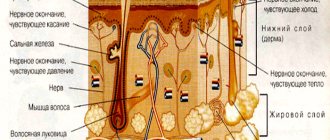
It is well known that human skin is of particular importance in ensuring the vital functions of the human body. It is entrusted with very responsible functions, and how well and harmoniously they work will certainly affect the general condition of a person - his health. What are these functions?
- Among the first, we can probably name the function of protecting the body from the influence of negative external factors. The first blow - be it thermal or mechanical impact - is taken by the skin. There are many pain receptors located on it, which make it possible to inform a person in time about the upcoming danger.
- The barrier function and, of course, the excretory function play a significant role. Therefore, the condition of the whole organism can be assessed based on how well their joint work is structured. After all, almost all diseases that affect human organs, both internal and external, certainly leave their mark on the skin.
Therefore, it is not surprising that experienced healers, healers and other folk healers, without any tests, could determine a person’s illness through an external examination - thereby striking those present and the patient himself with an accurate and quick diagnosis. Modern doctors also know and are able to identify the disease by changes in the skin, inflammation, and rashes that form on it.
Such diseases are currently dealt with by a dermatologist. Parents often turn to him about the appearance of various formations on the skin of their children, including spots that have a reddish tint. Moreover, such spots form in different places, for example, on the skin of the abdomen, head and other places.
There are many reasons that can cause the onset of the disease and the appearance of skin rashes. It is possible that this is how an ordinary allergic reaction manifested itself. But it may happen that reddish spots are the result of a dangerous infection in the child’s body. Even some sexually transmitted diseases can manifest themselves as a similar rash on the skin.
But you can guess for a long time and only guess, based on the general clinical picture, what exactly the child is sick with. By contacting the right specialist in a timely manner, the child’s parents will be able to protect him from possible complications. Only a doctor, based on laboratory tests and test results, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and make decisions about treatment methods
Heat rash and diaper rash
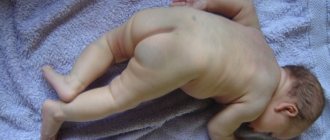
Red spots on a child's body with heat rash can look very different.
The photo with description clearly demonstrates this. Most common in children, heat rash is a skin irritation caused by excessive moisture. Sweat does not have time to evaporate, remains on the skin and causes discomfort. Miliaria blisters are localized on the back, buttocks, neck, armpits, and other places with high humidity.
To get rid of the symptoms of prickly heat, it is necessary to eliminate the factors that cause pollution and waterlogging of the skin. If you provide good ventilation in the room and follow hygiene rules, the phenomenon will soon go away on its own. In advanced cases, body temperature may rise.
An allergic rash is extremely difficult to remove; it persists even after contact with the irritant has been eliminated.
Diaper rash (diaper dermatitis) is a complication of prickly heat, an infectious inflammation localized in the natural folds of the skin. The baby is capricious, sleeps poorly, cannot sit in one place - everything hurts and itches.
The most common causes of redness in young children are the body’s natural reaction to hot weather on delicate skin. Miliaria forms on the folds, neck, back, chest, armpits due to difficulty sweating.
The surface layer of the skin swells slightly and small red blisters appear. Miliaria usually does not cause itching or discomfort and disappears quickly with proper care.
Diaper rash may appear as red, swollen, tender patches or flaking. The skin in the area of diaper rash becomes moist.
Both prickly heat and diaper rash can occur due to poor child hygiene, synthetic clothing, especially if parents dress the baby too warmly, or the use of greasy skin creams in the summer.
As for hygiene, delicate baby skin becomes irritated due to being in a diaper for a long time, especially with feces or urine.
Heat rash requires cleanliness
When heat rash occurs, a very small rash appears on the baby's body. This scattering of reddish spots seems to merge into one rough spot. She doesn't cause much concern. Appears for many reasons, for example:
- when the baby is in a warm room for a long time;
- if the ambient temperature is too high;
- the baby is rubbed with creams at high temperatures in the warm season;
- due to poor skin care.
Miliaria will disappear if you regularly perform hygiene procedures for your child.
Red spots like bites
Red spots on a child’s body can be not only bites, but also an allergic rash:
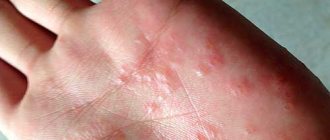
- Prickly heat. Small, light pink pimples located close to each other. The rash is localized in the upper chest, neck and shoulders. First of all, it is important to maintain hygiene. During the hot period, water procedures are carried out in decoctions of chamomile and string. Baby powder will help remove excess moisture; you should not lubricate the skin with cream - a humid environment will provoke the appearance of new pimples.
- Hives are often confused with mosquito bites - these are pink blisters that cause severe itching. When scratched, a bloody crust forms on them. Infections, physical irritants or allergies provoke the development of hives. For urticaria, the affected areas are treated with powder. Antihistamines are used in the treatment of mild forms: Zyrtec, Claritin, Telfast. The use of enterosorbents (activated carbon) has a positive effect. Use prednisolone ointment, Deperzolon or water-zinc pastes with 2-3% naftalan oil.
- Insect bites. Exposed areas of the body are covered with tubercles and red spots. The child is bothered by severe itching, but the general condition does not change. Wounds (not bloody) are lubricated with brilliant green to avoid bacterial infection. Lotions made from soda solution help relieve itching.
The second most common cause of stains is mosquito bites and midges. In this case, swelling at the bite sites, obvious itching or even pain (when bitten by stinging insects) are characteristic.
Acne
In newborns, very often in the first months of life, acne may appear on the face, neck, and sometimes head. It occurs due to the beginning of the functioning of the skin glands and does not require special treatment. By six months, acne goes away without leaving any traces. Hygiene is important for its speedy disappearance.
These are the most common causes of spots in newborns. In addition, there may be cases of an allergic reaction that appears after contact with the allergen and goes away after its removal, and single insect bites. Another cause of a rash can be infectious diseases. In this case, parents need to be very careful and rush to the hospital at the slightest suspicion.
Insect bite marks
Mosquitoes, midges and other insects readily bite not only adults. The signs of a bite are usually pronounced and you can easily notice it on your child's skin. Because of the itching, children scratch the bite site. Then the area of redness increases. In some cases, insect bites cause an allergic reaction.
Symptoms of a bite appear very quickly. On the skin there are:
- redness;
- blisters;
- swelling.
If a child is bitten by a poisonous insect and the poison enters the bloodstream, the following symptoms appear:
- swelling that quickly spreads to the skin;
- redness accompanied by inflammation around the affected area.
Types of bites vary in appearance. According to the severity and risk of complications, they are divided into three groups:
- They are hardly noticeable and practically do not bother the child. They leave behind small dots or a slightly reddened area.
- More pronounced marks from massive insect bites - while the skin itches.
- Redness and swelling are clearly visible on the skin - dangerous for children (bites from some large insects can be fatal).
Redness from insect bites goes away on its own after a few days. If this does not happen, consult a dermatologist.
How to distinguish an allergy from a bite
An insect bite can easily be confused with an allergic reaction. The spots on the child's skin in this case are very similar. There are several signs by which you can determine whether it is a bite or not:
- Location. Bite marks appear on the face, neck, and shoulders. An allergic rash is usually not localized this way.
- View. If the skin puncture site is clearly visible and looks like a tiny dot, then it is an insect bite. They are also characterized by small local hematomas. They appear due to subcutaneous bleeding caused by insect enzymes.
- Quantity. If there is only one spot and the swelling is also clearly localized in one place, then this indicates a bite. The allergic reaction manifests itself in multiple spots.
You may not always be able to distinguish redness after a bite from an allergic reaction or manifestation of a skin disease. In addition, sometimes a reaction on the skin is a consequence of numerous bites. If you have any concerns, it is always better to consult your doctor.
Spotted rash in children
Rashes are stressful for a child’s skin, so the following actions should be avoided so as not to worsen the condition even further:
- Do not apply ointments and creams to your skin without first consulting your doctor, especially if they may change the color of the rash.
- Do not self-medicate or give your child medications without a doctor's prescription. The exception is an allergic reaction if you have used the medicine before and know how the body will react to it.
- Whenever possible, minimize scratching and avoid squeezing, especially in case of infection.
Red spots signal health problems and are signs of several dozen different syndromes and diseases. If the rash is allergic in nature, then sometimes it is enough to take antihistamines or use ointments with glucocorticoids. This treatment is ineffective for infectious diseases. It is necessary to fight the cause of rashes - microbes and viruses.
The disease begins suddenly with a sharp rise in T° and general intoxication. Often a red spot appears in the child’s eye and nosebleeds. Occasionally, petechiae appear on the face and chest. The spots appear on the first day and disappear in the following days.
Diseases are caused by enteroviruses, which are most active from spring to autumn. Measles-like enterovirus exanthema most often affects young children. Spots with a diameter of about 3 mm are located on the face and torso and disappear after a day or two. Roseola-like exanthema is also called “Boston disease.” The rash on the face looks like round pink-red spots with a diameter of 0.5–2 cm. The spots disappear without a trace one or two days after their appearance.
Hand-to-mouth disease or viral pemphigus is caused by the Coxsackie viruses and enterovirus-71. Children under 10 years of age are most often affected. The oral mucosa becomes covered with painful pink-red spots and vesicles. In approximately 75% of cases, a rash appears on the face, palms and heels, sometimes spreading to the buttocks and genitals.
Pityriasis rosea
The exact reasons for the appearance of a large, rough spot with a diameter of about 5 cm on the waist or thigh have not yet been established. Scientists suggest that the activity of herpes viruses increases against the background of immunosuppression. Later, small “daughter” plaques of light red, crimson or pink appear.
Ringworm
The spots are often localized on the back of the head and limbs, have the shape of a ring or oval, and are very itchy and flaky. Treatment is carried out with antifungal ointment "Mikozolon", iodine tincture.
One of the causes of a small or large spotted rash is infection with thrush pathogens (yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida).
The cause is some kind of infectious focus, for example a purulent wound or phlegmon. A pinpoint “scarlet-like” rash occurs 3–4 days after staphylococcal inflammation. The disease resembles a sore throat: fever, redness of the throat. Elements of the rash are densely sprinkled on the lower abdomen, located in the groin, in the natural folds of the body.
The introduction of pyogenic streptococci into the skin is the cause of streptococcal pyoderma. This pustular disease affects the body against the background of decreased immunity, deficiency of vitamins A and C, infection of wounds and burns.
Pseudotuberculosis
If a child is covered with red spots, then he may be infected with bacteria of the genus Yersinia. When children suffer from pseudotuberculosis, the rash looks like dots, spots and papules of varying diameters throughout the body. Clusters form on the palms in the form of “gloves”, on the feet in the form of “socks”, and “hood” on the head and neck. The body temperature rises, signs of intoxication are observed. After about a week, dry scales remain in place of the spots.
There are quite a few reasons why red spots may appear on a child’s body. A photo with a description of the disease allows you to clearly see the characteristic differences between one pathology and another.
Causes:
- Erythema begins with small dots appearing on the face, later merging into large spots and spreading throughout the body. This is a natural skin condition caused by excess blood flow to the capillaries. The cause may be poor circulation, allergic reactions, chemical or sunburn. The rash does not require treatment; it will go away on its own within 2 weeks and does not cause discomfort.
- Hives may be accompanied by small or large blistering spots. A rash of allergic origin is triggered by food, infectious diseases, and hormonal disorders. Children are prescribed medications that soothe itching and strengthen the immune system. Cool vinegar compresses (1 tablespoon per glass of water) eliminate the burning sensation;
- Infantile roseola. The child suffers from fever for 3-5 days, after which a bright, small, and in rare cases extensive rash appears on the skin. The most serious complications are limited to febrile seizures. The spots cannot be felt by touch; some elements are surrounded by white rings. The rash is localized on the chest, rarely reaching the face and limbs. Treatment consists of bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking fever-reducing medications.
- Pityriasis rosea. Judging by the photo with the description, such red spots on a child’s body can reach very large sizes. Large round or oval plaques appear on the patient's body. The spots are localized on the abdomen, chest, thighs, and there is slight peeling in the center of the lesion. At the same time, there is an increase in temperature, enlarged lymph nodes, and general malaise. The child is recommended to have a hypoallergenic diet and take antihistamines to relieve itching.
Red spots on a child’s body from urticaria (photo later in the article) develop against the background of liver pathologies, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or leukemia.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox, which affects children under 15 years of age, is spread through the air or through contact with someone who is sick. First, the child feels unwell and has an increase in temperature, which after one or two days is accompanied by a rash - a pink spot.
Then it turns into itchy blisters. Do not allow the skin to be scratched, as if the blisters are injured, it can cause infection or leave scars. At the same time, a spot on the skin, blisters, and crusts may appear on them. The spots on the child’s body may remain for about a week after recovery.
A contagious and widespread disease. Transmitted after contact with an infected person (object).
The incubation period of chickenpox lasts up to three weeks, after which the temperature rises sharply to 40 degrees - in this case the child becomes lethargic and apathetic. Gradually, red spots appear on the body, degenerating into itchy blisters. The most striking foci of the rash appear between the fingers, in the armpits, feet, and even on the oral mucosa. The spots itch, especially intensely at night.
In young children, chickenpox is not always accompanied by a high fever. It happens that the temperature only slightly exceeds 37 degrees. It happens that a child with chickenpox has no temperature at all.
If the spots are rough and flaky
Flaky spots on a child’s skin can occur at any time due to allergies, infectious diseases or diathesis.
The most common pathologies accompanied by the appearance of rough spots:
- contact dermatitis;
- eczema;
- versicolor or pityriasis versicolor;
- psoriasis (scaly lichen).
Red spots on a child's skin from dermatitis occur as a result of exposure to external irritants: extreme heat, cold, cosmetics, friction, alkali or acid.
The hands most often suffer, less often the legs, if there was direct contact with an aggressive environment. The skin is red, rough and rough to the touch. Treatment: exclude exposure to the irritant, smear the affected areas with a moisturizer. Pediatricians advise pouring 3-4 bay leaves into a glass of boiling water and adding the infusion to the baby’s bathing water to relieve itching.
Red spots on a child's body can cause eczema, contact dermatitis, psoriasis and lichen.
Eczema is a complication of contact dermatitis. The rash appears mainly on the face: forehead, cheeks; these are red, scaly spots that cause unbearable itching. The treatment is the same as for the initial stage of the disease, plus hormonal ointments are prescribed.
Versicolor or pityriasis versicolor - this fungal disease is the result of vacationing in hot countries, close contact with an infected person or stray animal.
The spots are localized on the stomach, back, shoulders, chest and can be pink, yellow or brown. The peeling is strong and leaves marks on clothes and bedding. Therapy includes emollient and antifungal medications.
Psoriasis tends to be inherited. The disease is not contagious and appears as flaky and itchy red or pink spots. There are plaques on the head, hands, elbows, knees in the coccyx area.
The shape of the elements can be oval, round, ring-shaped, linear. Treatment is complex, including antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, and physiotherapy.
Skin spots in newborns
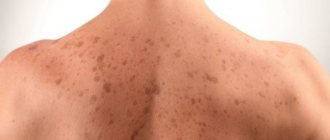
The color of pigment spots can vary from milky to dark brown, this is due to the natural production of melanin as a result of skin interaction with sunlight and hereditary predisposition. Moles and freckles are normal and do not require professional counseling or treatment. Concerns may arise when pigmented areas change color, contour and size. In children, these changes occur quite rarely.
Babies are often born with spots on their skin. Their nature can be very diverse and is not always associated with pigmentation. Often this is the result of vascular changes during intrauterine development and hereditary causes. The most famous of them:
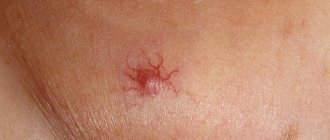
Hemangioma. A reddish spot of various sizes and shapes, formed due to the proliferation of blood vessels. Such a formation requires consultation with a surgeon, and, in case of excessive growth, is removed.
- Mongolian spots. They are noted at birth in children of the Mongoloid race. The blue-blue color of the spots resembles a bruise and disappears without a trace by two years.
- Medial spots are pink. Located on the back of the head and face and having a small area. They can be almost invisible, released only during crying or physical stress and disappear on their own.
- Telangiectasia. Small reddish-blue spots, which are a remnant of the development of the embryo, which disappear on their own by the age of one year.
- Warty formations. Gray-brown rough growths. They are an extremely rare pathology and can be removed surgically.
- Giant pigment spot. A large spot with hair, often having a hereditary predisposition.
- Nevus of Setton. A small mole with a colorless spot around it (possibly vitiligo).
Pigment spots in newborns require constant monitoring and are generally not a pathology.
Doctors recommend measuring the size of such formations and, if it grows, seek advice from a surgeon and dermatologist. Complex spots require special attention, such as Setton's nevus, which may be malignant. Sometimes the pigmentation of infants is confused with a rash, which has a wide variety of origins - from allergic to infectious. In these cases, the diagnosis takes into account the multiplicity of rashes and hereditary predisposition.
There are statistics according to which newborn spots are more typical for premature babies, girls or babies who have people with very fair skin among their older relatives.
Measles
Measles is an infectious disease. It occurs 7-2 days after contact with a sick person.
Measles does not start with a rash. For four days of illness, the child has a high body temperature (up to 40 degrees), accompanied by a runny nose, hoarseness, cough, swelling of the eyelids, photophobia, and conjunctivitis. On the fifth day of the disease, many pinkish spots appear on the body - they unevenly merge into spots of irregular shape.
The rash spreads throughout the body from top to bottom: first behind the ears, then on the face and neck, then the body, arms, and finally the legs. During this period the temperature remains high.
At the last stage, the rash disappears, leaving behind flaky brown spots. Pigmentation completely disappears two weeks after appearance.
90% of unvaccinated people will get sick if they come into contact with an infected person. The disease is considered highly contagious. First, a runny nose appears, the eyes begin to water, and the child may cough. After a couple of days, redness appears: it starts from the behind-the-ear area and face, spreads to the body, and the child develops red spots on the arms and legs.
At the moment of redness, the temperature may begin to rise again if it was brought down before. When the rashes reach the legs, they begin to turn pale on the face. This is a distinctive feature of measles: on the first day it appears on the face, on the second day there are spots on the child’s stomach, on the third day on the limbs.
The rash may be a little itchy. After treatment, traces of brown color or peeling may remain; after about a week to a week and a half, they disappear.
Rubella
A fairly common disease among children aged 5 to 15 years. It is accompanied by a sore throat, as well as headaches, increased tearfulness of the eyes and fever. Before the active phase of the disease, the temperature rises very slightly, the lymph nodes in the neck increase in size, this period is usually not noticed by parents.
Then pink rashes appear on the face and down the body, usually after three days they disappear on their own, and may be slightly itchy. Sometimes rubella goes away without any rash at all, then it can easily be confused with a cold.
However, for pregnant women, this disease can be very dangerous, since if infected in the first trimester of pregnancy, there is a possibility of abnormal development of the fetus.
This is an infectious disease characterized by a high degree of contagiousness. Rubella is transmitted by airborne droplets. The child becomes contagious a week before the rash appears!
Rubella is characterized by small pink spots distributed throughout the body. The largest clusters of spots appear on the child's face, back and chest. Often a rash occurs on the oral mucosa. The redness does not last long - after three days there is no trace left of it.
Rubella in children is rarely accompanied by fever.
Red spots on a child's body
Experts divide diseases characterized by the appearance of redness on the body into four main groups:
- infectious and parasitic;
- allergic reactions;
- blood and vascular diseases;
- improper or poor hygiene.
In this case, the rash can be either the first symptom of a current infection or appear on the 2-3rd day. Before this, the child may be worried about other manifestations of the disease:
- increase in body temperature,
- chills,
- cough,
- runny nose,
- a sore throat,
- abdominal pain,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- loss of appetite, etc.
Pityriasis rosea
The worst type of infection to treat is infection from an animal; if the mother does not recognize the development of the pathological process in time, it will become chronic. As a result of complications, pathogenic fungi will begin to spread with the lymph flow throughout the body, affecting not only the skin.
Symptoms of the disease:
- slight increase in temperature;
- a sore throat;
- headache;
- the appearance of edema;
- different sizes of plaques and uneven edges;
- peeling of the skin.
When the scalp, including the scalp, is affected, bald patches appear in this area. Due to severe itching, the child scratches the skin, and bloody wounds form at the site of the spots.
Therapy for severe forms of the disease includes corticosteroid ointments and creams; itching and flaking are eliminated with products containing zinc. Wet spots are dried with iodine; in addition, the doctor may prescribe immunostimulants and multivitamins.
When the fungus that causes lichen occurs, red spots appear on the child’s body; a photo of them will help you easily distinguish them from other rashes. They usually form where there is sweating. These spots itch and flake, they are dry.
Additional symptoms may include fever and swollen lymph nodes. Children become infected with lichen from dogs and cats.
Since there are several types of lichen, you should consult a doctor to determine what to do in a particular case. An accurate diagnosis is made after analysis - scraping from the affected area of skin.
Allergic reaction
Many medications can serve as a trigger for an allergic reaction. Therefore, never neglect to read the instructions that come with each medication - it is possible that the use of a specific medication caused the appearance of red spots.
In the case when spots on the body cause severe itching in a child, he continually scratches the affected areas, becomes irritable and restless, it can be assumed that the cause of the disease was the body’s reaction to any chemicals and substances used in everyday life.
The occurrence of allergic red (pink) spots may be due to the following reasons:
- the child has consumed foods that can cause an allergic reaction, for example, chicken eggs, candies and other sweets, some fruits, and shrimp. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that milk is one of the allergens that provokes this disease and occurs in almost five percent of children. The same intolerance can occur when eating beef;
- children's cosmetics;
- contact with clothing, bedding, purchased or new for the child;
- household chemicals.
The external manifestation of such red spots, as a rule, resembles bubbles containing colloidal liquid. They spread in most cases to all parts of the child’s body.
Self-medication of this kind is not only ineffective, but also extremely contraindicated, as it can lead to even more serious consequences than a regular allergy. Indeed, as a result of accidental actions, it can infect the affected areas of the skin.
In a word, if the emerging disease is accompanied by severe pain and itching, this should not go unnoticed by the parents; they should take measures to ensure that the child receives timely help. Otherwise, if treatment is delayed, the consequences can be extremely negative - even anaphylactic shock.
Infectious diseases
Red spots on the skin of children in the form of a rash that spreads throughout the body and is accompanied by an increase in temperature are one of the clearest symptoms of infectious diseases.
Such diseases include:
- Rubella manifests itself as a profuse rash on the body, fever, sore throat, and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Measles is an acute infectious disease that is accompanied by high body temperature - up to 40C°. The rash lasts for 10 days and is very itchy.
- Chickenpox is the most common childhood infection. Symptoms are blisters all over the body, often on the oral mucosa, high fever. Infection occurs in 100% of cases through contact with a sick child.
- Erythema is accompanied by severe redness of the skin as a result of dilation of capillaries due to abundant blood flow. A rash appears on the limbs and genitals, causing severe burning.
- Scarlet fever is different in that there are no rash elements in the area of the nasolabial triangle. In this case, there is an increase in lymph nodes, redness of the cheeks, and puffiness of the neck. The larynx becomes inflamed, bacteria mainly multiply in the nasopharynx.
- Roseola is characterized by transience and similarity of symptoms to many other pathologies. The disease appears suddenly and disappears just as quickly. The child’s body temperature often rises to 40°C and persists for 3 days. The patient loses his appetite, becomes irritable, and quickly gets tired.
Treatment is aimed at relieving symptoms, lowering the temperature, relieving itching and preventing injury to the elements of the rash. Chickenpox and measles are treated with brilliant green to dry the wounds and prevent the spread of infection.
Various allergens are the most common cause of itchy rashes. The effect of irritants on the skin is associated with the appearance of red, rough spots on the child’s body, which can rise above the level of healthy skin. The shape is very different: round, oval, polygonal. A red-spotted rash all over the body is a manifestation of allergic dermatoses, a reaction to parasite toxins.
Spots on the testicles in boys and on the vulva in girls appear due to irritation of the delicate skin by feces, after overheating, in conditions of excessive humidity. Miliaria is a disease that accompanies infants. You should wash your child correctly and in a timely manner, and use only products that are safe for children’s skin.
Prevention of red spots in the groin area caused by insufficient hygiene in infancy involves changing the diaper correctly. After removing the wet baby product, you need to wash the baby or wipe it with a damp sanitary napkin without alcohol. Allow the skin to “breathe” a little, then apply “” or zinc ointment, or use “” cream. After this, you can put on a dry diaper.
Rough spots under the knees and on the shins in infants can be a reaction to dry air in the room, hard, chlorinated water or herbs used for bathing.
The appearance of erythema in a child may not be associated with any disease. A large spotted rash occurs after a massage or as a reaction of the autonomic nervous system to strong emotions and physical effort. The body releases a substance from the immune system - histamine. There is tingling, itching, and redness of the skin.
An increase in histamine levels appears on any part of the skin - on the face, on the stomach, on the arms. If the spots do not go away and swelling and itching of the skin bothers you, then the child is given antihistamine drops “Fenistil” or “Zyrtec”. You can take a warm bath with potassium permanganate; After water treatments, apply Fenistil gel to the spots.
Types of stains
Spots are areas of skin of a different color. Often they seem to rise above its surface and may peel off. Based on the characteristics of the spots and accompanying symptoms in the child, the dermatologist makes a diagnosis.
The spots are:
- single and multiple;
- smooth and rough;
- white, red, pink, brown.
The period during which the stains do not go away depends on the reason for their appearance:
- in case of allergic reactions, they disappear within a few days from the moment contact with the allergen is eliminated;
- for infectious diseases - disappear within 1-2 weeks from the moment the first spots appear;
- fungal manifestations last longer - skin diseases take the longest to treat.
Allergic reactions
Children have weak immunity, so contact with potential allergens gives a pronounced allergic reaction. Skin rashes affect different parts of the body, but are most often localized at the point of direct contact. Allergy spots are flat and red. They are often quite large.
Allergens that cause reactions on the skin:
- animals;
- plant pollen;
- cosmetic preparations;
- house dust.
What allergy spots look like depends on how exactly the reaction manifests itself:
- with urticaria - large redness, reminiscent of nettle burns, appears on the limbs and throughout the body;
- with dermatitis - affects the folds of skin on the extremities, chin and cheeks, begins with pinpoint redness and turns into spots, itching and peeling appear;
- with eczema - pink-red spots on the body, turning into blisters, appear in the folds of the skin, on the face and body, in the scalp; with microbial eczema, the marks are red and round.
Urticaria and eczema in a baby
Why urticaria appears in children can be found at the link.
Skin diseases
The immature immunity of a child often provokes the appearance of spots due to skin diseases. If rashes, papules or spots appear, consult a dermatologist. After examining the child, he diagnoses the disease by the appearance of the spots.
How spots appear in various skin diseases:
- Psoriasis. Appears in adolescence. Itchy spots, usually red, appear on the face and body (back, elbows, knees, upper torso). The spots are rough to the touch. One of the causes of psoriasis is a hereditary factor.
- Vitiligo. The disease affects the skin of the face - white spots of irregular shape appear. Sometimes the spots have a so-called “lace” edge. There are no painful sensations. Vitiligo often accompanies a grown child and lasts throughout life.
- Lichen. A pale pink patch appears on the skin, from which the spots spread throughout the body, affecting small areas. Ringworm has a regular round shape and clear boundaries. There are several types of lichen. With pink marks, the marks will disappear in two months, while superficial ones will suffer for several years. The superficial one is characterized by a bright red color and itching.
Infectious diseases
Often spots on the skin provoke infectious diseases. Each of them has its own characteristics:
- Chickenpox - the rash is not localized, can be located anywhere, often on the mucous membranes. First, red spots appear, which turn into fluid-filled blisters. Over time, the liquid becomes cloudy and crusts form due to treatment with antiseptics.
- Erythema - the rash with this disease is bright red and appears on the second day. Redness occurs on the head and spreads throughout the body. Sometimes the dots merge and form huge spots with a clear relief.
- Measles - rashes appear on the body on the 3rd day, spreading throughout the body. After a few more days, they turn brown and peeling appears.
- Roseola - dense papules on the face and neck, arms and legs appear approximately on the 4th day of illness. Roseola is typical for children in the first year of life.
- Rubella - the appearance of red spots on the skin is characteristic of the first days of the disease. They are localized on the head and gradually move down; redness will be noticeable in the skin folds.
- Scarlet fever is characterized by the appearance of red dots at the very beginning of the disease. The rash is noticeable in the folds of the groin, armpits, and sides of the body. A characteristic white triangle is visible on the face - the area above the upper lip and near the nose untouched by the rash. The redness goes away on its own, leaving the skin a little rough.
Parasitic diseases
Infection of a child's body with parasites (helminthiasis) is reflected on the skin. Rashes and spots that are accompanied by itching resemble an allergic reaction:
- roundworms - a rash similar to hives that can spread throughout the body, is accompanied by itching, and the rash becomes severe;
- pinworms - certain parts of the body turn red, swelling appears;
- Giardia – the skin changes color, acne appears;
- opisthorchia - severe redness similar to an allergic reaction, burning and itching appears.
At different stages of the disease, the spots will appear differently:
- Acute - a severe allergic reaction in the form of a rash and spots, appears immediately after infection with helminths, the stage lasts up to eight weeks.
- Latent - the spots disappear along with all signs of the presence of parasites in the body, the stage lasts several weeks or even months.
- Chronic – resumption of a severe allergic reaction due to the laying of eggs by worms. Redness like urticaria appears on the skin. If they do not go away, then this indicates an exacerbation of the disease.
Erythema
In the case of erythema, the rash begins from the face. It turns red, as if the child had been slapped, then it begins to spread throughout the body, the rashes merge into a red spot on the child’s skin, then the spots turn white inside. Sometimes they have a blue tint. The feet and hands usually remain without redness.
And a couple of days before this, the child may feel unwell, have a fever, and may develop a slight cough. After a few weeks, the rash goes away. It is worth noting that during the period of the rash the child is no longer contagious, it is an immune reaction.
Cause: psoriasis
The nature of the occurrence of psoriasis in childhood has not yet been sufficiently studied. Its manifestation largely depends on the state of the protective functions of the child’s body, and the course of the disease will take place in various situations, depending on these factors.
What are the symptoms to know that a child may have developed psoriasis? First, the skin will be covered with reddish spots that are dry to palpation. Over time, the reddish spots will become covered with white scales. Dermatologists call such neoplasms psoriasis plaques. They cause discomfort to the child - they itch and hurt. At first, spots on a child's skin may appear in only one place. After some time they become quite dense.
Important! Psoriasis in a child is a serious disease! To get rid of this disease, a long course of treatment will be required. Do not self-medicate - it is strictly contraindicated!
Photodermatosis
Or photodermatitis is an increased sensitivity to sunlight; children under 3 years of age are at risk.
The disease is characterized by the following manifestations:
- itchy rashes on exposed skin;
- peeling of the skin (chronic form of the disease);
- redness of the affected area;
- rashes in the form of nodules, blisters;
- pigmentation after prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
Symptoms also appear, together with the signs described above, that are characteristic exclusively of photodermatitis:
- lowering blood pressure;
- heat;
- sneezing and runny nose;
- suffocation;
- lacrimation;
- swelling of the mucous membranes.
The best prevention is to protect the child from ultraviolet radiation, not just from direct sunlight. Even in the shade, he should wear a hat, long sleeves, mainly made of natural fabrics. For treatment, antiseptic drugs, zinc-based ointments, antihistamines, and anti-inflammatory creams are prescribed.
Roseola
Herpes, in addition to many other troubles, causes roseola, which at first looks like a fever or cold with an increase in temperature. After 3-4 days, the symptoms are replaced by pink spots of different sizes; they may rise slightly above the surface of the skin.
It does not cause pain and does not itch. The temperature drop is sharp. After 4-5 days the rash goes away.
Most often, very young children under two years of age suffer from roseola; they can be infected by parents or other adults. The disease may not be recognized by the doctor, since during the period when teeth are being cut, an increase in temperature is often explained by this. But if it exceeds 38 degrees, it is unlikely that the cause is teeth.
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is considered to be a group of inflammatory reactions of the skin that develop due to exposure to external or internal irritants. Causes of appearance in childhood: frequent infectious diseases, genetic predisposition, dysbiosis, use of certain medications.
There are several main types of dermatitis:
- atopic;
- contact;
- seborrheic;
- diaper
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LfOxdPhVT5c
Each pathological process is accompanied by characteristic redness of the skin, peeling, and abrasions. Vesicles, pimples, and blisters appear on the face, groin, buttocks, and genitals. Complications manifest themselves in the form of swelling, itching, pain in the affected areas of the skin, pustules form, the skin on the face around the mouth, hands and elbows becomes very dry.
What does Dr. Komarovsky say: are age spots dangerous?
The famous pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky, has repeatedly touched upon the topic of moles, vitiligo and other pigmentation disorders in childhood in his speeches. The doctor says that areas of hyperpigmentation need to be treated with special caution - because cancer cells can develop in them. But this is not a reason to immediately remove moles if they appear. Komarovsky says that the best way to prevent skin cancer (melanoma) is to constantly monitor the condition of nevi. A well-known doctor insists on a monthly examination of the skin, and moles in hard-to-reach places (in the groin folds, armpits, on the scalp) should not be ignored. In order to remember the main signs that it is time to see a doctor, the doctor suggests examining each mole according to the algorithm. This is an abbreviation that stands for:
- asymmetry (should not be observed);
- the edges of the mole (should be clear and even);
- color (the mole should be
Molluscum contagiosum
Red dense nodules with a diameter of up to 5 mm appear on the body. It all starts with one such nodule, then more and more of them appear. The weaker the immune system, the more nodules will appear.
If you squeeze out a nodule, a substance similar to cottage cheese in consistency will appear (it is not recommended to press or squeeze out nodules). They usually go away on their own, even without treatment.
However, they do not cause itching or pain, but for parents such diseases are a reason to strengthen the baby’s immunity.
Blood and vascular pathologies
Vascular red spots on a child’s body, according to the photo with description, can be of different sizes and colors. Rashes in these diseases are provoked by hemorrhages in the skin and spread throughout the body, otherwise they are called hemorrhagic.
Causes:
- disruption of the functioning of platelets involved in the process of blood clotting;
- poor vascular permeability.
Typically, vascular spots appear in a child immediately after birth or are diagnosed in the first days of life. The peculiarity of this rash is that it is not palpable, does not disappear when pressed, and does not turn pale. The color of the formations can be very different, from red and blue to dirty gray. It disappears completely after 3 weeks.
Ringworm is dangerous
The manifestation of ringworm on a child’s body is characterized by redness in the form of spots. They are localized on the skin throughout the body and can reach a diameter of up to 10 centimeters or even more. But they can be half a centimeter in size.
Just as in the case of an allergic reaction, the affected areas on the child’s body are subject to severe itching, which forces him to constantly scratch them. This causes the child great anxiety and discomfort.
In addition to the above symptoms, psoriasis also involves an important distinguishing detail - as a result of the disease, a change in the structure of the hairline occurs. Hair becomes brittle, especially at the roots. The consequences of such changes are extremely unpleasant and entail the first stage of baldness.
Ringworm is transmitted, as a rule, from sick people and animals that are infected with this disease and is considered one of the very serious and dangerous dermatological diseases. By its nature and danger, it is one step higher than those described just above. Therefore, you should pay very close attention to the first symptoms of ringworm and, most importantly, do not miss them.
This will make it possible to quickly take action and start treating it, then there will be a chance to cope with the disease quickly and successfully. Otherwise, the disease will progress and lead to the most undesirable consequences. If ringworm is detected in a child, you must immediately exclude his contact with other children and adults and go to a hospital where he will receive adequate treatment.
Meningococcal infection
Meningococcus can be in the human body without any consequences, without causing illness, but under certain conditions (for example, additional viruses or a decrease in living standards) it can cause meningitis and sepsis.
Sepsis develops very rapidly, so meningococcal infection is treated in the hospital with antibiotics.
With sepsis, a petechial rash appears on gray skin. It looks like small bruises that have a star-shaped structure and grow. The symptom appears on the legs, arms, and torso. During meningitis, nothing appears on the skin.
Possible diseases, but do not deprive
White spots, similar to lichen, appear due to the fact that the amount of melanin in the skin decreases.
Reasons for their appearance:
- Internal:
- Autoimmune destruction, that is, when the body kills melanocytes (cells that produce melanin);
- Disease of the liver, kidneys, stomach or intestines;
- Heredity;
- Failure of the hormonal cycle, functions of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland;
- Skin diseases of natural origin;
- Poor functioning of the endocrine system and thyroid gland;
- Complex viral infections;
- Avitaminosis;
- Constant nervous tension and stress.
- External:
- Physical trauma to the skin;
- Severe skin sensitivity to all chlorine-based household detergents;
- Frequent contact with various toxic substances
- Spending a long time in the open sun, frequent tanning.
The formation of white spots may be a consequence of some disease, and only a doctor can recognize this after a full examination and the necessary tests.
If their cause has already been found, then the very first thing to do is treat the disease that caused their appearance. What if white spots similar to lichen appear on the body, you need to go to the hospital.
There the doctor will examine the whole body and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists for examination.
To prevent such spots from appearing, try to spend less time in the open sun (in summer).
Before relaxing in the sun, lubricate your skin with protective creams or lotions.
In summer, you need to drink as much fluid as possible so that your skin does not have time to dry out. Fruit tea or fresh berry compote will help prevent white spots. Introduce more fruits, vegetables, and seafood into your food.
Pay close attention to your skin; if there are any strange formations on it, go to the doctor immediately.
Allergy
Red spots in a child from food allergies most often appear around the mouth and on the cheeks. This protective reaction of the body is provoked by certain medications.
The distinctive signs of allergies from other pathological processes are the good general condition of the child. As a rule, the patient is only concerned about itching, there is no high temperature, appetite does not disappear, and drowsiness is not observed.
Often there is lacrimation, a profuse runny nose, and the rashes are clearly visible, prominent, and bright. In addition to skin reactions, rhinitis and conjunctivitis develop. Antiallergic drugs and medications that soothe itching help eliminate symptoms.
Nuts, fish, citrus fruits, chocolate, mayonnaise, mushrooms, milk, pastry and other allergens are excluded from the diet. It is recommended to consume butter, sunflower, olive oil, fresh cucumbers, white bread, dairy products, and beef.
When to see a doctor
You should seek help if the rash does not go away within 7-10 days, and the child has a persistent high fever. Decreased appetite and causeless irritability should attract the attention of parents and specialists. A dermatologist will help when the rash is accompanied by bleeding, burning and tingling.
It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance when black formations begin to appear along with red spots. A medical examination is also required when the whole family falls ill at once, the patient complains of chest pain, or anaphylactic shock occurs (loss of consciousness, difficulty breathing).
Systemic therapy is carried out using antihistamines in the form of tablets, syrups, ointments for external use, and gels.
Allergic spots are eliminated using the following drugs:
- Gestan;
- cream for sensitive skin "La-Cri".
They have an anti-inflammatory, healing and soothing effect. If you are allergic to cold, you should lubricate your skin with olive oil before each time you go outside. Red spots, without fear of side effects, can be treated with Depanthenol, Bepanten, Panthenol, or regular baby cream with chamomile. These products promote rapid healing of wounds and cracks.
Zinc ointment helps well with chickenpox, eczema, diaper rash, bedsores, and dermatitis. This is one of the most accessible means for use in dermatological pathologies. The active ingredients accelerate the healing process and reduce the symptoms.
Since the rash is often caused by infectious diseases, parents usually call a doctor at home to avoid infecting other people. We need to measure the temperature. If it is elevated, this is a sure sign of an infectious disease. Monitor the child’s condition and the appearance of additional symptoms.
If there is no temperature, the cause may be insufficient hygiene. Mothers should pay attention to what products they use to wash their baby and whether they wash them often enough.
Before the examination, you should not smear the rash with any substances that can stain the skin and complicate the diagnosis.
In particularly difficult cases, you need to call an ambulance. If you see the following symptoms:
- it is difficult for the child to breathe normally;
- the baby loses consciousness or is confused;
- there are signs of anaphylactic shock, a severe allergic reaction (sharp drop in blood pressure, breathing problems, fainting);
- a significant increase in temperature, which is not interrupted by anything;
- chest pain in a child.
Folk remedies
If you have an allergic reaction to cosmetics, you can use traditional methods to eliminate pigmentation on the skin of your hands.
- The most accessible and simple remedy is lemon juice. You need to take a fresh lemon and squeeze about 10-12 drops of juice from it, mix with any baby cream. This mixture should be used every day, like a regular hand cream. Lemon juice is replaced with essential lemon oil, sold in pharmacies.
- The skin is well lightened by hydrogen peroxide (3%), diluted in half with boiled water, then soak a cotton swab in the solution and lather it a little. The area with age spots should be wiped with this swab for half an hour. This procedure can be carried out once every 7 days.