Features of atheroma
To independently distinguish an epidermal tumor from a wen, you should know the characteristics of atheroma, as well as its structure. This is a dense and mobile neoplasm, which consists of epithelial as well as fat cells. The formation rarely grows more than five centimeters. A skin cyst can appear in any part of the body where sweating is increased. These are the so-called seborrheic zones. Often there is a blockage of the sebaceous gland on the face; in most cases, the development of atheroma is often diagnosed in the forehead, upper eyelid, cheek, and wing of the nose. There is a risk of epidermal growth behind the ear or on the scalp. Epidermoid cysts of the coccyx and other parts of the back, groin, and armpit occur less frequently.
Atheroma tissue begins its development in the lower layer of the epidermis - the dermis. The tumor has a small hole that comes out and looks like a black dot. It is through this hole that infection often enters the tumor, causing an inflammatory process. The growth may have an oval or round shape; the base of the tumor has good adhesion to the skin, but inside the tissue it moves a little during palpation.
Clinical manifestations of atheroma
Atheroma appears in areas of the skin where there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands. Localized on the neck, armpits, chin, back, scalp.
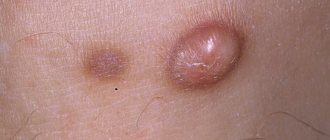
The neoplasm has clear boundaries and a spherical shape. It is soft to the touch and becomes mobile upon palpation. The consistency is dense and does not cause pain or discomfort. Size 3-10 cm. Large formations are recommended to be removed surgically, as they cause inconvenience to the patient. Localization can be either single or multiple.
The neoplasm does not pose a threat, but in complicated cases there is a risk of a subcutaneous abscess. In this case, swelling and severe pain are possible. The infection process is accompanied by fever and symptoms of general intoxication. Such an atheroma can spontaneously open.
Features of lipoma
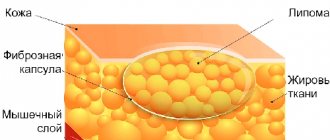
Lipoma is a benign tumor that is formed from overgrown adipose tissue, so it is advisable to call this neoplasm a wen. The neoplasm can be dangerous because it is difficult to distinguish it from a malignant liposarcoma tumor by its first signs. The formation grows slowly and can affect the back, arms, shoulders, and neck. The size of the wen can be very large (up to eleven centimeters), it can even develop on internal organs. The consistency of the neoplasm is soft-elastic, mobile during palpation, since it does not adhere to the skin.
More often, the pathology has a multiple form; according to the type of content, the wen is classified into several varieties:
- fibrolipoma – to a greater extent, includes fibrous tissue;
- lipofibroma - consists predominantly of adipose tissue;
- angiolipoma – composed of adipose and muscle tissue;
- myelolipoma - consists of fatty as well as bone tissue;
- myolioma – consists of muscle tissue and a large number of altered blood vessels.
Fatty tumors that appear on internal organs are very dangerous, so they need to be diagnosed and removed immediately.
Lipoma disease
Lipoma is a benign neoplasm on the skin.
It is located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, localized on the back, neck and limbs, and on internal organs. Its cells are located on internal organs. Education most often affects people over the age of 30.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:XPl1VnkNEX0
The formation does not cause pain upon palpation, is easily displaced, and does not grow into surrounding tissues. As the size of the lipoma increases, it becomes dense and enters the stage of fibrolipoma. There are varieties: angiolipomas, myxolipomas, myolipomas.
The formation has a size of no more than 5 cm, but in rare cases it increases to 10 cm.
Common features
Lipoma and atheroma have a number of common features, which is why they are often confused.
The common features of these two neoplasms include:
- Benign - both growths are not malignant, however, with a combination of risk factors, a lipoma can be a precancerous condition of liposarcoma.
- Causes of occurrence - both neoplasms can occur due to metabolic disorders, mechanical damage, or genetic predisposition.
- Localization - these two tumors can occur on any part of the skin except the palms and soles.
- Absence of symptoms - apart from a visual defect, the epidermal cyst and wen do not manifest themselves in any way - they do not cause pain, itching or discomfort.
- Visual similarity - in appearance, these two neoplasms are practically indistinguishable from each other.
Based on the general characteristics, the patient is unlikely to independently determine the type of formation. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and then prescribe the correct treatment.
Differential diagnosis
The main differences between atheroma and lipoma are the mobility and density of these neoplasms. The wen is softer and has greater mobility.
A doctor can distinguish these two neoplasms by the following signs:
- a lipoma is an accumulation of adipose tissue, and a cyst is a capsule with fatty and epithelial contents;
- cystic formation has a tendency to inflammation and suppuration;
- the wen has a soft consistency, and the epidermal tumor is dense and elastic;
- the epidermal cyst moves during palpation;
- lipoma can be localized on internal organs, and atheroma occurs only in the layers of the epidermis;
- the cystic formation must be removed, as it can become inflamed, and the wen can be observed and not removed if there are no unpleasant symptoms.
Despite the similarity of these diseases, their occurrence requires consultation with a doctor.
Is it possible to identify houses by external signs?
If the size of the lipoma is small, there are no symptoms. Formations on internal organs do not have characteristic features or are fundamentally different from other tumors. The clinical picture is similar to the inflammatory process of various human systems.
Atheromas can resemble fibroids. The difference in pathologies lies in the nature of the tissues and manifestations.
Dermatofibromas cause a cosmetic defect. Removal is prescribed for aesthetic reasons.
A conclusion about the compaction cells and the nature of their origin can be made through histological examination of tissue samples from a diagnostic biopsy or after resection.
What is the difference between atheroma and wen
In order to accurately find out the type of formation, you need to visit a doctor, but by some distinctive features you can distinguish atheroma from lipoma yourself:
- the wen always has no inflammatory process;
- lipoma does not have an outlet;
- the cyst is harder and denser;
- the wen is easy to move;
- the epidermal formation is adhesive to the skin;
- the growth of an epidermoid neoplasm is more rapid than that of a fatty one;
- an epidermal cyst never develops on the surface of internal organs.
The fatty tissue does not have to be removed if it does not cause any aesthetic discomfort, since this type of neoplasm almost never leads to complications.
Reasons for appearance
Based on the cause of its occurrence, the doctor can determine whether the patient has a lipoma or atheroma. Wen occurs due to the fact that adipose tissue begins to grow rapidly. This can be caused by factors such as trauma to the localization site, metabolic disorders, and heredity. An epidermal cyst grows in places where there are a large number of sebaceous glands and occurs due to blockage of their duct with detritus. The patency can be disrupted by particles of the upper layer of skin or mechanical damage to the gland.
The appearance of atheroma is often associated with damage to the skin, with the introduction of particles from the upper layer into the deeper layers of the skin, as well as with an increase in the density of detritus. Cyst factors include genetic predisposition, metabolic disorders, neglect of personal hygiene, and improper use of cosmetics.
Appearance and structure
The visual manifestations of a wen and an atheroma (cyst) are similar, so outwardly they can be confused, but there are also some differences. A cystic neoplasm is often smaller in size than a fatty one. Purulent contents can be released from the opening of the epidermal cyst when pressed, which never happens with a lipoma. If you touch the wen, it has a softer consistency, because it is a growth of adipose tissue under the skin. The cyst has a dense capsule, so it feels harder to the touch. If you press on the wen, it will move to the side without any problems. The epidermoid cyst is fused to the skin; it can only be slightly moved relative to the deeper tissues.
Subjective sensations and symptoms
There are no symptomatic differences between these two neoplasms. They do not cause pain, itching or discomfort. Lipoma never becomes inflamed, which often happens with atheroma.
Symptoms of an inflamed epidermal neoplasm:
- Redness of the skin over the cyst.
- Swelling of the tissue around the tumor.
- Pain syndrome on palpation.
- Isolation of purulent exudate during purulent course.
If there is at least one sign of the development of an inflammatory process, you should immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment.
Risks and complications
Lipoma can have one complication. Very rarely, a wen degenerates into a malignant tumor, liposarcoma. An epidermoid tumor never becomes malignant, but it very often becomes inflamed. Detritus, which is located inside the capsule, is a breeding ground for the development of bacterial flora, so inflammation of the cyst is not uncommon. The purulent contents corrode the membrane of the tumor and the skin above it, and can break out or in. In the second option, soft tissue phlegmon develops. The inflammatory process can develop without infection. In such a situation, doctors first stop the inflammation with Levomekol or Vishnevsky ointment, and then remove the epidermal neoplasm.
An epidermoid cyst is dangerous because it ruptures, which can cause the development of an abscess. When localized in the genital area, both the wen and the cyst can disrupt the process of urination or cause difficulties during sexual intercourse. After surgery to remove an epidermal cyst, it may grow back. When removing an inflamed atheroma, there is a possibility that the doctor will not be able to remove the entire cyst membrane, which becomes the main reason for the development of relapses.
Similarities and differences
There are a number of signs that help you make the right conclusion.
The first is the presence or absence of an inflammatory process. If inflammation is present, this indicates that the wen is an atheroma.
Lipoma and atheroma arise due to the same reasons, but the mechanism of development for each neoplasm is different. Atheroma is localized on the skin, and lipoma is located under the skin. It is soft to the touch. The subcutaneous formation is denser in consistency.
- Atheroma is an accumulation of fat in the gland, progresses quickly, increases in size, and has a hard consistency. It is subject to inflammation and suppuration.
- Lipoma is a cluster of cells in a capsule, localized in the subcutaneous tissue, soft to the touch.
It is impossible to distinguish these two formations on your own. Incorrect diagnosis leads to complications. Only a doctor can correctly determine the type of tumor through examination and diagnosis.
First, let's look at the similarities between lipoma and atheroma:
- both formations are considered to be benign tumors;
- similar in appearance;
- do not cause pain;
- form on the same areas of the skin;
- have common causes of development: metabolic disorders, slagging of the body, genetic predisposition.
The difference between the formations lies in the following characteristics:
- lipoma occurs as a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands under the skin, as a result of this process, fat residues accumulate in one place, while atheroma is a collection of fatty tissues in a capsule;
- atheroma, unlike lipoma, can become inflamed, painful and fester;
- lipoma has a soft texture, and atheroma has an elastic texture;
- the first grows much slower than the second;
- lipoma can form inside organs, but atheroma cannot;
- The atheroma must be removed, since it will grow and become inflamed when mechanically applied to it, but the lipoma does not need to be removed, it will not cause discomfort.
The only exception to the last rule is a lipoma in the internal organs: it must be cut out.
You cannot determine for sure on your own whether you have an atheroma or a lipoma on your skin. This can only be done by a competent specialist. You should not self-medicate; any formations on the skin require qualified diagnosis in a medical institution.
Modern diagnostic and treatment methods make it possible to get rid of skin growths once and for all without scars and a long rehabilitation period. That is why do not wait until the tumor becomes inflamed. It is better to remove the growth immediately, before suppuration occurs. Any changes in the skin are a good reason to consult a doctor. He will determine what caused the development of the subcutaneous formation and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Features of treatment
A lump or skin cyst can be completely and permanently removed only surgically or using hardware removal techniques. Doctors recommend cutting out atheroma, as well as lipoma, before complications arise. The method of removing atheroma depends on the size of the tumor. Small cysts are removed using laser or radio wave therapy. Treatment of atheroma by cutting with a scalpel is carried out only on closed areas of the body, since a scar remains after the operation. If the surgeon does not remove the entire capsule of the atheroma, relapse is possible, so surgical removal is performed less and less.
Prevention of cysts and fatty tissues
To prevent atheroma and lipoma, it is necessary to monitor hormonal levels, treat metabolic disorders, do not neglect personal hygiene, and wash off cosmetics with special products. Proper nutrition will help prevent changes in detritus density. Periodic examination by a doctor allows you to timely identify the presence of pathology and carry out treatment.
Atheroma is a benign tumor-like formation, a skin or subcutaneous cyst, consisting of a whitish elastic capsule in which mushy contents resembling cottage cheese accumulate. “Mush” is a secretion product of the sebaceous glands that has an unpleasant odor.
Atheroma is formed when the duct of the sebaceous gland is blocked. It can be congenital, caused by injury or inflammation of the hair follicles. The main symptom of atheroma is a painless nodule or lump in the skin. The formation appears on the scalp of the body. Lipoma is a benign tumor (limited) consisting of adipose tissue.
Lipoma can form on any part of the body, but most often appears on the neck, back, and shoulders. The tumor has a soft, elastic consistency, is painless, is located under the skin, is easily palpable, mobile, and grows slowly. Lipomas are more common among people 40–60 years old.
Features of diagnosing atheroma and wen
To determine atheroma, an examination by a doctor is sufficient. The main difference is the presence of swelling at the mouth of the sebaceous gland. To confirm the nature of the formation, a histological analysis of the removed compaction is performed. It is possible to prescribe an ultrasound or MRI to confirm the assumptions of the oncologist or surgeon.
When a wen is localized on internal organs, a comprehensive examination is required with the involvement of doctors of various specializations.
- In case of kidney disease, a consultation with a urologist or nephrologist is prescribed.
- If there is a tumor in the breast - a gynecologist, mammologist.
- When formed in the liver - gastroenterologist.
- If there is compaction in the spine, see a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Diagnosis excludes conditions of inflammatory origin. The mandatory list of measures includes ultrasound and MRI.
The difference between atheroma and wen is significant. Self-medication leads to consequences - secondary infection, organ necrosis with extensive lipomatosis.
Reasons for the appearance of wen
The cause of lipoma formation is unknown. The risk of developing a tumor increases with a family history. Other risk factors include:
- morbid obesity (adirositas dolorosa) is a rare disease characterized by multiple lipomas);
- Cowden's syndrome;
- Gardner's syndrome;
- Madelung syndrome.
Atheromas are formed when the outflow of sebum is obstructed. Provoking factors are considered:
- compaction/thickening of the epidermis;
- hyperhidrosis – increased sweating;
- hormonal imbalances;
- use of antiperspirant deodorants;
- incorrect personal hygiene.
Removal of fatty tissues (lipomas and atheromas)
It is advisable to remove lipomas and atheromas. No ointments, lotions, compresses, onions/garlic will help - the wen will not resolve. But atheroma can become inflamed.
Based on size, condition and location, atheromas are removed in one of the following ways:
- By radio waves. Removal of atheroma using radio waves is carried out under local anesthesia. The intervention consists of opening the capsule, extracting the contents and coagulating the atheroma. Scars after the radio wave technique are minimal. In this way, formations up to 7 mm are removed.
- Surgical intervention. Surgical removal of atheroma is the most common method. A thin incision is made along the upper part of the atheroma and the contents of the capsule are removed. Thus, the incision is significantly smaller than the original diameter of the wen. The sutures are removed after 3-12 days (depending on the location of the intervention).
- The incision of the atheroma is carried out only when the inflammatory process has developed due to the need for cleaning and removal of purulent contents. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia, but the patient may experience discomfort. Sometimes, after the inflammation has resolved, a second operation is required to completely remove the capsule.
Any atheromas should be removed immediately after their appearance - a delay leads to additional problems. You shouldn't try to squeeze out the contents - it's not a pimple. The doctor determines whether to remove or observe the lipoma. Tactics depend on many factors:
- lipoma size;
- number of tumors;
- personal and family history of skin cancer;
- lipoma pain;
- aesthetic component.
The most common treatment for lipoma is surgical removal. The operation is relevant for large lipomas that continue to grow. The radio wave method is suitable for getting rid of small lipomas. Another treatment option is liposuction (puncture-aspiration method). The fat is “suctioned out” using a needle. If a wen forms on any part of the body, you should consult a surgeon. To get rid of fatty deposits - lipomas or atheromas - contact the surgeons of the President-Med medical centers
New growths on the body, called wen, have signs of various skin diseases. Often, these are lipoma and atheroma, seals similar in appearance. But they have their own characteristics of appearance and development.
Similar symptoms of atheroma and lipoma
In almost all cases, lipomas, atheromas and other subcutaneous growths create only aesthetic discomfort, especially when localized on the neck, face, chest, arms, and genitals. On palpation, the tumors are painless and differ in density.
As it grows, compression of nerve endings, tendons, and joint structures is possible, which leads to pain with irradiation to distant parts of the body.
When infected, signs of an inflammatory process occur:
- swelling,
- hyperemia,
- increase in local temperature,
- symptoms of intoxication.
In most cases, the patient's complaints are limited to imperfect appearance.
Lipoma and atheroma are visually no different. Only a specialist can determine the type of wen during examination and diagnosis.
These neoplasms have a number of similar characteristics:
- formations of a benign nature, the risk of degeneration into an oncological process is minimal;
- same shape;
- similar causes of appearance - poor nutrition, nervous tension, metabolic failures;
- hereditary factor;
- are not amenable to alternative treatment and can only be removed surgically;
- upon palpation, both neoplasms become mobile;
- are localized on any part of the body, but affect those places where there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands.
Prevention for neoplasms is identical. It is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air and adhere to proper nutrition, eat fresh vegetables and fruits. A balanced diet will help to avoid metabolic disorders that cause the appearance of wen.
Wen have common symptoms, but to treat them it is necessary to accurately distinguish lipoma from atheroma.
Similarity of neoplasms
These benign formations are difficult to distinguish only by external signs. But in order to determine the method of treatment or surgical removal, the tumor must first be diagnosed. It has been established that the occurrence of lipomas and atheromas is facilitated by a disrupted metabolic process in the body, leading to clogging of the sebaceous glands.
Their appearance is also negatively affected by the quality of nutrition, lifestyle, frequent stressful situations, hormonal disorders (hyperhidrosis) and hereditary conditions.
Signs of lipoma
The lipoma resembles a small ball. It is formed from subcutaneous fat. This mobile neoplasm is located under the skin and does not cause pain. At the same time, from one to several formations of this type may appear on the body. When placed close together, they resemble a bunch of grapes with a lobed structure. Lipomas appear in people of any age group, but often in people older than middle age. It has been noticed that women suffer from them more often than men.
Different types of lipomas
Lipomas, differing in structure and location, are divided into the following types:
- Lipofibroma.
It is soft to the touch. It contains only adipose tissue. This type of tumor is located on any part of the body with a fatty layer. - Fibrolipoma.
Dense neoplasm. It contains a mixture of fat and fibrous tissue. Formed on the thighs of the legs and on the muscles of the buttocks. - Angiolipoma.
A tumor with a dense consistency. It consists of adipose tissue and muscles, with numerous interweaving of modified vessels for transporting blood. On the human body it is formed in muscle tissue, as well as in internal organs. - Myolipoma.
Dense formation of fat and bone tissue. Appears in the thickness of muscles and on some internal organs of a person. Sometimes it appears in the kidneys. - Myelolipoma.
It has a rigid structure. Consists of fat and hematopoietic tissue. Its distribution is observed deep in the peritoneum, as well as on some organs or inside them (in particular, in the adrenal glands).
Patients who have a lipoma do not complain of pain. However, when the tumor grows significantly, it compresses the organs located next to them. This causes discomfort and interferes with their functioning, and is also harmful to human health. Lipomas with a thin stalk are dangerous, since tissue necrosis occurs when it twists.
The only treatment for lipoma is surgery. It is recommended to consult a surgeon immediately after detecting such a tumor, because they have a tendency to grow.
Urgent surgery is required if the following symptoms are present:
- pain
syndrome; - rapid growth
of lipoma; - disruption
of the functioning of an internal organ.
Usually such a tumor is removed under local anesthesia, but if it is in a hard-to-reach place, general anesthesia is used. Some types of lipomas are removed using a laser or radio wave device, after which fewer relapses are observed.
Lipoma, atheroma, hygroma, fibroma - what's the difference?
When a subcutaneous nodule resembling a lump appears, almost all patients think about a wen, but dermatologists and surgeons identify up to a dozen varieties of subcutaneous growths, differing not only in filling, but also in structure, morphology, and the risks of serious complications.
What is lipoma?
Lipoma is a subcutaneous neoplasm of an initially benign nature without pronounced symptoms; it tends to spread and then unite into nodular conglomerates. Typical locations are the arms, head, groin, genitals, forearms and neck. There are cases of lipoma of internal organs.
Lipoma is characterized by unstable filling, subcutaneous migration and mobility, risks of malignancy and transformation into liposarcoma, unlike other benign neoplasms.
Based on the nature of their filling, there are several main types of lipomas:
- Lipofibromas – filling is up to 85% adipose tissue;
- Myolipomas - as part of the pineal growth, fatty and muscle tissue, an abundant vascular component, found on the kidneys;
- Myelolipomas - the structure consists of adipose and bone tissue, localized in the adrenal glands, peritoneum;
- Fibrolipomas - the internal composition includes fibro-adipose tissue localized on the lower extremities, buttocks, inner and outer thighs.
Subcutaneous lipomas become malignant under the influence of various negative factors. Read more about what a fatty lipoma is here.
What is atheroma?
Atheroma is a subcutaneous capsule-shaped neoplasm of limited localization with an exclusively benign course. The structure of the tumor consists of subcutaneous fat and epithelium. Atheromas are called wen, skin cysts.
Main localization:
- back,
- face,
- ears,
- neck,
- mammary gland,
- lower abdomen and genitals.
The size of the atheroma varies between 0.5 cm and 3 cm. Unlike lipoma, the filling of the atheroma is stable and does not change, which is responsible for the low oncogenic risks. However, the risk of infection remains due to contamination and dust. Atheromas are more common in men of different ages.
Hygroma
Hygroma (translated from Greek as liquid tumor) is a benign neoplasm - a cystic component with dense walls and viscous contents. The internal filling resembles a jelly-like mass. Hygromas are localized in tendon cavities and large joints.
When the tumor is small, it does not manifest itself in any way, but with intensive growth and compression of the nerve roots, they are accompanied by pain and disruption of innervation.
Hygromas occur mainly in young women; up to 65% of all benign tumors are hygromas of the wrist joint.
Fibroma
Fibroma is characterized by a nodular formation consisting of connective tissue fibers, typical of almost the entire body. Based on the base of the fibroma, the localization of the tumor can be multiple.
The exact causes of fibroids are unknown, however, there are several defining theories of their occurrence:
- hereditary factor
- hormonal disorders,
- injuries and metabolic disorders.
The classification of fibromatous neoplasms involves several main forms:
- Soft, which contains cellular elements with a low concentration of connective tissue, in appearance resembles a fibrous polyp of the skin;
- Dense, consisting of collagen fibers with a low content of cellular elements, resembling a mushroom in appearance;
- Desmoid is a dense tumor with a localization typical of the peritoneum, characterized by aggressive growth, the risk of cell malignancy and high recurrence after excision.
Location and causes of atheroma
This tumor-like formation is also called a fatty cyst. They have a round shape and do not exceed 5 cm in size. Atheromas form in those areas where there are sebaceous glands, that is, everywhere except the palms and soles.
They often appear on the back of the neck, upper back, armpits, face, scalp, scrotum and labia.
The main reason for the appearance of atheroma is a complete or partial rupture of the walls of the sebaceous gland due to mechanical damage to the skin or due to an inflammatory process.
A large number of atheromas on the human body appear as a result of a rare genetic disease called Gardner's syndrome.
It has been established that atheroma formation occurs more often in men than in females. At the same time, those who have previously suffered from acne are susceptible to the appearance of such wen.
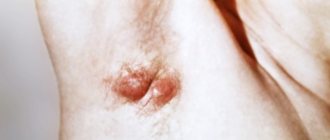
Atheroma: symptoms, complications, removal methods
Atheroma is a benign subcutaneous formation that has a round shape, is dense and mobile to the touch, and does not exceed 5 centimeters in size. The color of the skin around the atheroma does not change; sometimes, if you look closely at it, you can see a small dark dot that clogs the outlet of the sebaceous gland duct. Atheromas develop in the sebaceous gland duct. Such tumors are often called a fatty cyst. Atheroma is usually located in those areas of the body where there are sebaceous glands - on the face, on the scalp, on the back of the neck, between the shoulder blades, in the armpits, on the scrotum, labia, perineum, chest and upper back. Sebaceous glands are found on almost the entire surface of human skin, except for the feet and palms. The main difference between atheroma and lipoma is that atheroma is always formed from the sebaceous gland located under the skin, due to blockage of its duct or thickening of sebum. If something interferes with the removal of sebum to the surface of the skin, then it accumulates in a kind of bag (capsule) - this is atheroma. The composition of atheroma is always the same: fatty substances (sebum), epithelial cells and the sebaceous gland. One of the reasons for the appearance of atheroma may be a rupture of the sebaceous gland, which can be the result of skin inflammatory diseases and skin damage of varying severity. It has been noted that multiple atheromas can appear in people suffering from Gardner's syndrome (a very rare genetic disease). Atheromas appear more often in men than in women. People who have previously suffered from acne are especially susceptible to the appearance of these wen.
Complications of atheroma
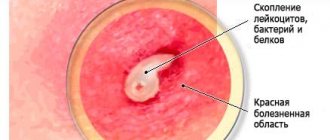
Typically, these small, painless lumps are harmless and almost never turn into anything cancerous. Any complications are associated with atheroma damage. Dangerous complications of atheroma are:
- Inflammation. Since the contents of atheroma are a breeding ground for bacteria, if they penetrate the atheroma capsule, inflammation develops very quickly and pus appears. Pus may break out. If it spreads under the skin, it can cause soft tissue phlegmon. It happens that atheroma becomes inflamed without infection. In this case, before removal, it is first necessary to relieve inflammation. For these purposes, Vishnevsky ointment and Levomekol are used.
- Break. Rupture of atheroma requires immediate medical attention, as an abscess may develop.
- Discomfort. Atheromas can cause serious physical discomfort. For example, atheroma on the genitals can interfere with normal urination or sexual intercourse.
Removal of atheroma
Due to the fact that atheroma and lipoma are very similar, an accurate diagnosis can only be made after a morphological or histological examination of the tumor tissue. These studies will rule out the presence of lipoma and malignant tumor. Modern medicine knows only one way to treat atheroma - removal. Therapeutic and traditional methods of treating atheroma have not proven effective. Removal methods can be different: surgical, laser and radio waves. The patient can choose the method of atheroma removal himself, since all of them can be used to remove atheromas of any size. Typically, patients prefer two methods: laser and radio wave, since their advantages are the absence of a rehabilitation period and a high cosmetic effect. However, if the wen is inflamed and suppurates, then only surgical intervention will help. In this case, the atheroma is opened, cleared of contents, and then subjected to drug treatment. The operation to remove atheroma is simple, it is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis and lasts about 15 minutes. The atheroma is removed only together with the capsule, since if even a fragment of the capsule remains under the skin, this will inevitably lead to a relapse of the disease. Doctors recommend removing atheroma without waiting for it to grow or break through - this can significantly complicate treatment and reduce the cosmetic effect.
Benign neoplasms under the skin are popularly called wen. This name does not correspond to the true cause of the disease. Lipoma and atheroma are different pathological formations that have a similar appearance. Lipoma is a benign tumor of adipose tissue. Atheroma is a cyst formed in a clogged sebaceous gland (also called epidermal and trichodermal cyst). The approach to treating formations is different. To prescribe adequate therapy, a full diagnostic study is carried out. A biopsy will help clarify the diagnosis.
Consequences of atheroma
Usually, wen does not degenerate into malignant neoplasms. But due to the fact that the contents of the capsule have a nutrient medium for the proliferation of bacteria, an inflammatory process may occur and an abscess may appear, and then phlegmon may develop.
In this case, before removing it, the inflammation is first relieved with medications.
Sometimes the atheroma ruptures. In this case, you should immediately contact a medical facility to prevent the occurrence of an abscess. Atheromas that cause discomfort are subject to removal; for example, if located on the genitals, they can interfere with the free flow of urine.
Treatment of fatty cyst
Like lipoma, atheroma can only be removed surgically. Conservative methods or treatment with folk remedies do not have an effective effect on the wen.
Surgical removal of atheroma and lipoma is performed on an outpatient basis, but the duration of the procedure is shorter, about a quarter of an hour. This completely removes the sebaceous capsule.
Education: 2020 - graduated from the A.I. Evdokimov Moscow State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine. 2020 - member of the Moscow Scientific Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists named after. A.I. Pospelov. 2017 — RUDN, advanced training under the program of additional education in the specialty “Trichology. Diagnosis and treatment of hair diseases” Department of V. P. Tkachev. 2020 - completed residency in the specialty “Dermatovenereology” at the Department of Dermatovenereology of the M.F. Vladimirsky MONIKI. 2020 — “ENDOCRINE ASPECTS OF REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH “MANAGE AGE: ENDOCRINOLOGY OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL BEAUTY””, RUDN. 2020 - advanced training in cosmetology at the Central State Medical Academy under the Administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Experience: 3 years. Place of work: REAL CLINIC.
Lipoma and atheroma are often similar in appearance, and patients often do not distinguish them from each other, defining them under the general name “wen.” Let's try to figure out what the difference is between a lipoma and an atheroma, and also what to do if you have one of these formations.
Treatment – surgery
The correct solution would be to remove the wen completely. At home, removing wen is ineffective and dangerous. There must be complete removal of the wen so that relapses do not occur later. Professionalism and sterility, in order to avoid bacterial infection and further aggravation of the problem, can only be ensured in medical institutions. Moreover, it is simpler and easier to remove the wen in the early stages, while it is still the size of a pea.
Modern medicine offers several ways to remove wen. The doctor, based on the examination and possible diagnostic tests, chooses the optimal method.
- Surgical method. Used if the tumor affects the scalp or is located on the back. Local anesthesia is used. Various techniques are used:
- The skin is cut through the center of the atheroma without damaging the capsule. After which the edges of the skin tissue are shifted, and the neoplasm with its contents is removed to the surface. Stitches are applied.
- Two incisions are made along the edge of the tumor and pathological tissue is removed with a special device. The manipulation ends with wound treatment and suturing.
- Radio wave method. Removing atheroma using the radio wave method is the safest and shortest. The operation does not require a special preparatory period. If the formation is located on the head, there is no need to remove hair on the surgical field. Removal lasts up to 10-15 minutes and is completely painless. Healing takes a short period of time and does not leave any marks in the form of scars. A procedure with proven effectiveness and is relevant for removing wen on exposed parts of the body.
- Laser method. Removing a wen with a laser involves exposing the tumor to a high-energy beam. The contents of the atheroma are evaporated. A positive point is that laser removal does not require any excision of the skin. After the procedure, there are no consequences in the form of damage to the skin. Infection during the operation is excluded and its duration ranges from several seconds to several minutes.
After the incision, the atheroma is squeezed out. Next, the cavity is cleaned and treated, and an antiseptic bandage is applied.
The disadvantage of the surgical method is the possibility of a postoperative scar, therefore it is not recommended when removing a wen on the face and other open parts of the body.
The advantages of laser and radio wave removal are obvious:
- Low chance of relapse.
- Painless procedure.
- There is no need for stitches.
- Short postoperative period.
- Bloodlessness of manipulation.
- Good cosmetic effect.
- The ability to take a sample of pathological tissue for histological examination (to exclude an oncogenic factor).
The main treatment method is removal of the wen.
Sometimes the use of an endoscopic method is appropriate. An endoscope is inserted into a small skin incision to excise the tumor. A microscopic video camera allows the specialist who performs the operation to see on the monitor screen and have maximum control over the processes taking place. It is advisable to use this technique in the case of formations in the face and head.
Any manipulations to remove the wen are not allowed at home. This may have unforeseen consequences.
Have you been fighting PAPILLOMAS for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of papillomas by taking every day...
Like lipoma, atheroma can only be removed surgically. Conservative methods or treatment with folk remedies do not have an effective effect on the wen.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with lung cancer with metastases, x-ray
For small lipomas, when aesthetic and subjective concerns are not expressed, clinicians resort to wait-and-see tactics. Given the slow growth of the fatty nodule and the low tendency for malignancy, waiting may be justified.
Indications for removal are:
- Severe pain when nerve endings and blood vessels are compressed;
- Numbness, disruption of innervation;
- Intensive growth, contrary to medical predictions;
- Frequent inflammatory foci in the area of tumor-like protrusion;
- Decreased organ functionality with internal localization;
- The patient's desire.
The choice of removal method depends on:
- location of the tumor,
- number of node units,
- general condition and age of the patient,
- clinical history.
There are minimally invasive and radical methods of intervention.
The traditional method of removing a lipoma is to excise the pathological focus with a scalpel - removing the subcutaneous fatty tissue along with the capsule. After desquamation of the fatty node, the wound bed is sutured. Sutures are removed 7-14 days after the intervention.
During the manipulation, the integrity of the tumor fragments is maintained, which makes it possible to evaluate the histological structure of the tumor. Subcutaneous localization allows the operation to be performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis. If the nodes are located internally, hospitalization is required.
Laser removal
The use of laser is a promising direction in minimally invasive removal of skin tumors. The targeted action of the laser ensures precise manipulation and layer-by-layer removal of the tumor within healthy tissue. For small fatty deposits, one procedure is sufficient.
Relapses after laser removal and rough scars on the skin are rather rare. The method itself is considered bloodless, since as the pathological focus is treated, simultaneous coagulation of the vascular component occurs.
The method involves removing the contents of the tumor by aspiration. A small puncture is made on the surface of the tumors with a needle, through which the fat is removed. Removal is possible through a special cannula. The method does not require incisions and has good aesthetic results.
The disadvantage of the method is the high risk of relapse due to incomplete removal of exudate and post-manipulative infections.
A modern minimally invasive method of removal using a radioknife without incisions or the need for sutures. The method allows you to remove tumors completely within healthy tissue.
Postoperative complications after a properly performed operation are rare and are often associated with secondary infection, hematomas, and the formation of rough keloid scars. A long-term complication is the recurrence of the lipoma or the formation of several new lesions nearby.
The prognosis for lipomas and other benign neoplasms is favorable with appropriate treatment. Against the background of intensive growth and regular exposure to negative factors, the risk of cancer transformation and damage to healthy tissue increases significantly.
What are liver polyps and how to treat them, read our article.
You can make an appointment with a doctor directly on our website.
Be healthy and happy!
Lipoma
This is a benign formation consisting of adipose tissue. In essence, it is a local accumulation of adipose tissue under the skin. Lipoma is a benign tumor, although in rare cases liposarcoma, a malignant formation, can develop under its mask.
Lipomas manifest themselves in the form of soft-elastic subcutaneous formations, mobile, painless, and can slowly increase in size. The skin over lipomas is not changed and easily moves over them. Small lipomas are not visible at all; they can only be detected by palpation. Larger lipomas stand out as “bumps” of round or oval shape. The size of lipomas is very variable - from 1-2 cm to 20 cm or more. Lipomas never become inflamed or suppurate.
What is atheroma
First of all, this is a benign formation that appears due to blockage of the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands located on the human skin. A similar growth appears in the upper layers of the skin. And also having a small hole through which the anomaly is connected to the external environment, inflammation most often occurs. The growth itself is quite small and rarely exceeds 5 cm in size. Moreover, it has a round or oval shape. And during palpation, the mobility of the neoplasm is revealed, despite the fact that its base is quite firmly connected to the dermis.
With the development of the inflammatory process, a white substance with a viscous consistency begins to be released from the wen, through a small hole in them. This process occurs due to the accumulation of sebaceous secretions, which is caused by blockage of the excretory duct, so they are deposited in the formation.
The biggest danger that such a growth has is suppuration. Thus, inflammation leads to the fact that the atheroma begins to increase, and purulent masses are released from the growth, which have an unpleasant odor.