General information about the virus
Some people call this strain of herpes “herpes simplex virus type 6,” but this is incorrect. The herpes simplex virus has two types - the first and the second. But herpes virus type 6 behaves a little differently in the body. The immune system, which suppresses the action of herpes virus cells type six throughout the life of the carrier, takes this strain more seriously than the herpes simplex virus. Therefore, with minor disruptions in the body’s immune system, a person is more likely to encounter problems with relapses of HSV than with the sixth type of herpesvirus.
Herpes virus type 6 can masquerade as other diseases, so the clinical picture of the symptoms of this strain is very blurred. When diagnosed, it is often determined by the presence of antibodies to herpes type 7 in the blood due to the fact that they are very related and often work together.
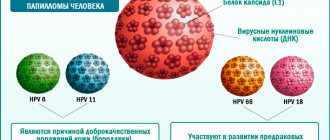
Human herpes virus type 6 has 2 types:
- HHV-6A - in theory affects the development of multiple sclerosis.
- HHV-6B - plays a role in provoking roseola of childhood and immunosuppressive diseases.
American scientists discovered this strain back in 1986; two years later they found a connection between the virus and childhood roseola. Then in 2012, the virus was divided into two types. It was revealed that herpes virus type 6 in adults affects diseases of the nervous system - this is HHV-6A. And in children, HHV-6B causes roseola, it is widespread and most people associate HHV type 6 with this disease.
Correct treatment of herpes type 6 and the most detailed description of the virus
Many known diseases occur in a very severe form when type 6 herpes is present in the body. This is one of 8 herpes viruses, which is difficult to treat under certain conditions. It has 3 main modes of transmission and a number of complications.
General information and features of the virus
Herpes type 6 is one of the strains of herpes that considers only the human body as a carrier. Therefore, in the abbreviation it is written as HHV-6 or HHV-6.
It should be recalled that there is no “herpes simplex virus type 6”. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is another type of herpes virus. In turn, the immune system reacts to HSV more aggressively, therefore, when the immune system is suppressed, a person experiences exacerbation of herpes simplex more often than relapses of type 6.
One of the characteristics of the virus is its ability to masquerade as other diseases. Therefore, it is quite difficult to diagnose it. Type 6 is often determined by the presence of type 7 herpesvirus in the blood.
There are two types of human herpes virus type 6:
- The first subtype is called HHV-6A (HHV-6A). This is a rarely diagnosed type in medical practice. It is often detected in people who are HIV positive. And also among doctors there is a theory that it is he who develops such a disease as “multiple sclerosis”.
- The second subtype is called HHV-6B (HHV-6B). More than 90% of the world's population is infected with this subtype. Doctors believe that HHV-6B provokes a disease called “infantile roseola.” Typically, type B begins its activity against the background of some disease, for example, hepatitis, pneumonia, etc.
Previously, type 6 was not divided into 2 different herpetic types. In 2012, it was divided because a pattern of different types of this herpesvirus was noticed. One of them affected diseases associated with the nervous system, the other caused “sudden exanthema.”
Routes of transmission of the virus
Herpes type 6 is a fairly active virus, which is very tenacious and quickly looks for a carrier. There are 3 main methods of transmission:
- During childbirth. Infection occurs from mother to child during childbirth. As a rule, primary infection occurs through the birth canal, and not through the placenta.
- Through saliva. The presence of type 6 herpes in the carrier's saliva allows the virus to be transmitted not only through a kiss, but also through airborne droplets during close contact.
- Through blood. If the carrier's blood comes into contact with the damaged skin of a healthy person or during a blood transfusion.
Symptoms of diseases caused by a virus
During primary infection, herpes type 6 usually causes sudden exanthema. Therefore, signs of primary infection with herpesvirus type 6 in adults are rare, since sudden exanthema occurs in childhood.
During primary infection, the body reacts quickly, with:
- the temperature rises to 38 degrees;
- stuffy nose;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- your throat starts to hurt;
- pain occurs in muscles and joints.
There are 2 main diseases that are provoked by the herpes virus type 6 in adults - chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) and mononucleosis, which is caused by HHV-6, and not by the Epstein-Barr virus.
Mononucleosis syndrome caused by herpes type 6 has the following symptoms:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- red throat, like a sore throat;
- heat;
- migraine feeling;
- painful condition of the joints.
With CFS, the symptoms are very vague. Typically, chronic fatigue syndrome does not have clear symptoms, but is accompanied by constant malaise in the body. A person cannot get enough sleep and always feels weak and depressed.
on this topic
Diagnostics
Herpes virus type 6 is diagnosed by taking a blood test for PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). The first is able to detect the presence of viral DNA, and the second will be able to understand the patient’s primary infection or exacerbation.
Tests for type 6 herpes through laboratory diagnostics are usually resorted to in rare cases. When a patient has enlarged lymph nodes and the doctor is unable to determine the cause or if it is unclear what antiviral drugs to prescribe to the patient.
After the tests, the presence in the blood of a ratio of negative (-) and positive (+) immunoglobulins of class M (IgM) and class G (IgG) will be detected. To decipher the analysis, use the following table:
DecodingIgMIgG
| If antibodies to herpes virus type 6 are both IgM and IgG negative, this means that the person is not a carrier. | — | — |
| There is no need to be afraid if IgM and IgG are positive. This means that there is immunity, but there is an exacerbation that needs to be treated. | + | + |
| This ratio of immunoglobulins indicates a latent form of the virus. An exacerbation can occur when the immune system deteriorates. | — | + |
| This indicates a primary infection of the patient; treatment must be started as quickly as possible. | + | — |
Diagnostics can also be prescribed if there is a suspicion of sudden exanthema, which is important to differentiate from diseases with similar symptoms.
How to treat herpes type 6
When treating type 6 herpes in adults, the following drugs are most often used:
- Acyclovir;
- Valacyclovir;
- Ganciclovir;
- Famciclovir;
- Valganciclovir;
- Cidofovir;
- Brivudine.
Acyclovir is used as an injection, but herpes virus type 6, unlike herpes simplex, is poorly treated with Acyclovir. Therefore, this drug is used only for mild forms of the disease.
Severe infections are treated with either Famciclovir or Valaciclovir. If the disease has severely affected the organs, doctors often prescribe treatment with Ganciclovir.
In addition to the above antiviral drugs, in severe stages of the disease, Valganciclovir may be prescribed. It is prescribed to adults, excluding pregnant women.
Cidofovir and Brivudine are new drugs to combat herpes, unlike the drugs described above. They are prescribed as a last resort when other medications do not control the infection or when the patient is in serious condition.
Photo No. 1 - Cidofovir, photo No. 2 - Famciclovir.
12
All of the listed medications cannot be used without a doctor’s prescription! Some of these remedies have a very long list of serious contraindications. Don't forget that the treatment methods for herpes type 6 are very different from the treatment for herpes simplex.
Possible complications
The diseases from the list below do not necessarily appear due to herpes type 6. There is a possibility that the exacerbation of the herpes virus, on the contrary, is caused by these diseases. If HHV-6 is present in the body, pathologies such as:
- multiple sclerosis;
- liver failure;
- diseases associated with oncology;
- meningoencephalitis;
- optic neuritis;
- and other dangerous diseases.
The pathogen itself is not so dangerous; it works in conjunction with other diseases and aggravates their course. But the presence of HHV-6 is very dangerous in AIDS.
Due to the possible complications of herpes and the pathologies that it causes, it is necessary to begin therapy as soon as the first signs appear indicating the presence of the pathogen in the body.
Transmission routes
The herpes virus is one of the most aggressive viruses in terms of its search for a carrier and one of the most tenacious. The virus is transmitted in three ways:
- through saliva - this is the most common penetration of the virus into a new body; usually type 6 herpes is transmitted from mother to child;
- through blood - the virus can be transmitted both through cuts and through blood transfusion from an infected person to a healthy one;
- during childbirth - we are talking about childbirth, and not about transmission through the placenta, infection occurs when the child passes through the birth canal.
Infection with herpesvirus type 6 occurs in 90% of cases in childhood from six months to two years. Until six months of age, the baby, if he has not been infected through the birth canal, has immunoglobulins of class G, transmitted from the maternal immune system. After the formation of its own immune system, the child is susceptible to infection. The older he gets, the lower the risk of infection.
Routes of infection
The main route of transmission of type 6 virus is contact with a carrier of a pathological agent. Herpes type six stays in the body for a long time and does not manifest itself until the immune defense decreases. Contact with the carrier may be of the following nature:
- Sexual path. Neglecting condoms during sexual intercourse leads to almost 99% of infections.
- Airborne path. Sneezing, runny nose, coughing and kissing.
- Contact and household. Using the same dishes, towels, toys.
- Hematogenous route. Infection occurs through blood (blood transfusion, hemodialysis procedures, insufficient asepsis of medical instruments).
Infection can occur during delivery, when the baby passes through the birth canal. The disease is highly contagious, which is why infection rates in society are so high. Despite this, some people do not experience any symptoms of a viral disease until the end of their lives, even with a decrease in immunity of various natures.
Herpes virus infection is transmitted:
- by airborne droplets;
- vertical (microorganisms are transmitted to the child in utero or when passing through the birth canal);
- parenteral (through blood) - with blood transfusion, organ transplantation.
“At the doctor’s appointment” Issue 39 - Herpes virus: types 3,4,5,6,7,8
Herpes - School doc. Komarovsky — Inter
Overview of Herpes Virus Infection
The incubation period is from 1 to 2 weeks.
Symptoms and signs of illness caused by the virus
Let's look at type 6 herpes in adults and the symptoms of diseases that it causes in the older age category. We wrote in detail about the course of the virus in a child in the article - herpes type 6 in children.
Infectious mononucleosis, caused not by the Epstein-Barr virus, but by herpes type 6, exhibits the same symptoms as with symptomatic exacerbations of mononucleosis:
- redness of the throat;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- joint and throat pain;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
When herpesvirus type 6 manifests itself as chronic fatigue syndrome, symptoms may include the following:
- depression;
- constant fatigue;
- in the morning you feel weak and not getting enough sleep;
- manifestation of causeless aggression;
- inability to control oneself;
- temperature changes;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- constant malaise.
Mononucleosis and CFS are the most closely associated diseases with herpes virus type 6 in adults. The remaining diseases will be listed as complications; they have their own symptoms.
Herpes infection in adults
Many adults suffered the infection as children. That is why roseola is extremely rare in older people. But this does not mean that type 6 herpes in adults will go away without a trace. The virus may reactivate and various diseases may occur.
This process can happen for several reasons:
- experiencing severe stressful situations;
- severe fatigue;
- acute viral illnesses;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases.
In civilized and developed countries, herpes virus type 6 in adults leads to the appearance of chronic fatigue syndrome. You can suspect the presence of an illness due to causeless rapid fatigue, apathy towards everything around you, increased aggressiveness and irritability.
Multiple sclerosis is another disease that occurs against the background of a herpes infection. The main mechanism for the manifestation of this pathological process lies in autoimmune reactions. That is, against the background of the virus, damage to the myelin sheath of nerve fibers occurs. As a result, there is a loss of communication between cells.
Diagnostics
Testing for herpes type 6 is most often carried out using two methods:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - detects viral DNA;
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a very accurate method that will detect DNA and indicate a primary infection or a recurrent form.
Diagnosis for herpes virus type 6 is not always necessary, even when symptoms are present. Typically, confirmation by laboratory methods is necessary in controversial situations when there is uncertainty in the choice of antiviral drugs by the attending physician or if it is impossible to diagnose the causes of enlarged lymph nodes. And also at times when the patient is in serious condition.
If you have already been tested for herpes virus type 6 and want to find out the decoding, there are four results:
- Immunoglobulins of class M and G are negative (IgM -, IgG -) - this indicates that there is no immune response and antibodies to the virus, the patient is at risk of primary infection.
- Immunoglobulins class M are negative, and class G is positive (IgM -, IgG +) - this indicates the presence of immunity to the virus. The risk of relapse depends on the state of the immune system.
- Immunoglobulins of class M are positive, and class G is negative (IgM+, IgG -) - this means that the patient has a primary infection. It is urgent to start treatment.
- Immunoglobulins class M and G are positive (IgM+, IgG+) - Relapse of the disease, but there is an immune response, treatment must be started.
In children, if symptoms of infantile roseola are present, it is also worthwhile to undergo laboratory diagnostics, despite the fact that, perhaps, while the results are ready, the child may already have recovered, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Roseola infantum can be confused with many diseases and if it is not roseola infantile, tests will be very helpful.
Diagnosis and treatment
To identify the disease, 2 tests are performed for herpes type 6. The first is the detection of antibodies (IgM, IgG) in peripheral blood using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The examination helps determine the stage of the disease and determine immunity to infection. The second is polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to determine the genetic material of the pathogen. The analysis makes it possible to determine the presence of herpes type 6 in saliva, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid with a high degree of probability and to identify the severity of the disease.
Infection with herpes virus type 6 does not require treatment. Children are prescribed multivitamins, plenty of fluids (fruit juice, herbal tea, mineral water), antipyretic drugs (Panadol, Nurofen), immunomodulatory herbal products (Echinacea, Immunal). Specific antiviral therapy is carried out in case of severe disease with damage to internal organs and the nervous system. The attending physician decides how to treat the infection depending on the state of immunity and clinical manifestations.
Medicines for the treatment of herpes
Treatment of herpes type 6 in adults is carried out with antiviral drugs:
- cidofovir;
- lobucovir;
- foscarnet;
- adefovir;
- ganciclovir.
Medicines are prescribed from the age of 12; at an earlier age, antiviral therapy is carried out for health reasons.
Prevention of recurrence of infection:
- good nutrition;
- physical education and sports;
- rejection of bad habits;
- optimal daily and wakefulness regime;
- fight against colds, chronic diseases, stress;
- walks in the open air.
So what is herpes type 6 and why is this type of infection dangerous? With a normal level of immunity, the disease does not cause dangerous consequences. Strengthening the body's defenses and timely treatment of immunodeficiency conditions allows one to avoid severe complications and deterioration of health against the background of exacerbation of viral infection.
Tweet
Pin It
- We care about safety: is it possible to go to the pool with herpes?
- Features of herpes in children
- Why is genital herpes dangerous?
- Interpretation of a blood test for the herpes virus
Treatment
If there are no complications yet and it is necessary to suppress the virus in the body, an integrated approach is used to treat type 6 herpes, aimed at combating symptoms and the virus, as well as stimulating the immune system. There are five groups of drugs for the treatment of herpes virus type 6:
- Antiviral - Foscarnet and Ganciclovir are worth highlighting among the drugs that fight viruses. Acyclovir and its analogues have not shown adequate effectiveness in the treatment of herpesvirus type 6.
- Immunomodulators - to maintain and enhance the body’s defense mechanisms, you should pay attention to drugs such as Viferon, Neovir and Kipferon.
- Vitamin therapy - for additional stimulation of the immune system, vitamin complexes containing vitamins A, E and C are often prescribed.
- Antipyretics are for symptomatic treatment; with an exacerbation of herpes type 6, as we found out above, a high temperature is characteristic and it must be normalized.
- Immunoglobulins - from this group of drugs, Lykopid, Amiksin and Gerpimun 6 are often prescribed against type 6 herpesvirus.
Do not forget that the prescription of a combination of medications should be entrusted only to your doctor. During pregnancy, you should take this even more seriously, since most of the drugs described above are not recommended for women to take while pregnant.
Mechanism of action of the virus
Herpes simplex virus type 6 has a dense shell with receptors. The main component for them is the CD46 protein, located on the surface of almost all cells. This is why the virus “establishes itself” in the body so quickly and so easily. Once in the human body, it tries to penetrate CD4+ cells, which differentiate into T-lymphocytes. The latter are capable of suppressing the immune response. Viruses, taking advantage of this property, induce a T-lymphocyte phenotype and bind to the CD46 protein. Since this protein works in all cells except red blood cells, it is easy to imagine the possibilities of this herpes virus in our body. It was first discovered in 1986 in adult patients with HIV. A couple of years later, it was also isolated from infants with roseola. After a series of studies, herpes virus type 6 was found in people on all continents in almost every country.
Complications
All diseases caused by HHV-6 are complications. Even CFS and roseola infantum. But let’s consider the most serious diseases that can develop due to activation or primary infection with HHV-6:
- multiple sclerosis;
- encephalitis;
- myocarditis;
- infantile roseola with severe course;
- autoimmune diseases;
- diseases associated with central nervous system disorders;
- retrobulbar neuritis;
- liver failure;
- pityriasis rosea.
These diseases can occur for other reasons, and it is impossible to say for sure that this is due to type 6 HHV. But scientific medicine has found patterns in the presence of relapse of herpes of this strain with the course of the above diseases. The problem is that perhaps these diseases cause HHV-6 to relapse, and not vice versa.
To summarize, it is worth noting that herpesvirus type six does not always require treatment. It very rarely appears and causes visible problems. Only one of the two varieties of this strain of human herpes virus has shown frequent activity, and this usually manifests itself in the form of infantile roseola.
Symptoms
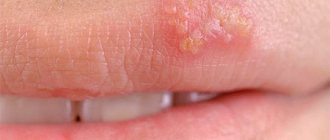
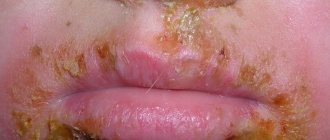
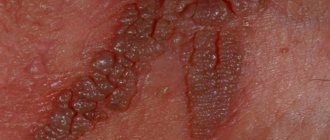
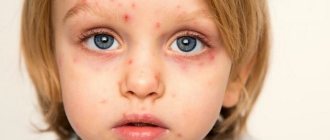
Type 6 herpes in children is characterized by an acute course, the clinical picture includes:
- A sharp increase in body temperature to 39-40°C. The febrile syndrome is observed for 3 days, it is not accompanied by coughing, sneezing or runny nose. It is quite difficult to eliminate fever from roseola in children.
- Signs of body intoxication. The child becomes lethargic and complains of general weakness and loss of appetite.
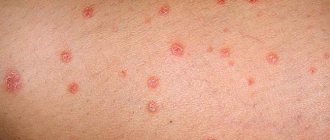
- The appearance of rashes. Locations vary: on the back, abdomen, face, neck, buttocks and limbs. In severe cases of the disease, a rash may appear in the throat, mouth, and pharynx. It occurs after a sharp drop in temperature. The elements look like small dark pink spots or dots with a diameter of up to 5 mm. The rash does not itch or cause pain. The child is not contagious to others. During this period, his activity returns and his condition improves. After 3-4 days, the spots disappear without leaving a trace.
- Signs of inflammation of the cervical, submandibular and occipital lymph nodes.
- Redness of the mucous membranes of the throat, allergic runny nose, diarrhea. Characteristic of severe disease.
- Febrile seizures. They develop against the background of febrile syndrome in children with reduced immunity. During this period, the child falls to the floor, trembles, stretches out and stops responding to external influences. Sometimes there is a loss of consciousness. The development of convulsive syndrome requires immediate medical attention.
Sometimes diseases caused by herpes virus type 6 are not accompanied by skin rashes. Parents may not notice a rash that appears at night and disappears by morning. Relapses in children with a normal immune system are asymptomatic and do not require treatment.
Type Features
The sixth type of herpes virus was discovered relatively recently (in the mid-80s of the twentieth century). This is a DNA-containing viral agent that infects T-lymphocytes (responsible for the immune response). Its study continues today. Within HHV type 6, two subtypes of pathogens can be distinguished:
- 6A (HHV-6). It is more typical for adults. The virus negatively affects the functioning of the central nervous system; presumably, its presence in the body is associated with the development of sclerosis;
- 6B (HHV-6-B). The variety is most often diagnosed in younger patients.
Herpes type 6 is considered an incurable disease. Antiviral drugs can reduce the activity of the pathogen and achieve remission, but it is impossible to completely cure a herpes infection with the current level of medicine .
Often primary immunity to the disease is innate (if the mother has antibodies to this type of herpes). Therefore, for the first six months of life, such babies are protected from infection; they are extremely rarely diagnosed with herpes type 6 (children from 7 months to a year are in the main risk group). Infection, as a rule, occurs during the first 3 years of life, after which specific immunity arises, allowing re-infection to be tolerated almost asymptomatically.
The virus remains in the human body in a latent form. It begins to actively multiply and have a destructive effect on health only during periods of significant decrease in immunity.
In most cases, herpes virus type 6 is diagnosed in patients with HIV (it was discovered for the first time during studies of immunodeficiency).
A special feature of the virus is that external signs of infection often imitate completely different diseases (colds, allergic rashes, measles or rubella). This makes diagnosis difficult.
Causes
Herpes type 6 in children occurs when an infectious agent becomes active and is infected by:
- By airborne droplets. Herpes is found in the saliva, nasal secretions and tear fluid of an infected person. The virus is quickly transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, which explains its prevalence in children's groups.
- During the period of intrauterine development and childbirth. In this case, the disease takes on a relapsing course and is accompanied by the development of complications. Infection with the virus during breastfeeding is rare.
- For blood transfusions and organ transplants.
Treatment
Treatment begins immediately after the first symptoms appear.
It is impossible to cure herpes, but you can reduce the activity of the infection, improve the general condition of the child, and prevent the development of dangerous complications.
For this purpose, etiotropic and symptomatic therapy, restorative and preventive measures are used. During the treatment period, the child is provided with bed rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids. Berry fruit drinks, natural juices and herbal teas are useful.
Diagnostics
To confirm the diagnosis of herpes in a child, use:
- PCR study. Aimed at identifying the DNA of the infectious agent in the patient’s blood or saliva.
- Enzyme immunoassay. Specific antibodies are detected a week after infection. The presence of IgM indicates an acute form of the disease. A positive IgG indicates that infection has occurred at some point.
- Culture method. An informative method for diagnosing herpes, which allows identifying cell damage even in the absence of manifestations of the disease.
Drugs
Diseases caused by herpes virus type 6 in children are treated with the following medications:
- Antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Ganciclovir, Foscarnet). The tablets are taken 4-5 times a day, the dosage is selected depending on the weight and general condition of the child. Pediatricians prescribe such medications only for severe infections.
- Antipyretic drugs (Ibuprofen, Panadol, Paracetamol). They relieve high fever, headaches and chills, and prevent the development of febrile seizures. When treating children under 6 years of age, they are used in the form of suppositories and syrups.
- Water-salt solutions (Regidron). Used to prevent dehydration in severe febrile syndrome.
- Immunostimulants (Groprinosin, Immunal) and vitamins. They normalize the functioning of the immune system and have a general strengthening effect.
- Antiviral ointments (Acyclovir). Apply a thin layer to the skin affected by rashes up to 5 times a day. Preliminary treatment is carried out with an antiseptic solution (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine).
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine for the treatment of disease in children offers the following remedies:
- Tea tree oil. Apply to affected areas 3-4 times a day. It has an antiseptic and healing effect, prevents bacterial infections.
- Honey. Contains a large amount of vitamins and has a beneficial effect on the immune system. It is enough to eat 1 tsp. product per day. Before using this product, you need to make sure there are no allergic reactions.
- Carnation. Included in most folk remedies used to treat herpes. The twigs are chewed once a day.
- Melissa infusion. 2 tbsp. leaves, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. To strengthen the immune system, drink 100 ml 4 times a day.
Prevention
Help prevent your child from contracting herpes type 6:
- long-term feeding with breast milk containing specific antibodies and all the nutrients the baby needs;
- maintaining a daily routine;
- long night sleep;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- proper nutrition (the diet should contain fresh vegetables and fruits, meat and dairy products);
- taking vitamin supplements;
- exclusion of contacts with patients;
- refusal to visit public places during periods of ARVI and influenza epidemics;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases.
Herpes type 6 in adults: symptoms, treatment, possible complications and consequences - Venereologist
The first five types of herpes virus were identified in the middle of the last century, and type 6 virus was discovered only in 1986.
Human herpes virus type 6 (HHV-6) is a pathogen that cannot be controlled and exists in a latent form with normal immunity.
Any malfunction of the immune system leads to activation of the virus, which is fraught with severe painful manifestations, including death.
How is herpes type 6 transmitted?
Human herpes type 6 includes serological infections 6B and 6A, which have genetic and epidemiological differences. Herpes of any type and subspecies is transmitted by airborne droplets or contact, primarily through sexual contact.
There have been cases of transmission of infection during organ transplantation from a person infected with the virus and during manipulation of medical instruments that were used in the treatment of virus carriers. Herpes type 6 is mainly concentrated in saliva, although it is found in almost all tissues of the body.
It should be noted the thermal resistance of the intracellular parasite, which allows it to withstand temperatures up to +52 degrees for half an hour, and maintain vitality under short-term exposure to temperatures of + 70 degrees.
Symptoms of herpes type 6 infection
Primary infection manifests itself acutely: a person’s body temperature rises to 38-39 degrees. In this case, the following are observed:
- minor intoxication;
- feverish condition;
- a sore throat;
- nasal congestion;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Often there are muscular and joint pains that occur in various parts of the limbs.
Signs of damage to the nervous system are:
In severe cases, the patient is completely immobilized and loses vital functions. After a few days, the temperature returns to normal, and a pale pink rash appears on the body in the back, chest, abdomen, bends of the legs and arms, which disappears after two to three days.
Often the symptoms of herpes infection are confused with manifestations of acute respiratory viral infections, rubella and other infectious diseases. But it should be remembered that the presence of herpes type 6 in the body can cause serious malignant diseases:
- lymphoma;
- leukemia;
- lymphadenopathy;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- optic neuritis;
- multiple sclerosis and a number of serious diseases.
The virus is most often detected not as a separate disease, but as aggravating the course of other diseases, including AIDS. Therefore, if you suspect a herpes virus infection, you should undergo an examination for the presence of infection in the body, passing the biological fluids necessary for analysis.
Treatment of herpes caused by type 6 virus
Treatment of the disease caused by herpes type 6 is symptomatic. Unfortunately, at the moment there are no medications that completely eliminate the virus that has entered the body. But timely detection and competent therapy prevent dangerous complications.
Typically, medications are used in various combinations, which are determined by the attending physician. In order to activate the immune system, a herpes vaccine is often prescribed.
Herpes type 6: what you need to know?
Important! Herpes remedy recommended by Elena Markovich! Read more.
Most carriers do not realize that herpes 6 is already present in the body. Like other human herpesviruses, it cannot be destroyed: medicine has not yet come up with such a cure.
This virus is especially pronounced in children.
Scientists believe that it is mainly transmitted through saliva, so babies become infected with this disease almost from the first days of contact with their mother or other carriers of the virus.
Infecting a child in the first few months of life will not lead to consequences, since the innate immunity transmitted from the mother suppresses viruses.
Only if the mother does not have the virus, and the child becomes infected from another person. Children usually get herpes between the ages of 4 months and 13 months.
Herpes virus type 6 can occur against the background of other diseases. Often the virus in the body is determined by the presence of immunoglobulins in the blood, which are common or very similar to those of the herpes virus. Because of this reaction, incorrect diagnoses are often made.
Broadcast
In most cases, this virus is transmitted through saliva. This is where it is present in 90% of people. Less commonly, the palatine tonsils are the reservoir of the virus.
The possibility of a child being infected with this virus from the mother during breastfeeding is almost excluded. In some cases, transmission of this virus to the child from the mother during childbirth is recorded.
During childbirth, it can enter the newborn’s body through mucosal injuries and skin damage.
To treat and prevent herpes, our readers successfully use Elena Markovich’s method. Read more
Symptoms
The main symptom is small rashes on the child’s skin, they spread over the entire surface of the body. Slightly raised above the skin. There is usually no itching. They are also called roseola infantile, sixth disease or pseudorubella.
A few days before the onset of the rash, the child's temperature rises, but the baby feels well. The temperature lasts 4 - 5 days, then drops sharply and a rash begins.
Sometimes the disease goes away without a rash. Then an exacerbation of herpes can be confused with measles or enterovirus infection.
The rash lasts from a short amount of time (several hours) to several days. The baby loses his appetite, becomes irritable and inactive, and sometimes the lymph nodes become enlarged.
More serious manifestations also occur:
- meningoencephalitis;
- myocarditis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- fulminant hepatitis;
- mononucleosis-like syndrome;
- pneumonia.
Let us remember that herpes often accompanies other diseases. Against the background of herpes, eosinophilia, as well as hypersensitivity syndrome to certain drugs, can sometimes develop.
Very rarely, if a type 6 virus enters an adult body for the first time, it causes the same symptoms as with the disease in children: rashes and fever.
These signs are often confused with side effects from antibiotics.
We recommend articles on the topic:
The prognosis for life with the disease is positive. But the presence of the virus in the human body and its unnoticed activity often leads to the development of other, more dangerous diseases.
Complications
When the temperature rises, children may experience convulsions (their consequence may be epilepsy) in rare cases - encephalitis, meningitis, pneumonia.
In adults, complications appear if immunity decreases as a result of disease, with a lack of vitamins or with suppressed immunity (treatment of cancer and blood diseases). These complications can be very dangerous.
It has been proven that herpes virus type 6 affects the occurrence of the following diseases:
- pityriasis rosea;
- multiple sclerosis;
- chronic fatigue syndrome. It is characterized by disorders of the central and peripheral nervous systems, metabolic disorders and a feeling of fatigue;
- autoimmune thyroiditis, which often develops into hypothyroidism;
- retrobulbar neuritis. There are isolated cases of the appearance of this neuritis due to relapse of the virus in infants. The disease is dangerous due to loss of vision;
- liver failure;
- oncological diseases. All herpes viruses can lead to the development of cancer, including herpes type 6. More often it leads to the development of lymphomas, brain tumors, Kaposi's sarcoma, leukemia, and cervical cancer.
Treatment
Medicine does not have methods to completely rid a person of this virus. Treatment of a primary infection may be considered pointless; it is wiser to allow the body to develop lifelong immunity.
When symptoms appear, drugs are used to combat herpes viruses:
- ganciclovir;
- cidofovir;
- foscarnet has proven itself in the treatment of both types of herpes virus type 6;
- the common acyclovir shows rather low effectiveness in treating this type of virus.
Antipyretics (paracetamol and ibuprofen derivatives) are used as medications to relieve symptoms. For children, Panadol and Nurofen are more often prescribed for treatment. Doctors note that taking interferon-based drugs reduces the risk of exacerbation. But just to prevent reactivation of the virus, it is not worth treating with interferon. It makes more sense to use a set of preventive measures.
Prevention
To support a healthy immune system, you need to take a set of measures:
- normal level of activity, physical education;
- consumption of vegetables and fruits in any season, and especially in spring and winter;
- compliance with work and rest schedules;
- walks in the air, hardening;
- taking vitamins;
- for newborns - breastfeeding.
Herpes type 6 and its dangerous consequences
Herpes is the most common virus on the planet. The majority of the population, if not sick, are carriers of this virus. There are 8 known types of herpes virus.
The first 5 have been studied quite well, but little is known about herpes viruses types 6, 7 and 8. Herpes type 6 can affect both adults and children. Timely treatment of the virus is necessary.
Herpes type 6 is dangerous due to its complications.
Description of the virus
Herpevirus type 6 (HHV-6) was first found and isolated from peripheral blood lymphocytes of people infected with various lymphoproliferative diseases (including HIV). This virus is similar to other herpes viruses, but differs from them in certain characteristics (properties, structure, genome composition, mass of molecular proteins, etc.).
The first studies were conducted in 1986 in Nevada (USA), where an infection was detected in a recreation area. Clinically, the disease resembled ordinary flu. Then the same infection was discovered in Europe and Africa, and the disease was found in absolutely healthy people.
Routes of infection
The vertical route of transmission of the virus from mother to child is recognized. Perinatal (intrauterine) infections quite often affect the fetus. The herpes virus was discovered during examination of tissues after an abortion.
Once a child reaches five months of age, the number of antibodies to the virus decreases, however, herpes virus type 6 in children is still detected when the child gets older.
Perhaps this is due to his immediate environment, among which there are carriers of the virus.
During the transfusion of blood, its components and organ transplantation, the virus also quite often passes to the patient who receives an organ transplant or blood transfusion.
This virus was detected in 80% of healthy blood donors. Also, 65% of those infected with HIV and more than 70% of patients with oncology have antibodies to herpes type 6.
Clinical picture
Flu-like symptoms are observed with the manifestation of herpes type 6. This type of virus, together with herpes virus type 7, have been recognized as provocateurs of chronic fatigue syndrome.
In this case, the patient experiences symptoms of herpes type 6, such as increased body temperature and night sweats. His lymph nodes are enlarged. In addition, the general and psychological state of the patient changes. He experiences general fatigue and depression.
Virus 6A has been described as a type that occurs in patients with neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
In addition, this type can cause serious manifestations such as pneumonitis, encephalitis and bone marrow suppression.
If you have these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Virus danger
Herpes virus type 6 poses a serious danger to both adults and children. In addition to multiple sclerosis, roseola infantile, and encephalitis, there are other dangerous diseases that can occur in patients who have type 6 herpes virus in their bodies.
Infectious mononucleosis in adolescents and adults, malignant lymphomas, and histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis are also thought to be caused by the herpes virus. HHV-6 is considered a co-factor of AIDS, and also, in combination with HSV-7, one of the prerequisites for the development of cervical and nasopharyngeal carcinomas.
Source: https://okvd-br.ru/zppp/gerpes-6-tipa-u-vzroslyh-simptomy-lechenie-vozmozhnye-oslozhneniya-i-posledstviya.html
Complications and consequences
HHV type 6 is dangerous because the diseases it causes are accompanied by febrile convulsions, against which epilepsy can develop. With severe immunodeficiency, the infection is complicated by viral damage to the liver, heart, lungs and brain. In combination with cytomegalovirus 6, type of herpes leads to impaired mental development. Long-term consequences of the disease include:
- Multiple sclerosis is a lesion of the nervous system, accompanied by deterioration of memory, concentration and intellectual abilities.
- Pityriasis rosea. A skin disease that leads to the appearance of multiple itchy rashes. The disease has a chronic course and requires constant drug therapy.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome. The complication is characterized by damage to the central and peripheral nervous systems and metabolic disorders. This contributes to constant drowsiness, delayed physical and mental development.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis. With frequent exacerbation of herpes infections, the functions of the immune system are disrupted; it begins to produce antibodies that destroy healthy cells.
Danger of HHV 6 and possible consequences
The virus becomes a threat to health and even life when there is a pronounced decrease in immunity. This happens in the following cases:
- the presence of severe chronic diseases that have not been treated for a long time;
- lack of vitamins;
- prolonged and severe overwork, stress;
- hormone therapy;
- radioactive exposure, development of radiation sickness;
- treatment of cancer tumors - chemotherapy;
- presence of immunodeficiency, AIDS.
- prevention of organ transplant rejection using immunosuppressants.
The “awakened” virus begins to have a destructive effect, affecting various systems and organs. This often manifests itself in the form of diseases of the blood, liver, central nervous system, lymph nodes, kidneys and salivary glands. With a high degree of probability, a connection has been established between type 6 herpes and the development of the following pathologies:
- oncological diseases;
- mononucleosis;
- multiple sclerosis - an autoimmune lesion of the nervous system;
- CFS - chronic fatigue syndrome. Manifests itself in apathy and increased fatigue. At the same time, performance decreases, irritability increases, behavior becomes aggressive;
- atrophy of the optic nerve and, as a consequence, blindness.
- thyroid disease. The resulting hormonal imbalance has serious consequences for the entire body;
- rapid deterioration of the condition of HIV-infected people, transition of the disease to the AIDS stage.
If a woman planning a pregnancy has been diagnosed with primary infection with HHV (human herpesvirus), then conception should be postponed until specific immunity is formed (antibodies appear in the blood). Otherwise, the risk of miscarriage increases.
During the period of remission, type 6 virus does not pose a threat, but against the background of decreased immunity, the infection worsens, which is extremely dangerous. It contributes to the development of serious illnesses, including death.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Dr. Komarovsky believes that type 6 herpes in a child, with proper treatment, is not a dangerous disease, so parents should not worry if the virus is detected in the baby’s blood. If the doctors' recommendations are followed, the patient lives a normal life even with several types of herpetic infections.
Among the factors contributing to the activation of the virus, Komarovsky identifies poor nutrition, excessive physical activity, injuries, and overwork. For mild forms of infection, the doctor advises not to rush into taking systemic antiviral drugs; it is recommended to limit yourself to local therapy.
To date, human herpes virus type 6 (HHV-6) has been the least studied. It was found relatively recently, in 1985-1986, but, nevertheless, the scale of its distribution does not allow us to consider it insignificant and harmless.
Features and general description
The disease that is caused by this type of herpes virus is divided into 2 types:
- Herpes virus 6 A (or HHV-6 infection);
- Virus 6B (or HHV-6-B infection).
Like other herpes viruses, HHV is completely incurable. At present, no medicines have yet been created that could remove the virus from the body without leaving a trace and prevent its return.
Most often, a patient who has been ill once develops immunity, as a result of which the external manifestations of the disease become invisible or become mild. However, the absence of external signs of the presence of strains in the body does not mean their complete absence. They continue to stay in it, waiting for the right opportunity to appear outside again (usually for the successful development of the virus, even a slight weakening of the immune system, acute respiratory viral infections, colds, and the like are enough).
As a rule, everyone is born with immunity to this disease, as it is transmitted from the mother. But, in the absence of these antibodies in the mother (this happens if she has not suffered from pathologies caused by these microorganisms), the child, usually during the first year of life, becomes infected and develops a protective mechanism on its own.
Another important feature is the parasite’s resistance to antiviral drugs, which makes it very difficult to treat. It is worth noting separately that type 6 herpes is quite difficult to diagnose, because it is often disguised as other diseases.
Herpes type 6 is often confused with its similar type, HHV-7. Therefore, it is almost impossible to accurately determine the type of strain in a particular person.
Diagnosis of the virus
Unfortunately, during a primary infection, it is difficult to detect and accurately recognize a virus of this group. It is even more difficult to identify it during the inactive stage. It is determined in the laboratory. There are several detection methods, depending on the manifestation of the infection. All of them come down to immunological, biochemical and microbiological studies.
For example, they are used for myocarditis, which can be fatal. It has been established that it is also caused by herpes virus type 6. There are no symptoms, unlike myocarditis caused by other causes. For this disease, the virus is identified in a biopsy taken from the heart muscle or in the blood. If the results are questionable, additional studies are carried out. In case of pneumonitis, the virus is detected in sputum and blood serum, and chest X-ray data can serve as a reason to assume its presence. For hepatitis caused by a virus, liver biopsy samples and blood serum are tested. For various tumors and enlarged lymph nodes, special monitoring and serological tests are carried out, as well as blood PCR. This test is widely used when the virus is reactivated and when its form is inactive.
Virus subtypes
There are several varieties of herpesviruses of the 6th group, characterized by their defining characteristics:
- Subtype A. Herpes type 6 in adults has subtype A. It is also known as a neurotropic infection. Herpes simplex virus type 6 (HSV-6) group A in adults usually causes complications on the activity of the central nervous system, and can subsequently cause the development of sclerosis. The disease is especially common in patients with poor health, for example, in patients with HIV.
- Subtype B. Herpes virus type 6 in children is more common in this subtype.
At the moment, the individual symptoms of herpes virus type 6 have not yet been assigned. It is only known that if a person gets sick with it for the first time, then, as a rule, the signs of the disease are recorded in the form of roseola, and there are also a number of diseases whose connection with herpes has not yet been definitely proven, however, the frequency of its occurrence in infected people is much higher .
Such diseases include:
- chronic fatigue;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- lymphadenitis;
- febrile seizures;
- mononucleosis and some others.
In rare cases, aggravation of the course of the disease and the development of diseases such as:
- malignant lymph;
- lymphoproliferative pathologies.
It should also be noted that the sixth herpes virus can have a detrimental effect on the development of the child while still in the womb. With severe infection, even the death of the baby is possible.
Also, HHV-6 can initiate the development of the following pathologies:
Peculiarities
The course of infection caused by herpes type 6 in adults differs from that in children.
In adults
Almost all adults have encountered type 6 herpes at an early age, so they do not experience sudden exanthema.
The infection does not activate in the body of a healthy person, even when exposed to provoking factors characteristic of other types of virus. The main causes of the disease are exhaustion of the body, HIV infection and severe chronic pathologies. Herpes type 6 in women and men affects the central nervous system, significantly worsening the patient’s quality of life.
In children
Children under six months of age rarely get sick with herpes type 6, and subsequently any contact with the source of infection ends in infection, but sudden exanthema does not always occur. The disease begins acutely, with an increase in temperature. After fever symptoms subside, a patchy rash appears. Herpes type 6 does not pose a significant threat to the life and health of a child. Having been ill once, the little patient acquires lasting immunity.
Symptoms
Children are often affected by this virus due to weak immunity. The onset of infection with type 6 virus in a child is indicated by a slight low-grade fever, which lasts for 2-3 days and is accompanied by a slight fever. The disease can then take several paths.
Light form
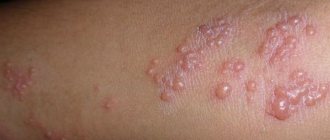
Herpes type 6 in children can occur in a fairly mild form, and therefore it can be confused with diseases with similar symptoms (rubella, chickenpox, etc.). However, a detailed analysis will help to accurately determine the nature of the unhealthy condition. It is also possible for the parents themselves to determine the disease - if they press on the skin rashes, they will change color to white, which cannot be observed with rubella.
In general, this path of development and manifestation of the disease is characterized by itchy skin rashes on such parts of the body as:
- back;
- neck;
- limbs;
- stomach;
- There are isolated rashes in the throat and on other mucous membranes of the body.
Complex shape
If the infection follows the second path of development, then in addition to skin rashes the child experiences:
- a sharp increase in temperature;
- fever;
- convulsions are possible.
This form of manifestation may be accompanied by purulent nasal discharge, cough, vomiting and other unpleasant conditions. After these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a specialist.
Analysis for the presence of infection should be done at the first symptoms, because this disease can become complicated, causing the following consequences:
Features in adults
Herpes type 6 in adults is not excluded, the symptoms of which will appear when conditions favorable for the development of pathology are formed. As a rule, any adult who was ill as a child received lifelong immunity to this infection.
The virus strain lies dormant in the body, waiting for the right opportunity to arise again. The development of the disease is favorably influenced by weakened immunity, fatigue, and various diseases. If the disease has not previously been tolerated, then in adults the symptoms appear similar to children.
Currently, a particularly common cause of the development of herpes virus type 6 in adults is overwork. This is due, first of all, to the ever-increasing role of intellectual and mental stress in life.
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of HHV-6:
- aggressiveness, intolerance;
- chronic fatigue;
- general depressed state;
- apathy;
- constant stressful state.
How is HHV-6 transmitted?
There are several ways the virus can be transmitted to the human body:
- Through blood - during transfusion. You should be extremely careful during this manipulation, because many serious diseases are transmitted along with blood that have no treatment options or methods, including AIDS.
- Mother to Child - A test of the mother's blood and vaginal secretions may test positive for the strain. In this case, the virus is transmitted to the child during childbirth. An important fact is that during breastfeeding the virus cannot be transmitted from mother to baby. However, you should avoid contact between an infected person and a newborn, especially kissing, as this can lead to infection through saliva.
- Physical contact with an infected person.
- Oral (HHV is also found in saliva) method.
It is necessary to know how this disease is transmitted in order to prevent its occurrence in yourself and your family, or, in case of infection, to prevent the infection from starting.
Diagnostics
Only an experienced specialist can make an accurate diagnosis indicating herpes in the body. There are several laboratory methods for detecting this disease:
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
It is one of the most expensive and complex tests. Nevertheless, thanks to it, it is possible to judge the presence of the disease by the presence of titers of two types of antibodies igm and igg and identify the DNA of the herpes virus, as well as diagnose the presence of immunity to it (whether it is a primary infection or a repeated one - relapse).
Igm antibody titers indicate primary infection of the body; igg captions are about repeating. If no antibodies are found in the body, this is proof that the person is absolutely healthy.
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
Study of the main set of biological fluids of the human body to detect the DNA of viruses, including HHV.
Complete virological analysis
It occurs by seeding cells isolated from the patient’s body onto a nutrient medium containing strains of herpes.
Based on the observed development of cells and the virus itself, as well as igg indicators, one can conclude the presence of this disease, as well as determine its type.
Despite the fairly large capabilities of medicine, prescribing tests for the presence of HHV in the body is not always advisable. If the patient’s disease is in a fairly mild stage, then there is no need to take him for examination, because most likely it will go away on its own even before the test results arrive.
Diagnosis of herpes type 6 in the laboratory
This virus sometimes has symptoms characteristic of other diseases. In this regard, many doctors, even quite experienced specialists, may make a mistake in making a diagnosis. Pediatricians may mistake a herpes virus for measles, rubella, or even an allergy to formula or newly introduced foods.
The method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) will help determine herpes type 6 in saliva and blood. He is able not only to detect the presence of a virus in the test material, but also to determine whether the infection is primary or whether the patient is experiencing a relapse. Also, for the diagnosis of herpes type 6, the polymerase chain reaction - PCR method is widely used. In special laboratories, diagnostics are also carried out using the cultural method.
Treatment
It is worth noting that treatment of herpes type 6 will not completely destroy this virus in the body. But, nevertheless, treatment of type 6 herpes in adults and children includes taking the following drugs that inhibit the activity of microbes:
- Antiherpes drugs - the most active effect on HHV-6 was noted for the drug brivudine. In addition, doctors ask patients to pay attention to the fact that acyclovir cannot be used to treat type 6 herpes, and the drug foscarnet has many side effects.
- Immunoglobulins are drugs containing an active protein that acts as a stimulator of the human immune system. Antiherpes immunoglobulins include amixin and polyoxidonium. However, the greatest effectiveness was observed with the use of herpimmune 6.
- Interferons are drugs aimed at increasing immunity. A necessary remedy, due to the fact that a weakened body stimulates the development of the virus. The most common include Derinat and Panavir. If the body is significantly weakened, if the drugs considered are ineffective, the doctor will prescribe a special antiviral vaccination.
- Vitamins – during the period of weakening of the body’s protective properties, it is necessary to supply it with individual vitamins, such as A, C, E. Vitamin complexes are allowed.
- Antiviral drugs – drugs. aimed specifically at suppressing the virus. To combat herpes virus 6 subtype A, the drug foscarnet is most often used.
- When treating subtype B, the drug ganciclovir is necessary. It is important to remember that antiviral drugs can only be taken according to the doctor’s instructions. Children under 12 years of age are strictly prohibited from using them.
- In addition, if the patient’s condition is serious, it is possible to take antipyretic drugs such as Nurofen, ibuprofen and others.
Features of symptoms and treatment of herpes virus type 6 in adults
Herpes virus type 6 in adults, the symptoms and treatment of which overlap, comes in two types: A and B. This infection is caused by betaherpesviruses that have DNA.
The causative agent of the pathology is present in almost every person. Most populations are infected with it.
The main danger of infection is the impact on the immune system by damaging T-lymphocytes and provoking dangerous diseases.
The main prerequisite for the active stage of the pathogen is a decrease in immune defense. Subtype A virus affects people with immunodeficiency or AIDS, and subtype B most often occurs in young children due to chronic fatigue syndrome.
Development of the disease: routes of infection
Herpes type 6 in adults is often present in a latent form. Infection occurs in childhood. After entering the human body, the infection contacts the cells and creates a nutritious protein environment for itself. At this moment, the body tries to fight the pathogen by producing antibodies. Using their determination, you can find out whether the patient is sick and in what phase the infection is.
The causative agent of herpes simplex type 6 is transmitted through household contact (using the same dishes or toothbrush). The disease can be passed from mother to child through traditional pacifier licking, which is so opposed by doctors. The infection is transmitted during a kiss.
When you cough or sneeze, the virus is released with microparticles of saliva. It is quite easy to become infected with it. Having penetrated the body of a new host, the virus accumulates mainly in saliva, and can also be found in the pharyngeal tonsils. Subsequently, it is released into the external environment as a new carrier.
This method continues to spread the herpes infection.
At-risk groups
Despite the fact that almost everyone has herpes virus type 6, there are groups of people who are most susceptible to this infection. Statistics show that they often experience a relapse of the disease, accompanied by severe symptoms. The risk group includes:
- patients with severe or complicated diseases;
- people with reduced immunity;
- HIV-infected;
- patients with blood diseases;
- persons taking immunosuppressants for various indications;
- young children;
- people who come into daily contact with a large number of strangers.
All the reasons for the appearance of type 6 viral infection come down to one thing - a decrease in immune defense and suppression of the body's resistance. To prevent infection, and later exacerbation, it is necessary to take measures to strengthen protective functions.
Diagnostic methods
Determination of herpes viruses in the patient’s body is carried out through laboratory tests. Based on the clinical picture, one can only suspect an infection, but the doctor cannot be sure that it is a type 6 pathogen. In order to confirm the guesses, the following tests are prescribed:
- microscopic examination of mucus from the nose and throat;
- polymerase chain reaction and detection of viral DNA;
- enzyme immunoassay for antibody detection.
For proper treatment, it is important for specialists to distinguish HSV type 6 from an allergic reaction, pneumonia, erythema infectiosum, rubella and measles. The most reliable way for this is a venous blood test.
ELISA and PCR are of primary importance in the diagnosis of pathology. Their results are interpreted as follows:
- DNA is detected - the disease is present in the body, DNA is not detected - the person has never been in contact with the pathogen (which happens very rarely);
- high titer of IgG and IgM – the pathology is in an active stage, the infection occurred relatively recently;
- IgG is present, but IgM is absent – the infection occurred a long time ago, now the pathogen is in the latent stage;
- there is no IgG, but IgM is present - the infection occurred quite recently.
Even in the latent stage, the carrier of the virus poses a danger to others. The infection spreads rapidly, and an infected person with a strong immune system may not notice the disease at all.
Therapeutic methods
It is necessary to treat herpes type 6 based on the symptoms. To date, no effective remedy has been invented that can remove the pathogen from the body completely.
Despite all the tricks and efforts of doctors, the viral infection will remain in human cells, taking on a latent form.
This does not cause any discomfort to the patient until a decrease in immunity occurs and the pathogen takes on an active form of development.
The use of vitamin complexes and herbal compositions is indicated. To strengthen the body and increase its resistance, the patient must lead an active lifestyle and maintain a nutritious diet.
During exacerbation
To combat the sixth type of herpetic infection and its manifestations, systemic medications are prescribed to patients in the active phase. In order to suppress the activity of the pathogen, antiviral drugs are recommended, but the effectiveness of their use is questioned.
Causes of herpes on the stomach and its treatment
- Ganciclovir – 3 g per day (in 3-6 doses). Contraindications for use include childhood and impaired renal function. Do not use the medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as for congenital cytomegalovirus.
- Cidofovir is used intravenously in a hospital setting. The initial dose is 5 mg/kg. Further adjustments are made by the doctor in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Foscarnet is administered as an infusion, slowly. The initial dose is 60 mg/kg.
Often, during an exacerbation of a herpetic infection in an adult, Acyclovir or its structural analogues are prescribed. However, in relation to type 6 they are ineffective.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend the use of topical antiseptics, for example, Miramistin or Chlorhexidine.
Symptomatic remedies
For acute infections caused by type 6 herpes, antipyretics are recommended. These drugs have antipyretic and analgesic effects. As a result of use, the patient’s well-being significantly improves: muscle pain disappears, temperature drops, and chills go away.
Also, for nasal congestion, sneezing and itching, antihistamine and vasoconstrictor sprays or drops are recommended: Nazivin, Vibrocil, Snoop. To quickly suppress the active stage of a viral infection, medications based on sea water are used: Dolphin, Aqualor, Rinostop.
There are usually no pronounced rashes with herpes type 6. They often occur when a child’s body is affected by subtype B. Local medications are usually not prescribed.
Use of immunoglobulins
In order to increase the body's resistance, immunoglobulins are used in some cases. When attacking the herpes virus type 6, Herpimun-6 is considered effective. It is prescribed for intramuscular administration.
The drug is represented by an active protein fraction, which was obtained from plasma and serum of human blood. As a result of use, the body's resistance increases and the number of antibodies that neutralize the antigen increases.
The main indication for the use of the drug is a complication of the disease: damage to the nervous system, convulsions, chronic fatigue or exanthema.
These conditions indicate that the body cannot cope on its own and needs help.
As a result of using immunoglobulin, body temperature may increase on the first day, but the indicators will not reach critical limits. Also, redness is sometimes observed at the injection site, which goes away on its own.
Preventive actions
To summarize, we can say that the main goal when a pathogen is detected in the body is to prevent its activation. To do this, certain rules must be followed:
- strengthen the body by hardening;
- adhere to a daily routine, sleep at least 7 hours a day;
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports in the absence of contraindications;
- adhere to a proper diet, consume a large amount of seasonal vegetables and fruits, remove fatty foods from your menu;
- eliminate bad habits, do not smoke and minimize the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- Do not take medications on your own, especially antibiotics.
When the first signs of illness appear (during primary infection or during an exacerbation), you must seek medical help. It is impossible to independently recognize type 6 herpes infection, and infection is inevitable for every person, since even in the latent stage the infection is released from the body with saliva.
Source: https://venerbol.ru/gerpes/6-tipa-u-vzroslyh-simptomy-lechenie-virusa.html
Treatment of children according to Komarovsky
Evgeniy Komarovsky developed his own method of treating herpes. According to its principle, treatment of herpes type 6 in children includes:
- quarantine - isolating a child from contact with peers, and also, if possible, with family members for seven days;
- treatment with antibiotics, as well as taking anti-inflammatory medications;
- After quarantine, the child can safely attend kindergarten or other educational institutions, freely contacting the people around him.
This method is also actively used in the treatment of chickenpox at an early age.
Prevention of HHV-6
Prevention of this disease will help prevent you or your child from developing type 6 herpes virus, because the infection is a consequence of weakened immunity. It is necessary to carry out measures aimed at strengthening it. These include:
- Proper and balanced consumption of food - it is useful to include more fruits and vegetables in your menu, this is especially important in the autumn-winter period.
- Newborn babies really need breastfeeding, because it is mother's milk that contains the full composition of nutrients necessary for the development of the body, which will have a beneficial effect on the immune system in the future.
- Active life - physical activity strengthens the body, preventing the development of viruses or other diseases.
- Correct daily routine - there should be a clear division between work and rest. Each person should find a daily routine in which his body will be most comfortable. In no case should you forget about getting enough sleep.
- Taking vitamins - in winter it is quite difficult to include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet. In this regard, the supply of useful vitamins and elements to the body practically stops. To maintain your health, you need to take vitamin complexes (vitrum, alphabet), which can significantly strengthen the body. But, it is worth considering that before starting to take any medications, you need to consult a specialist.
So, although HHV-6 is incurable and difficult to diagnose, it can be avoided by taking good care of your health. If the first symptoms are observed in an adult or child, then immediate contact with a specialist is necessary to further determine treatment measures.