Causes of skin pathology
Rosacea is a chronic disease, which among professionals is called rosacea. Red spots appear on the face, capillaries are visible, then lumps and rashes. The formation of rosacea can be confused with regular acne. In fact, these are two completely different problems.
This complication is usually encountered by residents of northern countries who have white skin and blond or red hair. People with sensitive skin are also at risk of the disease. According to statistics, a tenth of the population suffers from this disease. The main contingent is women who have crossed the 30-year mark. The disease also affects men and sometimes occurs in newborns.
Rosacea is determined by the dilation of blood vessels that are located on the nose, chin, cheeks, then inflamed nodules and cysts form. Most often this happens in cases:
- consumption of drinks containing alcohol (cognac, whiskey), smoking;
- temperature changes (usually when they come from a cold street to a warm house);
- visits to the sauna, bathhouse, solarium;
- emotional outburst in mood;
- facial cleansing with scrubs, cosmetics with acids;
- eating food with a lot of spices;
- allergic manifestations.
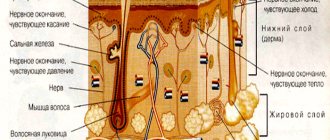
During the course of the disease, the condition of the skin changes and sebum secretion increases. Demodex mites may appear, which complicates the pathological process. Although previously it was precisely this that scientists considered to be the cause of rosacea.
Against the background of the following internal diseases of the body, a pink rash may also occur:
- ailments of the stomach and intestines;
- weakened immunity;
- imbalance of the endocrine system;
- medications;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Difference between pimples and acne
Pimples are considered a mild form of acne. The main difference between these two concepts is that acne in medicine is considered a cosmetic problem, and acne is a serious skin pathology.
On this topic
- Pimples
What causes white pimples to appear on the face?
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2020
Externally, the problems have some similarities and differences. Pimples can appear on the skin in both single and multiple quantities, and with acne, entire islands of purulent rashes appear in the face and body. In the first case, no traces remain on the skin after the wound heals, in the latter, a post-acne scar forms.
Acne most often occurs due to disruptions in the digestive system or metabolic disorders of the skin. Acne is considered a multifactorial pathology.
Clinical signs and stages of pathology
Rosacea, or rosacea, develops gradually, moving from a mild condition to a more severe one. There are several stages:
- Prodromal stage. The disease begins with transient redness of the face and dilation of blood vessels in the form of hot flashes. This happens due to a sharp change in temperature, drinking alcohol in small quantities, as well as dishes with spices. In this case, the affected skin has clear boundaries, the spots look like flames. Such manifestations last a short time.
- First stage. If you do not pay attention to the occasional redness of the facial skin, then at the next stage they become permanent. Spider veins are visible - the so-called rosacea. Skin changes cover the nose, cheeks, chin, and less often spread to the neck, chest, and back. Increases fat secretion. The patient begins to independently fight its excess, using care products with aggressive components. As a result, the water balance is disrupted, the surface of the face begins to peel off, and sebum is released with even greater intensity.
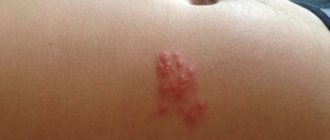
- Second stage. Against the background of a reddened face, tubercles and lumps form, which then turn into blackheads and pimples with purulent contents. The face looks aesthetically unattractive. The rash brings suffering to the patient due to pain.
- Third stage.
This is the most difficult period, which rarely occurs. It is mainly the male population that suffers from the disease. Against the background of these symptoms, skin changes occur. It swells and becomes inflamed, and on the nose and ears it grows and thickens. Redness takes on shades of blue. The only way to get rid of the pathology is through surgery. The disease progresses in waves: exacerbations are replaced by remissions. The weakening of the inflammatory process at each subsequent stage becomes shorter and shorter. In the second and third stages, remissions are no longer observed.
Clinical picture of the disease
The initial stage of rosacea is otherwise called rosacea diathesis or episodic erythema. Redness in the cheeks, middle part of the forehead, on the nose, and sometimes on the chest in the décolleté area occurs periodically. Red spots appear and disappear without causing any particular problems for a person. Therefore, sick people do not pay attention and most often skip this period of illness. The following factors can trigger the first attack of redness:
- hot drinks (tea, coffee);
- hot spicy food;
- exposure to strong winds;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body;
- alcohol consumption;
- stressful situation;
- taking medications;
- cosmetics applied to the face;
- the onset of menopause;
- physical stress.
Attacks of facial redness in the sick person gradually occur more often. Then persistent patches of bright red color appear on the forehead, cheeks and nose, which eventually become bluish. This affects the superficial veins, which appear through the skin in the form of spider veins. In addition to the listed symptoms, facial swelling, burning sensation and peeling of the skin also appear.
Stage of papulopustular manifestations of rosacea
With the papulopustular form of rosacea, pimples and pustules begin to appear against the background of facial redness. Rosacea acne lasts for several weeks and occurs in clusters. After they disappear, scars, as a rule, do not remain, or they are barely noticeable. Swelling of the facial skin is located mainly in the forehead and in the area between the eyebrows.
At this stage, the skin's sensitivity to sunlight increases. After prolonged exposure to the sun, bumps appear on the skin (solar comedones). The burning and tingling sensation of the skin subsides at this stage. Gradually, pustular rashes affect the entire skin of the face, scalp, chest area and, in rare cases, the back. The rash on the head is accompanied by severe itching.
Phymatoid stage
Phymatoid stage of rosacea
As the disease progresses, at this stage some patients begin to thicken certain areas of the skin, causing it to appear bumpy, resembling an orange peel. Often there is thickening of certain parts of the face - the ears, nose, forehead. The most common complication, which occurs mainly in men, is thickening of the nose.
In Greek, such a thickening is called phyma, which means a bump - accordingly, the nose is called pineal. The pineal nose (or rhinophyma) is enlarged in size, has a bluish coloration with many blood vessels. Gradually, deep grooves appear that divide the nose into separate tuberous lobules.
Less commonly, similar changes appear on other areas of the skin: thickening of the eyelids, skin of the chin, pillow-shaped thickening of the skin of the forehead, cauliflower-like growth of the earlobe. These symptoms of rosacea on the face practically do not occur in women, which is due to the possible influence of female sex hormones.
Eye damage due to rosacea
Eyes with rosacea are affected quite often, and in 20% of patients, eye diseases occur even before damage to the skin. The most common eye disease that develops is blepharitis. It is characterized by redness and peeling of the skin of the eyelids, and the appearance of crusts in the corners of the eyes. Conjunctivitis may also develop:
- Conglobate rosacea. This form is characterized by the appearance of huge spherical growths - conglobates - on the reddened skin. This situation often occurs when taking medications that contain iodine or bromine.
- Steroid rosacea. It develops in people who use local hormonal ointments (especially with fluoride) for a long time for a particular skin disease. The steroid form of rosacea is very difficult to treat.
- Lightning form. Develops mainly in young women. Among the factors that can cause this form of rosacea are neuropsychiatric disorders, pregnancy, and hormonal changes in the body during menopause. The fulminant form is the most complex variant of conglobate rosacea. The disease develops suddenly and progresses rapidly, leading to facial disfigurement. Against the background of such an appearance, young women often develop depressive states and neuroses. Treatment of rosacea on the face in this form has a very low effect.
- Rosacea-lymphoedema (edematous form). A rather rare variant of the skin disease rosacea, manifested by severe swelling of the face, which is located on the cheeks, chin, forehead, nose and eyes. The swelling has a purplish color, and when pressed, there is no hole left on it, because the face swells not due to fluid, but due to the proliferation of the subcutaneous layer. The general condition of this form suffers little, but facial disfigurement is severe.
Diagnostics
When examining a patient, a dermatologist accurately determines the disease and its stage. To prescribe the correct treatment for late rosacea, additional tests are performed:
- scraping and bacteriological examination of the purulent contents of the pustules to exclude staphylococcal infection;
- demodex tests;
- general blood analysis.
The absence of comedones and blackheads allows the doctor to exclude diseases such as acne or acne. The presence of the previously mentioned subcutaneous mite requires adjustment to take into account the complication.
Symptoms
The disease can be recognized by several signs:
- Redness of the skin, most often in the central area of the face. It is not uncommon for the rash to spread to the chest and back.
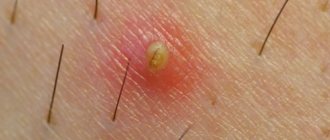
- Presence of a rash: small pink bumps eventually turn into ulcers and pimples.
- Thickening of the affected skin.
- The presence of a constant feeling of skin tightness and burning.
- Redness and tearing of the eyes, as well as a feeling of dryness and cutting pain.
You should seek help from a dermatologist if your facial skin becomes red when drinking hot drinks, drinking alcohol, or eating spicy food. The progression of a serious disease can also be recognized by the unusual reaction of the skin to soaps and cosmetics.
In addition to a visual examination, a dermatologist, if necessary (if the development of a staphylococcal infection is suspected), may prescribe a number of additional studies: culture, as well as examination of pustules. You may also need to take blood for general and biochemical analysis, histology tests, lipid profile, and coagulation tests to determine what caused the appearance of rosacea on the face.
A photo of the advanced stage is presented below.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of rosacea on the face is complex. Home methods are supported with medication. At the onset of the disease, medication intake is minimal. As you progress, the appointments increase.
Traditional methods
At the first stage, the disease proceeds so unnoticed that patients do not attach importance to short-term redness of the skin. Although treatment during this period is most favorable, symptoms disappear quickly. It is enough to change your lifestyle, adjust your diet and choose the right facial care products, namely:
- exclude visiting the bathhouse, solarium, sauna;
- limit direct sunlight on exposed skin;
- remove foods with a lot of spices from your diet;
- do not consume hot foods and drinks;
- do not use abrasive facial care products;
- wash with water at room temperature;
- exclude visiting the gym, running, and skiing.
At this stage of treatment, the doctor recommends applying tea, chamomile, and calendula lotions to the skin. They have a calming effect and reduce sebum secretion. Prescribed drugs that contain vitamins that strengthen the walls of blood vessels and capillaries: A, B, C, PP, or nicotinic acid. These substances also tidy up the nervous system.
As the disease progresses, it becomes more difficult to treat rosacea due to the persistent inflammatory process. Removing it is the main task of a dermatologist. Antibacterial gels are prescribed: Metronidazole, Metrogyl, as well as compositions with an antibiotic. They relieve inflammation and cool painful skin. An ointment based on corticosteroids, for example, Sinaflan, works similarly. It is prescribed for a short period of time if the patient has not previously taken medications of this type.
Modern technologies
When the inflammatory process is stopped, treatment of vascular changes begins. In this case, cold therapy, such as cryomassage, is useful.
Capillaries and small vessels are exposed to electricity, using electrocoagulation, and photo and laser treatment is used. During these procedures, excess vessels are blocked by cauterization and gradually dissolved. The impact of the laser pulse is short-term and targeted, so nearby tissues are not injured. After the procedure, burns, redness, and swelling are not visible on the skin. After the first session, a positive result is visible, but in advanced cases, several procedures are required.
Contraindications to laser therapy:
- tendency to form keloid scars;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- pregnancy.
Rosacea cannot be completely cured. If the patient consults a dermatologist on time, completes a therapeutic course, and subsequently follows the doctor’s recommendations, then a relapse of the disease will not occur. In advanced cases, the patient has scars and cicatrices on his face.
Folk recipes
You can treat rosacea using advice from traditional medicine. By themselves, they are effective in the initial period of the disease, when anti-inflammatory and soothing lotions and washes based on medicinal herbs can be used.
When the disease develops, traditional medicine is used as a concomitant treatment, along with pharmaceutical compounds. At home, both lotions and means for oral administration are prepared.
Traditional medicine suggests treating rosacea with the following recipes:
- According to patient reviews, cranberry juice has proven itself well. A piece of gauze is soaked in liquid and covered the face for 40 minutes once a day. Repeat until redness disappears.
- Cabbage juice, which is diluted with water, is moistened with cotton swabs and applied to painful areas for 15 minutes every day for a month.
- A spoonful of rosehip is poured into a glass of boiling water. After cooling, soak a piece of gauze in the solution and apply it to your face for 20 minutes. This procedure is repeated several times a day.
- Fresh cucumber is grated and aloe juice is added. The paste is applied to the entire face and left for half an hour. Wash off with water at room temperature. The mask is repeated 2-3 times a week for a month.
- A decoction is prepared from nettles for oral administration. Take 2 tbsp. l. leaves pour 2 cups of boiling water, leave for 2 hours. Take 100 ml before meals 3 times a day.
- Apply low concentration alcohol tincture of propolis to the affected areas at night for a month.
- Drink green tea at least three times a day.
Using cosmetics for rosacea
How to treat rosacea has already been discussed. But proper hygiene and cosmetic care is no less important. In winter and autumn, you need to protect your facial skin from strong wind, cold, snow and rain. In summer and spring, it is recommended to protect your skin from direct sunlight: wear a wide-brimmed hat, dark glasses, or use a sun umbrella. It is also necessary to apply sunscreen with SPF 15 or higher to your face before going outside. Visiting the sauna and solarium is prohibited.
Rosacea disease requires the use of only mild cosmetics. It’s good if they contain extracts of grapefruit, blueberries, chamomile, and cucumber. All cosmetics for rosacea (lotions, tonics, creams) should not contain alcohol, and it is better to choose from those products that are marked “hypoallergenic” or “anti-rosacea”.
For rosacea in men, it is recommended to use an electric razor. Blades can only be used if they are very sharp. The application and removal of cosmetics must be extremely gentle: do not rub creams too hard or rub your face with a towel after washing.
Prevention of rosacea
For those who have achieved lasting remission and those at risk, it is recommended to follow the following simple rules:
- do not overcool or overheat;
- avoid tanning both under the sun and in a solarium;
- be responsible when choosing the amount of physical activity;
- adhere to proper nutrition, remove fatty, fried, spicy foods from the diet, add vegetable and dairy products;
- Avoid drinking coffee, chocolate, and alcohol;
- A face care cream should have a high degree of protection from sun rays.
These tips will help you avoid the onset of this dangerous disease. In order for your skin to always be healthy and beautiful, you need to react to the occurrence of symptoms and start treatment on time. Otherwise the struggle will be difficult and long.
Treatment
General therapeutic measures
A prerequisite for getting rid of rosacea will be the maximum removal of all provoking factors (following a diet, avoiding alcoholic beverages and strong coffee, protection from the sun, wind and cold, changing hazardous work).
It is necessary to treat common diseases: correction of gastrointestinal disorders, restoration of hormonal balance, effects on the vascular and nervous systems. This will require consultation with relevant specialists (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, vascular surgeon). Restoring the psychological state and preventing stressful situations is of great importance.
Local treatment
You should cleanse your face of rosacea together with a dermatologist. The following medications should be used:
- herbal lotions with an astringent and antiseptic effect;
- metronidazole in gel form;
- antibacterial cream;
- cryomassage.
Types of pimples
There are two main types of acne: vulgaris and rosacea. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Common acne, which appears during puberty in almost every teenager, especially males, damages different layers of the skin.
Most often, dermatologists encounter superficial types of acne. These include the following formations:
- comedones - when the hair follicles become inflamed, cysts are formed from keratinized masses; a distinction is made between black (open) and white (closed);
- papules;
- pustules.
Deep acne is an inflamed cyst or abscess filled with purulent contents. The compacted type of acne is accompanied by deep infiltration of the subcutaneous tissue, large pustules, followed by extensive scarring of the skin.
Acne rosacea, according to its pathomorphological characteristics, has much in common with the teenage version, but comedones are not typical for it.