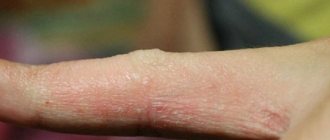
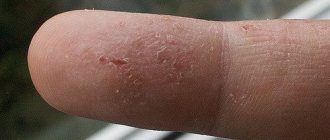
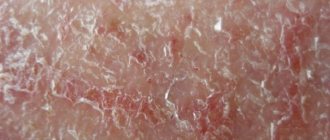
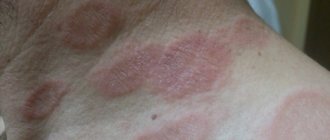
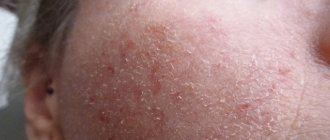
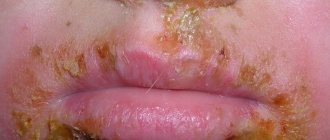
In medicine, weeping eczema is called true or idiopathic. In ancient Greek, this word means “boiling,” which is a good description of the symptoms accompanying the disease.
The usual areas for eczema are the arms and legs, but it can occur in other places.
With weeping eczema, blisters form on the skin; when they burst, they release a serous fluid that resembles boiling water. If the disease passes without intervention, then under favorable conditions it will definitely remind itself of itself, only, unfortunately, in a more serious form.
Eczema is a chronic disease, where processes of exacerbation and remission periodically replace each other. Fortunately, these skin problems are not transmitted through contact.
Weeping eczema is difficult to respond to any treatment method, therefore, in order to reduce the consequences of its manifestation, it is necessary to exclude from the patient’s life any irritating factors, both internal and external.
Under no circumstances should you scratch the affected areas of the skin with your nails: if infected, secondary inflammation is possible, complicating any treatment method.
Symptoms of weeping eczema
When a weeping type of eczema occurs, the patient experiences symptoms such as swelling of the skin, blisters and redness of the skin. Next, the blisters spontaneously open and form wet eczema, which aches and itches.
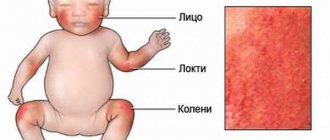
A characteristic feature of the disease is the symmetry of the manifested processes. In children, eczema often develops on the face, chin, and less commonly on the head, back, chest, knees and elbows. In adult patients, eczema is often diagnosed on the arms, neck, ankles, as well as in bends - on the inside of the elbow or on the outside of the knee.
To determine how to treat a disease, it is important to initially attribute the manifested disease to a specific type. After seeing a doctor and undergoing the prescribed treatment, many people completely get rid of the symptoms of eczema.
However, it is possible that even after several years, eczema will not flare up again, affecting an even larger area of skin. Such a relapse can be caused by severe overwork, a nervous breakdown, or even poor nutrition.
Causes
Weeping eczema is the result of immune inflammation of the skin. Usually there are several reasons for the development of dermatosis, so it is difficult to accurately determine the etiology of the disease. It has a chronic relapsing course. The disease can occur regardless of age and gender. The risk group includes people over 40 years of age.
Main provoking factors:
- genetic predisposition (the probability of developing eczema in children whose parents suffer from a similar pathology is 40%);
- psycho-emotional instability: stress, mental stress, depression;
- allergies to chemicals or food;
- immune diseases;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, disruption of the endocrine system, infections;
- exposure to external factors (physical activity, poor ecology in the region of residence).
The course of eczema can be complicated by fungal infection. If the disease becomes chronic, the risk of frequent relapses increases. Even after the complete disappearance of symptoms, there is a high probability of re-infection and development of pathology.
Treatment with traditional methods
Traditional medicine has accumulated its own arsenal of ways to alleviate the condition of patients with eczema, proven over centuries. And yet they are most likely auxiliary in nature, to alleviate the manifestations of the disease.
With the permission of the treating doctor, you can use some folk remedies, for example:
- Compresses made from sea buckthorn and fir oil, cucumber brine relieve inflammation and swelling.
- Taking warm baths with the addition of a decoction of the following herbs: clover, chamomile, pine needles, knotweed, millennial, elderberry, plantain. As well as essential oils of geranium, tea tree, ylang-ylang, lavender, etc.
- To soothe injured skin, you can add essential oils of tea tree, geranium, ylang-ylang, and lavender to your bath.
- You can lubricate the affected area with lime ointment, which you can prepare yourself by adding the same amount of water to 100 g of slaked lime. The mixture must be brought to a boil, allowed to stand until completely cooled, strained and mixed with vegetable oil in equal proportions.
It must be remembered that before using any treatment method, you need to consult with your doctor, because self-treatment of weeping eczema can be dangerous for the general condition of the patient.
How to treat weeping eczema on the legs
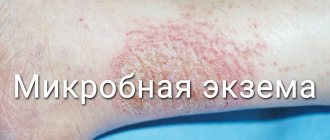
Weeping eczema is a skin disease characterized by a rash with fluid-filled blisters, redness, and swelling. Often weeping (wet) or true eczema affects the hands and feet. On the legs, rashes most often appear on the inside of the knees. This type of eczema is the most difficult to treat. The disease is not contagious.
General recommendations
Often skin disease is triggered by other health problems. For skin eczema, risk factors include endocrine diseases, kidney disease, digestive disorders, the presence of parasites, nervous disorders, and untreated foci of infection (sore teeth, tonsillitis, stomatitis). Before treating eczema, you need to say goodbye to the listed pathologies.
The disease develops mainly due to contact with an allergen. Therefore, patients with eczema on the legs should monitor their own lifestyle. To prevent the development of the disease, avoiding exacerbation, it is indicated:
- avoid contact with substances that cause an allergic reaction: detergents, cosmetics, perfumes;
- metals to which allergies are often manifested (chrome and nickel included in alloys of jewelry, fasteners on clothes, shoes);
- abstain from tobacco and alcohol, especially during an exacerbation;
- wear clothes made from natural fabrics;
- abandon woolen and nylon or synthetic socks and tights in favor of cotton ones;
- avoid heavy sweating;
- avoid nervous tension;
- Clean the house regularly.
If you have weeping eczema on your legs, it is not recommended to wet the affected areas. If a microbial infection occurs, you can wash with baby soap without coloring or aromatic additives.
A dermatologist can determine the cause of weeping eczema on the legs. The doctor will prescribe a treatment that is suitable for a particular patient in a particular case; treatment of eczema is prescribed in a comprehensive manner. Treatment measures include eliminating the cause of the disease, internal and external medicinal treatment, diet, physiotherapy and prevention of exacerbations.
Consultation with a dermatologist
Drug treatment
Eczema is a disease of an allergic nature; taking antihistamines is an important part of treatment.
Modern drugs of the second or third generation are used more often, sometimes 1st generation - depending on the resistance of the patient. It is better to administer medications intravenously.
To eliminate intoxication, sorbents (enterosgel, polysorb, activated carbon) are prescribed orally, and hemodez is administered intravenously.
For eczema, desensitizing drugs are prescribed to reduce the allergic reaction. These agents include calcium gluconate and calcium chloride. A solution of 5-10 ml of calcium chloride in 100-200 ml of saline is administered intravenously.
Calcium chloride must not be administered intramuscularly - such an injection can lead to abscess and necrosis of the muscle at the injection site. Calcium gluconate is administered intravenously or taken orally in tablets.
Hexamine and sodium thiosulfate have a similar effect.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, for example, corticosteroids, and are used for severe or long-term disease when other drugs do not help. These drugs include prednisolone and dexamethasone. In mild cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used:
- nimesulide;
- ibuprofen;
- meloxicam;
- diclofenac.
If an infection occurs, antibiotics are prescribed. In severe cases, cytostatics that suppress the reaction of the immune system and diuretics (diuretics) are used. To correct the functioning of the immune system, immunomodulators are prescribed: cycloferon, polyoxidonium, sodium nucleinate, a combination of vitamins A and E, aloe extracts, echinacea, and vitamins B, A, E, C as a general tonic.
When treating weeping eczema, a systematic approach is important. While reducing skin manifestations, it is important to tidy up the digestive system. Therefore, enzymes are prescribed (festal, pancreatin, mezim). Taking enzyme preparations continues for several months. For dysbacteriosis, Bifiform, Linex, and Hilak Forte are recommended. Fermented milk products improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Stress can cause eczema or worsen the patient’s condition; sedatives and antidepressants are often prescribed for weeping eczema. Non-addictive herbal preparations based on valerian, St. John's wort and plants that have a sedative effect are preferred.
Eczema requires complex treatment. The doctor chooses the most suitable ones for a particular case.
Antiseptic lotions are prescribed locally:
- 2% boric acid solution;
- 2% tannin;
- silver nitrate;
- potassium permanganate;
- soda;
- dimexide;
- resorcinol.
When crusts form in place of wet areas, use zinc, ichthyol paste, moistened lotions with tar, and boric acid solution.
Hormonal ointments containing corticosteroids (Elocom, Advantan, Lokoid), combination agents (Triderm), ointments with topical calcineurin inhibitors (Pimecrolimus, Protopic), which reduce itching and irritation, are used.
To soften the skin, salicylic, boric ointment, creams with ketoconazole, and Lorinden-S are used. Castellani liquid and aniline dyes are used to lubricate the crusts.
Physiotherapy
In addition to medications, physiotherapeutic treatment helps with weeping eczema. Its task is to correct the response of the immune system, reduce inflammation, and relieve excitement of the nervous system.
For weeping eczema on the legs, the following procedures are prescribed:
- Electrophoresis with antihistamines.
- Phototherapy is irradiation with long-wave ultraviolet light. The method is often used to treat children; it does not require taking photosensitizing drugs.
- Laser therapy - this method treats erosions in weeping eczema; irradiation is carried out with a low-intensity infrared laser.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Darsonvalization - reduces itching and weeping.
- PUVA therapy (PUVA - Psoralen + UltraViolet A) - ultraviolet therapy with the photosensitizing drug psoralen. The method treats eczema and other skin diseases. Not everyone tolerates the ingestion of photosensitizers well, but now PUVA baths have appeared, where psoralen is dissolved in water. An effective method of treating eczema includes contraindications: pregnancy, increased sensitivity to light, melanoma, aphakia (lack of lens), severe myocardial pathologies, in which you cannot stand for a long time. Side effects occur in people with fair skin, patients with cancer, cataracts, and kidney failure.
- Electrosleep - calms the nervous system, which has a good effect on the patient’s condition.
- Acupuncture.
For weeping eczema, spa treatment in a dry coastal climate is indicated. Treatments include baths with salt, soda, and therapeutic mud.
Diet for eczema
By nature, eczema is an allergic disease. It is recommended to exclude foods that cause allergies from the diet, especially during an exacerbation.
Similar products include:
- citrus fruits and other yellow and orange fruits and vegetables;
- chocolate, cocoa products;
- coffee;
- honey;
- smoked meats;
- mayonnaise and ketchup;
- alcoholic drinks.
Regardless of the allergen that caused eczema, a plant-dairy diet helps treat the disease: cereals, green vegetables, fruits, dairy products.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating eczema are used in combination with complex treatment; the methods should not be the only therapeutic measures. The use of folk remedies is recommended to be coordinated with a doctor.
Folk remedies usually include plants that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. It is recommended to use plants to which there are no allergies.
A number of recipes to help with eczema.
- Willow bark decoction - wipe the rash areas several times a day.
- Infusion of birch buds. Pour a glass of birch buds with hot water, boil, filter. Wipe sore spots with this infusion. The duration of treatment is two weeks.
- Lotions made from raw potatoes, grated together with the skin. The potato mass is wrapped in a napkin and applied to the rash areas, changing every two hours.
- Lotions made from an infusion of a mixture of chicory root, creeping thyme and chamomile - two tablespoons of each in two glasses of boiling water, leave for 30 minutes. Use the cooled infusion for lotions.
- Wet areas are sprinkled with river shell flour.
For eczema treatment to be successful, a systematic approach is required. At the first signs of weeping eczema, you should consult a dermatologist; it is easier to treat the disease before the pathology becomes chronic. Treatment of weeping eczema requires the patient to take medications, follow a diet and revise their lifestyle to eliminate factors that can trigger the return of the disease.
Source: //OtNogi.ru/profilaktika/kak-lechit-moknushhuyu-ekzemu-na-nogax.html
Ointment for weeping eczema
Sometimes, during the period when weeping stops, it is effective to use ointments together with pastes or combine them with oil, oil solution (Retinol, Carotolin or Tocopherol Acetate). If the patient has poor tolerance to fatty bases, then low-fat ointments are prescribed, the basis of which is gelatin, glycerin, casein, agar, starch.
You can also soften the skin with boric ointment, salicylic ointment, Lorinden cream, Castellani liquid, cream containing Ketoconozole, and baths with potassium permanganate.
Symptoms
Typically, the lesions of weeping eczema are located on the arms, legs or head. In severe cases, the disease spreads to other parts of the body.
Initially, the skin turns red. Reddish areas of different shapes and sizes form. The surface of the skin becomes swollen and inflamed.
Then small bubbles appear. They are of 2 types: vesicles (filled with clear liquid) and papules (containing a purulent secretion of a grayish or whitish hue). The patient experiences severe itching.
A characteristic symptom of weeping eczema is a combination of rashes that are at different stages of development: peeling skin, old and new blisters.
Over time, the blisters spontaneously open, releasing serous exudate. In their place, characteristic “wells” appear, which are refilled with liquid. Their diameter and depth are very small, but there are a lot of such depressions. Because of this, the affected areas practically do not heal.
Gradually, the wounds dry out and become covered with a crust: a layer of epithelium forms under it. The skin begins to actively peel off, which is also accompanied by severe itching and discomfort. Often these symptoms cause sleep disturbances, irritability and other neurotic disorders.
The main feature of weeping eczema is the combination of a rash that is at different stages of development. In the area of one lesion, peeling, opening of old and emerging new blisters are simultaneously observed. Sometimes the lesions disappear over time, and pigmented spots or scars appear in their place.
With proper treatment, acute symptoms become less intense. However, the disease can become chronic with relapses. The skin in the area of the rash undergoes a process of lichenification: a characteristic pattern appears on the epithelium, peeling increases, and pigmentation is disrupted. Foci of the disease become denser, increase in diameter and spread throughout the body.
Weeping eczema: causes of pathology
Despite the fact that the disease has been known to medicine for a long time, the exact prerequisites for its development are still unknown. It is believed that the appearance of eczema is influenced by dysfunction of the endocrine system, disruptions in metabolic processes, disorders of the nervous system (for example, a serious stressful situation or chronic stress), problems with the gastrointestinal tract, frequent allergic reactions, friction and scratching of the skin, as well as genetics. - caused by hereditary predisposition to skin diseases.
Separately, it is worth noting the influence of nutrition on the development of pathology. The risk of developing food weeping eczema increases by more than 30% if you regularly consume foods rich in trans fats (fast food, hydrogenated confectionery fat, processed foods, etc.). On the contrary, if you include fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs in your diet several times a week, the likelihood of developing eczema is reduced.
The development of the disease is usually rapid. The disease presents with an undulating course with alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions.
Treatment
The process of treating weeping eczema has a complex structure. This disease must be treated comprehensively, using medications of different spectrum of action, both external agents and drugs for internal use. How to treat weeping eczema should only be determined by the attending physician.
In order for the treatment of weeping eczema to produce tangible results, it is important to eliminate all provoking factors. For these purposes you will need:
- reduce the impact of stress on the body;
- follow a special diet;
- protect the skin from irritation, do not scratch it;
- identify and eliminate the allergen.
A fairly effective remedy in the treatment of eczema is Thiamine, otherwise known as vitamin B1. This substance has a positive effect on the nervous system. At the same time, doctors discovered its antipruritic properties. Thiamine helps reduce pain. This substance has a number of positive characteristics, it is capable of:
- regulate metabolism;
- improve heart function and vascular function;
- have a positive effect on digestive processes.
All kinds of pastes are used to treat skin lesions. These agents have a different spectrum of action. There are several types of pastes:
- preparations containing ichthyol;
- medicines containing zinc;
- bismuth;
- boron-containing;
- tar;
- mothballs.
Patients suffering from eczema are prescribed ointments that need to be combined with pastes or oil solutions. At the initial stage of the disease, ointments containing steroids are used. Ointment for weeping eczema helps reduce itching, they speed up the healing process of wounds and cracks, and also moisturize the skin. Chronic eczema is treated with hormonal ointments.
To soften the skin, use boric or salicylic ointment, creams that contain Ketoconozole.
The therapeutic plan may include intramuscular agents. For injections, sodium thiosulfate, magnesium sulfate, and calcium gluconate are used.
In case of an infectious form of the disease, the patient receives physiotherapeutic procedures, which include:
- laser treatment;
- ozone therapy;
- cryotherapy.
To cleanse the body, the doctor prescribes diuretics. And to strengthen the body, immunostimulants are indicated.
To prevent the spread of infection, scratching should be avoided. Because this will contribute to additional inflammation, which will significantly complicate the healing process.
To reduce itching, take cooling baths. The baths are made using ice.
If the cause of eczema is an allergen, the doctor will prescribe antihistamines.
To speed up the healing process, the patient must follow the doctor’s instructions, follow a diet and regimen, take care of the affected areas of the body, and treat them regularly. Fried and fatty foods are excluded from the diet. The daily menu includes porridge, vegetables, and herbs. It is beneficial to drink plenty of fluids to flush out harmful toxins from the body. Coffee and tea in this case are considered harmful drinks.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of weeping eczema
Treatment with modern drugs does not always produce the desired result. Therefore, it makes sense to supplement this type of treatment with folk remedies, the most effective of which are:
- lotions made from sea buckthorn oil;
- warm baths with medicinal plants: chamomile, sage, plantain, lavender;
- treatment with Kalanchoe juice.
Raw potatoes are very useful in the fight against eczema. It is grated together with the skin. Lotions are made from the prepared mixture.
Folk remedies only complement the main course of treatment. It will not be possible to overcome the disease with the use of folk remedies alone.
Prevention
After stopping an acute attack of weeping eczema, measures should be taken to prevent relapses. To avoid the appearance of foci of disease on the feet, monitor foot hygiene, choose comfortable shoes, and give preference to natural materials. Avoid contact with allergens. If there are residual patches of pigmentation on the skin, regularly treat them with an ointment based on birch tar, petroleum jelly, ichthyol, and sulfur.
Stick to a hypoallergenic diet, daily routine, and avoid nervous overload. It is not recommended to visit saunas or steam baths: prolonged contact with water and hot steam can trigger a relapse. Treat infections and bacterial diseases promptly.
By taking precautions, you can avoid relapses of weeping eczema. Using local and systemic drugs, you can relieve the symptoms of an acute attack and normalize the condition.
Rate this article 4.5 4.5 (1 rating)
About the right lifestyle
Let's talk about how to treat the mentioned disease. To cure eczema on the legs you need to follow a certain diet.
You will need to eat often, but in small portions. It will be enough to eat 3-5 times a day. After you have eaten the main course, you should not immediately eat fruit or sweets. If you do not follow this advice, the food will rot in your stomach.
You can eat desserts, but you need to keep a pause of 1.5 hours. You should not wash down your food, much less use sweet tea for this. It would be a good idea to drink a lot of clean, plain water.
Weeping eczema: folk remedies to combat the disease
The use of traditional medicine recipes can be successful only if the following rules are observed:
- Before starting unconventional treatment, you should consult your doctor, as some ingredients of folk remedies may be allergens.
- You can resort to “grandmother’s” advice only after the acute phase of weeping eczema comes to an end.
- It is recommended to use traditional methods only as additional means of combating eczema, while traditional drug treatment should act as the basis of therapy.
Traditional medicine involves the preparation of decoctions and infusions from herbs, which can then be used for oral consumption, bathing, and application. You can also prepare ointments and balms at home.
What to apply to weeping eczema to dry it? For this purpose, you can use a mixture of chopped garlic (3 medium cloves) and honey (0.5 tsp), which is wrapped in a clean bandage and applied to the affected areas. Fresh, undiluted celandine juice also has drying and antipruritic properties. A small amount of juice is applied to the skin, being careful not to get on healthy areas.
Good results can be obtained if you lubricate the rash areas with homemade ointment prepared from 7/10 parts of baby cream and 3/10 parts of beeswax (can be replaced with fir oil).
To reduce weeping, it is recommended to use a herbal infusion prepared from equal parts of chamomile, chicory root and creeping thyme, poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. The infusion is left until it cools completely (about 30 minutes), after which it is used for lotions.