Herpes pubis is a type of clinical manifestation of the genital form of a viral infection.
Genital herpes is a widespread infectious disease transmitted through sexual contact.
Pubic skin lesions occur predominantly in men, while in women the appearance of herpetic blisters on the mucous membranes of the genital organs predominates.
Why does herpes appear on the pubis?
In addition to infection during sex, other ways of contracting the disease cannot be ruled out, for example, through close contact of a healthy person with a sick person.
But if herpes appears on the pubis, then this most likely means that sexual intercourse has taken place.
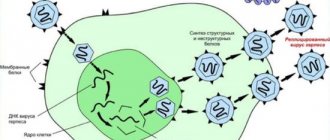
Reproduction of the virus begins at the site of penetration of the pathogen into the mucous membrane or skin.
At this point, vesicles containing clear liquid begin to form.
After this, the pathogen penetrates the bloodstream and affects the nerve endings.
It remains in them forever and periodically provokes relapses.
The virus leads to a decrease in the body's immune defense.
The disease can differ in various forms.
In approximately half of the cases the disease is accompanied by relapses.
After the process has completely subsided, a herpetic infection may make itself known several months or even years later.
Diagnostic methods
Initially, differential diagnosis is used, which makes it possible to distinguish herpes from the initial stage of syphilis. It is important to distinguish pathology from pemphigus, lichen ruber, relapses of candidiasis, and staphylococcal impetigo. To make an accurate diagnosis, the information obtained during the tests, as well as external signs and complaints of patients, is studied.
Additional laboratory tests are also used to detect the virus. Tests are taken: material from the urethra and cervix, urine, examination of prostate discharge. After this, culture is carried out on favorable media to detect the virus. Using the polymerase chain reaction, the presence of the HSV antigen is clarified. Laboratory blood testing is used to determine antibodies of other types: G and M.
Causes of relapses of herpes
The risk of relapse is often associated with:
- with high sexual activity
- with the last days of menstruation in women
- with what types of virus cause damage. The second type of virus provokes the development of relapse more often than the first
The occurrence of relapses can be influenced by factors that provoke a decrease in the body’s immune defense.
The most common influences on a disease outbreak are:
- changes in hormonal levels
- alcohol abuse
- presence of chronic infections
- hypothermia of the body, especially the lower torso and legs
- abuse of exposure to sunlight
The manifestation of pathology is often local in nature.
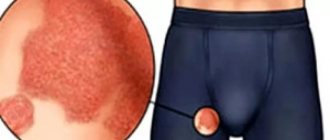
When the pubic area is primarily affected, a rash occurs in this area of the skin.
In some cases, the infection spreads to other areas of the skin and mucous membranes, involving the internal organ systems, including the brain.
If an exacerbation of the process occurs no more than one episode within 3 months, then such a course of the infectious process is considered favorable.
More frequent exacerbations are associated with a decrease in immune defense at the cellular level, which is characteristic of HIV.
In such patients, the appearance of new elements occurs against the background of old rashes.
The incidence of relapses in patients of both sexes is approximately the same.
But in men, the duration of the process is longer, and it is characterized by multifocal lesions.
In women, the period of exacerbation is reduced, but the process is more pronounced.
Preventive recommendations
You can reduce the risk of infectious diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of blisters on the pubis by adhering to the following rules:
- maintaining personal hygiene, taking a shower daily, using intimate products;
- exclusion of a chaotic lifestyle, use of barrier contraceptives during sexual intercourse with new partners;
- wearing underwear made of natural material (synthetic products create a “greenhouse” effect, preventing the delivery of a sufficient amount of air to the intimate area);
- elimination of bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol, taking drugs;
- exclusion of stressful situations, emotional stress, depressive states;
- maintaining proper nutrition;
- maintaining an active lifestyle.
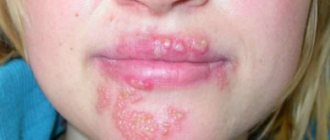
What does pubic herpes look like?
The classic manifestation of herpes is the presence of a blistering rash on the pubis and other areas of the anogenital area.
In case of infection through the oral-genital route, specific elements may appear on the lips.
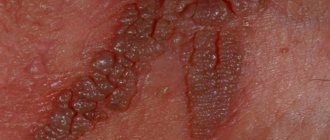
The affected area of the skin turns red and becomes swollen, and vesicular rashes form on it, arranged in groups in a chaotic manner.
When vesicles appear, patients present the following complaints:
- burning sensation in the pubic skin
- swelling of the skin or mucous membranes
- soreness
- sometimes upon examination an enlarged lymph node is detected
The rash goes through the following stages in its development:
- The appearance of vesicles. Most of the elements are formed in a very short period of time (overnight), but over the next two days a few rashes may still appear.
- The contents of the elements become cloudy, as a secondary infection may occur.
- Spontaneous opening of the bubbles. Within three days, the vesicles burst and erosions form in their place, which is the most favorable outcome. When ulcerative lesions form, they leave behind scars.
- The appearance of crusts when erosions dry out, which then disappear, leaving behind pigmented areas that gradually disappear.
Herpes infection is characterized by relapses.
Exacerbations are not as pronounced as during the primary infection.
Their frequency will depend on the state of immune defense.
As a rule, if during the initial lesion the symptoms of the disease are severe and the disease lasts a long time, then relapses will be more severe and frequent.
Methods of transmission of the virus
The simplest and most common way of transmitting infection is through contact between partners, that is, a certain relationship, but it is not necessarily sexual contact, even touching is enough. But there are several other options that genital herpes will take hold of your body and will exist there for a long time.
Although herpes is divided into 10 types, the most active viruses are considered to be the first and second types. Most often, genital herpes manifests itself as herpes of the first type, but there are cases when infections are mixed, and the virus of the second type also becomes active in the manifestation of genital herpes.
Sexual contact is the easiest way for the virus to spread, but often during childbirth, or if hygiene rules are not followed, cases of infection can occur, sometimes even children suffer. An insidious and secretive virus can hide anywhere, and at the moment when the body weakens, it will definitely shoot out, appearing exactly where it first hit.
Symptoms of herpes on the pubis
During the initial manifestation of infection and during exacerbations, rash elements form on the pubic skin.
Thus, the main symptoms of herpes are specific rashes, including general signs of infection.
These include:
- soreness of the elements
- enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area
- rise in body temperature
- manifestations of malaise, weakness
This condition is caused by intoxication of the body, which is caused by the pathogen entering the blood and lymph.
Such cases occur if the immune defense is weakened.
Herpes infection can be primary or caused by a relapse.
Primary is associated with fresh penetration of infection; with recurrent herpes, the virus is activated, which is already in the body in a latent form.
For a relapse to occur, sexual intercourse with the source of the pathogen is not required.
Depending on the manifestations of the pathology, the form of the disease can be:
- asymptomatic
- typical
- atypical
After the body is damaged by herpes, events can develop as follows:
- The patient does not feel signs of the disease, but is a virus carrier without even realizing it.
- The appearance of clinical manifestations of infection. The incubation period lasts from two to ten days. If the incubation period is short, then the infectious process has more pronounced characteristic symptoms, the duration of the disease will be one month or more.
The typical form of the disease has characteristic features:
- appearance of hyperemia
- formation of watery elements on the skin or mucous membranes
- opening of rashes followed by erosion
- epithelialization process
In the event of a relapse, the following symptoms may appear about a day before the formation of vesicles:
- redness of the skin, pain and itching
- enlarged lymph nodes
- appearance of general signs of intoxication
If such manifestations are present, the patient should immediately begin antiviral therapy to alleviate the subsequent course of the disease.
Features of the manifestation of herpes are that the inguinal lymph nodes become enlarged.
On palpation their pain is noted.
In the area of lymphatic vessels and nodes, swelling and hyperemia of the skin (lymphangitis) is sometimes observed.
Possible complications
The information known to doctors about HSV allows us to conclude that the virus threatens the following complications:
- has some effect on the progression of nervous system disorders, in particular neuritis and others;
- sometimes provokes diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- affects the urinary system, in rare cases – the gastrointestinal tract;
- increases the likelihood of infection with other pathologies that are transmitted through sexual intercourse;
- It is particularly dangerous for children, pregnant women, the elderly and patients with immunodeficiency.
Antiviral therapy is prescribed to both sexual partners. During treatment, it is possible to be sexually active, since the person is not in danger, except for discomfort in the affected area. Intimate relationships can lead to infection of the partner or an exacerbation of his signs of pathology.
Source: dermatologiya.su
Atypical forms of herpes
In the presence of an atypical form of the disease, diagnosing herpes has certain difficulties.
Wherein:
- non-standard localization of rashes is noted
- the order of formation of rashes changes, their characteristic signs may differ
- subjective signs prevail over objective symptoms, which may have milder manifestations or be more pronounced
The following atypical manifestations of herpetic infection are distinguished:
- Disseminated form. Characterized by simultaneous damage to two or more areas of the skin. The manifestations of herpes are the same, even if the rashes are localized in distant areas.
- Migrating. During each relapse, the area of localization of inflammation changes.
- Hemorrhagic. Characterized by the formation of vesicles filled with blood. After opening the elements, ulcers remain in their place, and scars subsequently form. This increases the risk of formation of foci of necrosis. The crusts that form after the vesicles open are dark in color. The area where the rash appears is very painful. The reasons for the development of the hemorrhagic form of herpes include the presence of immunodeficiency and blood clotting pathology.
- Rupioid form, the development of which is caused by bacterial infection. After the bubbles open, large brown crusts form. The duration of the disease is up to 3 weeks. The longer the inflammatory process, the greater the likelihood of scarring on the skin.
- Necrotic. Characterized by multiple rashes with blood. After opening the elements, necrotic areas form. The process is painless. Within a couple of weeks, the rashes regress, leaving scars in their place.
- Abortive. This form of pathology is considered favorable. Characterized by the reverse development of elements. Hyperemia and swelling appear on the pubic skin, a tingling and burning sensation may be present, but vesicles do not form. Typically, such manifestations are associated with timely treatment.
- Edema. Atypical forms of herpes, in which edema develops, have an unfavorable course. Few rashes form, but after the exacerbation of the disease, the swelling does not go away for a long time. Papules may form on swollen skin instead of vesicles.
- Impetigo-like. It resembles streptococcal impetigo in appearance.
- With signs of folliculitis. Since there are many hair follicles on the pubic skin, the pathogen can penetrate them. Pustules form, after opening which erosions form, followed by the formation of crusts. The central part of each element is permeated with hair.
What tests to take if bubbles appear in the groin
Patients often ask about this when visiting their doctor.
Usually, a person is prescribed standard tests first. With their help, you can determine what the general condition of the body is. Also roughly suggest in which direction to conduct further diagnostic search.
After general tests, a genital smear is usually performed. Biological material obtained with its help is examined using several different methods. It is necessary to exclude viral, bacterial and fungal diseases. With the help of a smear, it is possible to exclude a fairly wide range of ailments in a short time. It usually includes almost all sexually transmitted diseases. In addition to a genital smear, you can take a scraping directly from the rash. In this case, the obtained biological materials are evaluated using the same techniques as for genital smears.
If STDs are excluded, the patient may be advised to donate blood for allergies if there are blisters in the groin. The study will help to accurately understand whether the patient’s body is in a state of allergization. If the answer is yes, your doctor may recommend allergen testing.
Why is herpes dangerous during pregnancy?
Even with the formation of vesicles on the pubis, the pathological process spreads to the organs of the reproductive system.
- According to research, herpes infection can cause miscarriage in early pregnancy.
- Herpetic infection has a negative effect on the development of the fetus and, after rubella, the infection is in second place in terms of the impact on the fetus.
- A mother can infect her baby with a viral infection, both during fetal development and during childbirth.
Among the most common complications:
- development of polyhydramnios
- intrauterine infection of the fetus, which can be fatal
- birth of a premature baby
- weak labor
- protracted labor
- low birth weight of a newborn baby
- fetal death due to asphyxia
- inflammation of the uterus or mammary gland in a woman during the postpartum period
Women who suffer from a chronic form of the pathology are less at risk of complications.
The greatest danger comes from transmission of the pathogen to the fetus when the infection enters a woman’s body during pregnancy.
If a newborn is infected during childbirth, there is a risk of pneumonia, pathologies of the organs of vision and hearing, cerebral palsy, and mental development disorders.
The immune defense of such children is very weak, so the risk of contracting other infections is very high.
They are very difficult and often cause complications.
When a pregnant woman is diagnosed with the herpes virus, specific treatment is required.
Before 34 weeks of pregnancy, prophylactic medications are prescribed to prevent infection of the fetus.
A month before birth, treatment is carried out with Acyclovir.
In case of infection or relapse of the disease that occurs after the 34th week of pregnancy, delivery by cesarean section is indicated.
Provoking factors
It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease. Once infected, the infection will occur with varying frequency.
The number of relapses is individual and determined by the state of immunity, both general and local.
Factors that provoke infection and subsequent exacerbation are:
- frequent trauma to the pubic skin;
- wearing synthetic underwear;
- violation of the acid-base properties of the skin, its normal microflora, protective properties in various diseases - diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism, eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lice pubis, candidiasis, metabolic pathologies, kidneys;
- chronic sexually transmitted infections.
Recurrence of infection is most often observed against the background of decreased immunity due to hypothermia in the pelvic area, after swimming in a polluted body of water, sexual intercourse and repeated exposure to the virus, or stress.
Also, the immune response is suppressed by treatment with hormones, therapy for tumors and other serious diseases. But in such cases, herpes appears not only on the pubis, but also on other parts of the genital organs, and is widespread.
How to treat herpes
The basic principles of treating a viral infection in the genital area and pubic area are to destroy the pathogen and increase the body's defenses.
Therapy can be directed:
- to relieve the acute stage
- to prevent the development of exacerbations
- to exclude infection of a sexual partner or newborn child
- to prevent the development of negative consequences
Treatment of herpes pubis is carried out on an outpatient basis, but hospitalization may be required.
Placing a patient in a hospital is a necessary measure if:
- CNS complications occurred
- side effects from internal organs developed
- the herpetic infection has become severe, and the patient cannot take drugs with antiviral effects, as they have side effects
Among the drugs that are prescribed to patients with genital herpes are Valaciclovir, Famciclovir, Acyclovir.
The mechanism of action of all drugs is the same, so any of them can be prescribed.
The differences between the drugs include the features of their use and cost.
They do not destroy the virus in the body, but are able to stop its reproduction.
The most convenient is Valaciclovir, since it does not require frequent use.
The dosage regimen depends on the form of manifestation and severity of the process and is prescribed by the doctor.
The course of medication for primary infection is the longest.
The effectiveness of injections and tablets is not the same.
Injections for the treatment of herpes are prescribed if the pathology is accompanied by pronounced symptoms and if complications develop.
After opening the blisters, the eroded areas are disinfected to prevent the spread of infection.
Features of treatment for relapse are that the duration of taking the antiviral drug is shorter.
With frequent exacerbations of the disease, maintenance therapy is necessary.
Its duration depends on the severity of the relapse.
Sometimes this treatment continues for several years.
After discontinuation of drugs, the clinical manifestations of the disease are assessed on the basis of two relapses.
If there is deterioration, suppressive therapy is resumed.
ethnoscience
Along with classical methods of treatment, folk remedies that are prepared at home are widely popular.
Fir oil
The desired result can be achieved by treating the affected skin with fir oil. The procedure is repeated daily, at least 7-10 times a day.
Propolis tincture
This remedy is often used to cauterize rashes. The tincture is applied to the bubbles, and after 15 minutes they need to be lubricated with an emollient cream with calendula or chamomile extracts.
Black tea
For the treatment procedure, you need to brew a strong drink. For this, 1 tsp. The tea leaves are poured with boiling water (500 ml), and left for half an hour. After this, you should soak a cotton pad in tea and lubricate the rash. Therapy is carried out over 5 days.
Kalanchoe juice
This composition is especially effective against herpes in the intimate area. It neutralizes the effect of the virus, dries out pimples and activates the process of damage regeneration. The juice is applied to the genitals up to 6 times a day.
Arnica
Pubic herpes quickly disappears when using compresses with infusion of arnica flowers. 1 tbsp. l. plant material must be poured with boiled water in the amount of 2 glasses. The medicine is infused for 2 hours, cotton pads are dipped into it and applied to the rash localized in the perineum.
Vishnevsky ointment
The medicine is applied to the affected areas until they are completely restored. If you don’t have this ointment in your home medicine cabinet, Ichthyol will do. It quickly draws out pus, which promotes a speedy recovery. Before going to bed, you need to lubricate the rash with ointment, apply a piece of gauze on top and leave it overnight.
Before using the recipe you like, you should consult a dermatologist and strictly follow the contraindications. Plants that are used to prepare recipes at home can cause an allergic reaction. That is why before use it is worth conducting a test on a small area of skin.
Prevention of infection in the family
The herpes virus is a highly contagious infection.
To avoid infection, it is necessary to beware of entering into an intimate relationship with a patient during an exacerbation of the disease.
If one of the spouses suffers from pathology and the other is healthy, then planned prevention is used.
Typically, the doctor prescribes Valacyclovir in a daily dose of 0.5 g.
The patient will decide for himself how to take the medicine.
It all depends on how often he enters into intimate relationships.
For regular sex, the medicine must be taken constantly, and for occasional sex, it must be taken three days before possible sex.