Parents often face the problem of herpes in children (the types, symptoms and treatment of this disease depend on the immune system). And babies who have imperfect homeostasis and a low immune threshold are exposed to maximum damage. Let's look at how to recognize a virus attack and treat your baby below.
Routes of infection
Epstein-Barr virus can be transmitted in the following ways:
- airborne;
- contact;
- during blood transfusion;
- in case of unprotected sexual intercourse.
As a result of herpes entering the bloodstream, the body begins to counteract it. With a strong immune system, it can be suppressed. If the immune system is weak, this microorganism develops, up to the chronic form of the disease.
Herpes virus type 7
Herpes type 7 prefers special CD4 lymphocyte receptors for long-term stay. Since these cells are responsible for immunity in the human body, a natural consequence of its presence is a decrease in immunity. Weakness, lack of tolerance to physical activity, and low mood levels develop—“Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.” Only a psychiatrist or immunologist can suspect the herpes virus type 7 in the manifestation of such symptoms.
Like other representatives, herpes virus type 7 in severe immunodeficiencies can cause viral sepsis and other serious manifestations. Herpes type 7 is transmitted through saliva and blood.
Characteristic symptoms
The main signs of herpes in the initial stages are:
- sudden increase in body temperature;
- discomfort in muscles and joints;
- exhausted state;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
In this case, symptoms of tonsillitis and pharyngitis may appear:
- nasopharyngeal congestion;
- swelling of the tonsils and redness of the throat cavity;
- the formation of purulent inflammations in the palate.
The following signs of pathology are periodically observed:
- formation of rashes, blisters;
- nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- gastrointestinal disorder;
- enlarged liver, spleen.
If the infection spreads throughout the body, many internal organs can be affected.
After a month after the virus enters the body, the patient’s condition gradually improves. Subsequently, the manifestation of herpes type 4 is similar to an acute respiratory viral infection.
The Epstein-Barr virus leads to the activation of cancer cells in the patient's body. The following signs are characteristic of the formation of a malignant tumor:
- tinnitus;
- migraine;
- nasal purulent bleeding.
Asymptomatic progression of this disease is extremely rare.
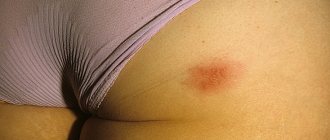
Herpes virus type 2 (Herpes simplex genitalis)
Genital herpes Herpes virus type 2 is similar in structure and properties to HSV 1. The differences lie in the method of transmission: infection usually occurs through the genital route.
It can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth if the mother has a rash during this period. HSV 2 prefers to live in the body in the nerve nodes of the pelvis, so typical places for rashes in both men and women are the skin and mucous membranes of the external genitalia, buttocks, anus and perineum; this type is also called genital. Herpes simplex type 2, like HSV 1, can remain dormant for a long time without symptoms. A provoking factor for exacerbation of HSV 2 is also suppression of the immune system.
Herpes simplex virus type 2 Exacerbations of HSV 2 disease in men and women begin with the appearance of pain and itching in the affected area. At this stage, enlarged lymph nodes in the groin can be detected. Then a vesicular rash appears, the blisters quickly open. The surface of the affected skin with HSV 2 is painful. The peculiarities of the localization of the rashes determine a longer course of exacerbation than with HSV 1, since the affected area is subject to constant trauma by clothing and human secretions (urine, sweat). Limiting oxygen access promotes the addition of bacterial flora, which complicates recovery.
HSV 2 can also cause rashes in places typical of the first type, which is also a consequence of different types of sex in men and women. This often happens during homosexual contacts. In children, the localization of HSV 2 rashes on the lips is a consequence of transmission of the virus from parents through a kiss. Herpes simplex type 2, like the first type, with serious immunodeficiencies can cause a rash on any other areas of the skin, as well as severe systemic internal lesions
Diagnostics
To determine an accurate diagnosis, laboratory tests are required. These include:
- General blood analysis.
- Biochemical analysis.
- Enzyme immunoassay of blood serum.
- Polymerase chain reaction.
- Ultrasound examination of internal organs.
If cancer is suspected, a biopsy of tumor tissue is performed.
Treatment tactics
The course of therapy for type 4 herpes consists of a whole range of measures:
- suppression of infection;
- reduction and elimination of symptoms;
- restoration and strengthening of immunity;
- elimination of general intoxication of the body.
To suppress the development of the virus, antiviral drugs are prescribed, such as Acyclovir, Ganciclovir. When a bacterial infection is observed, antibiotics Metronidazole and Fluconazole are prescribed.
To eliminate general intoxication of the body, it is recommended to drink large amounts of water. In the acute course of the disease, a course of intravenous injections is carried out using a glucose solution or water-salt solution.
To reduce and eliminate signs of the disease, medications for fever and pain are used. In the presence of edema, hormonal medications and mouth rinses with various antiseptic drugs are prescribed.
Also, in the process of maintaining and restoring immune activity, a complex of drugs consisting of vitamins, immunomodulators, and immunoglobulins is used.
If a malignant tumor is diagnosed, chemotherapy and radiation treatment are used.
Treatment of herpes type 4 in children is carried out inpatiently. This is due to more severe symptoms of the disease.
Traditional medicine recipes
It must be remembered that the use of alternative methods of treating herpes must be agreed with the attending physician.
The most common methods of traditional medicine:
- The use of choleretic tinctures is recommended, since the virus lies dormant in the pancreas. To make the tincture, you need to take a teaspoon of one of the dry herbs: immortelle, tansy or corn silk, pour one glass of boiling water and let it cool. Strain the solution and warm it slightly before use. It is recommended to drink the tincture fifteen minutes before meals. The course of treatment should continue for a month;
- in case of exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to make a tincture of viburnum. It is necessary to chop four tablespoons of viburnum berries and add boiled water. Leave to infuse for four hours. Drink half a glass of the solution four times a day;
- Drinking fresh aloe juice also helps relieve exacerbation of the disease. To do this, you need to drink one teaspoon three times a day before meals. You can use the juice as an antiseptic to moisten inflamed areas. It is not recommended to use aloe juice if you have hemorrhoids, kidney failure, or during pregnancy.
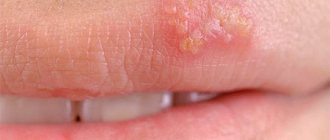
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (Herpes simplex labialis)
The most famous member of the family. It is this that causes “colds” on the face. It is transmitted by contact and also by airborne droplets. Penetrating through lesions on the skin and mucous membranes, HSV simplex selects for life the nerve fibers and ganglia of the facial and trigeminal nerve.
A carrier can transmit the virus only in the acute phase of the disease.
Exacerbations of the disease occur during periods of weakened immunity against the background of:
- ARVI;
- prolonged hypothermia;
- stress;
- long-term malnutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- decompensation of chronic diseases;
- taking medications that suppress the immune system.
Herpes simplex virus type 1 Primary infection with HSV 1 usually goes unnoticed.
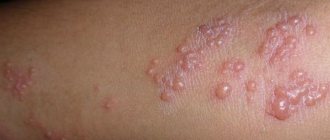
Once in the body, Herpes simplex labialis can remain without manifestations for a long time. When favorable conditions arise and the host body cannot suppress the rapid proliferation of the virus, an exacerbation occurs. The incubation period usually takes several days. At this time, a person may feel slightly unwell and weak. On the eve of the appearance of the rash, the body temperature may rise, but an exacerbation of HSV 1 often occurs against the background of a normal temperature reaction. At the site of future rashes, tingling and itching are felt. A few days later, the skin becomes red and covered with small blisters containing a cloudy liquid. During this time, the affected area may be itchy and painful.
Structure of the virus Over the next few days, the blisters break open to form ulcers. Rashes at this stage are accompanied by severe pain. Healing of ulcers lasts from one to two weeks with the formation of crusts. After recovery, the skin is completely restored, without scars or defects.
A typical site of rash with HSV 1 is the skin and mucous membranes of the face (lips, nose, cheeks, neck), which is due to the location of the nerves in which HSV 1 is in the latent period. However, herpes simplex virus type 1 simplex can affect other parts of the body (back, chest, abdomen, limbs), and with a significant decrease in immunity, it becomes the causative agent of meningitis and sepsis.
It is not uncommon for HSV 1 rashes to appear in the pelvic area and genitals of adult men and women - typical locations for the second type. This manifestation occurs during the genital (sexual) method of infection with the virus, during oral sex.
Danger for a pregnant woman
Type 4 herpes poses the greatest danger to a pregnant woman and her fetus during initial infection. This is due to the lack of a developed immune defense in the body against this type of bacteria. This can lead to infection of the fetus through the placental barrier. The probability of such infection is sixty percent.
If there are repeated manifestations of the Epstein-Barr virus during pregnancy, the risk of illness in the child is reduced due to the developed immune defense. At the same time, the probability of infection of the fetus is present and amounts to five percent.
The presence of the virus in the mother’s blood contributes to the development of protection against infection in the baby. For several months after birth, the baby is protected from the effects of this virus.
Complications
With the development of chickenpox and shingles, blisters appear on the body, which can become injured and burst when scratched. Infection often penetrates through wounds, which causes complications:
- Nephritis.
- Arthritis.
- Phlegmon.
- Abscess.
- Pneumonia of bacterial type.
- Myocarditis.
On this topic
- Herpes
Why is herpes on the fingers dangerous?
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- August 16, 2020
In cases of damage to the nervous system, meningitis or encephalitis develops. These are serious and dangerous diseases for human health.
Severe consequences can occur in women during pregnancy. Infection in the early stages leads to the development of fetal abnormalities that are incompatible with life. But when infection occurs in the third trimester, the baby suffers chickenpox in the womb. This significantly increases the risk of developing shingles after birth.
Prevention
To prevent the disease, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Use condoms during sex.
- Treat the skin with antiseptics.
- Wash your hands frequently.
- Use only personal hygiene products.
- Periodically disinfect toilets.
- Avoid sexual intercourse if you have genital herpes.
- Limit contact with people who have recovered from this virus for a month.
Laboratory blood tests must be performed before transfusion or when using donor blood.