How does human skin work?
In order to better understand the causes of acne, it is necessary to understand how human skin works. Firstly, the skin is larger than all other organs in the body, and secondly, the skin performs many of the most important jobs for human life - thermoregulation, sensitivity (receptors), protection, signaling and metabolic systems, and many others.
The thickness of the skin is not the same, it differs in different parts of the body, ranging from 0.1 to 4 millimeters. The condition of a person’s skin depends on many factors, both individual and hereditary, but regardless of race, age and gender, it is structured the same for everyone.
The skin consists of three layers – Epidermis, Cutis and Subcutis:
- The deep layer is the thickest, it mainly consists of fatty tissues, located in separate layers one below the other. It nourishes all other skin layers and serves as a kind of airbag, absorbing shocks and preventing possible damage to internal organs and internal vessels.
- The middle layer is the most difficult. It contains connective tissues, hair follicles, glands that produce sebum and sweat, nerve endings, blood and lymphatic vessels, many receptors - tactile, temperature, and others.
- The top layer is the thinnest, it is constantly regenerated, new cells grow inside, and the top ones die and peel off. The entire cycle takes about 6 weeks. It is this layer of the skin that is responsible for color, melanin is formed here, and the body’s defense against bacteria; Langerhans cells work as predators, eat them, and process them.
Violation of the normal functioning of the system in the middle and upper layer of the skin leads to improper metabolic processes, and as a result, acne forms. They can be caused both by the outside world and have reasons hidden within the body.
Rashes of any kind appear in the middle layer of the skin - the dermis.
Professional methods for getting rid of acne
To completely eliminate acne marks, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination. If the causes of acne on the face are internal problems of the body, the doctor will prescribe medication.
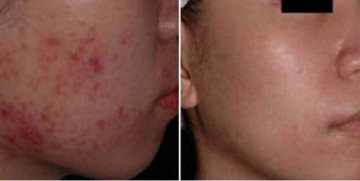
In the photo: face before and after fractional thermolysis
In other cases, a specialist may prescribe such cosmetic procedures as:
1. Jessner peeling – a mixture of resorcinol, lactic and salicylic acid is applied to the skin with massage movements; After the procedure, excellent exfoliation of skin cells is observed, and sebum secretion is reduced.
2. Fractional thermolysis - a laser beam directed at the skin creates microcracks in the upper layer of the dermis; Thanks to this effect, young and healthier cells are produced.
3. Salicylic peeling gives excellent results in the fight against acne and comedones in combination with mechanical facial cleansing. Primarily, peeling is suitable for young, oily skin with minor problems, as well as for mature skin with signs of photo- and bioaging.
4. TCA peeling – involves applying a composition of trichloroacetic acid to the face with a special brush; As a result, deep cleansing of the inner and outer layers of the dermis occurs, reducing the oiliness of the skin.
Whatever the reason for the appearance of acne on the face, you should never delay the treatment of inflammation. This guarantees quick relief from acne and restoration of facial beauty.
Only a qualified cosmetologist can choose the method that is right for you, who will draw up an individual schedule of procedures.
Traditional ways to get rid of acne
Traditional cosmetology methods are an aid to combat acne on the face. We offer the most universal recipe for getting rid of inflammation.
Chamomile lotion 2 tbsp. Pour boiling water over chamomile flowers, let it brew for a quarter of an hour, then soak a cotton cloth in the infusion and wipe your face, rinse with water at room temperature.
Onion mask: chop and boil 1 onion, then apply the mixture to the face, cover with plastic wrap; After an hour, remove the film and wash with warm water.
You can read how to make effective masks based on cosmetic clay against acne here.
If you are patient and follow these instructions, your acne problem will finally get off the ground. Depending on the severity and form of the inflammatory processes, choose those methods and recipes that will tell you in detail how to treat acne on the face yourself or with the help of specialists.
How does a pimple work?
A closer look at the structure of the middle layer of skin shows that the hair follicle has a wall, called the outer hair sheath, inside which there is a sebaceous gland closer to the surface of the skin. The gland actively secretes fat to lubricate the hair shaft itself, through which the fat enters the surface, is distributed and serves as protection from high temperatures and attacks from microorganisms.
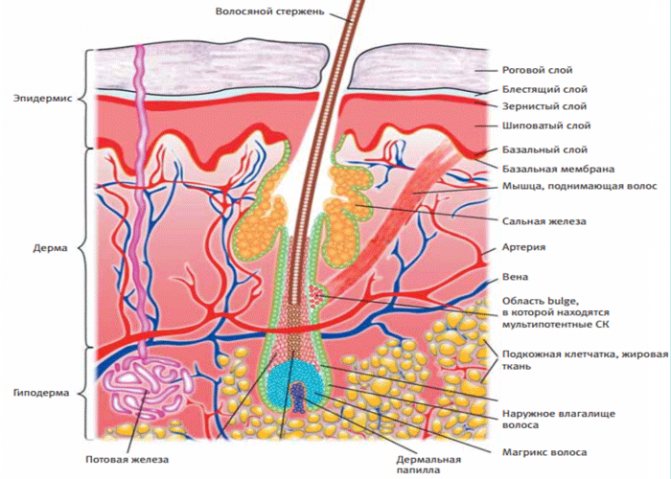
When a plug forms on the surface of the skin, the fat secreted by the sebaceous gland is not able to come to the surface, it accumulates under the skin and over time a favorable environment is created for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, and the inflammatory process begins.
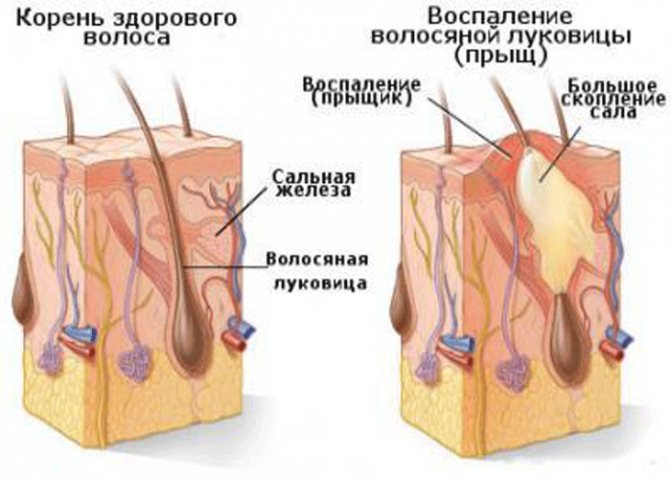
The structure of a pimple, popularly called a wen, or a closed comedo, is the same, with one difference. The plug does not form on the surface of the skin, but inside. Fat does not have the opportunity to come to the surface, so it sinks lower in the middle layer of the skin. This can lead to the formation of fairly large lipomas and benign tumors.
A furuncle is a severe inflammation of the hair follicle caused by bacteria; the pimple stem is formed from purulent necrotic fluid and can reach the lower part of the hair follicle.
You should not try to treat boils on your own; the disease can cause serious complications - blood poisoning, abscess, and even meningitis.
What types of acne are there?
Skin rashes are not the same in structure and type. You can live peacefully with some types of rashes; they do not cause any particular trouble, only some aesthetic discomfort. But there are acne that not only spoils beauty, but also brings a lot of negative sensations that are not related to aesthetics - pain, itching, residual scars after healing. What do different types of acne look like, which ones are dangerous, and when should you consult a doctor for help? In medicine, there is a classification of skin rashes by type - closed and open. Closed ones are located under the skin, and open ones are visible on the surface of the skin.
- Blackheads, or acne, are small bumps on the surface of the skin. They are both closed and open. Closed type, subcutaneous formation. In the middle layer of the skin, fat accumulates in the hair canal (pore). These pimples look like white or yellowish dots with a small diameter of 0.5-1 mm. Open types of acne include black formations on the surface of the skin. A mixture of fat and dead skin accumulates in the pore, forming a plug. When exposed to air, this mixture oxidizes and turns black. Such pimples come in different sizes, from 0.5 mm to 0.5 cm.
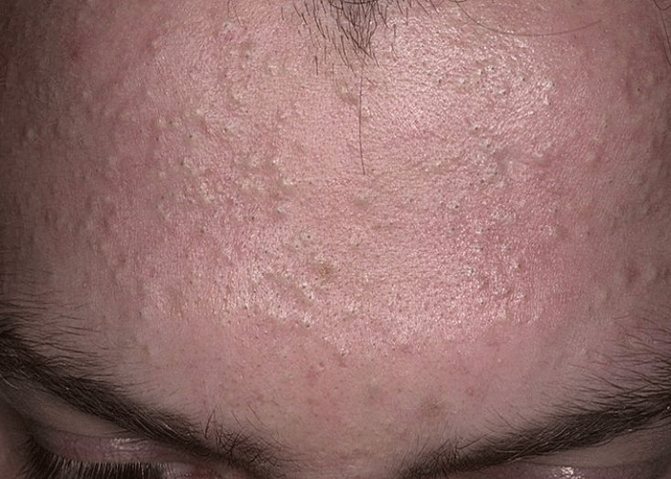
- Acne is pimples of any type with the onset of an inflammatory process. In most cases, swelling and redness appear on the skin, and the small bump increases in size. After 1 - 2 days, a whitish top appears, and purulent formations accumulate inside. The top layer of skin breaks through, necrotic fluid comes to the surface and the healing process begins. Typically, such inflamed formations do not leave scars and cause mild pain only when pressed.
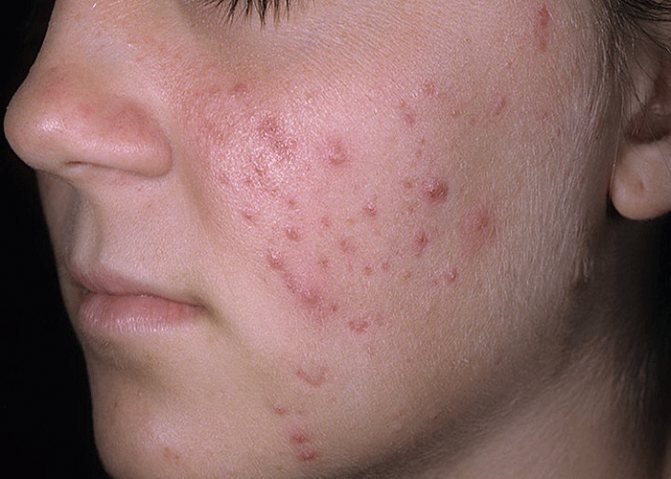
Further, the classification becomes wider, in turn, acne, pimples with an inflammatory process are divided into subtypes:
- Papules are a type of acne, these red inflamed bumps up to a centimeter in size, their appearance resembles reddish or purple dense formations. After healing, they may leave spots on the skin, but do not leave scars;
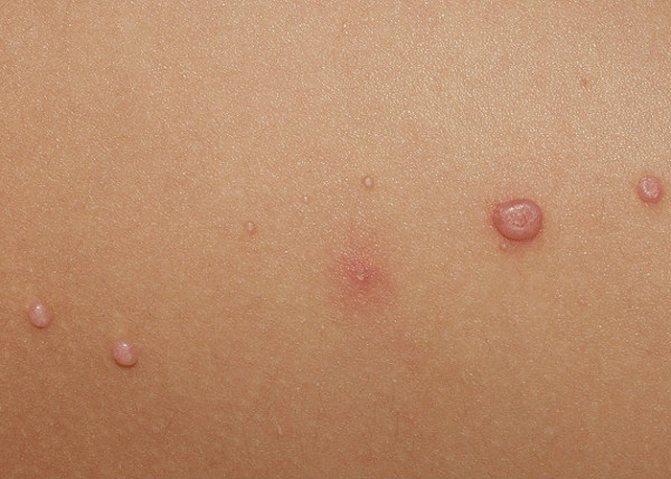
- Pustules – formed from papules or independently. Pus accumulates inside the inflamed area of skin; it can be flat, cone-shaped, or sphere-like in appearance.
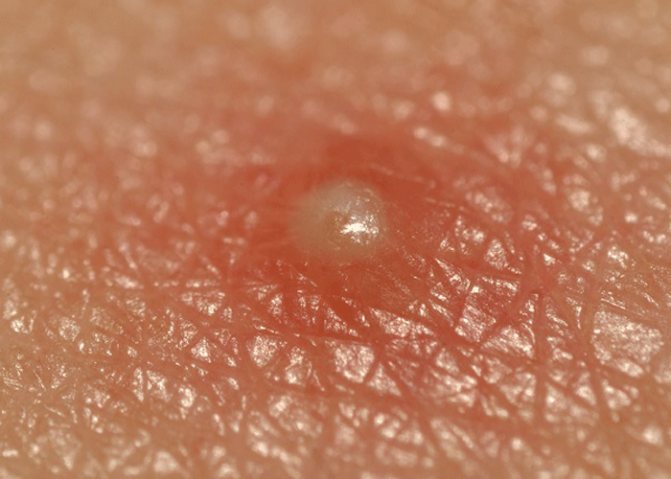
- Nodules are large painful inflammations that may acquire a bluish tint.
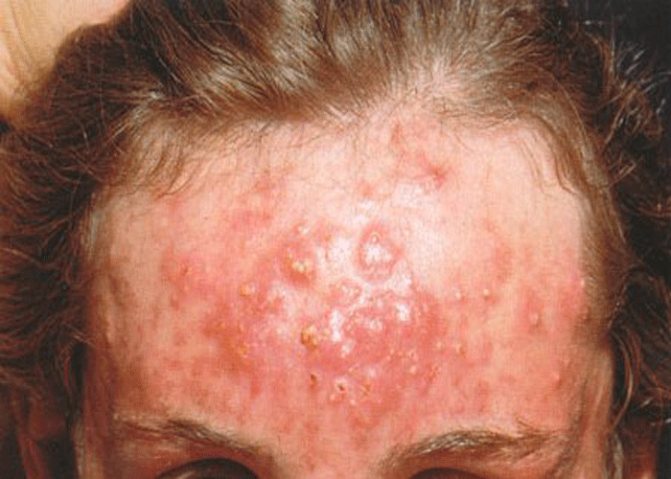
- Boils are inflammation of the follicles with suppuration, the size can be large up to 5 cm. They are very painful, their appearance affects the entire body as a whole. There are single and multiple. In the second case, they have the ability to merge under the skin, the affected area increases in size.
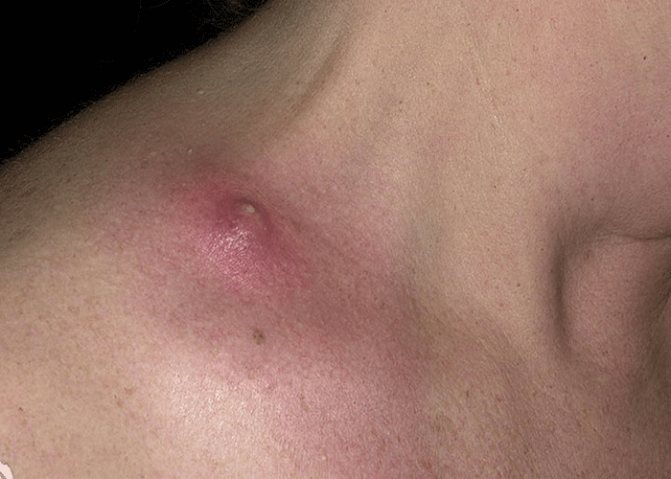
Doctors do not recommend squeezing out any of the existing types of blackheads and acne. If you independently squeeze out black or whiteheads, inflammation can begin, and if you press on the acne and it breaks through, bacteria can get under the skin, causing blood poisoning.
Acne formation and symptoms
A subcutaneous pimple can develop on the skin of the face, regardless of a person’s age. At the very beginning, a small compaction begins to appear under the skin. As the milium matures, a white or yellow tubercle appears above the surface of the skin; if small blood vessels are affected, the color will be pink or even burgundy-red. On palpation, a sharp but short-lived pain occurs. Inflammatory lesions are most often localized on the face, involving the tissues of the chin, nose, forehead, and cheeks.
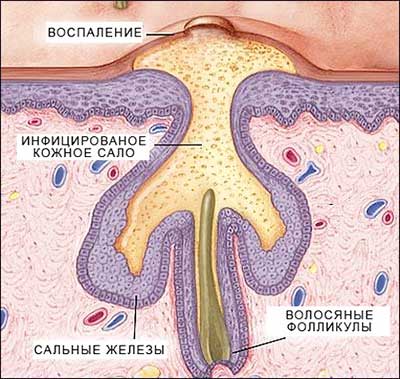
Inside the pimple there is a pustule, a cavity filled with keratin mass and pus. Inflammatory elements can remain in this form for a very long time, without ripening or bursting. At first they reach only a couple of millimeters in size, but then they become larger, and the pustule begins to accumulate pus. The lump is getting larger, but it is difficult to remove the pimple because its base is deep under the skin.
Classification of acne according to the works of G. Plewig and A. Kligman
Gerd Plevin, a German dermatologist, together with the American scientist Albert Montgomery Kligman, proposed a clinical classification of acne, dividing the disease by cause and age characteristics. In their joint study, there are six types of acne on the face and body:
- Pediatric acne is divided into a disease of newborns and childhood acne. Cases have been recorded where a child is already born with closed-type acne on the face. There are many white dots on the cheeks, nose or forehead. This rash is due to hormonal reasons; such wen goes away on its own. If acne appears in children aged 3 months and older, it requires special attention. Parents urgently need to show their child to a doctor, as acne can signal congenital pathologies.
- Acne in youth is a common phenomenon. Their appearance is associated with natural hormonal changes in the body. Normally, the rash disappears by the age of 18-20.
- Adult acne - it includes several subcategories of acne; according to statistics, 3 to 5% of women and men suffer from this disease:
- Late acne usually affects women of childbearing age. Their appearance is associated with hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle. Other causes may be gynecological diseases;
- Accumulated acne of a spherical shape - appears in adolescence and does not go away after the restructuring of the body. Doctors classify this type of acne as a severe form.
- Inverse acne is usually a chronic form of the disease, limited to several areas - the groin, armpits, lower abdomen. Appears due to improper functioning of the sweat glands. These are multiple purulent rashes of greenish-pink or dirty yellow color.
- Steroid acne or bodybuilder acne - associated with the use of drugs of a certain group. A side effect is increased work of the secretory function of the sebaceous glands, which leads to the appearance of nodular cystic acne.
- Contact acne - associated with the external environment, can be a reaction to microcracks and damage to the skin, cosmetics, friction or contact of the skin with synthetic materials.
- Aneiform rash is a consequence of various types of skin diseases - dermatitis, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, subcutaneous molluscum and others. In this type of disease there are no comedones, that is, plugs in the follicle.
- Occupational acne – caused by frequent contact with oils, dust or chemicals.
As can be seen from this classification, the risk group includes children with pathological disorders, adolescents, regardless of gender, young and middle-aged women with a hereditary predisposition or gynecological diseases. People with difficult working conditions.
The video shows part of the program in which doctors explain what types of acne there are and the reasons for their appearance.
If acne appears in any form, it is necessary to consult with a specialized specialist; skin rashes may appear due to diseases of internal organs or improper functioning of systems in the body.
Who gets acne more often - women or men?
Acne is widespread in adults, but women tend to get it more often than men . Figures vary, but a large 2008 study found that across all age groups, women were significantly more likely to have acne than men; for example, at age 20, 51% of women compared to 42.5% of men reported having acne, with rates declining for older age groups. In another study, 41% of women aged 25 to 40 had acne, and many participants had never had acne in their teens. Acne can persist after menopause.
Scientists have long concluded that black and Hispanic women are more likely to suffer from acne than Indian, Asian and white women. But it all comes down to the same process happening under your skin.
Although acne is a cosmetic problem, its consequences can go much deeper. Besides the inconvenience of unwanted blemishes and the scarring they can cause, adult acne can have a serious psychological impact. Research shows that adult women with acne experienced symptoms of anxiety and depression, anger, problems with self-esteem, and trouble concentrating at work or school.
Forms and degrees of acne
The American Academy of Dermatologists has proposed a classification of acne severity for general use. If there is one pimple with a black head, then it cannot be classified as a painful rash on the skin, but the frequent appearance of rashes and inflammations and their number and types fall under the following forms of the disease:
- Any types of rashes (open or closed) located close to each other in the amount of no more than 10 pieces, and not exceeding 1 mm in diameter of one pimple - mild or 1st degree;
- On a small area of skin there are up to 25 pimples without an inflammatory process, no more than 10% of them can be inflamed and have heads with a purulent accumulation - medium or 2nd degree;
- There are about 50 pimples nearby, the ratio of inflamed to non-inflamed is 50/50. Among them there are large formations of 5 mm or more. There are already scars from previous rashes - 3rd degree;
- More than 50 pimples at different stages of the disease, a large area of skin is inflamed and painful. From ruptured pimples, residual abscesses and scars are the 4th, severe degree of acne.
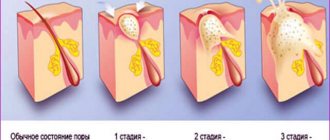
As can be seen from this classification, dermatologists take into account not only the number of rashes, but also the stages of development of the pimple, and there are only three of them. The first includes the appearance of the first signs of inflammation near the plug in the pore. The blocked canal turns red, thickens, nearby tissues swell, itching or minor pain appears.
At the second stage, an exacerbation occurs, purulent-necrotic fluid accumulates under the skin, a white head appears on the pimple, and the pain intensifies. With boils, this stage is accompanied by general malaise, fever, and weakness. The completion of the second stage is the breakthrough of the upper layer of skin and the release of fluid.
The third stage is regeneration. If the formation was small, then healing occurs within 1-2 days, without any consequences. In the same case, if the inflammatory process went deep and affected a large area under the skin, then healing takes longer and scars may remain.
The main difference between acne and pimples is the presence of an inflammatory process.
Methods for preventing and treating acne
Depending on the degree, type and stage of the disease, dermatologists recommend various preventive procedures to prevent acne and remedies for acne on the face. First of all, it is following the rules of personal hygiene; neglecting the rules leads to skin contamination, and too zealous use of soap causes dryness. Both contribute to the appearance of acne.
The second recommendation concerns lifestyle and proper nutrition. Bad habits and an unbalanced diet lead to a general weakening of the immune system, and the functioning of the secretion organs is disrupted. At the first signs of acne, you need to exclude sweet, fatty and any other “heavy foods” (smoked, fried, fast food).
The appearance of acne can be associated with allergies to various cosmetics or fabric compositions, so you should pay attention to new lotions and creams, as well as bedding. In addition, the cause may be contamination of the skin pores, and you can read about how to effectively deal with this here.
In the video, a specialist dermatologist reveals the secrets of the profession. How experts can get rid of a mild rash in 3 days.
If the appearance of acne is frequent, then you need to consult a dermatologist. He will conduct appropriate tests and may refer you to other specialists for additional research. Acne can be caused by reasons hidden in the body - diseases of the stomach and liver, hormonal disorders, both natural and caused by an imbalance of hormones, malfunctions of the immune system. In this case, it is necessary to treat not only the manifestations on the skin, but also the factors causing them. You can completely get rid of the disease with correct diagnosis and an integrated approach to treatment.
Only a doctor, based on professional experience and laboratory results, is able to make an accurate diagnosis. The symptoms of the disease may be the same, but the causes that cause it are completely different. Do not use medications prescribed for another person, as this can lead to serious complications.
Treatment of acne with blood
Acne of this kind cannot be treated on your own; you need to consult a specialist.
The following methods are used in treatment:
- ozone therapy;
- ultrasonic cleaning;
- peeling (chemical or laser).
In cases where it is not possible to see a doctor, it is recommended to use ointments: zinc, heparin, ichthyol, as well as Klindevit, Zinerit, etc. Before applying them, problem areas on the skin should be wiped with hydrogen peroxide.