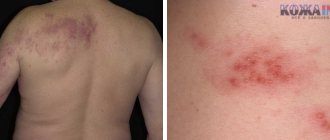
Herpes zoster during pregnancy is dangerous not only due to complications for the expectant mother, but also for the developing fetus. It should be remembered that shingles (the same chickenpox) not only causes pain during the rash, but also affects the nerve nodes (since this is the habitat of the virus).
The impact of the chickenpox virus on the fetus varies by trimester. The consequences of a viral attack also require different reactions, including the need for curettage. Otherwise, the birth of a sick and disabled child will not bring joy to parents.
Yes, you can “suppress” viral activity with the help of medications. But the question remains: how will the pills taken affect the development of the fetus?
Is shingles dangerous during pregnancy?
Herpes zoster during pregnancy poses the highest level of danger to the developing fetus. The disease can lead to spontaneous abortion, premature labor, damage to the central nervous system and internal organs of the fetus.
The consequences of herpes zoster during pregnancy depend on the timing of the onset of the disease.
For reference. It should also be noted that, despite the fact that herpes zoster during pregnancy can lead to severe damage to the fetus, with timely treatment, the consequences for the unborn child are more favorable than in the case of primary infection of a pregnant woman with the varicella zoster virus.
Chickenpox in pregnant women is always accompanied by an unfavorable prognosis for the fetus and is accompanied by a high risk of damage to the child’s nervous system, intrauterine fetal death, and the development of severe chickenpox pneumonia after the birth of the baby.
In this regard, early detection of symptoms of the disease and initiation of therapy play a critical role in preventing the development of complications in the mother and the formation of congenital developmental pathologies in the fetus.
Traditional methods
As already mentioned, no special treatment is required for pityriasis rosea during pregnancy. You can get by with traditional methods. The affected areas are lubricated with onion pulp or juice. Cabbage leaves, previously greased with sour cream, are applied to the stains.
The rashes are wiped with a mixture of castor oil and calendula tincture, which are taken in equal parts. As an alternative remedy, a solution of mustard and vinegar is also prepared.
To treat lichen versicolor during pregnancy, herbs are used:
- St. John's wort;
- celandine;
- fresh sorrel;
- Sandy immortelle.
Infusions and decoctions are made from them, which are used to wipe the affected areas. They are also suitable for indoor use. The main condition for a quick cure is good immunity. To restore it, vitamins are used and a special diet is prepared.
Causes of herpes zoster in a pregnant woman
The development of this disease during pregnancy is associated with the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus ( herpes type 3 ). Upon initial contact with the virus, chickenpox develops.
For reference. According to official medical statistics, chickenpox in pregnant women is registered in less than two percent of cases.
This is due to the fact that chickenpox is a classic childhood infection with a high degree of contagiousness, so most children are immune to varicella zoster by the age of 10-14 years of age. In older age, the disease is extremely rare.
Also, many countries have now introduced mandatory vaccination against chickenpox, which has made it possible to almost completely eradicate chickenpox in pregnant women.
For reference. In the Russian Federation, vaccination against chickenpox is not included in the mandatory list of vaccinations for children. However, when planning pregnancy, women who have not previously had chickenpox may be recommended to undergo routine vaccination against varicella zoster.
At the same time, previous chickenpox and vaccination do not reduce the risk of developing herpes zoster in a pregnant woman.
Causes
Often a pregnant woman becomes infected with lichen after contact with a sick animal or person. In addition, the causes may be allergies, fungi, or viruses. In some situations, the pathology is provoked by an anxiety state caused by stress.
The following provoking factors for the development of lichen can be identified:
- Lack of vitamins. In this case, the doctor specifically prescribes a vitamin-mineral complex, because the expectant mother’s body requires a double dose of all substances, and she does not always receive them with food.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Reduced immunity is the main problem, because against the background of this, various diseases begin to cling to a woman.
- Constant colds, ARVI, past flu.
- Chronic skin and other diseases.
A pregnant woman's body is more susceptible to various diseases. Thus, the main causes of lichen infection in a pregnant woman are:
- direct contact with a person infected with a fungal or viral infection;
- infection received from a cat or other animals;
- lack of vitamins in the body of a pregnant woman;
- general weakness and loss of strength;
- frequent exposure to stress that negatively affects the entire body;
- prolonged stay at low temperatures, which is also very dangerous for the woman and the fetus;
- weakened immunity due to a cold;
- presence of chronic diseases.
Pityriasis rosea or Gibert's disease is a type of viral infection that appears on the skin in the form of rashes and red spots. It is not uncommon to see them on the arms, back, shoulders, thighs or stomach.
According to statistics, the infection occurs in people aged 1 to 45 years. You can become infected with it only once in your life - in the future, the body develops a strong immunity. Full recovery occurs after 2 months.
How can you get herpes zoster during pregnancy?
The development of herpes zoster in pregnant women occurs against the background of decreased immunity.
Provoking factors that increase the risk of virus reactivation in a pregnant woman are:
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- avitaminosis (vitamin deficiency);
- poor nutrition;
- anemia of pregnant women;
- exhaustion;
- the presence of concomitant endocrine diseases;
- severe concomitant chronic infections;
- treatment with cytostatics, glucocorticoids or immunosuppressive drugs before pregnancy;
- presence of HIV infection.
For reference. Primary infection with chickenpox in women who have not previously been ill is most often carried out by airborne droplets. Less commonly, infection can occur through household contact (using shared utensils and personal hygiene items).
The source of the varicella-zoster virus is predominantly patients with chickenpox. Infection from patients with shingles occurs extremely rarely (usually through direct contact with damaged blisters on the skin).
What is pityriasis rosea
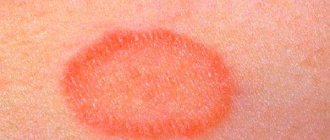
Pityriasis rosea (Roseola exfoliates or Zhiber's pityriasis) is an infectious-allergic disease, which is accompanied by the formation of pink spots on the body with a bright, clear rim of a round shape and flaking inside.
Doctors believe that this form of lichen is caused by a virus - a type of viral herpes. As the disease develops, the patient may first observe the appearance of one “maternal” spot, and after some time several more such spots on the chest, on the shoulders, on the sides and on other places of the body.
The affected areas begin to peel off, and quite severe itching is felt.
Autumn and spring are considered the most dangerous periods for infection with this type of lichen, and its main risk group is children over 10 years of age and young people under 35 years of age. In general, people with strong immune systems need not worry about possible infection.
But for those who have a weakened immune system, in order to avoid infection, you need to follow basic hygiene rules: do not use the personal belongings of a sick person (bath accessories, comb), do not overcool, do not get nervous over trifles, do not communicate with stray animals, even if they look absolutely healthy, etc..
Pityriasis rosea (Zhiber's pityriasis) is infectious and allergic in nature, caused by a special type of viral herpes. Its characteristic feature is the appearance of round pink spots with a clear outline and a bright rim.
Symptoms of chickenpox in pregnant women
Manifestations and symptoms of the disease during pregnancy do not differ from those in non-pregnant women.
The main manifestations of herpes zoster in pregnant women are:
- pain in the area innervated by the affected nerve;
- the appearance of herpes rashes in the affected area (one-sided rash);
- febrile and intoxication symptoms (chills, fever, weakness, lethargy, nausea, loss of appetite, muscle and joint pain);
- enlargement of regional (located near the affected area) lymph nodes;
- crawling sensation, tingling, numbness in the affected area.
If the branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected (herpes zoster on the face), severe pain in the teeth may occur. The development of herpes eye lesions may also occur, accompanied by decreased visual acuity, severe pain in the eyes, and the appearance of ulcers in the conjunctiva and cornea.
Manifestations and diagnosis
Pityriasis rosea in women during pregnancy is similar to some other diseases, such as various dermatoses, cytomegalovirus, herpes, syphilis, Epstein-Barr virus and others. For this reason, it is important to differentiate it from other pathologies as quickly as possible and apply the correct therapy.
Pityriasis rosea is characterized by the formation of pink, round spots on the body, the appearance of which is preceded by the formation of a larger maternal spot (or maternal plaque).
First you should pay attention to the symptoms, among which the main ones are:
- Pink or light red rash. They are enclosed in a clear frame of a darker shade, filled with a bubbly spot, which soon after formation wrinkles, turns yellow and begins to peel off. The development of pityriasis rosea during pregnancy begins with the appearance of a red spot, which is called the maternal spot. Then they spread in a smaller size throughout the body, covering the torso (hips, sides, upper, lower limbs), while not affecting the head, face, feet, hands. The rash reaches its greatest spread throughout the body a week after the first manifestations.
- Itching and peeling of pathological spots distinguish them from the symptoms of many other dermatoses. Unbearable itching causes a lot of inconvenience to a pregnant woman, especially if pink spots appear in the abdominal area, the stretching skin of which often itches anyway. Exfoliating skin particles are the source of the spread of spots throughout the body.
- In rare cases, a pregnant woman's body temperature may rise or her lymph nodes may become enlarged.
Manifestations of lichen are observed for 4 to 6 weeks, and then the spots gradually disappear and the disease recedes.
In order to accurately diagnose this disease, it is enough to consult a dermatologist. The specialist conducts a visual assessment of the rash and dermatoscopy - examination of the affected areas through a magnifying device. If the characteristic rashes do not disappear after 6 weeks, additional examination methods are used, such as a skin biopsy for the purpose of histological examination of its particles. In case of complications of an infectious nature, a scraping is taken for bacterial culture.
To differentiate pityriasis rosea from pityriasis versicolor, a luminescent diagnostic method and scraping of skin particles are used.
Consequences for the fetus
The severity of fetal damage depends on the duration of infection.
The infection can lead to:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- fading pregnancy;
- damage to the fetal skin;
- damage to the fetal nervous system (development of mental retardation, underdevelopment of the brain, the appearance of hydrocephalus, convulsive symptoms, development of Horner's syndrome);
- damage to the limbs and anomalies in their development (atrophy, underdevelopment of the arms and legs, paresis and paralysis);
- eye damage, manifested by optic nerve atrophy, cataracts, chorioretinitis, microophthalmia, nystagmus;
- disruption of the development of the gastrointestinal tract (development of intestinal atresia, stenosis, gastroesophageal reflux);
- low birth weight;
- premature birth.
Attention. It should also be noted that the infant mortality rate for the development of chickenpox syndrome in the first months after birth is about thirty percent.
There is also a risk of a child developing herpes zoster (fifteen percent of cases).
In the first trimester
When shingles develops in a pregnant woman in the early stages, there is a high risk of the fetus developing congenital chickenpox, which is manifested by impaired development of the limbs, eye malformations and severe damage to the fetal nervous system.
Intrauterine growth retardation, miscarriage, or miscarriage may also occur.
For reference. In this regard, a woman is recommended to undergo an ultrasound immediately after the onset of symptoms of herpes zoster and some time after (after the symptoms subside).
You should also undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist. If there are signs of pregnancy fading, curettage is performed.
Consequences in the second and third trimesters
When the disease develops in the second trimester, severe damage to the fetal extremities, development of brain atrophy, damage to the nervous system, and eye damage are possible.
Herpes zoster at the beginning of the third trimester is also fraught with severe damage to the skin, internal organs and nervous system of the fetus.
For reference. If the disease develops at 38-39 weeks, emergency delivery by cesarean section may be recommended.
When a fetus is infected with herpes zoster five days before birth or during the first two to three days after birth, severe chickenpox develops. The disease often occurs in the form of chickenpox pneumonia.
In the future, children in the first three months of life who are breastfed rarely get chickenpox, since they receive maternal antibodies to chickenpox.
Treatment
Any treatment for lichen during pregnancy begins, first of all, with maintaining cleanliness and hygiene. Rashes should be lubricated with disinfecting ointments (they can be antifungal and antiviral, depending on the etiology of the disease), bedding should be changed regularly, only clean clothes should be worn, ironed on both sides, and excessive sweating and skin contamination should be avoided.
A prerequisite for treatment is to improve health, increase immunity and normalize hormonal levels. Drugs that enhance immunity may be prescribed.
Ringworm should be treated based on the degree of neglect, its type, and the course of the disease.
It is possible to prescribe antihistamines due to constant irritation and insomnia due to annoying itching.
Ringworm of a viral nature is treated with antiviral drugs. Treatment of fungal lichen (pityriasis versicolor) is carried out with antifungal agents and ointment is used.
Regeneration and vitamin therapy must be carried out to strengthen the immune system, if there is no allergy and the lichen does not threaten the development and life of the child.
During pregnancy, women should avoid wearing tight underwear and clothing made from artificial fabrics, which cause chafing of the skin and increased sweating.
It is useful to wipe multi-colored lichen and ringworm with table vinegar (9%). For lichen planus, valerian officinalis preparations are used in complex therapy.
For pityriasis versicolor, remove flaky spots with green soap, resorcinol or salicylic alcohol, as well as a 2% iodine solution. Treat with drugs: Mycoseptin or Nitrofungin.
Lubricate problem areas with calendula tincture mixed with regular castor oil (1:1), without affecting healthy skin.
During pregnancy, many pharmaceutical drugs should not be used because they have a negative effect on the baby, so it is recommended to use alternative methods of treatment:
- Fresh onion juice. The product should be used to lubricate damaged skin.
- Cabbage leaves with homemade sour cream will help quickly cure lichen.
- It is recommended to wipe the affected skin with a mixture of castor oil and marigold tincture.
Thus, a pregnant woman should take special care of her underwear - it should be natural, clean, and best ironed. In case of illness, all laundry must be boiled for about 20 minutes.
Only timely detection will help prevent a number of unpleasant consequences. Don't worry if you do get sick.
No matter how hard you try to take care of yourself, against the background of a weakened immune system, all pregnant women begin to catch diseases, including skin diseases. Ringworm is not a terrible disease, so you can rest assured, but it’s better to play it safe in such an important period of life and go to the doctor.
For pregnant women, treatment of the disease must be comprehensive, first of all it is necessary to restore immunity. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to use antifungal drugs and antiviral immunomodulators.
To restore the normal state of a woman’s skin, it is recommended to take advantage of a therapeutic course of treatment, including therapeutic measures.
It is important to know: specialized treatment is not prescribed for the appearance of lichen rosea. Within a couple of months, the dermatosis goes away on its own.
If you notice severe and unbearable itching, you should urgently visit a specialist. It will help the expectant mother get rid of the unpleasant symptom with the help of systemic antihistamines.
Drug intervention is necessary when lichen versicolor appears during pregnancy. This disease is accompanied by antifungal treatment.
Apple cider vinegar should be used to treat the affected areas of the epidermis. After treatment with the product, the itching disappears, peeling goes away and pigmentation is restored.
For external use, you can use Clotrimazole ointment or wipe with a solution or cream. During the last trimester of pregnancy, the drug should be used with caution, only after the recommendation of a specialist.
READ MORE: Pregnancy test for thrush
After water procedures, the product is applied no more than 2 times a day. In some cases, the causative agents of the disease affect the scalp, which also needs to be treated.
Treatment of the disease depends on what type of lichen (tinea or herpes zoster, pink or ringworm) is observed in the pregnant patient. Also, the means for treatment are determined by the degree of neglect of the disease.
As a rule, to relieve severe itching, a dermatologist prescribes safe antihistamines to the patient. If lichen appears during pregnancy due to a virus, then it is necessary to use antiviral agents, if due to a fungus, antifungal agents.
Taking restorative and vitamin preparations is necessary for pregnant women to strengthen the immune system and in the future not to encounter lichen diseases, which are carried not only by people, but also by cats and other animals.
Are folk remedies effective for treating lichen?
Like any disease, lichen can be treated during pregnancy using folk remedies. Such treatment methods should only be auxiliary, because pregnancy is not the time for experiments. Among the popular folk remedies used in folk medicine to treat pink, multi-colored, ringworm and shingles during pregnancy, it is worth noting:
- applying tincture of calendula and castor oil, mixed in equal parts, to the affected areas;
- applying a fresh cabbage leaf with sour cream to the affected area;
- rubbing a mixture of vinegar and mustard into the affected areas;
- smearing foci of disease with ash from a burned newspaper.
In addition, there are many more methods that can alleviate the occurrence of colored, pink and other types of lichen, as well as prevent their negative consequences for the health of the mother and child. But in any case, the advisability of using folk remedies should be previously discussed with a doctor.
Pityriasis rosea in pregnant women does not require special treatment, since it goes away on its own after 1.5-2 months. However, if the itching causes inconvenience and becomes unbearable, then first of all you need to contact your doctor during the pregnancy or a dermatologist.
Firstly, this must be done to ensure that the diagnosis is correct and to exclude diseases with similar symptoms (herpes, parvovirus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus or syphilis); secondly, doctors will select the necessary treatment (drug or non-drug) or recommend folk remedies.
To relieve unbearable itching, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines and drugs to strengthen the immune system, but first of all he will recommend:
- wear fairly loose, non-tight clothing made from natural fabrics (silk, cotton), but avoid woolen items,
- do not use cosmetics during treatment and for at least 2 weeks after it, which may aggravate the symptoms of the disease,
- do not overheat the affected areas of the skin,
- When washing, use mild soap,
- After washing, apply calamine ointment to the affected areas of the skin.
As necessary and in particularly advanced cases, the doctor may prescribe antiviral or antifungal drugs that block the activity of fungi and viruses. In addition to their main effect, these drugs are able to restore affected areas of the skin.
1. For oral administration:
- antihistamines (for example, Suprastin, Claritin),
- vitamin therapy (vitamins A, all group B, C),
- broad-spectrum antibiotics (Erythromycin, Tetracycline),
- sedatives - prescribed as needed.
2. To treat affected skin areas:
- ointment from a number of corticosteroids,
- a shaken suspension of water, glycerin, zinc oxide, talc and starch,
- topical steroids (such as hydrocortisone or clobetasol cream) to relieve itching.
Pityriasis rosea during pregnancy is rare, but does occur. In this article we will answer the most popular questions that a woman may have.
Before taking any action on your own, we recommend making an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
In order for the treatment of pityriasis rosea to be as fast and effective as possible, you must adhere to the basic rules:
- limit physical activity;
- change your underwear daily, do not wear tight, tight-fitting clothes, giving preference to cotton or linen fabrics;
- do not shower more than once a day, using mild soap;
- refuse hard towels, sponges, cosmetics for skin care;
- follow a diet, avoiding fatty, salty, spicy foods, sweets, exotic and out-of-season fruits.
Drug treatment may include taking antihistamines, broad-spectrum antibiotics in the presence of complications, sedatives and vitamins B, C, A. To treat the affected lesions, a special “mixture” of glycerin, zinc oxide, starch, talc, and water is used , corticosteroid ointments, hydrocortisone or clobetasol creams.
When the first signs of the disease appear, it is recommended to immediately contact a dermatologist. The treatment method and means are selected depending on the type of disease, type of course and degree of neglect.
How and how to treat lichen during pregnancy? Antihistamines are prescribed to relieve irritation. If the cause of lichen development is a virus or fungus, then antiviral and antifungal agents are prescribed.
If there is no threat to the child’s life, vitamin and restorative therapy is indicated to strengthen the body’s defense mechanisms.
It is recommended to use folk remedies only after consulting a doctor, since their effectiveness in treating different types of lichen differs.
The best medicine in this case is fresh air, good mood, positive emotions and proper nutrition.
The disease goes away on its own within 1.5-2 months; to ease its course, it is recommended to take anti-allergenic drugs and ointments.
These remedies will not speed up healing, but will help get rid of the itching. As part of therapy, antihistamines are prescribed.
Pityriasis
Treatment:
- taking antifungal drugs;
- topical products (solutions, tinctures, shampoos, ointments, lotions, creams).
If red or pink spots appear on the skin, the expectant mother should definitely consult a doctor. Only a dermatologist can accurately diagnose and find out the cause of the disease. Many skin diseases are similar in appearance to Zhiber's lichen, and it can be quite difficult to distinguish one condition from another at home.
There is no specific treatment for pityriasis rosea. The disease goes away on its own without any therapy within 2-12 weeks. A prolonged course (up to 6 months) is quite rare.
Pregnant women are not recommended to take medications on their own to get rid of unpleasant spots and itching from pityriasis rosea. Many drugs are prohibited for use in expectant mothers as potentially dangerous to the growing fetus. Attempts at self-medication can lead to disastrous results and even cause termination of pregnancy.
READ MORE: Thrush in early pregnancy
In some cases, pityriasis rosea is accompanied by severe itching. Antihistamines are used to relieve itching.
During pregnancy, such drugs are prescribed with great caution and only for a short course. In the first trimester, you should not use antihistamines unless absolutely necessary.
In the second and third trimesters, priority is given to relatively safe antiallergic drugs of the latest generation. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
Corticosteroid ointments used for severe itching are practically not used in pregnant women. As an exception, the doctor may prescribe weak hormonal drugs locally. The course of therapy should not exceed 7-10 days. In the first trimester, the use of corticosteroid ointments is not recommended.
In some cases, special treatment is not required, while in others, the use of medications agreed with a dermatologist and obstetrician-gynecologist is permissible.
The expectant mother may be prescribed the following types of medications:
- antihistamines to relieve itching;
- antibiotics are acceptable for pregnant women;
- vitamin-mineral complexes and immunostimulants;
- sedatives.
For external use it is recommended to use:
- topical steroids;
- corticosteroids;
- zinc ointment.
In addition, to alleviate the condition you need:
- Minimize water procedures or, if the stain is single, try not to wet it.
- Avoid using body washes and washcloths for the duration of your illness.
- Wear loose clothing made of natural, breathable fabric.
- Refuse to use any body cosmetics.
- Follow a hypoallergenic diet, that is, exclude from the diet citrus and red fruits, products containing cocoa and caffeine, nuts, spices, and smoked meats.
- After water procedures, lubricate the skin with moisturizing creams (for example, containing calamine).
If spots of unknown etiology are detected in a pregnant woman, it is advisable to immediately visit a dermatologist, who, after examining the skin formations, will be able to give recommendations for treatment.
If a doctor has diagnosed a pregnant woman with lichen, she must adhere to some rules:
- Limit physical activity;
- Change linen daily;
- Use only natural cosmetics for body care;
- Shower procedures maximum once a day, and stains should not be washed with soap;
- Do not use a hard towel for the body.
informationThe patient should also adhere to a certain diet. It is not advisable to eat fried, spicy, fatty, salty foods, exotic fruits, alcohol, and sweets.
Diagnosis of herpes zoster in pregnant women
If laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis is necessary, PCR is performed. To diagnose intrauterine damage to the fetus, an ultrasound examination is performed.
To carry out postpartum diagnosis of congenital chickenpox syndrome, an analysis is performed for viral DNA or IgM to the varicella zoster virus in umbilical cord blood.
Standards of treatment for pregnant women with herpes zoster
Treatment of herpes zoster in pregnant women should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. Self-medication is absolutely unacceptable and can cause irreparable harm to both the health of the woman and the unborn child.
For reference. The most effective method of treating herpes zoster during pregnancy is taking acyclovir during the first three days after the development of symptoms of the disease.
In this case, the most favorable prognosis for the fetus and the lowest risk of developing severe complications in the future are noted.
Early administration of acyclovir is effective both for chickenpox in pregnant women and for herpes zoster. For chickenpox, acyclovir significantly reduces the risk of developing chickenpox pneumonia in pregnant women (the mortality rate for this complication is about 40%) and the risk of damage to the fetus.
According to indications, immunomodulators, immunoglobulins, multivitamins, and NSAIDs are also prescribed.
Prevention of herpes zoster in pregnant women
Prevention is divided into post-exposure vaccination and pre-pregnancy vaccination.
Prevention protects against the development of chickenpox during pregnancy, but does not reduce the risk of developing herpes zoster.
For reference. When exposed to the varicella-zoster virus, women who have not previously had chickenpox are prescribed immunoprophylaxis using specific immunoglobulins.
To prevent the development of shingles (against the background of decreased immunity), women who are immune to chickenpox are advised to regularly visit a gynecologist, take multivitamins for pregnant women, eat well and rest, and walk more in the fresh air.
Common symptoms of lichen
All types of lichen have their own symptoms. But there are also general signs of the disease. Microorganisms that become causative agents of lichen can live in the human body for a long time and yet not manifest themselves in any way. The virus is activated mainly when immunity decreases.
The first signs of the disease:
- changes in skin pigmentation;
- hair loss;
- peeling of the skin or its individual areas;
- the appearance of spots of unclear shape, often having different sizes;
- itching in the area of the rash.
These symptoms are complemented by a deterioration in overall health. The person becomes irritable and nervous. This occurs due to unpleasant sensations and the visual appearance of the disease. Symptoms may vary in location, speed of spread, and degree of contagion.
With Zhiber's rosacea, pinkish spots appear on the skin of the torso, sometimes legs, and arms. During pregnancy, spots are often localized on the skin of the abdomen. They are located, as a rule, along the so-called skin stretch lines (semi-horizontally).
Often, one large spot about 2-3 cm in diameter appears first. This spot is called the mother's plaque.
Then the rest appear, but of a smaller diameter. All spots are round in shape, pinkish or yellowish-pink in color, and after a couple of days they begin to peel off slightly in the center. During this period, some patients report mild itching. But this is optional. During pregnancy, patients may mistake it for itching of stretched abdominal skin.
For some, when this disease occurs, there may be a slight malaise and a slight increase in body temperature that goes away on its own.
The effectiveness of therapy and the health of a pregnant woman largely depends on the correct diagnosis of the type of lichen. Since each variety of this skin disease is caused by different pathogens, their symptoms and treatments vary. Let's look at the most common types of lichen found among pregnant women.
Shingles is considered the most undesirable and insidious form during pregnancy. The disease is caused by a type 3 herpes infection called Varicella-Zoster virus. When infected in the first trimester, the fetus in 80% of cases succumbs to pathological changes: the structure of the central nervous system is affected, hearing and vision defects are formed. In subsequent trimesters, provided that the baby is treated correctly, no pathologies are observed.
The defining symptoms of this lichen during pregnancy include:
- Headaches of spasmodic neurological origin.
- Pinkish spots up to 5 cm in diameter, transforming into a blistering rash.
- Pain syndrome localized in the projection of the ribs, muscles, joints.
- Painful and enlarged lymph nodes throughout the body.
- Itching, burning and irritation in places where rashes gradually appear.
- Rapid increase in body temperature.
- Severe weakness, depressed mood.
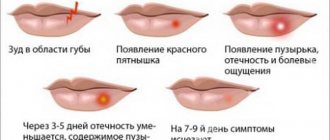
Shingles rashes can appear on one side, affecting the area of the intercostal nerve endings, face, head, as well as the area from the spine to the chest. The disease appears rapidly: the temperature rises, a feeling of fatigue appears, then the skin tingles and itches, where multiple spots begin to appear, merging into one whole. At first they are pale pink, but soon they are filled with liquid.
The blisters are painful to the touch and hurt during movement, so the woman feels discomfort all the time. The rash lasts a long time, about a month, then little by little the blisters dry out, forming dense crusts. When they fall off, the skin remains pigmented for a long time.
In women under the age of 40 with an increased tendency to allergic reactions, pityriasis rosea may develop. The second name of the disease is Zhiber's lichen. The disease manifests itself as small pale pink spots with one dominant spot up to 6 cm in diameter. Any part of the body can be affected, including the arms, hips, as well as the neck, shoulders, and abdomen.
Other symptoms of pityriasis rosea include:
- Pink color of the spots, with a focus of peeling in the center.
- Enlarged axillary lymph nodes.
- Periodic muscle pain.
- Increased skin sensitivity to chemicals, against the background of exacerbation of allergies.
Tinea versicolor is caused by a fungus that enters the usual microbial environment on our skin. Its spontaneous progression is facilitated by certain triggers - immunodeficiency status, hormonal imbalance, stress, poor hygiene, vitamin deficiency. When suitable conditions arise, the fungus multiplies rapidly, forming multi-colored spots of various shapes and structures on the skin. The rash does not cause any particular discomfort, so the disease is not noticed immediately.
Lichen versicolor during pregnancy is determined by the following signs:
- Colored spots on the skin - bright red, yellow, brown, beige-pink.
- Placement of spots on the back, buttocks, places with increased sweating.
- The spots form under the skin and do not rise above it.
- As the number of spots increases, they may merge together.
- Large lesions are prone to peeling and may itch.
- There is no water exudate from the spots.
- After the spots disappear, a defect in the form of a smooth scar is noticeable on the skin, which does not tan in the sun.
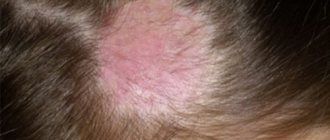
This lichen gets to a pregnant woman during contact with a sick animal or an infected person. Indirect infection through hairdressing supplies, shared beds, and personal hygiene items is also possible. In this case, only the scalp and nails are affected. An impaired immune system and damage to the skin increases the risk of getting sick.
We suggest you read how long it takes to become infected with lichen from a cat. Is lichen transmitted from cat to person? Possible routes of infection
Ringworm is recognized by the following external manifestations:
- Spots with increased flaking on the head.
- Hair loss in areas where the rash occurs.
- Destruction or complete loss of nail plates.
- A gross change in the aesthetic appearance of the scalp and nails.
Ringworm can cause self-infection again, so it is important to take special precautions during pregnancy:
- You need to change your underwear 2-4 times a day.
- Use a replaceable clean towel at all times.
- Avoid close contact with family members.
- Regularly ventilate the apartment and do wet cleaning with antifungal agents (vinegar, soda, boric acid, bleach).
This is a rare type of lichen of non-infectious nature. During gestation, the cause of its appearance is immune and metabolic disorders. Its symptoms are quite unique, so it can be diagnosed without additional tests:
- An irregularly shaped rash of purple, red-violet color.
- The surface of the rash is smooth, glossy, without traces of peeling.
- The structure of the spots can be varied: convex, flat, nodular, in the form of ulcers or tubercles.
- Small, light pink nodules in the mouth and external genitalia.
- Hyperpigmentation at the sites of the missing rash.
- "Scallops" on the nail plates.
The only, but very typical symptom of Zhiber's lichen is the appearance of skin rashes: flat or slightly convex pink spots ranging in size from 1 to 2 cm, shaped like a medallion. The boundaries of such a spot are clearly defined, and its central part may be covered with scales that peel off easily. The rash is usually localized on the upper torso, less often on the face, lower abdomen or legs.
Such a spot with a well-defined bright pink border lasts 2–4 weeks, then gradually changes color to a darker one and disappears on its own. In its place, the skin remains depigmented for some time, almost colorless. Since the disease is cyclical in nature, there may be both fresh and already “fading” lesions on the skin at the same time.
The progression of pityriasis rosea is usually accompanied by slight itching and a slight deterioration in general well-being. In some cases, these relatively mild symptoms are accompanied by joint pain, low-grade fever, and enlarged cervical and mandibular lymph nodes.