Fungal skin disease or athlete's foot is a known problem that people have faced for many years. Among all known infectious diseases, skin fungus occupies a well-deserved first place. This spread is associated with a decrease in human immunity and insufficient awareness of the methods of spreading and preventing the disease. In this regard, people go to the doctor’s office only in cases where the disease has progressed to an advanced form.
Fungal skin diseases - symptoms and treatment
Disease groups
It is quite difficult to distribute fungal diseases into groups, taking into account the localization and etiology of the pathological process. But if we consider a more simplified type of division, then there are the following groups of mycoses:
- keratomycosis . Accompanied by fungal infection of the upper layers of the skin. These include pityriasis versicolor and trichosporia;
- dermatophytosis . Leads to the development of an inflammatory process that affects the tissue on a larger scale. We are talking about favus, epidermophytosis, microsporia, and also trichophytosis;
- candidiasis. The peculiarity of this group of diseases is that it affects not only the patient’s skin, but also internal organs and even nails;
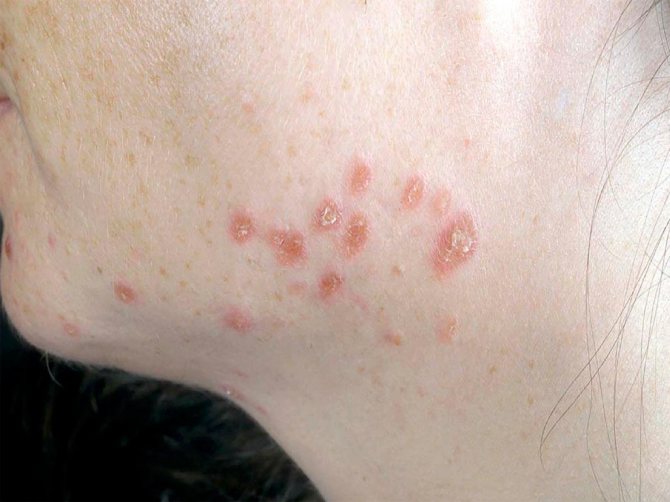
Cutaneous candidiasis
- deep mycoses . Another group of mycoses, accompanied by the development of an inflammatory process in the internal organs of the patient and damage to the skin. It includes diseases such as sporotrichosis, histoplasmosis, blastomycosis, and so on;
- pseudomycoses . Unlike previous groups, pseudomycosis does not belong to fungal pathologies, although their symptoms are very similar. First of all, these are actinomycosis and erythrasma.
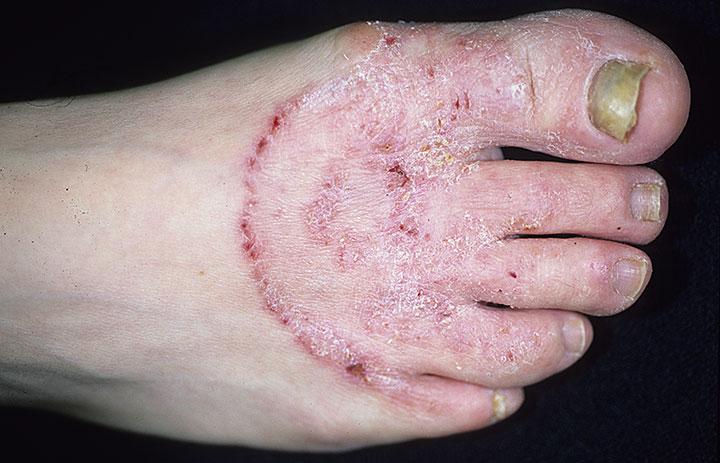
Athlete's foot is the most common fungal disease that affects the soles and toenails.
Important! Only a qualified dermatologist will be able to make a diagnosis based on the results of a laboratory study of the affected part of the patient’s skin and prescribe the appropriate treatment package.
Treatment
Fungal infections require contacting a dermatologist to determine the type of pathogen. Only in this case the correct treatment is prescribed. The healing process must be comprehensive. Doctors recommend:
- systemic antifungal drugs;
- local remedies in the form of ointments, creams, solutions;
- vitamin complexes with microelements;
- correction of immune disorders;
- treatment of infections, allergies;
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- low carbohydrate diet;
- eliminating stress;
- disinfection of clothes, shoes;
- normalization of intestinal function.

Systemic drugs
Severe disease requires the use of medications for internal use. The drugs help cope with the symptoms of a fungal infection and eliminate the pathogen. Dermatologists prescribe:
- Itraconazole is active against most types of fungi and is effective in advanced cases. It is necessary to take into account contraindications and side effects.
- Natamycin is an antifungal antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action. Destroys microorganisms at the cellular level, has limitations for use.
- Immunal is a plant-based product that improves immunity.

Local preparations
If a fungal infection is detected early, treatment with local remedies is effective. In advanced forms, this is part of the general scheme of combating mycoses. The external lesions are treated with medications. Popular drugs:
- Nizoral - the active substance is clotrimazole. Used as a shampoo to treat scalp and hair. In case of onychomycosis, it destroys the fungus on the legs; it is allowed during pregnancy.
- Terbinafine cream – counteracts most types of microorganisms, has contraindications. The active substance - terbinafine - destroys fungi, penetrating deep into the skin.

Treatment with folk remedies
The use of recipes with medicinal herbs and plants should be agreed with a doctor and become part of the overall treatment regimen. Independent use of folk remedies can complicate the situation and increase inflammation. To combat fungus use:
- chamomile decoction for baths for candidiasis, mycosis of the legs;
- a mixture of salt and water for applying to a sore spot;
- soda solution for washing the genitals for candidiasis;
- a decoction of celandine to lubricate lesions on the body;
- treating the skin with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, iodine;
- applying tea tree oil to sore nails.

Causes
All fungal diseases are highly contagious, that is, highly contagious. The only exceptions are candidiasis and pityriasis versicolor, which develop against the background of a weakened immune system or as a result of a violation of the microflora of the patient’s skin.
Fungal diseases are contact diseases; it is very easy to get the pathogen through wearing someone else’s shoes or walking barefoot in public places with high humidity.
Other types of mycoses are transmitted through contact with an infected person, animal or plant. Also, the fungus can be transmitted through household contact, so if one of your family members suffers from mycosis, then it is undesirable to touch his personal belongings. Even contact with clothing or shoes will lead to infection. Swimming pools, baths, saunas and public toilets are an ideal habitat for deep mycoses; even dust can contain spores of this disease.
In the presence of mechanical damage to the skin, the chance of infection increases significantly, since the infection can enter the body through cracks, scratches or abrasions in the skin. When wearing tight and uncomfortable shoes, fungus also often occurs. Risk factors include foot grass, the development of an allergic form of dermatitis, flat feet and the anatomical features of the patient’s feet.
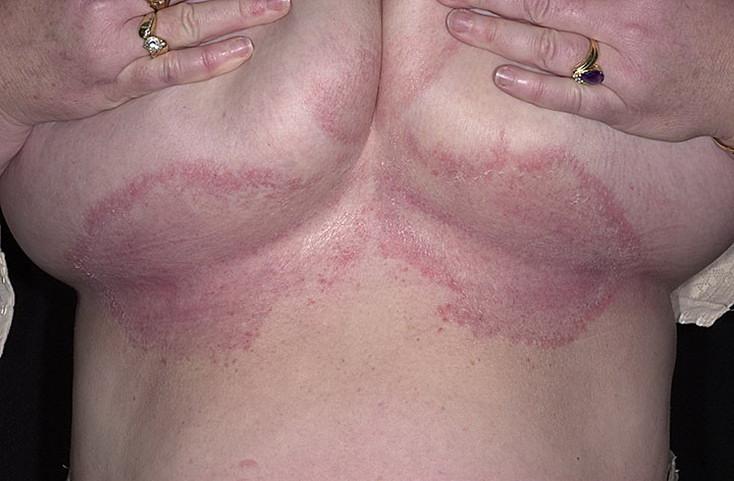
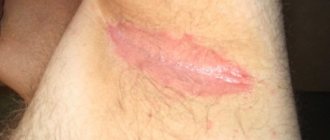
Fungus under the breast
Traditional medicine in the treatment of fungus on the body
Along with pharmaceutical drugs, you can use folk remedies at home, which will lead to a speedy recovery.
Traditional methods alleviate the symptomatic manifestations of mycosis, but they do not affect the original cause of the pathology.
If fungus appears on smooth skin surfaces, additional treatment can be carried out using the following methods:
- Garlic. Take one clove of garlic, crush it and mix in a 1:1 ratio with butter. The resulting mixture should be applied to the affected areas.
- Soda. Dilute half a glass of baking soda in warm water. Take a bath in this solution for fifteen minutes.
- Onion. Use fresh onion juice to wipe off pathological stains several times a day.
- Transverse mint. The leaves of the plant are crushed and ground with a small amount of table salt. The resulting pulp is spread on the affected areas of the body and covered with a bandage on top. After exactly one hour, the mixture is removed.
- Horsetail. Two tablespoons of herbs are brewed in 200 ml of boiling water. The resulting tea leaves are used to wipe the damaged areas several times a day.
- Lilac. Flowers are infused in alcohol for two weeks. After fifteen days, the tincture is filtered and used to treat the body.
- Propolis. If the patient is not allergic to honey products, then the foci of infection should be wiped with an alcohol solution based on propolis several times a day.
- Kalanchoe. The leaves are washed, cut and applied to the affected nail or body area.
- Coffee. A freshly brewed unsweetened drink can be used for compresses and baths. Any remaining unused drink must be thrown away after the procedure.
- Celandine. You need to squeeze the juice out of the plant and soak the lesions with it. This procedure should be carried out three times a day for three months. It is worth noting that celandine is considered a poisonous plant, so you should not abuse this herbal medicine. When carrying out procedures with celandine, you should never touch your eyes or allow even the slightest contact of this substance with human mucous tissues. After each herbal treatment session, you must thoroughly wash your hands with plenty of running water.
Characteristic symptoms
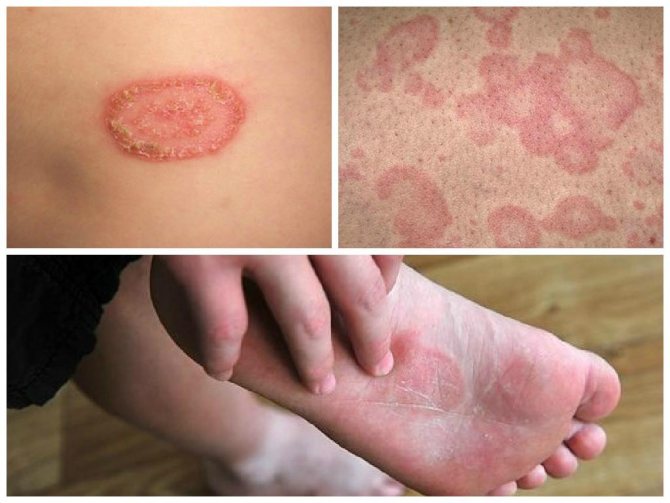
When a fungal infection enters the skin, characteristic symptoms may develop, which differ depending on the type of fungus. Let's look at the main ones. First of all, the affected areas of the patient’s skin begin to peel off and become inflamed. Peeling is replaced by small bubbles that burst over time. In their place, itchy and inflamed areas appear. The skin becomes more loose and can separate in large parts.
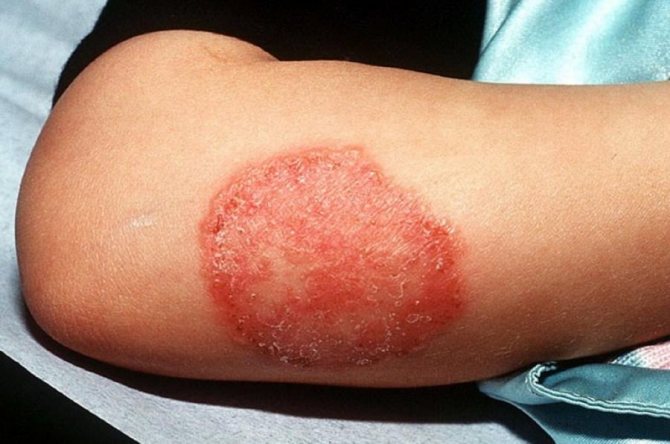
Fungus on the body
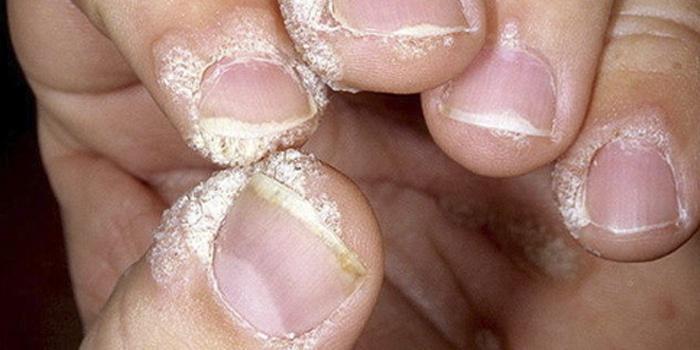
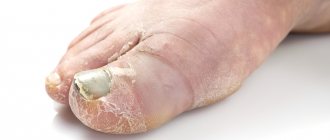
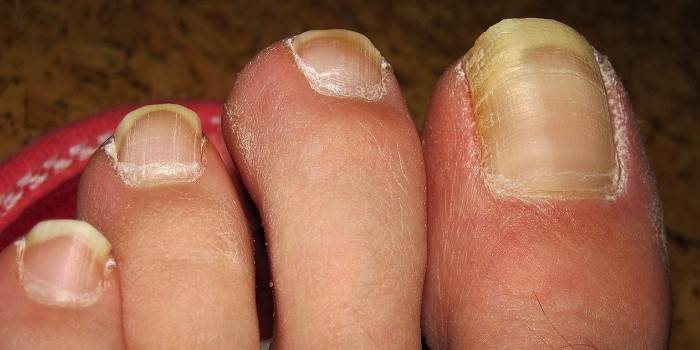
Fungi under fingernails
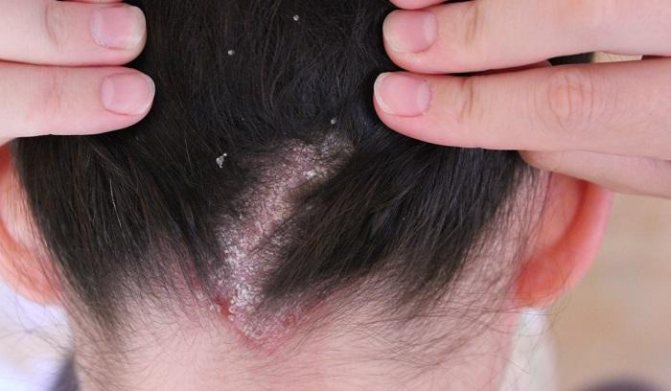
Scalp fungus
As the disease develops, all symptoms go away on their own, but the fungus will still live on the previously affected area of the skin. The disease enters the chronic stage. The stratum corneum of the skin becomes thick, becomes covered with yellow spots, and then the nails begin to crumble.
What does fungus look like on the skin?
Pathogenic microorganisms, even those belonging to the same genus, can cause different symptoms. The appearance of the affected areas depends on the stage of the disease, location, and pathogen. Observed in the following cases:
- onychomycosis - fungal infection of the nails - thickening of the plates, discoloration, appearance of stripes, spots;
- localization of infection on the head - dry hair, oiliness, dandruff, itching;
- candidiasis - curdled white discharge;
- infections of the sole - inflammation, itching, cracks, peeling.
- How to choose a voltage stabilizer for an apartment
- Apple puree: recipes
- Treatment of diabetes mellitus with folk remedies - diet. Diabetes mellitus - folk remedies for treatment
Microsporia
The spreaders of this type of mycosis are infected cats, so children who frequently come into contact with animals are at risk. The causative agent of microsporia is fungi of the genus Microsporum. Pathogenic microorganisms are resistant to environmental influences and can remain on skin scales and in hair for years. Characteristic signs of microsporia:
- single round-shaped lesions appear;
- along the periphery - a roller that rises above the surface, has crusts and bubbles;
- peeling develops;
- The scalp of the child is most often affected.
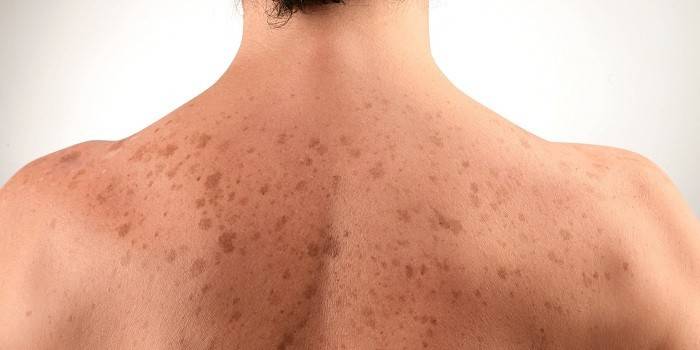
Pityriasis versicolor or versicolor versicolor
If you examine skin scrapings from this type of fungal infection under a microscope, you can observe clusters of microorganisms that look like thick, curved threads. The causative agents of infection - Malassezia furfur, Pityrpsporum orbiculare - spread in the stratum corneum of the epidermis in young and middle-aged people. Causes of fungal infection:
- weakened immunity;
- violation of the chemical composition of sweat in the presence of excessive sweating;
- neurovegetative pathologies;
- diseases of the endocrine system, gastrointestinal tract.
Pityriasis versicolor is called mycosis of the trunk and has the following features:
- skin fungus affects the chest, abdomen, neck;
- rarely observed on the head, limbs, groin area;
- there is a fungus on the back;
- pink spots appear, which lighten when exposed to the sun; in winter they can turn brown - the reason for the name pityriasis versicolor;
- peeling is observed;
- fusion and the formation of extensive foci of infection are possible.
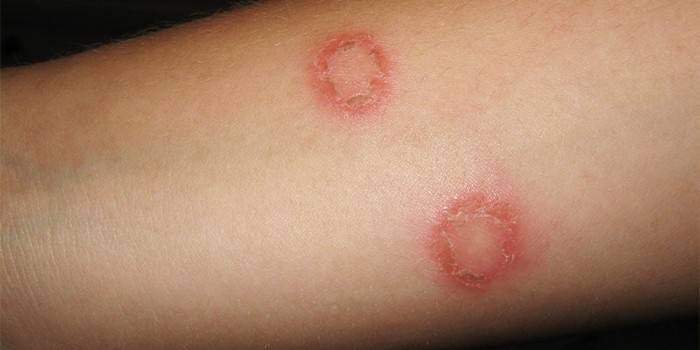
Ringworm
This skin lesion is considered very dangerous for children and adults. The causative agents of ringworm - fungi Trichophyton, Microsporum - spread inside cells. Sources of infection are sick people and animals. Localization of ringworm on the body:
- inguinal folds;
- feet, skin of legs;
- nails;
- interdigital spaces;
- skin folds;
- armpits;
- Hands;
- skin on the face;
- hairline;
- palms.
The fungal infection got its name due to the formation of round lesions on the head, when the fungus destroys the structure of the hair, it loses its elasticity and breaks off at the same height. Mycosis of the trunk with ringworm manifests itself:
- oval red spots with a raised ridge along the edge, which, as the disease progresses, becomes covered with small pimples;
- the emergence of new foci of the disease.
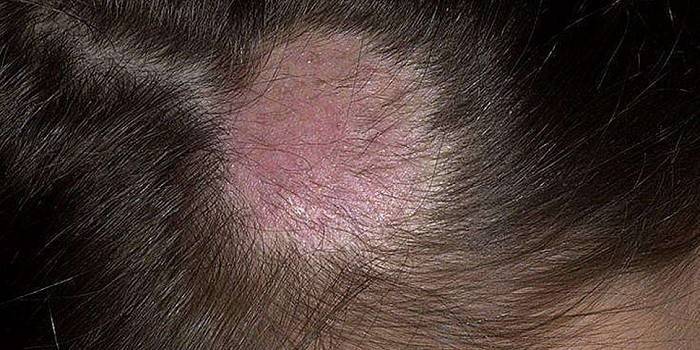
Candidiasis
The cause of fungal infection is yeast-like microorganisms of the genus Candida. Being human saprophytes, they participate in the work of the body, but with a sharp weakening of the immune system, they begin to rapidly multiply on the mucous membranes, causing unpleasant symptoms. Infection through sexual contact is possible. Candidiasis manifests itself:
- curdled vaginal discharge with a sour odor;
- redness of the head of the penis;
- the appearance of erosion;
- red blistering rashes on the skin accompanied by itching;
- burning;
- pain.
- Methods of home rehabilitation after ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke
- Diffuse changes in the pancreas
- What is trypophobia
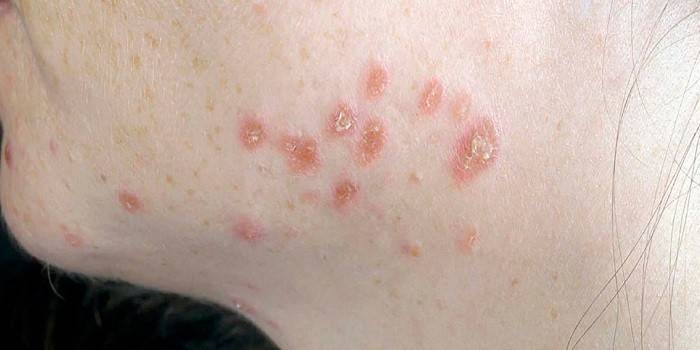
Trichophytosis
The causative agent of the infection is fungi of the genus Trichophyton, which parasitize the skin of people, rodents, and livestock. Trichophytosis is a highly contagious (infectious) disease. Exposed parts of the body are susceptible to fungal infection; in case of prolonged illness, the knees and buttocks are affected. Symptoms of the pathology are observed:
- rounded areas of bright red color with small nodules and peeling of the skin;
- the presence of an inflamed cushion along the edge;
- the appearance of infiltrates and suppuration is possible.
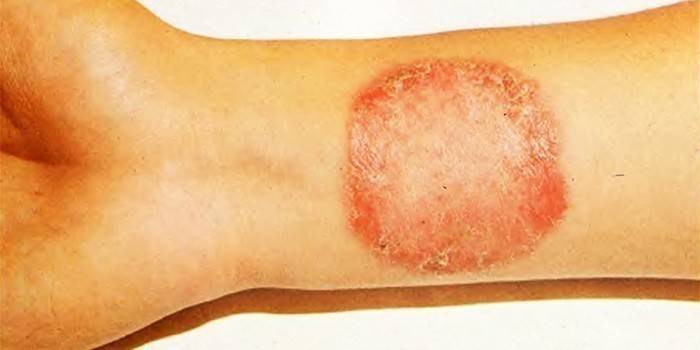
Diagnostic features
If suspicious symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for help. In this case, the examination is carried out by a dermatologist. Often, a simple visual examination is enough to determine the pathology, but the doctor can also take a medical history, culture, or fluorescent light.
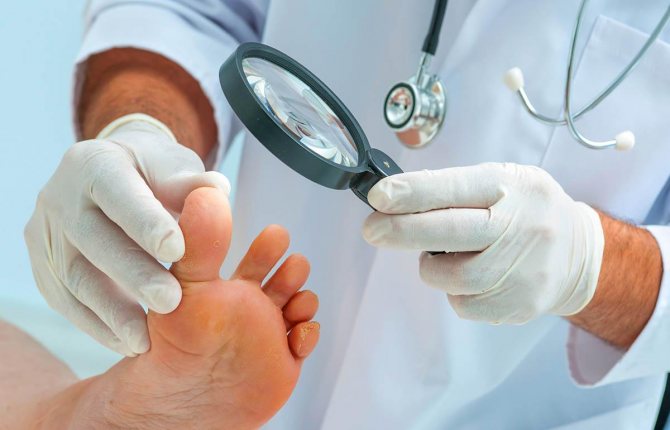
Diagnosis of mycosis
If the fungal infection is too deep, the patient is sent for X-ray diagnostics. To make a diagnosis, the doctor may take a piece of hair or nail from the patient, but most often a scraping of the skin at the site of the lesion is taken.

Laboratory analysis
Diagnostics
To check for the presence or absence of a fungal disease in the human body, you must contact a professional dermatologist. Only this specialist will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
It is worth remembering that such infections can “take over” many parts of the human body; they can be located on the surface of internal organs, as well as on the mucous membrane. In this case, the fungus manifests itself only after a strong “invasion”.
There is an opinion that skin fungi destroy and split nails, that is, according to many people, this problem only affects nails. However, no one thinks that the appearance of such a problem is associated with a weakening of the human immune system.
The fact is that the fungus is part of the human microflora, which is also inherent in our skin. And the negative impact of the fungus begins to manifest itself only under favorable conditions.
Have you noticed that some changes have appeared on the nail surface? Start worrying! Of course, you can get rid of the affected nail at any time, but there is no certainty that the infection has not spread to another nail or part of the body.
Correct diagnosis can only be made by a dermatologist who has studied the types of mycoses in textbooks and has also encountered them in his practice.
An experienced doctor can determine the type of fungus by the location of the affected area and its appearance. However, to confirm the diagnosis, a skin scraping, a fragment of hair, or a piece of nail must be taken for analysis.
Treatment options
The development of mycosis is accompanied by a violation of cellular immunity, so treatment of the pathology cannot be called easy. Most often, antifungal drugs are used for this. But for mycosis, many people use proven traditional medicine recipes as a complement to traditional therapy. Let's consider each of these treatment methods separately.
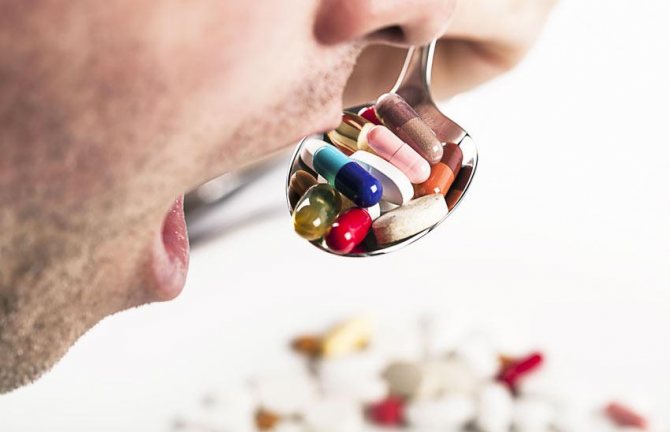

Treatment of mycosis
Pharmacy drugs
The use of antifungal drugs leads to the cessation of fungal growth as a result of a negative effect on their cell walls. But before starting treatment, the affected areas of the skin must be examined by a doctor . Often people, resorting to self-medication, mistakenly mistake some other, more serious pathology for a fungal disease. Because of this, treatment is incorrect, and a real illness can result in serious complications for the patient. Below are the most common antimycotic drugs prescribed by doctors.
Table. Effective drugs for treating fungus.
| Name of the drug, photo | Description |
| Lamisil | The product, which has antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties, is available in the form of an ointment. The active ingredient is Terbinafine. To treat fungal diseases, it is necessary to treat the affected areas of the skin once a day for 3-4 weeks. Positive changes will be noticeable after just a few days of treatment. |
| Orungal | An excellent oral antifungal drug. Available in capsule form. After entering the body, the drug inhibits the growth of fungal cells, disrupting their synthesis. Before use, be sure to read the instructions. |
| Fluconazole | An excellent drug that has a negative effect on infectious diseases or yeast-like pathogens. Begins to act 20 minutes after application. The drug must be taken every 7 days, but the doctor can change the dosage and frequency of administration if necessary. |
| Nizoral | Antifungal ointment, the active component of which is ketoconazole. The drug, also available in tablet form, has antipruritic properties. The duration of the therapeutic course for the treatment of fungal diseases is 3-4 weeks. The drug has a number of contraindications; it should not be used by children and pregnant women. |
| Forkan | Prescribed mainly for the treatment of skin fungus caused by saprophytes. The medicine enters the blood approximately 1 hour after administration, and then leaves the patient’s body through the kidneys. The drug should be taken once a week, 150 ml. The duration of the treatment course is 4 weeks, but if necessary, the doctor can extend it to 6 weeks. |
| Mikoket | An effective antifungal ointment that contains ketoconazole, a substance that prevents the proliferation of fungal bacteria. When treating a fungus, you need to carefully apply the product to the affected areas of the skin several times a day. The duration of the treatment course is 2-4 weeks. |
| Salicylic ointment | This drug can be used to treat fungus in two ways. The ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin or applied as a compress at night. Both methods are good in their own way. Due to its effectiveness and low cost, salicylic ointment is one of the most popular remedies for the treatment of skin fungus. |
Regardless of the form or cost, all antifungal drugs have some contraindications. When prescribing this or that remedy, the doctor must be careful, especially if a child has mycosis of the skin. For example, the use of antifungal drugs is not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers, or patients suffering from liver failure . In rare cases, the patient may have an individual intolerance to the drug or its individual components. This also needs to be taken into account.
Folk remedies
Many people, faced with a fungal skin disease, are in no hurry to go to the pharmacy for antifungal drugs. They prefer to be treated with folk remedies. Sometimes they really help, but only in combination with traditional methods of treatment. Traditional medicine is effective as a supplement, as its proven remedies can enhance the effectiveness of fungal treatment.
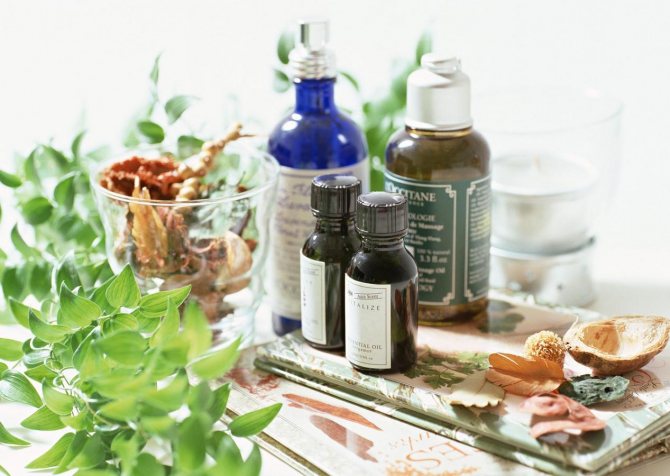

Effective folk remedies
Below are the most common and effective traditional medicine recipes that can be used to treat fungus at the initial stage of development.
- Coffee bath. To do this, add a little instant coffee to your regular shampoo and mix these two ingredients. Then use the product when washing your hair or face.
- Garlic ointment. This is a unique remedy used in folk medicine to treat various forms of fungus and other diseases. To prepare the ointment, you need to mix a few cloves of chopped garlic with 2 tsp. butter. As a result, you should get a homogeneous mass in the form of a cream. Apply it to the affected skin every day, preferably before bed. Cover the top with film. Just a few days of such treatment will get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the fungus.
- Oregano oil. This is an effective remedy in the treatment of scalp fungus. To eliminate the symptoms of this disease, you need to add a few tablespoons of oil to shampoo and wash your hair with it once a day. The result will not take long to arrive.
- Herbal decoction. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour 500 ml of boiling water into 50 g of herbal tea prepared from yarrow, burdock, wormwood and plantain in equal proportions. Leave the product for 30 minutes, then take it orally in the morning before meals.

Treatment of the fungus should begin immediately
On a note! Despite such a variety of folk remedies, it must be remembered that an incompletely cured disease can soon lead to a relapse. Therefore, fungal diseases are best treated comprehensively.
Fungal skin diseases and their prevention
Today we will talk about one of the most common types of skin diseases - fungal infections. And we will try to answer the most common questions that patients ask in the dermatologist’s office.
So what is a fungal infection?
This is a disease caused by fungi, the number of which is very large in nature. Today there are more than 200 species of different mushrooms.
Where do fungi live and how does a person become infected?
Fungi are widespread in the environment. They live in the soil, on plants, live on animals, and there is even a saprophytic species of fungi that happily coexists with us, i.e. live on human skin. Fungi pathogenic to humans that affect the skin are called dermatophytes, and the diseases are called dermatomycosis. Infection can occur in 2 ways: direct infection through contact with soil, plants, a sick animal or a sick person; indirect - in contact with various things and objects that were used by patients, also through animal care items.
Why does fungal infection occur?
Susceptibility to fungal infection is determined by numerous factors: weather conditions (hot season), the state of the immune system, skin condition, and the presence of concomitant diseases. Age, gender, and professional factors also matter. More often, of course, the manifestation of the disease occurs in the hot season, after returning from the “seas,” where a hot, humid climate prevails, accompanied by increased sweating. These factors are especially favorable for the introduction of pathogenic fungi and for the transition of saprophytes into pathogenic flora.
What are the types of fungal infections?
There are mainly 4 groups of fungal diseases:
- keratomycosis.
They are quite superficial, as they affect the stratum corneum and cuticles of the hair, without causing inflammatory reactions and do not affect skin appendages (hair, nails). The most common disease from this group is pityriasis versicolor, or pityriasis versicolor. It is manifested by the appearance of cafe-au-lait spots, mainly on the chest, back, and shoulder girdle.
- dermatomycosis.
This is a large group of fungal diseases that affect the skin, hair and nails. The most common disease from this group is athlete's foot, or mycosis of the feet. The disease is very common among the adult population - about 80% have this disease.
- candidiasis of the skin, mucous membranes, internal organs.
The disease is caused by a yeast-like fungus of the Candida series, an opportunistic flora. What does it mean? This means that the fungus exists in our body, but whether it will cause disease or not depends not so much on it, but on the state of our body as a whole. All factors contributing to the transition of a saprophyte into a pathogenic flora have been listed above.
— deep mycoses with systemic damage to the skin and internal organs.
A severe group of diseases that requires long-term treatment in specialized medical institutions.
Is it contactable?
For adults it is practically non-contagious, but children, due to the structural features of the epidermis, can become infected from sick family members.
Prevention and treatment?
The disease can be treated quite well, but there is no immunity to it, so preventive measures are very important. For treatment, antifungal drugs are used externally, in the form of solutions, creams, gels, which are applied to the affected areas 2 times a day for 2-3 weeks. UV therapy is also used. It is advisable to use different antifungal drugs in the morning and evening. For prevention, it is recommended to use special shower gels labeled “for skin prone to fungal infections.”
How does infection occur?
It should be remembered that mycosis of the feet is a contagious disease. Infection occurs both through direct contact and through objects infected with the fungus. Particularly dangerous are bathhouses, showers, beaches, gyms, swimming pools and items of clothing - shoes, socks.
Why do some people get infected and some people don't?
The transition of the fungus from a saprophyte to a pathogenic state is facilitated by a whole range of reasons, for example: structural features of the foot (flat feet, narrow interdigital spaces), a tendency to increased sweating with changes in the chemical composition of sweat, metabolic and endocrine diseases, hypovitaminosis, vegetative dystonia.
Prevention and treatment?
A huge role in the prevention of fungal diseases is played by the treatment of shoes, the treatment of manicure and pedicure scissors with special antifungal agents, in the form of solutions and sprays. It is also important to combat excessive sweating of the skin of the feet, if necessary. For treatment, depending on the severity. The course and extent of the process use local and systemic antifungal therapy.
In the last few years, a modern method has been successfully used in the treatment of fungal nail diseases (onychomycosis) - laser treatment of onychomycosis.
Prevention measures
Most diseases can be prevented, including mycosis. After all, it is much easier to prevent the development of a disease than to treat it later. Prevention of fungal diseases consists of following the rules of personal hygiene. If there is an infected person in the house, then his things cannot be used. Even if you come into contact with a patient’s shoes or jacket, you can become infected, so try to protect the patient as much as possible.
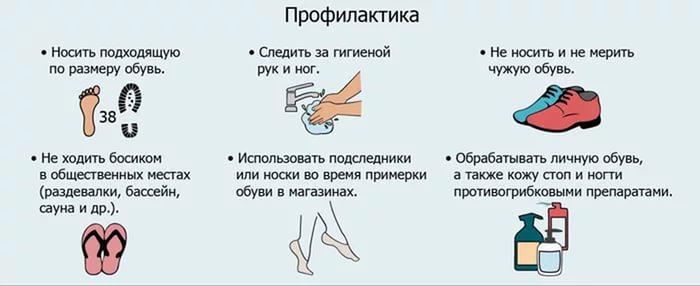
Fungus prevention
You should also avoid contact with stray animals, as they are carriers of various diseases. If you have a dog or cat in your home, they should be taken to the veterinarian regularly for examination. Otherwise, the risk of infection with a fungus or other pathologies transmitted by contact will increase. With the development of chronic diseases, it is necessary to provide timely treatment, since ignoring the symptoms can lead to serious diseases, including mycosis of the skin.

Prevention of fungal infections
To avoid the development of many ailments, doctors recommend strengthening your immune system . To do this, exercise regularly, eat right and give up bad habits. By playing sports, we do not mean going to the gym every day, where you will strain your health in every possible way in attempts to lift unrealistic weights. It is enough to regularly ride a bike or take walks in the fresh air. Give up the elevator for a few months and you will soon see a positive result (not only strengthening your immune system, but also losing extra pounds).
Find out the truth about fungal disease to defeat it
Knowing the characteristics of a fungal disease is necessary not only to cure it, but also to prevent it. What kind of knowledge is this?
- You need to have an idea of the sources of infection: who and where can infect you.
- It is good to understand how a fungal infection is transmitted - through touch, some objects, or otherwise.
- It is important to know how you can protect yourself from infection and what you need to do (and what not to do) to do so.
We present all this, and some other useful information, on the pages of this section.
Where and how can I get a fungus?
Symptoms and signs of the problem
Symptoms of a fungal disease include itching, redness, intoxication and fever. Sometimes it is asymptomatic and makes itself felt at the acute stage. In appearance it appears as red, itchy, scaly red spots.
If you notice symptoms and signs of a fungal infection, you should immediately make an appointment with a doctor.
The fungus is a contagious disease and can be transmitted from person to person through close contact. Let's look at the symptoms of individual types of fungus.
The appearance of mycosis in the foot area
The main risk groups include people who often visit public places: baths, saunas, swimming pools and places with high humidity levels. And people wearing uncomfortable tight shoes.
Athlete's foot appears as flaky patches of skin between the toes and on the foot. Itching and severe scratching of the affected area lead to the formation of erosive areas. The disease leaves both pain and discomfort when moving.
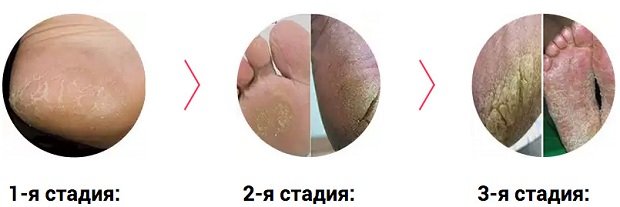
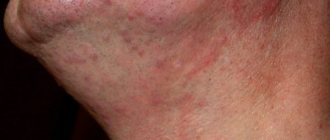
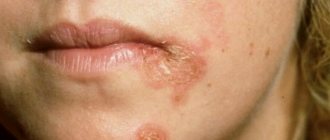
Mycosis formed in the facial area
Problem areas will vary in scale and have both the appearance of blemishes and the appearance of pimples. Many ulcers have a lumpy, rough texture and are very itchy. Fungi appear in the cheeks and chin area.
Affected the scalp
If a scalp fungus is suspected, a change in the structure of the hair is noted. They will be greasy and the skin underneath will be dry. Peeling and hair loss are noted.
All these symptoms are accompanied by itching, leading to the appearance of small erosions. When the head is affected by a fungus, the lesion manifests itself in the form of a hairless area with the presence of ulcers with a whitish coating.