Formation of a boil shaft
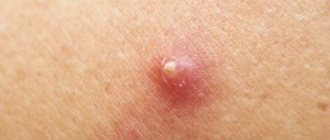
At the first stage, a dense infiltrate of bright red color appears. It immediately differs from a regular pimple in the intensity of pain. The development of a boil is associated with a rapid increase in swelling of the tissues around it. The pain gets worse. Usually, by the end of the fourth day from the moment the boil begins to develop, a slight softening forms in its center. A small amount of pus drains from this area to make room for necrotic tissue to form. It has a greenish tint and is called the core of the boil.
What does a boil look like?
Instructions
A boil can appear on any part of the skin, except the sole and palms. It often forms on an area of skin that has been subject to prolonged contamination and irritation. Such places are: lower back, forearms and hands, neck and face. It is worth noting that boils form in men about 10 times more often than in women.
There are many reasons why a boil appears on the surface of the skin. Firstly, pollution, including chemicals (lubricating oils, cooling mixtures, etc.), dust particles of cement, lime, coal and other materials. This factor becomes especially relevant in combination with a certain friction of the corresponding area of the skin. Also, the appearance of boils is promoted by various microtraumas and scratching, which are often observed in skin diseases accompanied by itching. The cause of the appearance of a boil on the skin may be increased sweating or the body’s special sensitivity to staphylococcal infection.
A boil in its course goes through three main sequential stages: infiltration (a certain accumulation of cellular elements in the skin tissues mixed with lymph and blood), formation and complete rejection of a purulent core, scarring of the surface.
External manifestations on the surface of the skin during a boil correspond to the stages of the disease. At the stage of infiltration, a small painful nodule with visible redness forms in the thickness of the skin. At its center is a hair. After about 1-2 days, a pustule (yellow pustule) will mature at the mouth of this hair follicle.
At the second stage of follicle manifestation, the adjacent sebaceous gland gradually undergoes purulent melting. Externally, an expansion of the area of skin redness and an increase in the size of the infiltrate are formed. During this period, the infiltrate rises slightly above the surface of the skin and takes the shape of a cone without certain clear boundaries. In its center, over time, a grayish-green mass of purulent core begins to appear through. At this stage, as a rule, local painful sensations increase and appear. General symptoms: headache, general weakness, slight increase in body temperature.
After the thin skin melts in the center of the conical infiltrate, the purulent masses gradually begin to be rejected. The pus comes out and the tip of the shaft can be observed. Over time, along with blood and pus, the rod is rejected. As a result, a fairly deep wound is formed. In the third stage, this skin defect is filled with connective tissue. After 2-3 days, a small scar appears in this place.
www.kakprosto.ru
Removing the boil stem
To safely remove the rod, you must immediately contact a specialist. Attempts to squeeze out or puncture a boil in most cases do not get rid of the problem, but cause new ones. In the best case, the patient can get furunculosis throughout the body, which will be activated at the slightest opportunity. In the worst case, the infection penetrates the brain, causing the development of purulent meningitis or leading to death.
When examining a patient, the doctor determines the degree of development of the boil in order to prescribe:
- surgical intervention,
- antibiotic therapy,
- treatment using means to draw out pus.
It usually takes about 10 days for a boil to fully mature. All treatment during the maturation period comes down to accelerating the process. For this, appropriate antiseptic ointments are used.
Boils are often treated with antibiotics
Treatment of purulent boil
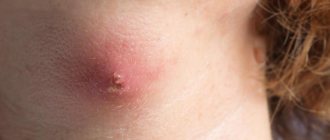
The problem of a purulent boil is a local inflammation of tissue that forms in the fiber. Through the hair follicle, bacteria enter inside, which leads to infection.
Photo 1 - Purulent boil
The skin turns bright red, purple or blue. The protective function of the skin loses its abilities, and an abscess forms at the site of microtrauma. When an area of skin becomes inflamed, the pain at the site of the abscess intensifies, the wound festers and does not heal, then mandatory treatment is required.
Photo 2 - Abscess
If this process ends quickly enough with a breakthrough, then pus with dead cells comes to the surface, and in its place there remains a small hole and blood can come from it. The location on the body can be anywhere, but areas with thin skin and more often in contact with clothing are more prone. The onset of the disease is characterized by redness and thickening of the skin, as well as pain.
Photo 3 - Ulcers appear more often on thin skin
The most common causes of this disease are:
- increased sweating; Photo 4 - Cause of boil - sweat
- careless shaving, tissue damage; Photo 5 - Improper shaving - the cause of a boil
- metabolic disease; Photo 6 - A boil appears due to improper metabolism
- poor nutrition; Photo 7 - Poor nutrition - the cause of boils
- state of illness, reduced immunity; Photo 8 - Reduced immunity - the cause of the boil
- hypothermia; Photo 9 - A boil may appear due to hypothermia
- insect bites, scratching, leading to infection. Photo 10 - Scratching insect bites can cause a boil
Attention! If a boil has formed in the head, face, or there are signs of elevated temperature, you should definitely consult a doctor. Inflammation in the facial area is dangerous due to the closely located network of blood vessels and rapid infection of the brain.
In order to speed up the healing process and alleviate the patient's condition, pus is drawn out. Which method to choose and how to treat depends on the complexity of the disease.
Photo 11 - You need to draw out the pus
If the situation is standard and does not require serious intervention, then you can try traditional methods. Many people are interested in the question: how long does it take for pus to come out?
Photo 12 - You can try to draw out the pus using traditional methods
Usually, pus comes out within a few days to a week from the moment the measures to draw it out begin. It happens that the boil has opened, but the pus does not come out, this indicates the immaturity of the abscess, and it is still necessary to take measures to ensure its maturation.
Photo 13 - Pus can come out for up to a week
When it matures and a breakthrough occurs, at the first stage pus mixed with blood often comes out, then only pus at the final stage. Rubbing the damaged area with alcohol medicinal tinctures provokes the process of rapid release of the abscess.
Photo 14 - At the first stage, pus comes out with blood
You need to wipe from the edge to the center, so the infection will be localized and not spread further.
Photo 15 - You need to wipe the wound from the edge to the center
How long it takes for the pus to come out depends on several factors:
- The sooner treatment measures are taken, the easier and faster the healing will be. Photo 16 - Treatment should begin as early as possible
- Frequency of compresses applied. Photo 17 - The more often you apply the compress, the faster the pus will come out
- Cleanliness of the body during the period of illness, the use of antiseptics to treat the damaged area of the skin. Photo 18 - Hygiene is important during treatment for a speedy recovery
The body's reaction to this disease can manifest itself in symptoms such as:
- nausea; Photo 19 - During treatment of a boil, the patient may suffer from a headache
- elevated temperature; Photo 20 - Temperature may rise during treatment
- headache;
- enlarged lymph nodes. Photo 21 - During treatment of a boil, the lymph nodes may be enlarged
IMPORTANT: Do not squeeze the boil if you are not sure that it is ripe, this may worsen the situation
How to draw pus out of a boil
The questions that arise: how to make the pus come out, how to draw it out, what draws out the pus better, how to calm the suppurative process, what ointment is used to treat purulent furunculosis, etc. can be answered as follows.
Photo 22 - There are many ways to draw out pus
The main goal in treating a boil is to relieve suppuration and allow the pus to come out. Applying an aloe leaf, cut into two parts, which needs to be wrapped and changed every three hours, helps to draw out the pus quite quickly.
Photo 23 - Aloe helps draw out pus
This method is an excellent folk remedy that is accessible and well suited for soothing a boil that is festering. A boil that has not yet reached maturity will be without pus and without a purulent head, which requires additional time and measures to accelerate ripening.
Photo 24 - Aloe needs to be changed every 3 hours
There are remedies that are great for drawing out pus:
- Ointments that draw out pus, such as Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment are the most common and affordable. Photo 25 - Ichthyol and Vishnevsky ointment draw out pus
- Folk remedies in the form of compresses of aloe and Kalanchoe, grated raw beets, gruel of garlic, onions and vegetable oil mixed in equal proportions, applying baked onions. Photo 26 - Beets, onions, vegetable oil will help draw out pus
After the goal is achieved and the pus is released, the patient’s condition begins to ease and measures are required to disinfect and soothe the site of the breakthrough. To do this, you need to rinse the wound well with hydrogen peroxide and apply an antiseptic ointment, for example, Levomekol ointment and then calendula ointment as a wound healing agent.
Photo 27 - When the pus has come out, you need to apply a healing ointment
Attention! Due to possible complications and unpredictable course of the disease, it is prohibited to carry out warming at home.
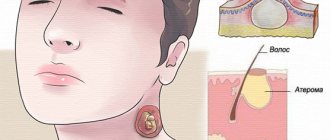
Boil stem
If a person encounters this problem for the first time and it is not known how to remove the rod, sometimes the question arises about how to find out whether the rod has come out and what it looks like. As soon as the bulk of the pus comes out, a compacted area of greenish-yellow color with a dense structure is visible.
Photo 28 - The core of the boil is a compacted area of greenish-yellow color
This is the necrotic core itself, which consists of dead cells, in other words, the root of the boil. When it is possible to remove the rod, a small hole forms in its place, which after a couple of days closes and a scar forms in its place.
Photo 29 - The root of the boil consists of dead cells
When looking for information on how to pull the rod and how to pull it out, you can often come across the fact that it is recommended to squeeze it out or puncture it, but this is only permissible when the abscess has opened, but the rod does not come out. When the disease drags on and after all the procedures there is still a boil without a rod, you need to consult a specialist so that he can give recommendations on how to remove it, or if the rod comes out, what to do next for a complete recovery.
Photo 30 - After removing the root, a hole remains
Drug treatment for a boil without a developing head includes treatment with antibiotics, immunostimulating therapy, and physiotherapy prescribed according to the severity of the disease.
Photo 31 - Boils can be treated with medications
After the rod has come out, antiseptic treatment must be done, and therapy aimed at tissue healing is indicated. If at the site of the boil, after the rod comes out, a painful red lump remains, it means that the purulent process has not yet passed and this signals the need to do stretching compresses.
Photo 32 - After removing the rod, you need to do an antiseptic treatment
The main goal is to pull the rod out. As mentioned earlier, dry heat and compresses can do this. Inflammation will be present as long as the root of the boil is inside and as soon as the rod can be removed, the pain and elevated body temperature will subside.
Photo 33 - Dry heat and compresses will help stretch the shaft
Sometimes sick people wonder whether the boil will come out on its own. If the maturation process is underway, then it can go away on its own; if an abscess has already begun, then you just have to wait until a breakthrough occurs.
photo 34 - If an abscess begins, a breakthrough will definitely occur
In the case when a boil without a head is located in a dangerous area, and the stem does not come out of the boil, the doctor may decide to remove it surgically, in order to avoid complications that can even lead to death.
Photo 35 - A boil can be removed surgically if it does not burst on its own
These methods are often used when treatment does not bring results and it is not possible to remove it yourself.
Photo 36 - Do not remove the boil yourself
IMPORTANT: Do not delay visiting a specialist if you cannot cope with the elimination of the boil on your own. This can lead to worsening of the condition and blood poisoning. Timely prescribed treatment will help relieve serious consequences.
udermis.ru
The most popular ointments
Regardless of which product was chosen, the same application rules apply to them. First of all, it is important to ensure clean skin. It is forbidden to touch it with dirty hands, and before each application of the ointment, be sure to treat it with hydrogen peroxide or a solution of potassium permanganate.
The ointment is applied under a compress, which is changed every three hours. It is important not to create strong compress pressure on the skin, so as not to complicate the course of the disease.
The best drugs for the treatment of boils are:
- Ichthyol ointment. The active ingredient is ichthyol, which has a disinfectant and analgesic effect. Using the drug helps cope with itching and prevents the infection from spreading to other tissues.
- Vishnevsky ointment. During the period of maturation of the abscess, it accelerates the process many times over. During the wound healing stage, it prevents re-infection and promotes rapid healing.
- Syntomycin ointment. The active ingredient is the antibiotic Sintomycin. Used for a short time, requires caution in use.
- Streptocide ointment. The active ingredient is streptocide. The drug is effective due to its high antimicrobial effect.
- Levomekol ointment. The action is based on a combination of the immunostimulant methyluracil and the antibiotic chloramphenicol. When applied to a boil, purulent formations are quickly drawn out, and at the same time the process of regeneration of healthy cells is started.
Synthomycin ointment contains antibiotics
Comparison with hidradenitis
Hidradenitis, or in popular terminology - udder knot - acute suppuration of the sweat glands located in the perineum, armpits, groin, and around the nipples. Infectious agents (staphylococcus) penetrate through the lymphatic vessels or through skin erosions into the ducts of the sweat glands and actively multiply, which is facilitated by the abundant secretion of sweat and its alkaline environment.
The causes may also be disturbances in fat metabolism and the function of the sex glands.
Development and symptoms
Painful pea-sized lumps form in the adipose tissue, which transform into pear-shaped nodes of 30–40 mm, tightly connected to the skin. In the middle of the lesion, softening of the tissue occurs, accumulation of pus and the formation of a fistula canal for the release of pus to the surface. But with hidradenitis there is no central necrotic core, as with carbuncle.
An abscess with hidradenitis ruptures spontaneously, releasing thick pus from the fistulous tract, which heals, forming a scar.
Sometimes several abscesses combine, creating a dense, uneven formation with many fistulas. Confluent abscesses with hidradenitis resemble phlegmon, but unlike it, the surface of the skin above the purulent conglomerate is lumpy, similar to the nipples of a dog, which is where the name “bitch udder” comes from. The purulent masses that pour out when hidradenitis ruptures are thick, sometimes mixed with blood.
Recovery is long - up to 2 - 3 weeks, and in the case of the formation of bilateral abscesses - up to 2 - 4 months. With a “bitch udder,” when the abscesses “burst” in the thickness of the tissue, new abscesses simultaneously appear.
Symptoms:
- inflammation in the form of bumpy, painful nodes that look like pears;
- intense pain when pressing, moving, bursting - at rest;
- red-bluish hot skin on the area of the abscess;
- signs of toxin poisoning - headaches, weakness, fever, increased ESR and leukocytes.
When diagnosing, hidradenitis is differentiated from phlegmon, lymphadenitis, sarcoma and tuberculosis of the lymph nodes, abscess, and lymphogranulomatosis. The difference is that the “bitch udder” develops in the thickness of the tissue, and, for example, inflammation of the lymph nodes of various types - in the fatty tissue.
Therapy
- General treatment of hidradenitis is carried out using antibiotics (Doxycycline, Erythromycin).
- When an abscess matures in the area of inflammation, hair is removed and treated with antiseptics: iodine, ethyl alcohol (96%), salicylic acid solution (2%). In case of large infiltrate and intense pain, the lesion is blocked with injections of antibiotics with novocaine 0.5 - 1%.
- For the first 5–7 days, apply quick-drying bandages with alcohol (50% solution).
- The use of ointments and compresses is contraindicated to avoid possible skin damage and increased inflammation. To ripen an abscess, dry heat is successfully used: a heated towel, heating with a “blue lamp” (5 minutes), in the summer - solar heating (10 - 30 minutes).
- A mature (softened) abscess is excised completely down to healthy tissue. After removing pus and inflamed tissue. The usual opening of hidradenitis is not effective, since the abscess consists of many abscesses at different stages of maturation.
- At the stage of infiltrate formation, UHF, UV and SMV therapy are often prescribed, which are recommended at the stage of abscess maturation.
Actions of the patient when opening an abscess on his own
All measures taken to draw out pus are aimed at speedy maturation of the boil. The main condition for successful treatment is the patient’s endurance, which will not allow him to damage the thin surface of the abscess. It should open on its own.
As soon as this happens, the patient must make every effort to cleanse the wound. The entire contents of the boil, along with the purulent core, are carefully removed with a swab soaked in hydrogen peroxide.
You can also try simple rinsing with a disinfectant liquid. It is important to completely clear the wound of pus, but do not apply pressure to the swollen area.
If not all of the pus has come out, the seal around the wound remains, you need to continue making compresses with Vishnevsky ointment. After the wound is completely cleansed, Levomekol ointment is used. It promotes rapid healing of the wound without the formation of a noticeable scar.
Levomekol will help avoid scar formation
Difference between carbuncle and cellulitis
Phlegmon is a diffuse acute suppuration of tissue (subcutaneous, perinephric, intermuscular, rectal, retroperitoneal), which actively spreads to tissues, muscles, tendons and bones. The outline of phlegmon, unlike a carbuncle, is not clear. The pyogenic membrane, as in an abscess, is also absent.
Cellulitis can be purulent, putrefactive, gaseous (anaerobic), which directly depends on the type of pathogen that has penetrated the tissue - staphylococcus, E. coli, anaerobic bacteria, streptococcus. The introduction of microbial flora occurs from foci of inflammation of adjacent organs, through lesions on the skin, with blood through the vessels from remote purulent foci.
Signs
Signs of phlegmon are similar to the development of any purulent-inflammatory process: fever, chills, thirst, soreness.
Observed specifically with phlegmon:
- Characteristic of the diffuse form of inflammation is rapid swelling.
- Diffuse redness of the skin in an area of shallow phlegmon.
Development and types
In the inflamed area, convex swelling quickly grows (with subcutaneous phlegmon), the skin is red, hot, tense, shiny. When palpated, a fixed compaction is revealed - extremely painful without definite boundaries. As suppuration progresses, softening at the site of compaction or the formation of a fistula tract is determined when the abscess is deep.
- With serous phlegmon, the adipose tissue resembles jelly, saturated with watery pus.
- The putrefactive form is characterized by the development in the tissues of many zones of necrosis with a large volume of foul-smelling pus.
- With gas phlegmon, tissue suppuration with large areas of dead cells and the presence of many small gas bubbles is detected.
- The chronic course occurs with the development of a focus of suppuration of abnormal density and bluish color. Reclus phlegmon, which develops when pathogenic bacteria invade the nasopharynx, manifests itself as a painless and pronounced lump on the neck, the inflamed tissues of which become hard as wood.
Indications for boil removal
The development of chiria at the very beginning is confused with a regular pimple. But it quickly becomes painful, and there is pus inside. To the touch, the boil is noticeably denser than a regular pimple. Increasing pain in combination with other signs requires consulting a doctor. During the period of maturation, the tumor noticeably increases in size and is very painful. But at this stage, opening the abscess is dangerous for the patient.
A specialist can help the purulent formation come out only when the boil is fully mature. The tumor is opened, helping all the pus to come out completely. Immediately after surgery, the patient notices a significant decrease in pain. The resulting wound must be carefully treated. In each specific case, the attending physician himself selects the appropriate drugs.
With proper care, only a small, almost imperceptible scar will subsequently remind you of the surgical intervention. Patients who neglect the recommendations of their doctor in the postoperative period risk acquiring a large and unsightly scar. It will be very difficult to get rid of it in the future.
The rehabilitation course is as important as the operation itself. Removing a boil does not mean immediately ridding the patient of the problem and acquiring lifelong immunity. Rehabilitation is aimed at preventing relapses. Otherwise, the patient can expect the appearance of a new boil on any part of his body with the slightest decrease in immunity, hypothermia or other factors. And after that, another few days await him, necessary for the boil to ripen.
Surgical removal is possible after the boil has matured
How to squeeze out a boil: is it possible and what will happen, how to remove the rod at home?
Furuncle (boil, abscess, abscess) is a deep local purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous glands and connective tissue around them. It is of infectious origin, in particular, it is most often provoked by Staphylococcus aureus. The inflammatory process is a response to the penetration and development of a pyogenic infection in the follicle. Is it possible to treat such formations independently using the squeezing method? Let's try to figure it out.
Experts' opinion
In the center of the infiltrate, a purulent boil core with elements of necrotic tissue is formed along the entire height of the hair follicle. An abscess manifests itself on the surface of the skin as swelling and redness. A sign of a mature shaft is a whitened tip on the surface of the skin above it. The boil can reach the size of a walnut, although it can also be the size of a regular pimple.
On average, the process of occurrence, development, opening and healing of an abscess lasts up to 2 weeks, but sometimes it drags on for a longer time. Since this disease is common and studied, some patients prefer to self-medicate. Especially if the boil is located on an open area of the body, it causes great discomfort - it can be pain, poor health.
Often patients accelerate the process of abscess maturation with the help of ointments, traditional medicine and mechanical action. In the best case, after opening the purulent-necrotic rod, the patient helps it come out and cleanse the wound by squeezing.
The most dangerous thing is premature piercing or cutting and further squeezing out a boil that is not yet ready for opening.
Doctors prohibit self-medication of ulcers, and even more so, they are against their opening outside the walls of a medical institution by non-professionals. This can result in severe complications, including sepsis, the prognosis of which is very poor. Complications such as:
- furunculosis;
- abscess;
- carbuncle;
- phlegmon;
- lymphadenitis;
- lymphangitis;
- thrombophlebitis.
The specialist will accurately determine when it is possible to open and squeeze out the purulent core - the root of the boil. He will do this with high quality and in complete sterility, which is very important.
After all, even if all antiseptic rules are followed, improper squeezing can spread the infection beyond the boil. A person who does not have special education does not know whether the rod can be squeezed out, whether it has been completely removed, how the wound has been treated, whether inflammation has been suppressed, or how healing is proceeding. The doctor knows exactly what a mature boil looks like.
Also, incompletely squeezed out pus does not cure the abscess; the inflammatory process continues and can become chronic. In addition, there are a sufficient number of places where boils are localized, where they are difficult to treat and squeeze out the boil on your own.
Medical workers warn against accelerating the opening of the abscess using warming procedures. This can facilitate the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into nearby follicles. Instead, it is recommended to use Ichthyol or Vishnevsky ointment if there is no allergic reaction to them.
Carrying out the procedure at home
Those who know how to properly squeeze out a boil from start to finish have a greater chance of recovery without complications. Let's consider the necessary actions. First of all, you need to know that only squeezing out a fully mature abscess can be successful. Therefore, you need to know the signs that indicate that the abscess is ready to open:–
- increasing pain;
- thinning of the skin over the shaft;
- softening of its top.
If these manifestations are absent, you can use ointments (Levomekol) or fresh aloe leaves to activate the process. They are used in the form of compresses, which are renewed after 4-6 hours. To successfully squeeze out a boil, it is also important to maintain sterility and thoroughly clean your hands, materials, affected area and adjacent tissues with alcohol before the procedure.
If the patient decides to open the boil on his own, he should prepare small scissors, preferably new ones, and understand how to squeeze out the boil. Before use, they are thoroughly treated with alcohol. Then the top of the abscess is pierced or cut off.
Extrusion begins from the edges - without unnecessary effort, gradually moving towards the center. Purulent discharge is collected with cotton or gauze swabs; it is important that they are sterile. A special container is prepared for them to prevent the spread of infection.
If it is noticeable that not all of the pus has come out or a lump in the boil is felt by touch, there is no need to continue squeezing.
It is better to apply Vishnevsky ointment and wait for the rod to completely withdraw without any effort. Bloody discharge oozes from the cleaned wound, and a deep cavity is visible. This means that all the pus has been removed.
Next, you need to properly treat the wound. What to do for this:
- rinse the resulting cavity and surface of the wound with an antiseptic - a solution of Hydrogen Peroxide, blot off the residue;
- cover the wound with a sterile bandage or napkin to ventilate it, do not apply a tight bandage;
- do not moisten the boil, apply healing anti-inflammatory ointments on a napkin and apply them to the wound, securing with a band-aid (Bepanten, Gentaxan);
- monitor changes in the boil, and if there are any deviations from the norm, contact a specialist.
It is important to apply ointments correctly and not to clog the wound with them. Otherwise, it will stop ventilating, healing will be disrupted, and favorable conditions will be created for the development of a new infection. It is necessary to treat the wound and apply ointment for a few more days. Next, a crust forms and falls off on its own.
Contraindications and possible consequences
Squeezing is a very dangerous procedure that has contraindications. It is prohibited to squeeze out a boil in the following cases:
- until the abscess is completely ripe;
- there is a high temperature, pronounced signs of intoxication - very poor general health;
- the inflammatory infiltrate is dense, severe pain is felt;
- green pus is visible at the top of the boil;
- the abscess has formed too large;
- if it is a repeated abscess, as it may be furunculosis;
- the boil occurred in a child, especially a small one;
- the spread of the boil is very rapid, there is an expansion of redness, swelling, and increased pain;
- old age of the patient;
- the purulent-necrotic core has not formed;
- within several days the boil does not develop (no changes);
- abscesses are located on the face, neck, nose, ears, scalp - the infection can penetrate the blood vessels of the brain and affect its membranes;
Patients with boils in the face and head are treated only in a hospital, since possible complications can result in death. The surgeon performs opening and squeezing out other abscesses in the outpatient clinic.
When performing uncontrolled squeezing of boils at home, you need to be aware of the danger of consequences that can cost your life. After non-medical removal of pus from a boil, the following complications may occur:
- sepsis with damage to the kidneys, liver, meninges;
- expansion of the inflammatory infiltrate if the patient squeezes out a boil with an immature purulent core;
- infection of other parts of the body and people present if the procedure is performed incorrectly;
- formation of fistulas;
- boil recurrence;
- the occurrence of abscesses with a malignant course (in the area of the nasolabial triangle, on the nose and chin).
It is difficult to talk about the effectiveness of home squeezing out a boil, even if it ended successfully. Any self-medication is dangerous and, most often, not justified. Only a specialist will perform high-quality removal of the rod and treatment of the boil and will monitor the patient until complete recovery in order to avoid complications.
Do you have warts or papillomas on your body? If not treated in time, then in the future this may result in cancer, an increase in the number of warts and other problems. Remember! You will forget about warts, papillomas and dry calluses in 3-5 days! Warts and papillomas will disappear if 2 times a day... Are you sure that you are not infected with the PAPILLOMA virus?
According to the latest WHO data, 7 out of 10 people are infected with the papilloma virus. Many live and suffer for years, not even suspecting diseases that destroy internal organs.
- fatigue, drowsiness...
- lack of interest in life, depression...
- headaches, as well as various pains and spasms in the internal organs...
- frequent rashes of WARTS and PAPILLOMAS...
These are all possible signs of the presence of the papilloma virus in your body. Many people live for years and do not know that there are time bombs on their body. If measures are not taken in time, then in the future this may result in cancer, an increase in the number of papillomas and other problems.
Perhaps it is worth starting treatment now? We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the new method of Elena Malysheva, which has already helped many people cleanse their bodies of the papilloma virus and get rid of warts and papillomas... Read the article >>>
doloypsoriaz.ru