The role of proper nutrition
Since eczema is a skin disease, often of allergic origin, people suffering from this disease are advised to adhere to a diet that excludes foods that cause an allergic reaction. During periods of exacerbation of eczema, proper dietary nutrition helps to get rid of such an unpleasant symptom as itching. During the period of remission, the diet acts as a preventive measure for the recurrence of the disease.
A hypoallergenic diet for eczema includes a variety of foods, which does not cause much discomfort to the patient. Some foods can even be fried a little, with a little oil and, preferably without salt, but only if it is pre-cooked.
Dishes during a diet are best absorbed and digested in pureed or finely chopped form. Vegetables recommended for consumption during the diet (except cabbage) can be eaten in absolutely any form, raw, boiled, baked. The exception is vegetables that can be fried.
Dangerous products
In most cases, exacerbation of eczema is caused by protein foods, dishes high in starch and sugar, as well as vegetables, berries and fruits of red, black, yellow and orange. However, since the diet must be balanced and complete, you cannot blindly give up all types of protein foods and sweets in order to completely switch to safe plant-based foods. That is why it is not recommended to create your own diet: this should be done by a qualified allergist, dermatologist or nutritionist. At the same time, the patient himself must be sufficiently familiar with permitted and prohibited products in order to find an appropriate replacement for potentially dangerous dishes.
At the stage of exacerbation of eczema, it is necessary to completely exclude from the diet of adults:
- tomatoes, strawberries, red apples, sweets, fatty foods, baked goods;
- canned foods that provoke acute eczema
- semi-finished products;
- eliminate or minimize the consumption of potatoes;
- foods that cause increased itching are chocolate, jam, honey;
- mayonnaise, pickles, marinades.
Proper nutrition for different types of eczema
For eczema of any type, you can follow general recommendations, but each type has its own specific rules to avoid exacerbation.
For hand eczema
The diet should help relieve symptoms and put the disease into remission. Regular proper nutrition helps reduce the likelihood of relapse. With such eczema, you need to avoid sweet, spicy and fried foods. Semi-finished products, marinades, pickles and canned foods are also prohibited.
carriers of vitamins PP and B
Diet for eczema on the hands allows the consumption of lean meat (preferably turkey and rabbit) and fish. But during an exacerbation, it is advisable to adhere to a vegetarian diet. Vegetables will benefit the body, the amount of potatoes is reduced, and it is advisable to avoid pasta altogether.
To restore the deficiency of vitamins PP and B, you need to eat more lettuce, turnips, carrots, rutabaga and fresh cucumbers. Greens will also be useful: parsley and dill. There are usually no restrictions on the amount of liquid, but it is better to exclude coffee, store-bought juices, alcohol and carbonated drinks.
In some cases, eczema causes weepy patches on the hands. They occur when the water-salt balance and the inflammatory process are disturbed. With this pathology, the diet for eczema excludes foods rich in carbohydrates. You can include lean meat, dairy, and vegetables in your diet. You cannot eat cabbage and legumes, and salt is also not used when cooking.
For eczema on the legs
The diet for eczema on the legs excludes foods with difficult-to-digest fats. These include:
- fat;
- sweets;
- flour;
- pork;
- pates;
- lamb;
- meat dishes with butter.
During an exacerbation, you need to include fermented milk, porridge with water, and vegetable soups in your diet. In the first few days of illness, diluted vegetable and fruit juices are needed to cleanse the body.
For meat products, you should give preference to boiled or stewed turkey and rabbit, boiled fresh fish and lean beef. In this case, you need to steam, boil or bake.
Fermented milk products and plant foods should be present in the diet every day. Cabbage, peas, cucumbers, zucchini, carrots, beets and other vegetables have a beneficial effect on the body. Leaf and watercress contain vitamin C, iron, iodine and carotene, therefore they are useful for the patient.
During the period of remission, it is useful to add berries (raspberries, blueberries, rowan, gooseberries, currants), nuts, and melons to the diet. But during an exacerbation, these products are contraindicated. The diet must include porridge, especially oatmeal, buckwheat and wheat. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, coffee and strong tea.
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema is an important component of treatment. Dyshidrotic skin lesions are a chronic disorder. Patients suffer from periodic rashes in the form of serous blisters on the skin of the soles and palms. A properly formulated diet prevents allergic reactions, and therefore the manifestations of the disease.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude red vegetables and fruits, as well as citrus fruits, from the diet. Any sweets and flour products are prohibited; sugar can be replaced with fructose. For meat products, low-fat dietary varieties of meat and fish are suitable. At the same time, many allergens are contained in smoked meats, pork and duck meat.
Spicy, fried, peppered and salty foods should also be removed from the diet, since such foods not only cause worsening of rashes and itching, but also negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The basis of the diet is fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and dairy products. Cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir and cheese contain lactobacilli, which are essential for the intestines and local immunity. Their regular use prevents relapses of dyshidrotic skin lesions.
So, therapy is based on following a strict diet. It is necessary to adhere to such a diet for 1-2 months, and to achieve lasting results - throughout life.
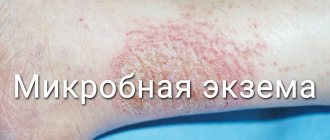
Diet for microbial eczema
The microbial diet is a vegetable-dairy diet. With this disease, the skin is covered with flat crusts, when removed, weeping areas appear. Most often, rashes appear on the legs, the back of the hands, and sometimes on the head. As a rule, a doctor compiles a list of permitted and prohibited foods. Coffee, chocolate, spices, pickles, soda, cheese, and alcohol are prohibited. The exception is plant allergens; the patient is allowed to eat nuts, corn, red vegetables, peas, and garlic. But if the disease worsens, these products are also prohibited.
The main diet consists of vegetable soups, unleavened porridges in water, river fish, steamed cutlets and meatballs, and dairy products. Restrictions also apply to the amount of spices in food. It is recommended to reduce or completely eliminate the use of salt and pepper. Don’t forget about maintaining water balance; you need to drink up to two liters of still mineral water every day.
Diet for allergic eczema
The diet for allergic eczema is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. Not only food products, but also dust, animal hair, pollen, cosmetics and much more can stimulate the appearance of skin rashes. Regardless of the pathogen, therapeutic nutrition can minimize the manifestations of the disease. It is necessary to adhere to a healthy regimen not only during the period of exacerbation to unload the body, but also during the period of remission.
This is interesting: Diet for allergic dermatitis in adults - menu
Smoked meats, sausages, fried, fatty foods, and foods with spices are prohibited. As well as seafood, canned food, eggs, nuts, citrus fruits, mushrooms, grapes, carbonated drinks, confectionery.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of pasta, semolina, butter, full-fat sour cream and whole milk.
The diet should be based on fermented milk products, lean meat, light fruits (plums, currants, pears, apples), vegetables and herbs. You can eat grain breads and products made from second-grade flour, ghee and refined butter.
Diet for dry eczema
The diet for dry eczema involves a vegetarian diet. The menu is based on protein and plant foods. During the period of remission, you can add weak meat broths, lean meats and steamed meat dishes to your diet. You should definitely eat porridge, but without oil and salt, vegetable casseroles and stews with a minimum content of potatoes. As for fish, it is best to eat river fish, baked or boiled.
Dairy products such as cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, yogurt and kefir help the body recover faster and accelerate skin regeneration processes. Plant foods are very useful, for example, peas and cabbage. Peas contain a lot of protein, so it is better to eat them during the summer period of exacerbation of the disease. Your daily diet should include carrots or carrot juice, as they contain a lot of B vitamins and carotene. The content of precisely these beneficial substances in patients with eczema is significantly underestimated.
If hypertension appears along with skin rashes and itching, then you should eat beans and beets, watercress and lettuce, as they are rich in vitamin C, iron, iodine and carotene. Dill helps with gastrointestinal disorders. Greens can be added to salads or made into smoothies based on kefir and dill.
Causes of microbial eczema
The emergence and development of microbial eczema occurs under the influence of a number of factors, both external and internal.
- Decreased immunity
- Nervous system diseases
- Endocrine system dysfunction
- Genetic predisposition
- Allergic factor
- Diseases of internal organs (liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract)
The cause of the development of the disease is often varicose veins, lymphostasis, and chronic fungal skin diseases. The disease can be triggered by hereditary predisposition and a tendency to allergic reactions. Allergic processes occurring in the body contribute to the development of a pathological immune reaction of tissues, accompanied by inflammation and damage to the skin.
When infectious irritants interact with possible allergens, a chronic course of the disease develops, with constant recurrent inflammation in the epidermis.
Microbial eczema often occurs around poorly healing postoperative wounds, fistulas, trophic ulcers and other skin lesions as a result of insufficient antiseptic treatment and contamination with pathogenic microflora (staphylococcus, streptococcus, fungi).
Symptoms of microbial eczema
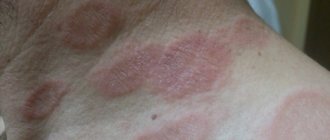
The clinical picture of microbial eczema is characterized by the formation of inflamed, sharply demarcated large lesions, with a detached stratum corneum along the periphery. In inflamed areas, rashes appear in the form of bubble elements (vesicles) with serous contents. After opening them, weeping erosions form, and a layer of purulent crusts forms on the surface of the eczema lesions.
The eruptive elements tend to merge and grow peripherally. Around the foci of eczema on apparently healthy skin, screenings are observed (individual small pustules and dry flaky areas). The process of appearance and opening of the elements of the rash is accompanied by severe itching. Developed foci of eczema are located asymmetrically, prone to growth and the formation of secondary rashes.
Doctors distinguish several subtypes of microbial eczema, characterized by characteristic symptoms:
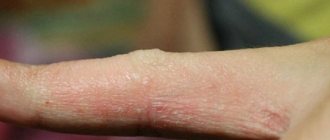
- Nummular (coin-shaped). It is characterized by the appearance of isolated eczematous lesions, having a round shape, with a diameter of 1 to 3 cm. Most often it affects the skin of the hands. Microbial eczema on the hands is characterized by a clear boundary of the affected areas, an erythematous, swollen, weeping surface, the formation of exudative papules and a layer of purulent crusts. This form of microbial eczema tends to spread and is difficult to treat.
- Varicose . Develops against the background of venous insufficiency and varicose veins. The main location is the lower extremities. Microbial eczema on the legs often accompanies trophic ulcers, around which an eczematous area forms with pronounced swelling and inflammation.
- Paratraumatic. Develops when the healing process of postoperative wounds, abrasions, ulcers and other injuries to the epidermis is disrupted.
- Mycotic . This type of eczema occurs against the background of fungal infections of the skin of the upper and lower extremities.
- Sycosiform . Sycosis is a pustular skin lesion caused by Staphylococcus aureus. The main location of sycosis is the scalp, beard and mustache area in men, armpits, and pubis. When microbial eczema is attached, weeping, severely itchy, recurrent erosions are formed.
- Nipple eczema . It develops in women as a result of trauma to the nipples during breastfeeding, as well as in persons infected with scabies. It manifests itself as red, inflamed areas around the nipple. The lesions have clear boundaries; the inflamed skin inside is covered with painful, itchy cracks.
When the first symptoms of microbial eczema appear, it is necessary to seek medical help, otherwise further development of the disease threatens the spread of the infectious-inflammatory process and damage to large surfaces of the skin.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a specialist can correctly diagnose the disease based on anamnesis, a general picture of the disease and a number of laboratory tests. A visual examination allows you to note characteristic external signs: rash, redness and swelling of the skin, the presence of weeping areas and purulent deposits.
To clarify the diagnosis, there are special research methods that allow you to study skin samples for the presence of mycotic cells. Based on examination of skin scrapings under a microscope or using histological or bacteriological analysis, a doctor can confidently diagnose microbial eczema.
An important point is to determine the type of microorganism and identify its sensitivity to drugs, which is necessary for further successful treatment of the disease. In doubtful cases, a histological examination of the biopsy is performed, a sample of which is taken from a deep focus of microbial eczema.
Microbial eczema must be differentiated from other types of eczema, other dermatitis and manifestations of psoriasis. If microbial eczema is suspected of transitioning to weeping (true) eczema, a general blood test is prescribed to determine the level of lymphocytes and immunoglobulins.
Only an experienced specialist knows how to treat microbial eczema and what medications to choose in each specific case. It is unacceptable to self-medicate; the doctor will select the optimal treatment regimen, taking into account the patient’s condition and possible contraindications, which will achieve the best results and ensure a lasting positive effect.
Treatment of microbial eczema
Treatment of the disease is complex, it includes systemic therapy, local treatment, measures to prevent the spread of eczema to healthy areas of the skin. Nutritional adjustments and personal hygiene play an important role in the treatment of the disease.
Systemic therapy
In severe cases of microbial eczema, accompanied by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed (ofloxacin, ampicillin, azithromycin, cefazolin). If eczema occurs against the background of a fungal infection, the use of antifungal agents is indicated. When the process spreads and affects large areas of the skin, systemic corticosteroids (prednisolone, triamcinolone) and cytostatics (cyclosporine) are prescribed.
Antihistamines help eliminate itching and reduce inflammation:
- diazolin,
- suprastin,
- Lorotadine
To strengthen the body's defenses and reduce susceptibility to irritants, intravenous infusions of sodium thiosulfate and calcium chloride are indicated.
Sedatives will help relieve tension and calm the nervous system:
- bromine,
- valerian,
- motherwort.
In severe cases, with sleep disorders and nervous disorders, sleeping pills and antidepressants will help.
The course of the disease is facilitated by taking vitamin-mineral complexes. To increase the body's resistance and strengthen the immune system, injections of vitamins (A, B, E) and immunomodulators are prescribed.
Local treatment (ointments and creams)
Foci of microbial eczema are treated with ointments based on zinc, tar, ichthyol, and naftalan oil. Make lotions with resorcinol solution, lead water, Castellani liquid. In the acute period, foci of eczema are treated with brilliant green or solutions of aniline dyes.
If a bacterial causative agent of eczema is identified, ointments containing an antibiotic (dettol, drapolene) are prescribed. In the presence of a fungal infection, ointments containing antifungal components (exoderil, bifonazole, loteril) are used.
In case of extensive lesions and severe disease, the use of sprays and ointments with corticosteroids (celestoderm, elocom, advantan) is indicated. They should be used in short courses and only as prescribed by a doctor.
A good effect is achieved by prescribing non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. These are ointments and creams: Radevit, Losterin, Eplan.
Recently, doctors are increasingly replacing hormonal ointments, which have serious side effects, with calciverin inhibitors. These are drugs such as tacrolimus, pimecrolimus. They cope well with the manifestations of eczema even in large areas, quickly relieve inflammation and eliminate itching without having a negative effect on the body.
Lotions based on undiluted fish oil, the use of neutral ointments, various powders and mash are effective. After the acute process subsides, it is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods
Physiotherapeutic methods for the treatment of microbial eczema include:
- Ozone therapy.
- Cryotherapy
- Laser therapy
- UHF, UFO
A good result is achieved by applying mud applications, aseptic dressings with herbal decoctions that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Basic recommendations for patients
- It is necessary to treat concomitant diseases and eliminate foci of chronic infection in the body.
- Avoid overheating and injury to affected areas of the body.
- Maintain careful personal hygiene, avoiding prolonged contact of affected areas with water.
- For varicose eczema, it is recommended to wear thick rubber stockings or bandage the limbs with medicinal bandages.
- Patients with microbial eczema should not wear synthetic, wool or flannel underwear. Clothing should be made from natural materials that allow the skin to “breathe”.
- Avoid psycho-emotional stress and nervous tension.
- Avoid prolonged exposure of affected areas to cold or sunlight.
- After the acute process subsides, it is necessary to periodically visit a dermatologist for a preventive examination.
- Patients with microbial eczema need to adjust their diet and follow a certain diet.
Nutrition for eczema
For eczema of the lips, face, groin, ears, scalp, dyshidrotic, it is very important to follow a diet, since some foods tend to worsen the well-being of patients. For example, sweets, citrus fruits, spicy and smoked foods increase itching.
Note: How the food is prepared is also important. For patients with eczema, it should be boiled or steamed.
It is especially important to adhere to a diet during the stage of exacerbation and remission of the disease: both in adults and in children and nursing mothers. It is not recommended to consume foods that cannot be stored for a long time. It is necessary to limit your diet by removing fatty foods, potatoes, tomatoes, and red apples. Strawberries are prohibited for eczema. It is advisable to give preference to soups made with vegetables and fermented milk products. You can eat porridge with water, lean meat (no more than 150 g per day) and fish (with the exception of sturgeon). It is allowed to drink light-colored juices.
Important! At the acute stage, it is better to refuse meat, giving preference to vegetarian dishes. When the condition improves, you can gradually introduce weak meat broths into the diet.
You need to eat fermented milk products every day. These include cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, and kefir. A diet designed for eczema involves consuming large amounts of plant-based foods. It is recommended to choose peas, cabbage, carrots, beets, beans, etc. When the exacerbation stage is over, you can add nuts, pumpkin, raspberries, black currants, apricots to your diet.
Allergic and dry eczema
Eczema of this form develops as a result of contact with an allergen product. With the help of research, this dish is determined and excluded from the diet. Stop consuming nuts, sweets, fried and smoked foods, and hot spices. You should not eat citrus fruits, they are strong allergens.
For allergic eczema, it is recommended to eat more kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese products, and vegetable broths.
Dry eczema
For dry eczema, it is advised to avoid eating meat during the acute phase. The diet includes porridge, vegetable dishes (potatoes in minimal quantities), and fermented milk foods.
During the lull of the disease, it is allowed to consume low-fat meat broths, peas, lettuce, cabbage, carrots, and various greens.
For any form of eczema, preference is given to plant and dairy foods due to their beneficial effects on the entire body.
Diet for eczema on hands and feet
Skin disease on the legs is often caused by a violation of water and salt balance. The skin becomes very dry. Thus, in addition to diet, it is important to adhere to the drinking regime. To do this, you need to use mineral water “Narzan”, “Arkhyz”, “Borjomi”. You should drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day, adding to this amount fresh juices, green tea and other permitted drinks.
As for the diet for hand disease, you need to include protein foods, as well as foods that contain a predominance of iron and iodine. These are parsley, cucumbers, carrots and others. You should definitely add folic and ascorbic acid, vitamins B, E, A to your diet, which promote rapid healing and restoration of the skin.
Microbial species
The diet for microbial eczema, like all others, involves the consumption of dairy and vegetable products. Chocolate, carbonated drinks, coffee, cheese, salt, as well as alcohol and spices are prohibited. The patient is recommended to include corn, nuts, garlic, peas, etc. in the diet. However, it is important to remember that all these products are prohibited during an exacerbation of the disease. The basis of the daily diet is vegetable soup, porridge without milk, steamed meatballs, river fish and fermented milk products. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water daily.
Diet for hand eczema: menu
With lesions of the hands and fingers, in addition to pain, there are also aesthetic inconveniences. Often the signs are weeping areas of the skin resulting from inflammatory processes, as well as disturbances in water and salt metabolism. In this case, the diet involves avoiding foods high in carbohydrates. It is necessary to include lean meat, milk, and vegetables in your diet. It is advisable to add as little salt as possible during cooking. It is important to stick to fractional meals. The liquid must be present in unlimited volume.
For breakfast you should cook porridge or eat cottage cheese with sour cream. Vegetable salads or fruits are suitable for a snack. For lunch, you can treat yourself to meat dishes (meatballs, steamed cutlets, etc.), not forgetting about soups. For dinner you can cook fish and make a vegetable salad.
Hand eczema
The diet for hand eczema excludes spicy, fried sweet foods, as well as semi-finished products and various canned food and preserves.
During an exacerbation of the disease, it is recommended to completely abstain from meat and prefer vegetarian food, and as side dishes, eat vegetables cooked without fat (with the exception of potatoes).
In addition, it is necessary to abandon all types of pasta. During the period of remission, the diet for eczema on the hands allows the inclusion of meat products (rabbit, beef, turkey), as well as lean fish.
To compensate for vitamin deficiency, it is recommended to include fresh carrots, lettuce, cucumbers, dill, celery and parsley in the diet. Often, eczema on the hands is accompanied by the formation of weeping areas of skin due to improper metabolism. If such symptoms develop, it is recommended to completely avoid carbohydrates and replace them with dairy products and fresh vegetables.
Avoid eating gas-forming foods (beans, cabbage, beans, soda, etc.). It is advisable to cook food without salt, steam it or bake it without adding oil. The diet for hand eczema does not limit fluid intake, so it is recommended to drink clarified juices from green fruits and vegetables, milk and clean water.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema
If patients are prone to allergic reactions, with eczema they simply need to follow a hypoallergenic diet. Its principle is to exclude from the diet foods that cause rash, irritation, itching and other similar manifestations.
The list of highly allergenic products is supplemented by:
- egg white;
- fish of the sturgeon family;
- milk;
- beet;
- chocolate, honey and many other sweets;
- coffee.
Below are products with average allergenic activity:
- peas, rice, corn;
- potatoes, bell pepper;
- cranberry, apricot;
- rabbit, turkey, lean pork.
Low allergenic activity is distinguished by:
- green apples;
- pumpkin;
- horse meat and lamb;
- gooseberry;
- prunes;
- watermelon;
- leaf salad.
If the patient has an acute stage of illness, it is necessary to include in the diet a list of products from the last group. In other cases, it is allowed to use ingredients from the second group. As for highly allergenic foods, it is advisable to avoid them until complete recovery.
Proper nutrition for eczema (psoriasis, dermatitis, allergies) plays a big role. Some experts indicate that you can get rid of the disease only with the help of diet, without resorting to drug treatment.
Making a diet
Must-have products
- Fish. If the disease is mild, it is allowed to eat fish. Please note that this should not be done in case of exacerbation.
- Fruits. It is best to prefer fresh juices; with their help you can improve your intestinal microflora. For severe forms of eczema, it is recommended to dilute juices with water: 100 ml of juice + 200 ml of warm water.
- Porridges help cleanse the body and fill it with the necessary amount of energy. It is recommended to include oatmeal and buckwheat in your diet. Please note that oatmeal is a kind of scrub for the body. But buckwheat improves blood condition and enriches the body with iron. If you consume porridge in sufficient quantities, you will not only protect yourself from eczema, but also from anemia.
Diet for eczema, useful advice from nutritionists
Eczema is a dermatological disease that occurs against the background of general dysfunction of the endocrine and nervous systems of the body. The disease is chronic, recurrent, and is not transmitted by contact. One of the reasons for the manifestation of pathology is genetic predisposition, so children whose parents suffered/suffer from dermatoses automatically fall into the risk group. Since the disease is neuro-allergic in nature, nutrition for eczema is very important. Following the advice of nutritionists, which involves eliminating certain foods from the diet, helps reduce the symptoms of the disease and achieve significant remission.
The article provides information about the clinical picture of the disease, its main symptoms, and also describes in detail what the diet should be for eczema in adults and children, and what foods should not be eaten with eczema. In addition, the material contains a table of foods that you can eat if you have eczema.
This is interesting: Pumpkin seeds for worms: how to take for children and adults? Reviews
Additional Information! According to statistics, every 15 children and every 30 adults on the planet are affected by eczema. The disease is considered relatively young, however, despite this, it has a number of cardinal features that distinguish it from other skin pathologies.
Dermatologists began to identify eczema as a separate disease relatively recently, so at the moment there are a number of issues that require additional research. So, the exact cause of eczema has not yet been established; this area is quite relevant.
Foot treatment
A diet for eczema on the legs involves excluding from the diet semi-finished and perishable foods that contain complex fats. These include meat pates, salads, baked goods, sweets, lamb and pork.
When eczema worsens, it is recommended to include vegetable soups, fermented milk products and porridges cooked in water in the menu. In addition, during the first 2-3 days of an exacerbation, when the limb is very itchy and bothers the patient, it is advisable to unload the body by consuming exclusively fruit juices diluted in equal proportions.
It is preferable to eat boiled turkey, rabbit, lean beef and lean fish. A nutritionist will give recommendations on what you can eat if you have eczema after the condition has normalized. It is necessary to consult him periodically to correct nutrition.
The daily menu should include foods with a low fat content. Peas, fresh cucumber, cabbage, beets, carrots and zucchini have a positive effect. It is advisable to eat salads. They contain vitamin C, as well as essential microelements.
It is recommended to fill your daily meals with whole grains and avoid the consumption of alcoholic beverages, tea and coffee.
Clinical picture of eczema, how the disease manifests itself
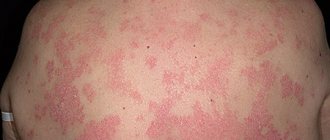
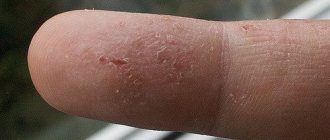
Eczema belongs to a number of dermatological diseases, manifests itself in the form of rashes on the skin, which, if left untreated, can grow. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of vesicles filled with clear liquid, which over time begin to peel off, then become crusty and burst. At the site of the cracks, weeps form, causing particular discomfort to the patient and requiring immediate treatment. Advanced forms of pathology can lead to the development of complications in the form of a bacterial infection.
Additionally, you will need to consult with a nutritionist, the latter will help you create a diet for eczema (menu).
Symptoms of the disease
- the affected areas change color and become warmer compared to other areas of the skin;
- in places where the disease is localized, a rash appears, accompanied by burning and itching;
- vesicles filled with a transparent substance form on the skin;
- problem areas become covered with a crust, after a certain time it cracks, and weeping appears in place of the vesicles;
- The patient's general condition worsens, body temperature rises.
Species classification of eczema
When eczema is detected, a diet for eczema is prescribed depending on the symptoms, type and stage of the disease. External agents are especially popular, in particular ointments and creams, as well as antiseptics, antihistamines and corticosteroids. If a bacterial infection occurs, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Before prescribing the drug, the dermatologist examines the patient and interviews him. This helps to make the correct diagnosis, determine the type of eczema and choose the appropriate course of treatment. A nutritionist will help you create a diet for eczema in a table.
Remember! Self-medication is not allowed when fighting eczema; you can take medications only after consulting a dermatologist. Self-treatment may lead to a deterioration in the patient’s overall health.
Types of eczema
- True eczema. The causes of the manifestation are usually associated with internal malfunctions, for example, such as disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid disease, vegetative-vascular dystonia, diabetes mellitus. In some cases, a predisposition to pathology is inherited;
- Atopic eczema occurs in patients suffering from food allergies. With this type of eczema, the patient’s daily diet is of particular importance; the patient is advised to adhere to the rules of a gentle diet and pay attention to what foods cannot be eaten with eczema, and to exclude allergens from the diet. The list of irritants that can cause such a reaction is determined by the doctor as a result of diagnostic measures;
- Microbial eczema. Accompanied by microbial and fungal infections of the epidermis. The pathology is characterized by constant burning and itching.
Treatment of eczema with nutrition.
Eat anti-inflammatory foods.
Many doctors know that food can cause eczema, and have long used it to treat patients with eczema.
In 2009, John Pegano’s book “Treatment of Psoriasis” was published in Russia, one chapter of which, namely “Eczema in Children,” is devoted to the treatment of eczema.
Here's what Dr. John Pegano wrote: “The main cause of eczema is an excess of toxins in the body, regardless of the patient’s age. Poor bowel movements and poor nutrition are the main causes of the disease. Most often there is a combination of both.”
If a person is already following a diet of organic fruits and vegetables, meat from animals that have grazed on meadows, but still has symptoms of eczema, then there is reason to suspect a sensitivity to one or more foods.
For people with eczema, the most common trigger for the condition is eating foods that cause inflammation, according to experts.
1) It is recommended to eliminate these foods from your diet:
- gluten,
- corn,
- soy,
- dairy products.
2) It is recommended to increase the amount of foods high in antioxidants (mainly fruits and vegetables) and anti-inflammatory compounds (found in fatty fish, nuts, avocado and turmeric) in your diet.
3) Experts point out that animal meat and poultry fed corn and soybeans could cause eczema.
To avoid this, you need to use meat from animals that graze on pastures and do not eat corn and soy.
Several studies have shown that diets high in fruits, vegetables and fatty fish are associated with a lower risk of developing eczema, while diets high in processed foods increase the risk.
Eat foods that are low in histamine.
If a person uses an anti-inflammatory diet, but eczema does not go away, foods high in histamine should be excluded from the diet.
Antihistamines are familiar to many people; they quickly provide relief from allergy symptoms, but are not harmless to the body.
This is because histamine's role in the body is to cause an immediate inflammatory response.
Histamine can enter any organ through the blood: intestines, lungs, skin, brain. Therefore, it contributes to a wide range of symptoms, including eczema.
A number of healthy foods that a person can eat regularly, including avocados, eggplant, spinach, tomatoes, bacon and dried fruits, contain histamine or promote the release of histamine in the body.
To learn more about histamine intolerance, how to change your diet to minimize histamine levels, reduce histamine exposure, I recommend reading this article "Histamine Intolerance"
3. It is necessary to treat the intestines.
As you know by now, what happens in your gut has a huge impact on your immune system.
Scientists believe that 80% of our immune system is located in the gut.
This is why one of the main causes of autoimmune diseases, including eczema, is poor functioning of the intestinal tract.
A healthy gastrointestinal tract is a barrier that prevents undigested food particles, germs, toxins and other unwanted substances from entering the bloodstream.
When the cells lining the intestinal wall are damaged, unwanted substances are able to “leak” from the intestines into the bloodstream, where they are attacked by the immune system, leading to inflammation.
The inflammatory response is initiated by an overactive immune system, and it can occur anywhere in the body.
In the case of eczema, it is the skin that becomes inflamed.
Gut inflammation caused by leaky gut can also compromise the skin's protective function, which can increase the severity of inflammation and worsen eczema symptoms.
Fortunately, leaky gut syndrome can be treated using functional medicine.
1) Remove from your diet what is bad for the intestines:
- foods that cause inflammation
- proliferation of bacteria and yeast, parasites and other irritants.
2) Start taking something that is good for your gut.
- digestive enzymes,
- HCL and other components for good digestion,
But this may not be enough.
3) Take beneficial bacteria supplements back into your system.
4)Repair the intestinal wall by supplementing nutrients to promote healing.
You can read more about leaky gut in the article “The True Causes of Autoimmune Diseases.”
Diet for various types of eczema: prohibited and permitted foods
For eczema (dry, weeping, tilotic, seborrheic, varicose, mycotic, idiopathic, occupational, microbial, pediatric), the doctor always selects an appropriate diet, because this is an integral part of successful treatment and long-term remission. The diet has to be changed completely, and during the period of exacerbation, nutrition is subject to even more strict correction. With constant implementation of the recommendations, it is possible to achieve a weakening of symptoms, as the body begins to function normally.
What foods should you avoid if you have eczema? What menu does the diet suggest for eczema in adults and children on the hands, feet and other parts of the body?
What to eat and what not to eat
Nutrition for eczema should be balanced and include healthy foods, vitamins and minerals. The main emphasis is on protein and plant foods. It is allowed to eat lean meat, fish, vegetables, cottage cheese, kefir, and yoghurt.
Exclude from the diet all fatty foods, sweets, baked goods, instant foods, and full-fat milk.
During an exacerbation period, berries and nuts are prohibited. Potatoes are allowed in moderation.
During the treatment period, special attention is paid to cosmetic products and compliance with hygiene rules.
A diet for eczema helps normalize metabolism and speed up the process of cleansing toxins. With proper nutrition, a person can cope with the disease without treatment with pills.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema on the hands and feet
There is eczema that develops after eating certain foods. Such an allergic reaction is not the most rare occurrence in sensitive people, so it is better to identify in advance what food intolerance is manifested.
It is convenient to do several tests to scientifically confirm or refute an allergy to a particular food. This recommendation is also useful because a hypoallergenic diet should always be individualized, adjusted to the characteristics of your illness and your own body.
A famous doctor in this video will talk about the features of a diet for eczema:
Product selection
Be sure to exclude from the diet foods that are allergens and can provoke an outbreak of the disease. These include:
- fat meat;
- coffee;
- spicy food;
- tomatoes;
- garlic;
- sweets;
- nuts;
- baking;
- smoked meats;
- citrus;
- whole milk;
- any fried food;
- strawberry;
- grenades;
- melon;
- wheat;
- beet;
- honey.
It is advisable to eat hypoallergenic foods, but the diet can be supplemented with foods that are moderately allergenic. You only need to exclude those names that provoke worsening of eczema symptoms. For convenience, use the eczema diet chart below.
Average allergenicity
Completely hypoallergenic
Substitutes for harmful products
Important Features
The total duration of the diet is determined by the doctor, but the standard period during which it is maintained is 3 weeks. Prohibiting certain types of foods does not mean that the patient must fast. On the contrary, an inadequate diet will also aggravate the manifestations of eczema. Therefore, you should adhere to reasonable limits without cutting back on the amount of nutrients and microelements.
- To avoid relapses of the disease, it is advisable in the future to consume as little food as possible that is included in the category of allergens. However, eating a small amount of them is still allowed, but only every 3 days.
- For eczema of the legs and arms, you should eat enough greens, carrots, rutabaga, cucumbers and other vegetables.
- It is imperative to choose other suitable dishes that increase hemoglobin and compensate for the lack of levels of vitamins PP and group B.
- In the most difficult cases, under the guidance of a doctor, products with moderate and low degrees of allergenicity are gradually abandoned.
- It is useful to additionally keep a food diary so that, together with the doctor, you can figure out what should be completely excluded. Supervision by a professional with such a strict diet is very important, otherwise there is a high risk of harm to health.
Next, we have selected nutritional (diet) tips for you in the treatment of various forms of eczema, which, according to reviews, are the most effective.
Nutritional features for various forms of the disease
For microbial
For microbial eczema, the basis of the diet (nutrition) is vegetable and dairy products. The doctor determines everything that needs to be excluded. The following are almost always prohibited:
It’s better to build your menu around steamed and boiled food.
- Low-fat cutlets, fish and meatballs, dairy products, vegetarian soups and water-based porridges are allowed.
- All kinds of spices and salt will also need to be excluded, but if the food seems bland, then you can use various greens.
- Water is replaced with mineral water, but exclusively without gas. Maintaining water balance is very important, and this means that you will have to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water.
For allergic
Therapeutic nutrition allows you not to overload the body with other foods that aggravate the symptoms of the disease, so at the stage of exacerbation you should immediately switch to a diet. During remission, it is recommended to repeat it periodically for 1-2 weeks, which allows you to achieve a sustainable positive effect over a long period.
This is interesting: Castor oil for parasites (worms): how to take for adults and children, reviews
Recommendations for allergic eczema are:
- The menu should include fermented milk products, grain breads, herbs, fruits (only light ones!). It is allowed to include refined oil, lean meat, and water-based porridge.
- During an exacerbation, do not eat seafood, fatty foods, sweets, mushrooms, red berries, grapes, nuts, or sausage.
- Full-fat milk and all kinds of products made from it, semolina and pasta are consumed, but in very small quantities.
You will learn further about what kind of diet suggests dry dyshidrotic eczema.
Experts will talk about a plant-based diet as a way to overcome eczema in the video below:
- If you have dry type of eczema, it is highly recommended to study the principles of vegetarian nutrition, since it is desirable that the main dishes on the menu be of plant origin.
- During remission, it is allowed to supplement it with protein dishes. Along with lean meat, they eat weak broths, casseroles, and soups.
- Porridge should be present in the daily diet, as they have a beneficial effect on the general condition and support the activity of the stomach.
- You should reduce your consumption of potatoes and seafood. But eating river fish is highly recommended, but, of course, not fried.
- Vegetable juices should be prepared daily. Carrot fruit has a particularly good effect on health. For variety, you can combine several vegetables or add permitted sweet fruits. It is the juice that contains a concentrated amount of vitamin substances, and most of all the body lacks B vitamins, so it is advisable to choose vegetables that contain them.
Dry eczema is sometimes accompanied by hypertension. A moderate diet does not overload the heart, but you should still inform your doctor about this phenomenon in order to prevent its progression.
For chronic
Any eczema is an exclusively chronic disease, only in some, under the influence of various irritants, it recurs much more often. It is required to adhere to the principles of hypoallergenic nutrition to prevent constant exacerbations. We talked above about which foods should be completely excluded.
It is best to avoid drinking alcohol throughout the diet. If the body is weakened by a long course of the disease, the doctor will not only recommend a certain diet, but also prescribe vitamin supplements.
Let's find out further what diet is required for weeping eczema.
When wet
This type of eczema is considered one of the most unpleasant, as wet areas require constant treatment. Bacteria can always get into constantly forming cracks and abrasions, which means that the disease will also be complicated by purulent inflammation. Because of this, the diet for weeping eczema is very strict, implying a categorical refusal of any food that can provoke an attack. Indeed, even a small portion of the prohibited product eaten can cause a strong surge in symptoms.
- Fruits and vegetables are almost always welcome in the diet, but in this case it is very important to exclude everything sour: kiwi, citrus fruits, apples. Watermelons and melons should also not be eaten.
- Food must be natural, preferably prepared independently, so dinner options made from semi-finished or instant products are strictly excluded.
- It is better to compensate for protein deficiency with plant components, cottage cheese. Lean meat is also allowed, but you should not eat more than 200 g of it daily. The diet is supplemented with river fish, cereals, and light soups.
- You can prepare recipes from vegetarian cuisine, but do not forget that the use of spices is kept to a minimum.
With any type of eczema, you can diversify your diet; you don’t have to eat exclusively bland food. Find suitable recipes, modernize them, use various herbs instead of salt and usual spices. This way your menu will be delicious, and the symptoms of the disease will gradually disappear.
The video below will tell you about the features of treatment and diet for facial eczema:
Healthy foods for eczema
If you eat right, it always contributes to a speedy recovery, relieving exacerbations of the disease and establishing stable remission.
Food should only be boiled and low-fat.
In first courses, preference should be given to soups with meat or fish broth. The meat should be light and boiled or steamed. Preference should be given to lean, light and dietary meat. For example, rabbit meat, turkey meat, lean beef, and chicken are good options.
You can eat boiled fish if it is fresh and fresh.
Various porridges are useful: barley, buckwheat, wheat, oatmeal, as they are rich in minerals and vitamins.
Cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir, fermented baked milk can be eaten in unlimited quantities.
Features of nutrition for eczema on the arms and legs ^
Most often, eczema appears on the arms and legs, and its symptoms depend on the specific type:
- Idiopathic: hyperemia, swelling at the site of the lesion, peeling;
- Microbial: inflammation, purulent crusts and erosions form around scratches and abrasions;
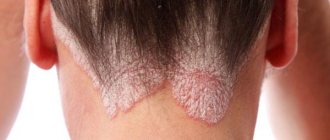
- Mycotic: its symptoms are combined with a fungal infection of the skin, and it is also characterized by weeping blisters, itching and rash;
- Seborrheic: Occurs mainly on the scalp, ears, face and chest. Manifests itself in the form of flaky yellow spots, which eventually form into plaques;
- Dyshidrotic: appears on the palms and soles in the form of blisters;
- Callosal: affects the palms and soles when blisters form on them that look like calluses;
- Varicose veins appear in the area of dilated veins in the form of an itchy rash.
Many factors can contribute to the appearance of such a disease: hereditary predisposition to allergies, weak immunity, dermatological diseases, hormonal imbalances, skin lesions of a chemical, thermal or mechanical nature.
Regardless of the form of the disease, it is necessary not only to start treatment in a timely manner, but also to rebuild your diet, and the question of whether a diet is needed for eczema is quite relevant. It is needed at a minimum because a person’s health depends on what he eats, and he can only get all the necessary vitamins and microelements with food.
Therapeutic diet for eczema: recommended foods
The diet for patients with eczema should be based on the following principles:
- During remission, to prevent exacerbation, it is advisable to eat watermelons, pumpkin, zucchini, watermelons, currants, gooseberries, lingonberries, cranberries;
- During an exacerbation, the menu should be dominated by plant foods: fruits, vegetables, cereals, herbs, as well as fermented milk products. Smoked meats, salty and spicy foods, milk, sweets, citrus fruits, canned food, pork, eggs and processed foods should be excluded.
By following a therapeutic diet for eczema of the hands and other parts of the body, you can significantly prolong remission, and exacerbations will bother you much less often and you can forget about the disease even for years.
Diet features
The diet for eczema includes plant and protein foods. All dishes are steamed, boiled or stewed. Various vitamins are added to the menu to speed up metabolic processes.
For chronic eczema on different parts of the body and on the face, there are dietary features that need to be taken into account.
Upper limbs
Eczema on the hands brings certain inconvenience to the patient physically and mentally. Damage to the hands is accompanied by itching and pain. By following proper nutrition, it is possible to avoid relapses of the disease.
Diet:
- The food includes lean meat products and fish. Vegetable side dishes are chosen; potatoes are eaten in minimal quantities. Pasta is excluded.
- You should eat more vegetables and fruits, herbs, especially dill.
- The amount of liquid is not limited.
- Limit the amount of salt consumed.
The diet for eczema of the hands is followed until complete recovery. In the future, they adhere to an approximate diet, excluding allergenic substances.
Lower limbs
Eczema on the legs requires following a proper diet. Vegetables, fruits, and dairy products are included in the diet. Meat is chosen from low-fat varieties, as is fish. All dishes are steamed or stewed. Be sure to eat various types of cereals - buckwheat, oatmeal, wheat.
During the first days of the acute phase, it is better not to eat food, but to drink juices from various fruits with the addition of water.
The diet for eczema on the hands and feet completely excludes the consumption of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
Meals for adults
Diet for adults includes all aspects of nutrition described above. Patients are recommended to eat more proteins and plant foods, give preference to vegetables and fruits, and foods containing unsaturated fatty acids.
Fried, fatty, smoked foods, and marinades are excluded from the diet. Hot spices, coffee, foods containing sugar, and baked goods are prohibited.
The diet for children is almost the same. The most suitable diet is selected in each individual case.
Diet for eczema: menu and features of therapeutic nutrition ^
Does a diet for eczema help achieve stable remission of the disease: reviews from doctors
Diet rules for eczema:
- Since eczema is most often a chronic disease, to maintain remission the diet must be followed throughout your life;
- You should remove from your menu all foods that can cause aggravation.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema
This diet option is suitable for all patients, and it is allowed to consume hypoallergenic foods in unlimited quantities, and limit food with more harmful allergenicity:
- Hypoallergenic: turnips, horse meat, lamb, gooseberries, squash, zucchini, prunes, bananas, plums, apples, watermelon, pumpkin, lettuce;
- Moderate allergenicity: green peppers, peas, broccoli, apricots, cranberries, peaches, rabbit, buckwheat, rice, potatoes.
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema
In general, with this form of the disease, it is enough for patients to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and adhere to a protein-carbohydrate menu, but if there are weeping erosions on the skin, the following products should be excluded from it:
Dairy-plant diet for eczema
This diet option is suitable for everyone, but it is recommended to consult a doctor before using it. What you can use:
- Low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream, kefir, yogurt;
- Porridge, fruits, vegetables, herbs;
- Fruit and vegetable natural juices.
Diet for dry eczema
To avoid exacerbation of dry eczema, you need to avoid a number of foods:
- Citrus fruits, strawberries, bananas;
- Eggs;
- Red fruits, vegetables and berries;
- Sweet pastries and chocolate.
Dyshidrotic and microbial eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema is often localized on the skin of the feet and hands. It is characterized by the appearance of rashes filled with serous substance. The bubbles burst and dried crusts appear. Intense itching and irritation are noted.
The menu for true eczema is drawn up by the attending doctor. Citrus fruits, alcoholic drinks, sweets, honey, smoked and pickled foods, and fast food are removed from the diet. Choose only lean meat; it is better to limit salt to a minimum.
For wet eczema, a dairy-vegetable diet is indicated. The consumption of fermented milk products, fruits, vegetables, and low-fat soups is allowed.
Microbial
It occurs as a result of harmful pathogens entering eczematous wounds. Blisters, cracks, and wounds are noted on the skin. The patient experiences severe itching.
The diet for microbial eczema is based on the consumption of large quantities of curd products, yoghurt, and kefir. Meat is allowed baked. It is allowed to eat varieties of fish with low fat content. A variety of plant foods and vegetable decoctions are included in the diet.