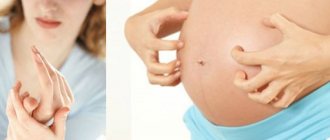
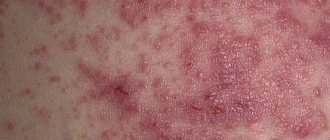
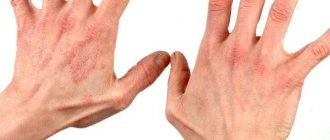
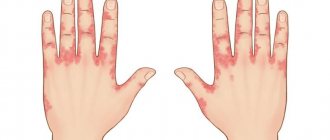
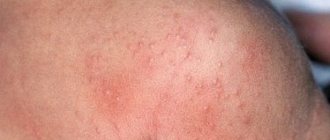
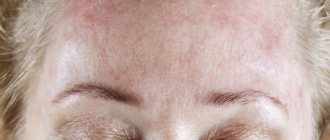
Why does dermatitis occur?
First, let's figure out how atopic dermatitis develops and what are the main reasons for its occurrence.
The main factor in diagnosis is the inheritance factor of predisposition. But something can cause an exacerbation, which subsequently manifests itself as a rash and peeling:
- household chemicals;
- food allergens;
- harmful effects of the environment;
- cosmetics and more.
Dermatitis is a class of inflammatory diseases of the skin of the face and body. Factors of the disease are food allergies, hereditary causes and the development of bacteria and fungi.
The disease can be chronic or acute. The first type is characterized by periods of exacerbation when exposed to external stimuli.
In the second case, typical symptoms are itching and redness, runny nose and fever.
The causes of dermatitis relate to various irritants, which can be either external influences or congenital characteristics of the body.
If you clearly know what exactly leads to such skin diseases, this will allow you to determine whether you can become infected with a certain type of dermatitis or not.
Skin damage occurs for one of these reasons:
- Exposure to the skin of irritating substances - toxins, acids, alkaline solutions, chemical household products, as well as the juice of poisonous plants.
- Mechanical influence leading to skin injury and cracks.
- Temperature changes and increased doses of ultraviolet radiation can cause disruption of cell function and even death.
- Excessive psychological stress over a long period can also become a prerequisite for the appearance of skin diseases.
- An increased reaction of the skin to certain allergic substances that come into contact with the surface of the skin or enter the body.
- Metabolic disorders, such as vitamin deficiency or endocrine diseases, can manifest themselves in the form of skin rashes.
- An individual characteristic of the body, expressed in the form of a hereditary predisposition to dermatitis.
- Infection, which can result in rashes of typhoid, rubella, smallpox or measles. Most often, pathogenic pathogens are microorganisms from the group of streptococci or staphylococci, as well as bacteria that cause pseudotuberculosis disease.
By examining the causes of skin rashes, you can see that almost all of these manifestations are independent diseases and are not transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one.
But if a patient develops infectious dermatitis, is it possible to become infected? In this case, this is possible, and this is the only reason when the disease can be transmitted from one person to another.
Types of dermatitis
The skin's response to any damaging factor may be the development of dermatitis.
The disease has several types:
- Allergic (toxic) dermatitis. The disease manifests itself after exposure to a specific allergen, which enters the body through the respiratory tract and stomach. Most often, a food product acts as such an irritant, so unpleasant symptoms can be easily eliminated by eliminating such food from the diet. If the provoking factor for dermatitis is a chemical irritant or a household allergen, then medications must be used to get rid of skin problems.
- Seborrheic. The cause of this type of skin disease is mainly endocrine or trophic changes that disrupt the functions of the sebaceous glands. This pathology often becomes chronic. The location of inflammation is the face, part of the head with hair, and neck. According to many experts, the source of the disease can also be a fungus, which under favorable conditions begins to multiply intensively.
- Atopic. This type of dermatitis is often a manifestation of a hereditary predisposition. The rapid spread of atopic disease is considered to be a consequence of incorrect treatment tactics, as well as a complete lack of therapy.
- Contact. This type of dermatitis develops upon contact with a specific irritant. As a result of this interaction of a negative factor with the surface of the skin, an inflammatory process begins.
- Medication. This dermatitis is a consequence of taking certain medications (antibiotics, drugs with novocaine), which cause a similar reaction in the body. As a rule, the disease recedes almost immediately after discontinuation of therapy with these medications.
Causes of dermatitis
Inflammation of the skin (or dermatitis) raises a natural question among others - whether it is contagious or not. Dermatitis is a term used to describe various skin disorders that cause inflammation and red, itchy rashes.
The condition is not life-threatening and is not transmitted from one person to another, although it may have a family history.

Are infectious agents found as the root cause of dermatitis? Let's look at this using the example of several forms of the disease. Theoretically, seborrheic dermatitis could be suspected of being contagious, because it actively multiplies the fungus Malassezia furfur.
But this fungus is not an infectious agent, as it is found on the skin of absolutely healthy people. Several reasons lead to its rapid growth.
This includes hormonal dysfunction of the body caused by improper functioning of the endocrine system, and problems and malfunctions in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
The development of the disease is also facilitated by a weakened immune system, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, stress and medication.
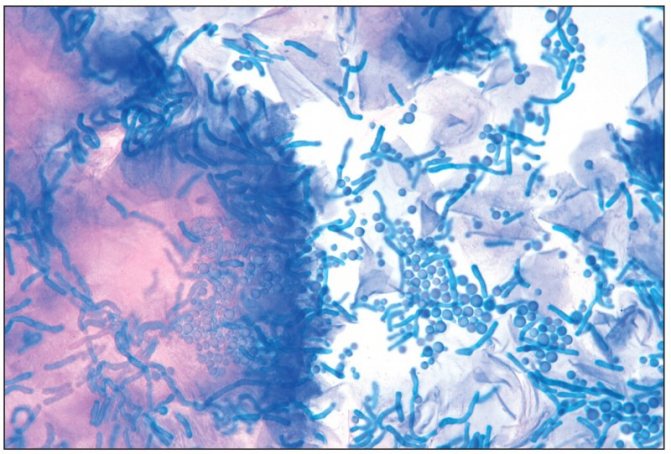
The fungus Malassezia furfur actively reproduces in seborrheic dermatitis, but is not contagious, because is present in absolutely all people
The allergic form of dermatitis is more common in people suffering from various forms of allergies. There is no bacterial or fungal nature of the pathogen here at all.
Allergen in the form of pollen, animal hair, etc. is the cause of this type of disease. And, yes, you can “get infected” with it through direct contact with the allergen.
But only if an allergic person comes into contact with the allergen. There is absolutely no chance of getting infected from another person.
Reasons for appearance
Dermatitis is the body's reaction to an external irritant. Most often, the irritant is an allergen, which can enter the body in several ways. Most often this occurs through food into the digestive tract, as well as penetration into the respiratory tract. Also, a negative effect can be exerted directly on human skin, then the disease manifests itself in a very pronounced form.
When an allergen enters the body, a lightning-fast reaction occurs. The immune system signals mast cells that there is an enemy inside. As a result, they begin to actively produce histamine. This substance causes an extensive inflammatory reaction, which manifests itself in humans as allergy symptoms.
Allergens can be of several types:
- Epidermal (pet hair).
- Chemicals (cleaning products, cosmetics, chemical additives).
Not every person experiences unpleasant symptoms when exposed to these substances. There are predisposing factors:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Early refusal of breastfeeding.
- Incorrect maternal diet during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Poor environmental conditions.
- Bad habits, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet.
- Congenital pathologies of the immune system and chronic diseases.
If a person is healthy, he does not have bad habits or chronic diseases, he is unlikely to become allergic and will struggle with dermatitis and other manifestations.
Dermatitis is a problem for people suffering from allergies.
How the disease is transmitted, besides the genetic path, you and I will be able to understand when we figure out how it develops. Dermatitis is the immune response to an irritant.
The latter can be various allergens or histamines, which we listed above. It can be ingested either through food from the inside or externally.
Inflammation of the skin (or dermatitis) raises a natural question among others - whether it is contagious or not. Dermatitis is a term used to describe various skin disorders that cause inflammation and red, itchy rashes.
Are infectious agents found as the root cause of dermatitis? Let's look at this using the example of several forms of the disease. Theoretically, seborrheic dermatitis could be suspected of being contagious, because it actively multiplies the fungus Malassezia furfur.
But this fungus is not an infectious agent, as it is found on the skin of absolutely healthy people. Several reasons lead to its rapid growth.
This includes hormonal dysfunction of the body caused by improper functioning of the endocrine system, and problems and malfunctions in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
The fungus Malassezia furfur actively reproduces in seborrheic dermatitis, but is not contagious, because is present in absolutely all people
The allergic form of dermatitis is more common in people suffering from various forms of allergies. There is no bacterial or fungal nature of the pathogen here at all.
Allergen in the form of pollen, animal hair, etc. is the cause of this type of disease. And, yes, you can “get infected” with it through direct contact with the allergen.
Symptoms and treatment of dermatitis in adults and children (photos, videos)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iB9TUj6q-Sg
Allergies again?!
Any allergy will go away forever in a week! Why was a cheap remedy that has long been used in Europe banned in our country?
Read more...
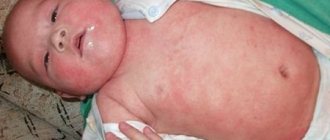
A person with dermatitis looks completely unattractive and even repulsive. Itching and blisters appear on the body. Therefore, everyone is afraid to touch such a sick person, so as not to get infected from him. People usually avoid all contact with him. Sometimes it manifests itself in children. The disease has three phases:
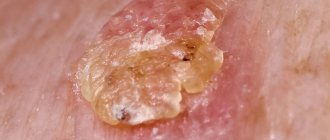
- Spicy. Bubbles of various sizes quickly form on the patient’s skin, which burst and become wet. They can appear anywhere: on the face, ears, eyes, legs, arms.
- Subacute. After the bubbles burst, crusts form.
- Chronic. The skin becomes thick and changes color to red-violet.
The appearance of dermatitis is explained by the influence of various factors, which are usually divided into 2 groups: internal and external.
Internal reasons:
- Hormonal surges;
- Vitamin deficiency;
- Scleroderma;
- Heredity;
- Decreased immunity.
- Stress;
- Metabolic disorder.
External factors are characterized by the influence of such stimuli as:
- Mechanical;
- Biological;
- Physical;
- Chemical.
Common external causes include:
- Wrong lifestyle;
- Solar radiation;
- Food irritants;
- Household chemicals;
- Ionizing radiation;
- Construction Materials;
- Temperature difference;
- Poor quality cosmetics.
Dermatitis is a disease shrouded in many myths and conjectures. To reliably understand whether dermatitis is contagious to other people, it is important to understand the mechanism that triggers the body’s inadequate reaction. There are several main types of disease:
- atopic;
- contact;
- seborrheic;
- infectious.
In each case, the reasons that cause the skin reaction are different, but the leading role is played by a malfunction in the immune system. Dermatitis is a consequence of the negative impact of external factors and ongoing internal disorders.
Dermatitis, which is caused by pathogenic flora, often occurs in young children. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system. But such a disease, under the influence of a number of factors, often occurs in adults.
At the moment, all the main causes of infectious dermatitis are known:
- Viral diseases that often occur in childhood (measles, chicken pox, rubella).
- Bacterial coccal flora.
- Candida fungus (rare).
In some cases, dermatitis is observed as a result of damage to the body by sexually transmitted diseases.
Dermatitis usually occurs under the influence of the following conditions:
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- sluggish infectious processes;
- low physical activity;
- physical and psycho-emotional overload;
- anemia;
- long-term use of certain medications (cytostatics, glucocorticoids);
- intoxication;
- violation of hygiene;
- burn or hypothermia;
- failure of metabolic processes and the functioning of internal secretion organs (often found in diabetes mellitus);
- genetic predisposition;
- surgical intervention;
- lack or absence of vitamins and other nutrients;
- poor nutrition or fasting.
Infection occurs through contact and through blood flow from foci of infection.
Human skin is the most important organ designed to protect against environmental influences: overheating, hypothermia, injuries. The produced subcutaneous fat nourishes the skin, thereby protecting it from drying out and the formation of cracks and abrasions. Sweating promotes thermoregulation and the elimination of harmful substances and toxins.
The epidermis takes an active part in all biological processes occurring in the body. It has bactericidal properties, which prevents the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. The pigment, which is produced in skin cells, protects it from sunlight and moisture.
Skin is a kind of indicator of a person’s condition. The appearance of any changes in its condition is evidence of disruptions occurring in the body and leads to a weakening of the protective functions of the skin.
The main causes of dermatitis are biological, chemical, physiological and mechanical factors (individually or in combination).

Exogenous (external):
- temperature conditions (frostbite, burns, overheating),
- mechanical damage leading to damage to the integrity of the skin (abrasions, diaper rash, cuts),
- chemical exposure.
Endogenous (internal):
- decreased immune strength,
- hereditary diseases,
- pathological features of the structure of the skin,
- metabolic disease,
- chronic diseases (stomach, intestines, kidneys, liver, diabetes),
- neurological problems,
- poisoning,
- insufficient or excessive amounts of vitamins,
- unhealthy diet
- hormonal changes in the body (in adolescents and women during menopause, pregnancy and childbirth),
- long-term use of medications (antibiotics, hormonal corticosteroids),
Allergens that provoke skin dermatitis:
- household chemicals,
- pet fur and fluff,
- pet food,
- insect bites,
- plant pollen,
- synthetic clothing,
- jewelry made of poor quality material,
- food.
Types of dermatitis
The causes of the atopic subtype are considered to be heredity, hormonal abnormalities or stress.
Depending on the microbe that caused the skin symptoms, dermatitis may be:
- Gribkov. Most often, skin lesions are caused by the yeast fungus Candida, but this can also be caused by the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor, the fungus Actinomycetes, Trichophyton and others.
- Bacterial. It is caused by streptococci - the causative agents of scarlet fever, impetigo, ecthyma vulgaris, and erysipelas. The causes of such infectious dermatitis can also be staphylococcus - the causative agent of folliculitis, pseudofurunculosis, Ritter's dermatitis, and epidemic pemphigus.
- Parasitic, caused by rickettsia (for typhus), scabies (for scabies).
- Viral dermatitis occurs most often in children. It develops with chickenpox, rubella, enterovirus infection, and measles.
Regardless of the cause of infectious dermatitis, your chances of getting it increase significantly if you:
- hypothermia and overheating;
- microcracks and deeper injuries to the skin;
- diabetes mellitus;
- renal failure;
- immunodeficiency;
- taking glucocorticoid drugs (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Solu-Medrol) or cytostatics (Methotrexate, Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and others);
- varicose veins.
The majority of infectious dermatitis appears on the skin as spots of different sizes and shapes; There are types when the rash is represented by blisters (chickenpox, enteroviral pemphigus).
But if the rash elements are nodules, this is infectious nodular dermatitis. It occurs with furunculosis, the appearance of carbuncles, the syphilitic process, and pseudofurunculosis.
If the infectious process is accompanied by the release of large quantities of histamine and other substances characteristic of allergic diseases, infectious-allergic dermatitis develops.
In this case, spots, nodules or blisters, characteristic of the normal course of the infectious process, become surrounded by redness around the perimeter or are located on an allergy-specific blister, accompanied by itching.
This pathology is more difficult to diagnose; an infectious disease specialist can do this.
Dermatitis is usually called a disorder of the skin due to a certain irritating factor, which leads to the appearance of inflammatory reactions in the body. In most cases, this disease is not transmitted through contact or other means, but there are exceptions in the form of special cases.
According to its characteristics, the disease can be classified into:
The most common are contact (simple), allergic, atopic and seborrheic dermatitis.
CONTACT. This type of disease is caused by aggressive exposure to external irritants (acid, alkali, ultraviolet radiation, etc.). It is NOT SPREAD from person to person.
ALLERGIC. Develops as a result of exposure to an irritant on an organism predisposed to allergies. Like other forms of dermatitis, allergic dermatitis CANNOT BE TRANSMITTED BY CONTACT, and therefore does not pose a danger to other people.
ATOPIC. Atopic dermatitis is an allergic disease and is TRANSMITTED BY INHERITANCE.
However, it should be understood that it is not the disease that is transmitted genetically, but the tendency to develop it. Atopic dermatitis does not have an infectious path of development, therefore it is not transmitted through direct contact.
INFECTIOUS. This form of the disease, like others, despite being classified as infectious dermatitis, is safe for healthy people.
The question is that this type of disease is quite often provoked by various infections, which can easily be transmitted from person to person.
In other words, when a healthy person comes into contact with a patient who has been diagnosed with infectious dermatitis, TRANSMISSION OF VIRUSES AND INFECTIONS of the immediate cause of the disease MAY OCCUR.
It often happens that a person who has this disease does not consider it a disease at all and does not consult a doctor. However, this should be done in order to establish the type of dermatitis, the reasons that caused it and prescribe treatment. There are several types of dermatitis:
Is dermatitis transmitted from person to person and is it contagious?
Dermatitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the skin.
The skin of a person with dermatitis looks scary. Seeing red, inflamed areas of skin, those around you shy away in horror, fearing infection. But is dermatitis contagious or are all fears in vain? Let's try to understand this issue. Many people consider dermatoses to be a childhood disease. Indeed, this skin disease is often observed in children. But adults can also experience manifestations of this disease.
Not everyone knows whether dermatitis is transmitted from person to person. Moreover, most are confident that this disease is contagious, since it is often possible to see that members of the same family are sick. But the point here is not an infection, but a genetic predisposition.
Varieties
To figure out whether you can get infected with dermatitis or not, you first need to understand what types of diseases exist.
Allergic
From the name it is clear that allergic dermatitis is a disease caused by an inadequate reaction to contact with external irritants. The cause of an allergic reaction can be:
- plant factor – pollen;
- house dust;
- pet hair;
- selected food products;
- medicines;
- cosmetics;
- household chemicals.
Manifestations of allergic dermatitis appear only after contact with certain substances. Thus, a patient with allergic dermatitis is not dangerous to others, since allergic reactions are an individual thing.
Advice! But there is a genetic predisposition to the development of allergic diseases, so members of the same family (blood relatives) often get sick.
It is difficult to treat this skin disease; the only effective method is to eliminate the allergen. In this case, skin healing occurs within several days. Remission will continue until new contact with the allergen.
Contact
Contact dermatitis is very similar to allergic dermatitis. The difference between contact skin lesions is that the inflammatory reaction occurs when the allergen comes into direct contact with the skin. That is, the cause of contact dermatitis is synthetic clothing, underwear, as well as household chemicals and cosmetics.
It is impossible to become infected with contact dermatitis, because the disease is not infectious, so it cannot be transmitted even through close contact with the patient.
Atopic
Atopic dermatitis is often a complication of the allergic form of the disease if appropriate treatment is not carried out. However, the atopic variety of the disease can also be hereditary.
The first manifestations of hereditary atopic skin lesions are observed in infancy. But sometimes the disease proceeds secretly, without manifesting pronounced symptoms. The impetus for the development of an inflammatory reaction can be:
- hormonal fluctuations (during adolescence, pregnancy, etc.);
- long-term improper skin care;
- stress, nervous shock.
You should not assume that this is a contagious disease; it is not transmitted from person to person through communication and tactile contact. But dermatitis is inherited, so if parents have this disease, then there is a high probability that their child will develop it.
Seborrhea
Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that affects the sebaceous glands. Under the influence of saprophytic flora, the glands begin to work incorrectly, as pathogenic microorganisms change the composition of their secretions. There are dry and oily seborrhea, these forms differ in symptoms:
- Dry seborrhea is characterized by severe peeling and dry skin;
- oily seborrhea is manifested by increased secretion of sebum, which provokes the development of pustular rashes.
Since the disease is caused by pathogenic microflora, we can conclude that seborrheic dermatitis is contagious. However, it is not. Any specialist, when asked whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious, will answer negatively.
The fact is that saprophytic flora is present on the skin of almost every person, but it does not cause negative changes. The skin and sebaceous glands begin to become inflamed only with uncontrolled proliferation of fungi, which can be triggered by stress, general illness, mechanical or chemical exposure.
Infectious
The types of dermatitis listed above are caused by internal causes, which means that the patient does not pose a threat to the people around him. The allergy will not be transmitted either through direct contact or through the use of shared things, so those around you do not have to worry about their health.
However, there are also infectious dermatitis, the cause of which is an infectious disease. To answer the question of how infectious dermatitis is transmitted, it is worth getting acquainted with its causes. The development of an inflammatory process on the skin can be provoked by:
- infectious diseases - measles, scarlet fever, chicken pox. The course of these diseases is accompanied by characteristic skin reactions. In this case, it is not the skin lesion that can be transmitted, but the infection that caused the disease;
- infection of wound surfaces with a secondary infection (most often staphylococcus or streptococcus). In this case, carbuncles, boils, and abscesses form on the surface of the skin. In this case, the disease can spread to another person through close contact only if the contactee has reduced immunity and has lesions on the skin;
- a disease caused by fungal microflora; the fungal infection itself is contagious, but the disease will develop only if a person has reduced immunity. In addition, a predisposing factor for the development of the disease is increased sweating and constant moisture of the skin.
Prevention measures
How can you prevent contracting an infectious variant of the disease? The main rule is careful personal hygiene. Necessary:
- use personal hygiene items, do not use other people’s combs, towels, etc.;
- Try to strengthen your immune system by leading the healthiest lifestyle possible.
An effective measure to prevent the development of infectious diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes in the skin (measles, chickenpox, etc.) is timely vaccination.
It is impossible to protect against the development of allergic or atopic dermatitis, but patients can take measures to prevent relapses of the disease.
To do this, you need to avoid contact with allergens and strengthen the body.
For allergic and seborrheic dermatitis, an important role in preventing relapse is played by a diet that excludes sweets, fatty foods, and foods that provoke allergic reactions.
Many people have to deal with a disease such as dermatitis: is this skin disease contagious or not? Patients with this skin disease, in most cases, are not dangerous to the people around them, since the disease develops due to an inadequate response of the immune system or other internal reasons.
Source: https://moidermatolog.ru/dermatit/zarazen-li-dermatit.html
Contagiousness of the disease
The answer to the question of whether infectious dermatitis is contagious or not is as follows: upon contact with a patient, a general infectious disease (especially caused by a virus) is transmitted, and not its skin manifestations.
If you interact with the sick person while wearing a mask, touching the elements of his rash with gloved hands, not eating or drinking from the same container, and also provide him with separate towels and place him in a well-ventilated room, the chance of getting sick will be minimized.

How is viral dermatitis transmitted?
It depends on the type of pathology:
- The following are transmitted by airborne droplets (during talking, kissing): enterovirus, measles, rubella infections, chicken pox, infectious mononucleosis.
- Through unwashed hands, particles of feces getting onto the hands, and then into food and food: with enterovirus infection.
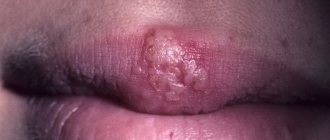
- Infection caused by herpes viruses is transmitted by contact (from touching the elements of the rash).
Dermatitis caused by bacterial and fungal flora and parasites is also transmitted in different ways:
- you can become infected with scarlet fever or meningococcal infection by airborne droplets;
- without washing their hands after interacting with a “sprinkled” patient, they become infected with yersiniosis, pseudotuberculosis, and typhoid fever;
- If you touch the elements of the rash, you can become infected with scabies. If there are microdamages on the hands, both fungal and bacterial infections will be transmitted. In the presence of intact and clean skin, even contact with the contents of boils, carbuncles and other pustular elements passes without a trace for a healthy person.
Is infectious dermatitis dangerous?
It is not the dermatitis itself that is dangerous, but the infectious process that is “raging” in the body at this time. The most dangerous are chicken pox, herpes zoster (can cause brain damage), and meningococcal infection (has a high mortality rate).
Rubella and enterovirus infections are dangerous for pregnant women: they can cause fetal malformations, stillbirths and miscarriages.
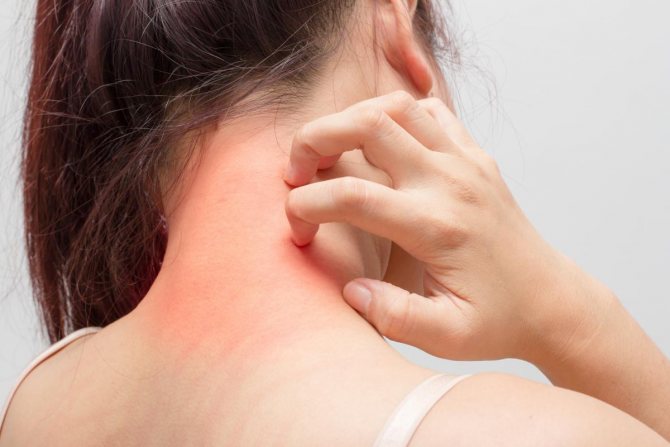
Symptoms of dermatitis
To understand whether dermatitis is contagious, let's repeat what the main symptoms of this pathology are:
- rash;
- peeling;
- swelling;
- redness;
- itching and burning.
Skin manifestations can occur all at once or appear separately.
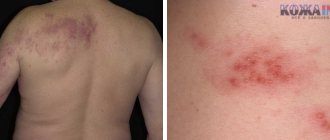
Probably everyone knows that dermatitis manifests itself in the form of redness on the skin. But there are many allergic diseases that have similar symptoms. How to distinguish dermatitis from urticaria or eczema?
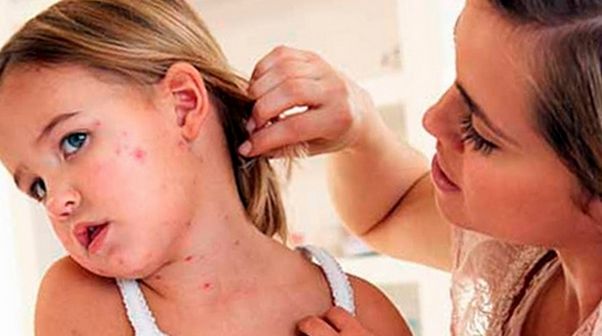
Manifestations of dermatitis depend on factors such as:
- Type of stimulus;
- Skin Features;
- The duration of the negative impact of a specific stimulus.
Main symptoms:
- Itching;
- Peeling;
- Intertrigo;
- Attrition;
- Allergic reactions;
- Chills;
- Ulcerative lesions;
- Red spots;
- Loss of sensitivity in damaged areas of the skin.
Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on the type, area of distribution or stage of dermatitis.
Stages of development:
- Spicy. This period is characterized by the formation of bubbles on the skin, of different sizes and filled with liquid inside.
- Subacute. At this stage, dermatitis is accompanied by the formation of crusts and scales on the affected areas.
- Chronic. During this period, the disease has already become advanced, so the skin thickens, and areas with redness become darker (sometimes even purple).
Treatment of genital dermatitis
Only a doctor knows how to correctly diagnose and how to treat genital dermatitis.
You should consult a doctor if you experience
- Unexplained lesions of the genital organs.
- Changes in the color or shape of the genitals.
- Unbearable itching and burning.
- Suspicion that the infection was acquired through sexual contact.
- Pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding.
- Fever, weakness.
The doctor conducts a survey and diagnostic examination, prescribes a general and differential blood test, a biopsy of the affected area of the skin or mucous membrane. If it is determined that this is genital dermatitis, treatment involves taking antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures and medications for the skin - creams, ointments, solutions. The type of treatment depends on the cause of the disease and may include antibiotics, antivirals and corticosteroids. The course of treatment for genital dermatitis lasts from several weeks to several months.
The causes of dermatitis can be different. Outwardly, it does not look very aesthetically pleasing, so people try to get rid of this disease as quickly as possible. Unlike psoriasis, dermatitis can be cured completely. Many people wonder whether dermatitis is contagious or not. Since the external manifestations of this disease are extremely unpleasant, intuitively some try to move away from people with this problem, experiencing hostility and fears about the contagiousness of the disease.

Effective methods for treating dermatitis
Depending on the type, the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy. It usually consists of antihistamines (if the type of dermatitis is allergic or atopic), antibiotics (for seborrheic dermatitis). For dermatitis of the eyes and ears, special drops are prescribed. For contact dermatitis, special ointments that have a hormonal composition are used. You cannot self-prescribe for yourself or your children with dermatitis. The resulting crusts and blisters should be treated with a special antiseptic solution to avoid the risk of infectious complications.
If you have digestive disorders, you need to take enzymes (Creon, Pancreatin, Mezim, Festal). For sleep disorders, sedatives can be used. Folk remedies are very helpful for various dermatitis. Some use urine treatment to eliminate symptoms. Traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of various dermatitis:
- Decoction of succession. You need to take a tablespoon of dry string grass and mix it with a glass of hot water. After the decoction has infused, you can use it for lotions and dressings. This product soothes the skin well, helps crusts fall off faster, and has antiseptic properties.
- This mixture is excellent for itching and inflammation in dermatitis: baby soap, tar and vegetable oil. Grate soap (100g), mix with two tablespoons of oil and add the same amount of tar. Mix everything and smear the inflamed areas.
- Celandine. This is truly a fantastically beneficial herb. It even helps with cancer. To treat dermatitis, you need to squeeze the juice of this plant. Dilute it half and half with water. Make a bandage and soak in the resulting solution. Apply for ten minutes. Make sure there is no allergic reaction.
- The use of birch tar internally according to a special scheme also has a very effective effect on patients with this disease.
- For eye dermatitis, lotions made from used tea bags help well. They perfectly relieve inflammation and disinfect.
- An infusion of St. John's wort helps relieve inflammation. It is brewed like other herbs and made into lotions.
Preventing dermatitis
To eliminate and minimize the manifestations of a disease, for example, seborrheic or allergic, it is necessary, after consulting a dermatologist, to carry out therapeutic measures.
They should include both external and internal (antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as ointments, creams and gels). Prevention of occupational dermatitis concerns, first of all, safety at work.
This is especially true for protection against harsh, caustic, alkaline or acidic substances. You should consider using protective clothing, gloves and masks (if there is contact with facial skin).
Seborrheic dermatitis on the head requires the use of external agents (shampoos, masks) for special purposes. You can also use traditional medicine recipes.
In particular, you can make decoctions of calendula, birch buds or apply compresses of celandine juice.

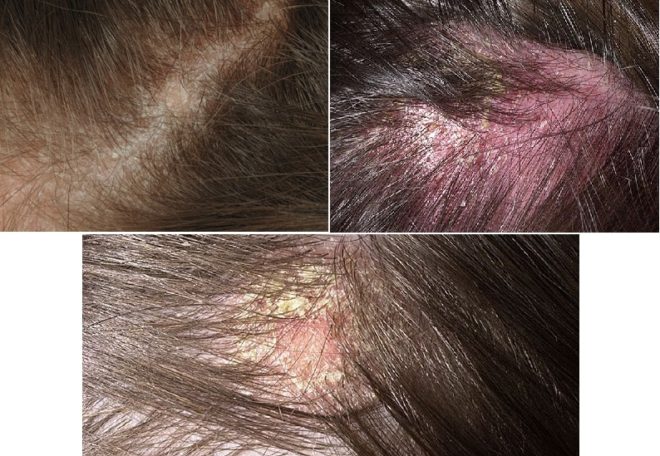
Seborrheic dermatitis on the head requires the use of special-purpose external agents
One of the standard measures to prevent dermatitis is rationalization of nutrition and normalization of eating habits. Doctors advise following a diet, especially if you have a disease.
In general, you should limit your consumption of sweets, sour and sweet foods, exotic fruits, and citrus fruits. Smoked meats, fast food, baked goods, fatty, fried foods and spices are strictly not recommended.
Thus, dermatitis is a complex disease that requires a whole range of therapy and treatment measures. But it is connected only with the physiological characteristics of a person or with reactions to external stimuli.
The type of disease determines the course and symptoms, as well as the option of therapeutic measures. Doctors note that even fungal dermatitis cannot be transmitted and cause inflammation.
Accordingly, there is no such type of dermatitis that is transmitted from person to person. As preventive measures, you should observe sanitary and hygienic standards in the workplace and at work, monitor your eating habits, limit the consumption and exposure to any food or non-food allergens, and regularly visit a dermatologist and endocrinologist.
Examinations of the hormonal, digestive and skin systems are something that must be done on an ongoing basis.
If it so happens that a person has a hereditary predisposition to dermatitis, special attention should be paid to the following preventive measures:
- constantly monitor the state of immunity;
- do not consume foods from the category of those that can cause allergies;
- Always keep medications with antiallergic effects with you;
- Frequently clean and ventilate the premises;
- wear clothes made from natural materials;
- avoid excessive anxiety by taking sedatives;
- the water in the bath or shower should be warm;
- carefully select cosmetics.
For all types of dermatitis, there are some general recommendations for preventing the disease and preventing relapses:
- support your immune system in every possible way with the help of immunomodulators and hardening;
- monitor the manifestations on the skin, fight the manifestations of acne;
- treat old chronic lesions and diseases, do not allow acute processes to become chronic;
- collect your allergic history, avoid contact with allergens;
- use clothes made from natural fabrics, keep them clean;
- do not accumulate objects that contribute to the formation of dust in the house;
- Choose your personal hygiene products carefully. It is desirable that they contain as little phosphate as possible. It is best to use special rulers recommended for dermatitis;
- avoid stress, use sedatives and antidepressants;
- pay close attention to your diet. Eliminate offal, semi-finished products, large amounts of citrus fruits and sweets.
The modes of transmission of infections, the symptoms of which are skin rashes, vary depending on the pathogen. Thus, “childhood diseases” - measles, scarlet fever, rubella, chickenpox are transmitted by airborne droplets, typhus - through lice bites, pyoderma - by direct contact.
Infection and subsequent skin reactions can be avoided by practicing good personal hygiene, avoiding contact with infected people, and preventing contamination of skin wounds.
An important point of prevention is vaccination.
Post Views: 2,203
Is seborrheic dermatitis transmitted and is seborrhea contagious? What is important to know
Reading time: 2 min.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by a rash with the formation of crusts on the scalp or torso, where the sebaceous glands are located.
The development of the pathological process is provoked by yeast-like fungi of the Malassezia species; more details about the reasons can be found in this article. Skin papular rash is accompanied by itching, burning and peeling. It can merge into large spots and become covered with yellow, greasy scales.
At the sight of red, flaky skin, many are interested in the question of whether seborrhea is contagious. Also read our material about seborrheic dermatitis.
Mechanism of the disease
Is the fear of “catching” seborrhea in close contact with a sick person justified? To answer this question, you need to familiarize yourself with the reasons for the development of the pathological process.
Yeast-like fungi Malassezia exist in the upper layers of the epidermis and are part of the normal human skin microflora.
To grow and develop, they need fatty acids, which are present in the secretion of human sebaceous glands.
Using sebum as food, they secrete specific decomposition products that provoke irritation and inflammation of the epidermis. This process of fat utilization weakens the skin barrier function and causes an imbalance of microflora.
Active reproduction of Malassezia fungi can be triggered by the following factors:
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- frequent severe stress;
- prolonged exposure to the sun or solarium;
- unbalanced diet, causing a lack of vitamins and microelements in the body; violation of sweating processes;
- general exhaustion of the body.
The influence of yeast-like fungi on the human body is closely related to environmental conditions - temperature, humidity, geographical factors. The slightest weakening of the host's immunity leads to the uncontrolled growth of Malassezia, which gives rise to the development of seborrheic dermatitis.