the disease on other parts of the body. This is the same set of procedures performed with the aim of regenerating the upper layer of the epidermis of the genital organs, normalizing metabolic processes and increasing the resistance of the body as a whole.
Physiotherapy methods used to treat male psoriasis include:
- electrophoresis;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- laser therapy;
- PUVA technique;
- low temperature treatment (cryotherapy).
The specific method is determined by the doctor, based on the characteristics of the disease and the capabilities of a particular clinic. The intensity and extent of the disease influence the volume of procedures.
Causes of pathology
For what reason psoriatic plaques appear on the penis and perineum has not yet been determined. The opinion of scientists leans towards disruption of autoimmune processes in the human body. This is due to the fact that the protective cells of the immune system, under the influence of changes, begin to attack healthy skin cells, mistaking them for an enemy. The affected area grows, and the lesions spread throughout the body or are localized in certain areas, often merging with each other.
Scientists believe that other reasons for the development of the disease are theoretically possible:
- Metabolic disease.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Allergy.
- Viral and bacterial infections.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Taking medications.
However, the influence of none of these factors has not been confirmed by research.
Causes of psoriasis on the penis
The main cause of psoriasis on the genitals in men is unknown. Doctors highlight situations in which the greatest number of infections with the disease were identified.
- When the immune system is disrupted, it begins to promote the development of pathological cells.
- Mechanical injuries to the penis.
- Infection of a viral and bacterial nature.
- Heredity. In 75% of cases, patients in the family have parents or more distant relatives with psoriasis.
- Various nervous strains, stress, and depression lead to illness.
- Overdose of toxic drugs and substances.
- Metabolic dysfunction.
- Insufficient skin hydration.
- Diseases in the endocrine system.
- Alcoholism, smoking.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation, overheating, hypothermia.
Typically, patients experience not one, but several causes of psoriasis. Depending on the stage of the disease, different symptoms appear and medications for treatment also vary. It is very important to follow preventive measures.
Psoriasis on the penis is a very unpleasant disease for men. It is impossible to get this disease by becoming infected from another person, but there are prerequisites for the disease, which are determined at the genetic level and due to changes in the structure of internal organs. But the main reason remains a mystery to doctors. The stages of development of the disease and symptoms practically do not differ from its localization; regardless of the affected area, itching appears and papules appear.
Symptoms can be relieved with modern medications and folk remedies. They will effectively relieve inflammation, itching, and the affected area. Depending on the stage of the disease, certain types of drugs are chosen - with or without hormones, with natural and synthetic components. After completing the course of therapy, preventive measures must be followed to prolong the time of remission. It is important to visit the doctor on time and take all the necessary tests, then the treatment will be effective.
At the initial stage and in complex treatment, doctors recommend using traditional methods of treatment.
Psoriasis occurs in women on the genitals against the background of hormonal disorders - this is the determining factor in the occurrence of genital psoriasis. Psoriasis on the labia, pubis and groin occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission.
First signs
Psoriasis in the groin in men appears spontaneously. Absolutely healthy skin is covered with specific
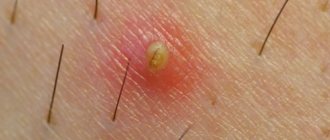
rashes in the groin area. At first, single and unnoticeable, and then multiple. These are reddish-pink spots rising 1–2 mm above the epithelium with a heterogeneous surface. The plaques are covered with small silvery flaky elements - scales. They are easily removed, exposing a thin terminal film, which bleeds slightly at the slightest damage. Also, almost always there is itching and flaking in a man’s groin.
Diagnosis of the disease is complicated by the similarity of symptoms of incipient psoriasis with other pathologies:
- allergic dermatitis;
- eczema;
- sexually transmitted infections;
- diaper rash;
- irritation;
- lupus erythematosus;
- we deprive.
Psoriasis in the groin area in men is often accompanied by rashes on other parts of the body. Plaques are localized not only in the inguinal folds, but also in the armpits. The danger of the genital form of pathology is that bacterial complications often occur. Due to increased sweating, a favorable moist environment is maintained in the groin for the growth of pathogenic microflora. Fortunately, infections can be successfully treated with antibiotics, and psoriasis rarely impairs a man's sexual function.
Signs in women
Rashes on the genitals are a serious disease that requires careful and proper treatment. For each patient, the doctor selects a series of measures aimed at eliminating symptoms and healing psoriatic plaques.
In more severe cases, specialists prescribe medications for internal use, as well as physical therapy methods, such as light therapy or the use of laser.
Among this group of drugs the following are used:
- Corticosteroid drugs. They are strong remedies for psoriasis. The disadvantages include a fairly large number of side effects. These are medications such as cortisone, hydrocortisone and others.
- Medicines containing vitamin D3. They are desirable in the treatment of any type of psoriasis.
- Non-hormonal agents. These are ointments such as salicylic, zinc, naphthalene. They are safer than corticosteroids, but the effect of use should not be expected quickly.
- Use of tar-based products. Tar is a natural component that has a detrimental effect on psoriasis. Soap, ointments, shampoos and other types of medicines are prepared from it.
In advanced forms of the disease, doctors often use stronger drugs intended for internal use. These are the following medications:
- cyclosporine;
- methotrexate;
- acitretin and others.
The drugs are selected individually for each patient and require strict adherence to doses. Treatment usually takes place in short courses, since long-term use is addictive and has a lot of negative consequences for internal organs.
The genital organs of women and men are structured differently, so the localization and symptoms of genital psoriasis should be considered based on the patient’s gender. General symptoms describe the following signs:
- plaque formation;
- redness of the upper layers of the epidermis;
- itching;
- painful nodules;
- irritation in places where psoriatic plaques accumulate.
For complete information about the characteristics of the symptoms of genital psoriasis, they should be presented based on the patient’s gender.
Psoriatic rashes usually affect the mucous membranes of the vagina, pubis, intergluteal space, labia minora and labia majora. Psoriasis also appears in the groin area in women, forming small pink papules that gradually become covered with whitish scales. If we talk about the symptoms of the disease, they are very similar to the symptoms characteristic of vulvitis.
In addition to the fact that this disease brings real pain to a woman, discomfort due to itching and cracking of the skin, psoriasis of the labia makes it difficult to live a normal life, experiencing all the joys of intimacy.
Since a woman’s genitals are affected by psoriatic rashes, intimate intimacy causes pain and also worsens the disease. There is a high risk of possible infection with a sexually transmitted infection.
The skin and mucous membranes of a woman's genitals affected by psoriasis easily become infected with microbes. It could be a fungus, or it could be a bacterial infection.
Due to the lack of air access and environmental humidity, atypical psoriasis of the labia is more difficult to treat than the same disease, but affecting other, more accessible and exposed areas of the skin.
However, this is not a reason to give up on your intimate life. Treatment brings long periods of remission, when women can lead an absolutely normal life, right up to pregnancy and childbirth.
IMPORTANT: Timely treatment of the disease will avoid serious consequences and help quickly solve the problem of the genital organs in men.
Psoriasis develops on the penis in males, most often between the ages of twenty-five and fifty. Signs sometimes appear several weeks after the pathological process has begun to progress.
Genital psoriasis is more common in women than in men. An exacerbation in patients is observed when hormonal levels change during puberty, during pregnancy or menopause.
Symptoms
A small child or teenager can develop psoriasis. But more often, sexually mature men aged 25–50 years experience unpleasant symptoms. The development of the disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- Intense itching and peeling of the affected areas. What is noteworthy is that the plaques and papules of psoriasis on the head of the penis do not peel off.
- Redness, pain, swelling of the lesions.
- Signs of a viral infection (fever, apathy, headaches, aches in muscles and joints, weakness, mental disorder, insomnia).
The moral component of the problem is dangerous for a man. A person is susceptible to complexes, is embarrassed by his skin, withdraws into himself, and stops communicating with friends and acquaintances. That is why, when treating psoriasis, you often need not only the help of an experienced dermatologist, but also an appeal to a psychologist.
What is this type of disease?
Psoriasis on the genitals is a source of discomfort, pain and discomfort. Most patients do not immediately seek specialized help from doctors when the disease is considered a form of neglect. Here, treatment must be carried out comprehensively; it will take a long time, since the fight against the disease in the later stages is difficult.
Men and psoriasis
In the groin of men, psoriasis on the penis is diagnosed at the age of 25–50 years. Patients diagnosed with genital psoriasis are boys and men of a slightly older or younger recurrent group. The symptomatology of this penis disease in men is that rashes appear on the head and other places in the groin area. They are red spots that rise slightly above the rest of the body of a person who has penile psoriasis.
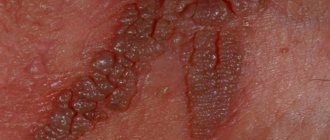
Psoriasis in the groin in men is manifested by redness and inflammation of the foreskin of the penis. It will cause itching of the scrotum and pubis. Genital psoriasis is manifested by the presence of numerous red plaques with white scales in the groin area.
Psoriasis on the head has a number of unpleasant symptoms, which are manifested by painful sensations, as well as swelling of the skin. In such cases, the inflamed areas on the genitals become hot.
Additional symptoms that psoriasis has on the pubic area are: a rash in the armpits, scalp, and ears. Doctors also diagnose psoriasis on the scrotum.
Psoriasis in the groin is often accompanied by damage to the ears and scalp
Inverse psoriasis, or atypical form, is a type of disease in which the rash is characterized by the presence of clearly demarcated bright red areas of the skin that form in places of natural folds. Such rashes do not have a scaly covering.
In addition, psoriasis on the pubis has a number of symptoms under the breasts, as well as in the intergluteal folds, and directly in the anal area. Taking into account the fact that such areas are subject to regular impact and friction, illness in such places causes additional discomfort and pain. Psoriasis between the buttocks is especially painful, resulting in ulcers and cracks in the intimate area.
Considering the fact that psoriasis in intimate places, or rather its atypical form, manifests itself not only in the genital area, but throughout the body, it is correct, and most importantly, to make a diagnosis on time on your own, without experience, education and special skills, it is not possible. That is why, if you detect suspicion of psoriasis in intimate places, on the head of the penis, you should immediately contact a specialist for advice.
Development in the groin in men or women:
- there are disturbances in the immune system,
- hereditary indicators,
- failure of both the functioning and regulation of the nerve endings of the spine,
- disorders,
- nervousness, stress.
In addition, people who have already suffered this disease once, especially in the intimate area, are automatically at risk, since any damage is fraught with the recurrence of the disease. It is very important to take care of yourself and adhere to strict hygiene, which is the prevention of disease.
Psoriasis is often accompanied by stress and depression
Psoriasis is a non-infectious disease that affects the skin. Among the main symptoms of this disease are excessive dryness, as well as redness of swollen areas of the skin. A fairly common disease diagnosed in men is psoriasis of the head of the penis.
Psoriasis in the groin is quite often diagnosed in men.
Female psoriasis
The genital organs suffer from this disease in women. Primary symptoms appear when there is a “discord” with hormones.
- Menopause in women after forty years.
- Pregnancy can cause the disease to manifest itself.
- Transitional age, which is accompanied by various changes in the body.
In some cases, women who experience discomfort caused by the disease mistakenly consider these symptoms to be a gynecological disease, whereas it is labia psoriasis, which worsens their situation.
Psoriasis appears on the labia in the form of small papules: round in shape, pink in color. Such rashes are covered with scales. The main area for the spread of such rashes is the pubic area, as well as the groin. The absence of itching makes it difficult to determine the presence of the disease in a timely manner.
We recommend reading: Vitamin complexes for children, vitamins for children with allergies
The disease in a woman’s intimate places manifests itself as a rash on the labia minora.
Female psoriasis affects the labia minora
Psoriasis appears on the labia in the form of small papules: round in shape, pink in color. Such rashes are covered with scales. The main area for the spread of such rashes is the pubic area, as well as the groin. The absence of itching makes it difficult to determine the presence of the disease in a timely manner.
Causes
None of the hypotheses about the origin of psoriasis are fully accepted. The only thing that all studies have in common is the assumption of the leading role of a hereditary factor. The type of inheritance is not clear: it is only clear that the genetic factor plays a large role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Even with a genetic predisposition to the disease, a person can live peacefully for a long time until his immunity is weakened by any external or internal factors. A drop in immune defense, illness or stress can cause psoriasis to spread.
The disease can affect any area of the skin. Lesions appear as single rashes or cover large areas of the body.
Localization of the disease in intimate places may be due to the following factors:
- Skin irritation from hard elements of underwear: lace, elastic bands, as well as rubbing from tight clothing.
- Inflammation of damage caused during shaving or epilation.
- Synthetic clothing prevents air from reaching the groin area. The lack of ventilation and high humidity of closed areas of the skin create optimal conditions for the development of additional diseases of an infectious and fungal nature.
- Poor genital hygiene.
- Excessive sweating.
- Psoriasis localized to nearby skin areas (legs, abdomen) can also spread to the groin area.
Excess body weight and fat folds in the groin aggravate the course of the disease: the skin in these places begins to become inflamed and cracks appear.
Psoriasis on the genitals
Psoriasis appears on the genitals (photo 2) due to general damage to the body by this disease. As a rule, a woman already has areas on her body affected by psoriatic changes, and the appearance of psoriasis on the genitals is evidence of a decline in immunity and the appearance of problems with sex hormones. All these factors make it possible for the disease to progress; psoriasis on the butt is possible, and psoriatic lesions appear in other areas.
Genital psoriasis occurs in the same way as on the body - women suffer from periods of exacerbation, and then they experience a time of remission. Psoriasis worsens during hormonal fluctuations, for example, psoriasis occurs in a child during puberty. In mature women, the disease appears during pregnancy, and in older women, during menopause. At this time, women should especially monitor the manifestations of the disease to prevent its worsening. Genital psoriasis can affect not only the genitals, but also the breasts.
Psoriasis appears on the genitals (photo 2) due to general damage to the body by this disease. As a rule, a woman already has areas on her body affected by psoriatic changes, and the appearance of psoriasis on the genitals is evidence of a decline in immunity and the appearance of problems with sex hormones. All these factors make it possible for the disease to progress; psoriasis on the butt is possible, and psoriatic lesions appear in other areas.
Nutrition rules
Treatment for psoriasis necessarily includes diet. Doctors advise adding foods to your daily diet that regulate the acid-base balance in the body. It is necessary to avoid coffee drinks, alcohol, sweet and spicy foods that cause irritation to the genitals. You should eat more fresh vegetables and fruits, rich in vitamins and microelements.
Traditional methods
In the arsenal of traditional medicine there are such means of treating genital psoriasis as salt baths, a compress made from tincture of bay leaves, string and celandine, and dandelion pulp. Golden mustache juice also helps treat psoriasis. These recipes are antibacterial and itching soothing in nature.
Traditional medicine cannot be used as the only method of treatment. Home methods can only be an addition to the main therapy.
Drug therapy
The course of treatment for genital psoriasis involves the use of the following medications:
- For topical use, the use of ointments and creams based on corticosteroids and containing antibiotics is recommended. Drugs at the local level improve metabolism and reduce active cell division at the site of the lesion.
- Preparations with vitamin D, which prevents the occurrence of joint psoriasis.
- Immunosuppressants, immunomodulators, retinoids.
- External ointments with tar, eliminating inflammation and itching of the skin. Tar also effectively heals the skin in the groin area.
- To prevent bacterial and fungal infections in the genital area, your doctor may recommend antiseptics.
It is strictly forbidden to use remedies for psoriasis in the genital area on your own. Many patients, embarrassed to contact a specialist, try to treat the disease with completely inappropriate medications, which often leads to a worsening of the situation.
Additional measures
Wearing underwear made from natural fabrics that does not press or rub the genital area, walking in the fresh air, regular light sports and good sleep will reduce the frequency of psoriasis relapses and make it easier to endure acute processes.
Do not shave the intimate area - additional trauma to the skin of the pubis can increase irritation.
Sexual intercourse is not prohibited if a patient with psoriasis does not suffer from pain during sex.
Traditional medicine cannot be used as the only method of treatment. Home methods can only be an addition to the main therapy.
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
Symptoms
Foci of psoriatic rashes protrude slightly above the skin level and have a smooth surface with sharply defined boundaries.
Characteristic symptoms:
- pink, red or purple rash;
- grayish coating (like a paraffin film);
- red borders of spots;
- slight swelling, redness;
- soreness of the lesions.
The diameter of the spots can range from 3 to 20 mm or more.
With severe sweating, the spots may not peel off or peel off slightly. Not all patients with inguinal psoriasis experience itching. In this case, most often the itching occurs in the anal area. Painful fissures may form in the fat folds. It is usually not difficult to diagnose psoriasis in the groin: in parallel with the intimate areas, plaques are also found on other parts of the skin.
Even if inguinal psoriasis is not accompanied by pain and itching, it significantly bothers patients from an aesthetic point of view. Despite the fact that psoriasis is not transmitted either by airborne droplets, or sexually, or through household contact, it significantly complicates intimate relationships.
Manifestations and symptoms in men
In men, psoriatic rashes are localized in the following intimate areas:
- head of the penis;
- testicles;
- pubis;
- perineum, buttocks and area around the anus;
- armpits and areas under the breasts.
Psoriasis in the groin area of men can provoke the appearance of blood impurities in semen and impair potency. When localized on the head of the penis, psoriasis can lead to balanoposthitis (inflammation of the inner part of the foreskin).
Manifestations and symptoms in women
In women, lesions can be localized in the following areas:
- on the labia majora and minora;
- in the anus and buttocks;
- on the bikini line and pubic area;
- on the vaginal mucosa;
- in the armpits and under the mammary glands.
Exacerbation of psoriasis occurs during periods of hormonal imbalance: at the time of menstruation, when carrying a child and in the postpartum period, during menopause. Insufficient or improper nutrition, mono-diets, hypothermia or stress can also cause an outbreak of the disease.
If treatment for inguinal psoriasis is not started in time, in women it can be complicated by vaginitis.
Disease prevention
Main stages:
- Progressive. A man may notice redness or a rash on the foreskin or head of the penis. Psoriasis will immediately make itself felt with itching and burning. A person experiences discomfort, refuses sexual activity, is embarrassed by the appearance of his penis, and the itching that occurs in the folds of the skin leads to nervousness, which in turn intensifies the symptoms.
- Stationary. This stage is characterized by a stable condition: no new plaques appear, but the old ones still itch and itch. If treatment is not started at this stage of the disease, psoriasis of the scrotum or penis will quickly return to its original stage.
- Remission stage. With timely treatment, the disease that poisons a man’s life enters a regressive stage, at which the skin gradually clears of plaques and the itching stops. To prevent psoriasis of the glans penis from returning, it is important to complete the course of therapy. Otherwise, the disease will quickly return.
How often the period of exacerbation and remission will alternate, and how long each stage will last, depends on the man’s attitude towards his health. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, follow all the doctor’s recommendations, have a healthy lifestyle and the absence of factors that provoke an exacerbation, the disease can “sleep” for quite a long time.
The causes of psoriasis in men and women are different. However, in order to prevent relapse, it is important to follow preventive measures:
- the likelihood of a disease occurring on the head of the penis will decrease if you strictly monitor hygiene and wear underwear made from natural materials;
- observe a rest and sleep schedule;
- Healthy food;
- treat infections regularly;
- get moderate physical activity;
- avoid stressful situations.
Many people are interested in the question of psoriasis and relationships with the other sex. As a rule, in the absence of concurrent diseases transmitted through intimate intimacy, contact is not prohibited. But you should protect yourself with contraceptives.
In general, the prognosis regarding the positive treatment of disease in the intimate area in an adult is positive. Provided you seek help in a timely manner.
An adult man may develop psoriasis on his penis. This is a non-infectious disease that brings the patient not only physical, but also psychological discomfort. Men aged 25 to 50 years are susceptible to pathology. It is extremely rare in children and adolescents. Treatment of psoriasis in the intimate area involves the use of a whole range of treatment procedures, thanks to which the patient’s condition improves.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with whether Psoriasis and cancer are incompatible or not
Genital psoriasis is considered a severe form of the pathology. But if symptoms are ignored, self-medication and delays in going to the doctor, the patient worsens his situation.
If the patient is not treated properly for a long time, the psoriatic papules may begin to coalesce, eventually forming a large affected area accompanied by severe pain.
First of all, the manifestations of this disease significantly worsen the quality of sexual life. Against the background of itching, libido decreases; the emotional state can also be affected by the very presence of rashes.
Sometimes the disease can even affect the skeletal system. In addition, the presence of pathology increases the risk of diabetes, stroke or coronary heart disease.
Despite the fact that genital psoriasis does not affect the reproductive function of both sexes, during its treatment hormonal medications may be prescribed, which can disrupt the normal course of pregnancy and cause miscarriage.
Prevention measures will help both avoid the appearance of genital psoriasis and delay relapse. Doctors recommend following these rules:
- Give up bad habits, namely smoking and alcohol.
- Maintain healthy sleep.
- Choose loose clothing made from natural materials to wear.
- Take walks in the fresh air more often.
- Adjust your diet. Limit fried, spicy, fatty foods, sweets and caffeinated drinks.
- Do not wear tight or chafing underwear.
- If you have a disease, avoid epilation of the bikini area; if you do not, reduce it to a minimum.
Genital psoriasis is a non-infectious disease that cannot be cured forever. It appears as pink or red papules, the affected areas are covered with scales and have a silvery color. As the plaques progress, they grow and can form quite large lesions, which will be accompanied by itching and pain. To make the treatment as easy and effective as possible, you should contact a dermatovenerologist at the first symptoms of the pathology.
Therapy
Treatment of psoriasis in the groin should begin with non-hormonal ointments and creams:
- Salicylic ointment;
- Zinc ointment;
- Sudocrem (based on zinc oxide).
Ointments are applied at night. For severe inflammation and flaking of the skin, you can apply them throughout the day. In the first stages of the development of the disease, they have a significant therapeutic effect: they relieve pain, itching, moisturize the skin and reduce peeling. Cracks in the affected area can be lubricated at night with Rescuer or Boro-plus cream.
Treatment of the disease with hormonal ointments should be started only when mild measures have no effect. Among the most effective hormonal drugs are the following drugs:
- Elokom in the form of ointment, lotion and cream. Mometasone and salicylic acid in the drug relieve inflammation and itching, exfoliate dead skin flakes, quickly returning the skin to a healthy appearance. The drug is applied at night for a month.
- Daivonex. A potent drug that stimulates the renewal of epidermal cells. For use only as prescribed by a doctor. Daivonex is applied to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day; it cannot be used on the face.
- Mesoderm. This medicine is used twice daily. The desired therapeutic effect is achieved after approximately 2 weeks of regular use. The duration of treatment should not exceed three weeks.
As additional measures of complex impact on the disease, the following are prescribed:
- Phototherapy, or UV irradiation, of the groin areas affected by the disease. This method of treatment is prescribed individually.
- Taking vitamin D (alone or as part of a comprehensive supplement).
- The use of antifungal drugs eliminates the possibility of developing fungus and bacterial infections.
Principles of treatment
Your doctor should tell you how to treat psoriasis in the groin. Not all external preparations are suitable for treating skin in the intimate area; this must be taken into account when choosing them. Treatment should be comprehensive, including external medications, physiotherapy, diet therapy, and folk remedies.
Drug therapy
Treatment always begins with the use of ointments to treat the plaques. At the early stage of the disease, non-hormonal agents, such as:
- Salicylic ointment;
- Tar-based preparations;
- Ointments with zinc.
Under the influence of the above mentioned remedies, inflammation is reduced, itching, flaking and pain are reduced, and the spots are prevented from increasing in size.
If non-hormonal therapy does not lead to the desired results or the disease immediately manifests itself in a severe form, then the plaques should be treated with hormone-based ointments, such as:
- Elokom;
- Daivonex;
- Mesoderm.
Ointments with glucocorticosteroids have a rapid therapeutic effect. Under their influence, inflammation decreases in a few days, swelling and itching disappear, and all dead skin is removed. However, only a doctor should prescribe hormonal drugs, as they can lead to extremely undesirable side reactions if used incorrectly.
The basic rule for using ointments with hormones is to comply with the duration of the course and the frequency of application of the drug. It is undesirable to use these drugs if psoriasis in the groin manifests itself easily, since they can become addictive to the body and further treatment will be successful only with the use of stronger, but at the same time toxic, medications.
In addition to external remedies for psoriasis, the use of vitamin complexes, in some cases, immunomodulators and agents that improve metabolic processes is indicated. The complete regimen of drug therapy also depends on whether the patient has chronic diseases - if they develop, appropriate therapy is necessary.
For psoriasis in the groin, antimycotic drugs are often prescribed; their use prevents the development of fungus and prevents the addition of a secondary infection.
Traditional methods of treatment
You can supplement the main therapy with all kinds of herbal remedies; they are used both internally and externally for psoriasis. Traditional therapy enhances the effect of drugs, improves local and general immunity, and promotes skin regeneration. The following methods of treating psoriasis in the groin show good effectiveness:
- Oak bark decoction. One hundred grams of crushed oak bark should be poured with a liter of hot water, heated over low heat for 20 minutes, cooled and strained. The prepared decoction is used to wipe psoriatic plaques 2-3 times a day, it dries the skin well, removes inflammation and itching;
- Aloe pulp. Peel the fleshy aloe leaf and apply it to the stain area, securing it on top with a band-aid. The compress can be left overnight. If psoriasis covers the areas near the anus or between the buttocks, then you need to prepare a paste from the pulp of the agave, apply it to a tampon and apply it to the plaque also overnight;
- Treating leather with oil – linseed, olive, almond. Oil is especially useful for lubricating cracked skin. Before processing, the oil is brought to a warm state in a water bath;
- Tincture of elecampane. You will need 250 grams of elecampane rhizomes, they need to be washed, crushed and filled with vodka in a volume of 0.5 liters. The product should infuse for about 2 weeks, after which it is used to wipe psoriatic lesions;
- Baths with medicinal herbs. To prepare an infusion for the bath, you need to take 2-3 tablespoons of herbs (chamomile flowers, sage, calendula inflorescences) and brew with a liter of water. After 40-50 minutes, the infusion is filtered and poured into a bath with 5-7 liters of warm water. You need to sit in such a bath for 20-30 minutes; it effectively removes irritation and itching from the genitals with psoriasis in the groin, and promotes skin healing.
Causes of psoriasis in men
Despite the fact that this disease has been known to medicine for hundreds of years, it has still not been possible to accurately identify the cause of psoriasis. Scientists name several of the most likely prerequisites for the development of psoriasis in men and women. They are:
- Genetic predisposition. In most cases, people suffering from psoriasis have close relatives who have been diagnosed with the same pathology. Therefore, if one of the partners has this problem, there is a high probability that it will be inherited by the child.
- Metabolic disorders. Psoriasis is almost always accompanied by disruptions in metabolic processes. In particular, lipid metabolism, carbohydrate and vitamin metabolism are disrupted, and the level of free cholesterol and sugar increases.
- Weakened immunity. Psoriasis in men can be provoked by any violation of the body’s defenses caused by past infectious and viral diseases, as well as severe pathological conditions of the body (for example, diabetes, cirrhosis of the liver, atherosclerosis, etc.)
- Stress, unbalanced diet, lack of sleep, general exhaustion of the body. Prolonged stressful situations “wear out” not only the nervous system, but also the immune system. As a result, the body's defenses are reduced, which makes the development of psoriasis possible. It is also worth noting that during strong experiences, a significant dose of adrenaline and norepinephrine is released into the blood, due to which a change in biochemical and metabolic processes occurs in the body.
- Living in a cold climate. If we compare the frequency of diagnosis of psoriasis in men in Europe, it turns out that the highest rates are in the Scandinavian countries (in particular, Norway). Separately, it is worth mentioning the population of the Arctic regions: the incidence rate here is about 12%. After moving to cold climates, some people with psoriasis experience an exacerbation of the disease and a decrease in periods of remission. It is worth noting that fair-skinned people suffer from this disease much more often than dark-skinned or dark-skinned people: among the indigenous populations of South and Central America, as well as Africa, psoriasis practically does not occur.
The first signs of psoriasis in men: photos
The main symptom of psoriasis is the appearance of unusual rashes on the skin. Typically, the disease begins with a small reddish-pink rash, accompanied by peeling, itching and the formation of a characteristic white, gray or silvery coating. Depending on the type of psoriasis, the rashes may later merge into so-called psoriatic plaques or remain isolated. The disease can affect the skin on any part of the body: psoriasis is quite common on the head in men, on the arms, back, chest, hips, knees, and elbows. In some cases, the disease also spreads to the joints, mucous membranes and internal organs.
Psoriasis of the genital organs in men (inguinal psoriasis) deserves special attention. In this case, a rash appears on the glans penis, scrotum, and perineum. The danger of this form of the disease lies in the potential for misdiagnosis. Some patients, having discovered a rash in the genitals, take it for a manifestation of a sexually transmitted infection and begin self-treatment. In such cases, there is a high probability that the disease may develop into an advanced form.
The male half of the population suffers from psoriasis somewhat less frequently than the female half. However, it is the male version of the disease that is often characterized by greater severity. The reason for this is the inattentive attitude of the majority of representatives of the stronger half of humanity to their own health. Many dermatologists note that male patients quite often come to the appointment with an already advanced form of the disease, while female patients seek medical help much earlier.
The first signs of psoriasis in men appear a little later than in women. They usually appear between 25 and 28 years of age. The second dangerous period begins in old age and occurs at 57-60 years.
Causes and provoking factors
Psoriasis on the penis is a non-infectious disease that brings physical and psychological discomfort.
Psoriasis on the penis in men is not uncommon. The disease is activated under the influence of various factors. At the moment, doctors cannot say exactly what exactly leads to the development of psoriatic pathology in a particular person. This is because the nature of the disease is very complex.
Experts put forward several theories that could explain the appearance of psoriasis in people. But none of them have been fully confirmed. According to doctors, psoriatic rashes on the genitals in men occur for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition to the disease;
- Disruption of the internal organs and endocrine system;
- Damage to the genital organ;
- Strong emotional shocks;
- Infectious diseases;
- Abuse of tobacco products and alcohol;
- Long-term use of potent medications.
Why is psoriasis dangerous for men?
In addition to the physical discomfort that accompanies the disease, many patients complain of significant emotional discomfort that affects their quality of life. If psoriasis is localized in open areas of the body, a person may experience discomfort when communicating with others, which cannot but affect his social activity, work and personal life.
Psoriasis on the glans penis and buttocks in men deserves special attention. Such localization of rashes can create a person’s feeling of inferiority, as well as interfere with his intimate relationships. However, the patient and his sexual partner must understand that inguinal psoriasis in men is non-infectious in nature, so it is unrealistic to become infected with it during sexual intercourse.
As for the dangers that arise from inguinal psoriasis, it is worth noting the following: some patients notice prolapse of the scrotum, the presence of blood in the semen, and deterioration in potency. To protect yourself from such troubles, it is recommended to contact a urologist or dermatologist immediately after detecting the first suspicious rash in the groin, on the head of the penis, in the perineum or on the testicles.
Features in men
A special feature of genital psoriasis in men is the manifestations of the disease in intimate areas:
- in the groin - psoriasis in men in the folds of the groin area and armpits most often occurs in people with excess body weight. Skin rashes, due to increased sweating in these places, do not have scaly formations and appear in the form of itchy red spots;
- on the penis - a pathology that can appear in men between the ages of 25 and 50 - psoriasis of the glans penis. Psoriatic plaques most often form on the flesh in the area of the head, and do not have the clinical picture characteristic of psoriasis: itching, peeling. Therefore, the patient may be misdiagnosed.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Beeswax cream with propolis for psoriasis
Attention! With a disease of the penis, skin rashes also spread throughout the patient’s body. Damage to the skin of the penis can provoke the development of a disease on the genital organ.
on the testicles: in men, testicular psoriasis is characterized by particularly severe itching in the affected areas. As a result, swelling, sagging of the scrotum, and the presence of blood in the semen may occur.
In the treatment of psoriasis of intimate places, topical drugs are used:
- ointments with corticosteroid hormones: Advantan, Lorinden, Laticort, Dermovate;
- immunomodulators: Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus;
- vitamin complex or preparation containing vitamin D;
- salt baths.
A healthy lifestyle and good nutrition, the absence of bad habits, reducing stressful situations, and maintaining immunity will help not only eliminate the signs of psoriasis, but also strengthen a person’s overall health.
Psoriasis in the groin in men: treatment
How to treat psoriasis in men should be decided by a dermatologist. A visual examination is usually enough for a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis, but in some cases a skin biopsy and blood test may be required.
At the moment, medicine cannot offer a remedy that completely eliminates psoriasis, but it has drugs at its disposal that help reduce the intensity of the symptoms of the disease and prolong periods of remission. For these purposes, doctors recommend complex treatment, including the use of antihistamines, enterosorbents, hepatoprotectors, vitamins, and the use of local agents - ointments and creams. Physiotherapy, sanatorium-resort treatment, diet, and normalization of work and rest schedules also give good results.
The patient must understand that treating psoriasis takes a long time. Even after the intensity of the symptoms decreases, he will have to adhere to a number of rules (in particular, diet, limiting contact with chemicals, avoiding stressful situations, etc.)
Separately, it is worth mentioning the need to use care products that help speed up the recovery process of affected skin areas. The patient should give up the usual soap or shower gel, since in most cases they additionally dry out the already damaged skin. As a safe alternative, we suggest using La Cree products. It is created on the basis of natural ingredients and does not contain hormones, parabens, silicones, fragrances or dyes. Intensive cream “La-Cri” is well suited for moisturizing the skin, eliminating flaking, redness and itching, and for washing the face and body -
cleansing gel "La-Cri".
Diagnostics
If the patient has psoriatic plaques on other parts of the body, diagnosing genital psoriasis is not particularly difficult. But if the disease begins specifically in the groin area, to make a correct diagnosis you may need:
- Examination and interview of the patient. If we are talking about vulgar psoriasis, it can be identified by the characteristic appearance of the skin.
- General and specific blood tests. In severe cases of the disease, studies show an active inflammatory, autoimmune and rheumatic process, as well as some endocrine and biochemical disruptions.
- Skin biopsy (tissue sampling) for histological examination. This helps to rule out other skin diseases.
To carry out differential diagnosis, additional consultation with a urologist or gynecologist may be necessary. In some cases, patients are also advised to visit an immunologist and endocrinologist.