Types of burns
Providing first aid for burns directly depends on the type of burn and its nature. All burns are divided by specialists into the following groups:
Thermal burn.
Develops when the skin or mucous membranes are exposed to extreme temperatures - both high and low. Thermal burns can be caused by contact with open flames or hot objects. Possible burns from boiling water, hot steam, liquid nitrogen, or hot gases.
Chemical burn.
It develops as a result of exposure to caustic chemicals on the skin - most often concentrated acids and alkalis, as well as their vapors.
Electrical burn.
It develops as a result of exposure to electric current on the skin, which, in turn, has a thermal effect on the human body, among others. However, due to the peculiarities of first aid and further treatment, electrical burns are classified as a separate group.
Degrees of burns and their characteristics
In addition to the nature of the burn, its depth, extent and severity are also important. All these parameters have a significant impact on the procedure for first aid for burns.
Classification of burns by degree, accepted in international clinical practice:
- A first degree burn
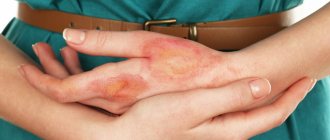
is manifested by redness of the burned area of the skin, burning pain, and swelling of the tissue. As a rule, it heals without a trace; for some time after the burn, peeling of the skin on the burned area may be observed, and a pigment spot may form. First-degree burns can be life-threatening if a large area of skin is burned, especially if a child is injured. - A 2nd degree burn
manifests itself as deeper lesions, however, they do not spread beyond the skin. In addition to redness, blisters filled with cloudy yellowish contents form on the skin. - Burns of degree llI
are usually divided into two subgroups: A and B. With degree llIA, the burn is deep, and there are large blisters with cloudy or bloody contents on the surface of the skin. IllB degree burns affect the germ layer of the skin, their healing is accompanied by the formation of a skin defect and its subsequent scarring. The sensitivity of the burned area for 1st degree burns may be reduced. - A 15th degree burn
is manifested by necrosis and charring of tissue.
The degrees of burns in a child correspond to the degrees of burns in adults, but you need to understand that the surface of a child’s skin is smaller, and even minor burns can lead to serious consequences for the baby’s health.
Anti-rating of anti-burn drugs
Since most often in case of burns they try to use what is at hand, you need to know that there are products that not only do not give the desired effect, but also worsen the recovery process after a burn.
Baby cream
Although the baby cream contains herbal extracts and vitamin components, their concentration is low and there is no analgesic effect, so there is no point in using it for burns. It is needed for daily skin care, and for treatment it is better to choose more effective products.
Baby cream with chamomile and natural vitamin complex
Ichthyol ointment
Due to the ichthyol content, the ointment has a resolving and warming effect, so it can increase pain from burns. The drug also has irritating properties, stimulates blood flow to the affected area, which increases tissue swelling.
Will Vishnevsky ointment help with 2nd degree burns?
Vishnevsky ointment is used for 1st and 2nd degree burns only when infection is attached and there is no choice. This drug has a local irritant effect and often provokes allergic reactions.
Vishnevsky ointment
Is there any effect of Zinc ointment for burns with boiling water?
Zinc ointment has the most pronounced drying and astringent effect; due to its thick ointment base, it creates a dense film on the skin, so if you are burned with boiling water, it is better not to use this product.
The drug is recommended when a weeping surface forms at the burn site. In this case, Zinc ointment will absorb tissue fluid and help relieve inflammation.
Zinc ointment
First aid for burns
The primary measure in case of a burn of any nature and degree should be to eliminate the damaging factor and stop its effect on the body. It is important that the victim is provided with all possible first aid at home.
Thermal burn due to high temperatures
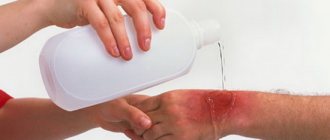
In case of a thermal burn, it is important, if possible, to ensure that excess heat is removed from the burned area of the skin. That is why it is not recommended to lubricate the burned area with oil - it impedes heat transfer. In case of a 1st-2nd degree burn, without compromising the integrity of the skin, you need to cool the burned area with cold water. It is important to act carefully so as not to damage the skin. First aid for a burn with boiling water is similar. If a large surface of the body is burned, it must be cooled with caution so as not to provoke hypothermia. In particular, a cold bath and ice are contraindicated; to cool the skin, you can use either running, disinfected cold water or gauze soaked in cold, clean water.
Sunburn
What to do if you have a sunburn? First aid boils down to moving the victim from the open sun to the shade and cooling the burned part of the skin. In addition, you can give the victim antipyretic or painkillers, if necessary, and apply special antimicrobial drugs to the areas where the skin is damaged, as described below in the paragraph treating burns at home.
Thermal burn at low temperatures
A cold burn, better known as a cold injury, occurs when the skin comes into contact with an icy surface (concrete, metal, any liquid, liquid nitrogen). According to the principle of impact, cold injury is very similar to a burn. What to do for cold burns depends on the degree of frostbite. For minor frostbite, rubbing the affected area with a woolen cloth until redness appears, putting on shoes with warm air (breathing), warming with warm hands, and a light massage will help. After warming up, apply a dry bandage. If frostbite is of degree II-IV, then you should act as if you were suffering from high-temperature burns.
Chemical burn
First aid for a chemical burn consists of long-term (at least a quarter of an hour) rinsing the burned area with water. In addition, neutralization of chemical burns gives a good result. If the burn is caused by acid, it is neutralized with an alkaline solution (soap, soda). Alkali burns can be neutralized with a weak solution of table vinegar or lemon juice. Neutralization allows you to stop the irritating effect of a chemical compound. In addition, some substances should not be washed off the skin with plain water. For example, sulfuric acid - when it comes into contact with water, it actively generates heat, which can aggravate the patient’s condition. Sulfuric acid is washed off from the skin surface only with an alkaline solution. A chemical burn can only be treated in a hospital.
Electrical burn
It is important to stop exposing the victim to current. Cover the affected area with a clean, dry bandage and call a doctor immediately. A burn due to electrical trauma is only one of the manifestations of severe damage to the body, and the patient requires emergency medical care.
Hogweed burn
The likelihood of getting burns from hogweed increases on sunny days; hogweed juice contains a photosensitizing substance and, when it comes into contact with the skin, increases its susceptibility to sunburn. Such skin damage takes a long time to heal, and the likely consequences of a hogweed burn are remaining ulcers, spots and scars.
What should be done:
- thoroughly, using soap, wash with water the place where the skin comes into contact with the plant and its juice;
- Protect the area of the suspected burn from sunlight. If the area is not covered with clothing, use any bandage, bandage, or patch to prevent the penetration of ultraviolet rays.
If burns have already appeared, it is not recommended to wet them. This area must be covered with a bandage and it is important that the area of the bandage not only covers the wound, but also covers the surrounding area of skin by 3-4 cm on all sides.
In case of danger of infection, opening of blisters, to protect the wound surface from infection and accelerate the healing process, apply Sulfargin® ointment with silver ions under the bandage, the active components of which destroy bacteria in the wound, help relieve inflammation and accelerate the restoration of damaged tissues. Sulfargin® ointment is not greasy, has a light texture, and is applied in a layer of 2-4 mm. The garter must be changed once a day.
Ointment for burns with boiling water “Levomekol”
"Levomekol" is a water-based drug, hydrophilic. The ointment is easily washed off and can be used with other medications. This is a highly effective ointment, since penetration into the skin of the affected area occurs instantly. In addition, the product has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. The main active ingredients included in the ointment are chloramphenicol and methyluracil. These components eliminate dangerous microorganisms that can cause suppuration.
A burn that was promptly treated with Levomekol festers less and the healing process proceeds faster. Methyluracil stimulates metabolic processes in cells, due to which the affected structures are restored very quickly. Also, this component of the ointment causes leukocytosis, which is very important in the fight against microbes, since the first defenders of the body are leukocytes. A single action of the medicine lasts approximately 20 hours. Subsequently, the burn must be treated again. In ordinary cases, a single use of the ointment leads to a reduction in inflammation in the area of the burned area, removal of swelling and removal of purulent mass. If the degree is severe, then the doctor prescribes the ointment for use at a later stage, after preliminary therapy. The method of using the ointment is as follows:
- the burn site is pre-washed with cool water;
- "Levomekol" is applied to a bandage made of gauze or a sterile bandage;
- a bandage with ointment is applied to the damaged area.
It is recommended to change dressings with Levomekol after 20 hours. If the effect is not noticeable, it is necessary to change the bandage more often. This ointment for burns has no contraindications. It can be used even during breastfeeding. Before you start using the ointment, it is recommended to check the expiration date. The ointment should not have a destroyed composition or changed color. The color should be white and even.
Treatment of burns
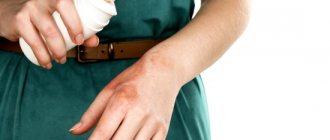
- For any type of burn, it is unacceptable to tear off the tissue adhering to the burned area of the skin. You need to carefully trim the adhered tissue and apply a sterile bandage over it.
- There is no single answer to the question of how to numb a burn. If we are talking about a small superficial heat burn, the pain subsides as soon as the excess heat is removed and the skin surface cools. For extensive and deep burns, painkillers are required.
- Is it possible to pierce a burn blister? Under no circumstances, their autopsy can only be performed by a doctor under sterile conditions. If the bubble bursts on its own, you need to cover it with a sterile bandage. At home, you can treat burns with an area of no more than 1% of the body surface (this corresponds to the area of the victim’s palm).
How to treat burns at home?
At home, it is permissible to treat only thermal burns, including solar burns of the 1st and 2nd degrees.
- Chemical, electrical and thermal burns, as well as third- and fourth-degree burns, are treated in a hospital setting. Therefore, answering the question of what to apply to a burn, it is understood that we are not talking about deep or extensive wounds. For any burns, do not treat the burned surface with oils and alcohol-containing lotions. It is worth noting that dexpanthenol-based ointments do not have an antibacterial effect and, accordingly, do not reduce the risk of wound infection.
- A good effect is obtained by daily treating the wound with an antiseptic solution (for example, chlorhexidine) followed by applying an ointment with an antimicrobial component, especially if the blisters burst and there is a risk of infection on the surface of the wounds. For example, Sulfargin®
with silver ions.
The active components of Sulfargin®
destroy bacteria on the surface of the burn, help relieve inflammation and accelerate the restoration of damaged tissue. - Sulfargin®
ointment is not greasy, has a light texture, and is applied in a layer of 2-4 mm once a day to a previously cleaned surface of the wound under a bandage or 2 times a day in an open manner. The drug was studied at the Russian Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, Federal State Institution “Institute of Surgery named after. A.V. Vishnevsky”, as well as at the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Moscow Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery” and is recommended as an effective remedy for the treatment of burns with a high safety profile, approved for use in children over 1 year of age.
note
that folk remedies for burns, popular among the general population, on the contrary, can provoke the development of complications. Washing with urine, applying cabbage leaves, potato slices, “homemade ointment for burns with boiling water with blisters” according to a neighbor’s recipe, lubrication with cosmetic creams and cooling anti-radiculitis ointments can provoke additional damage to the skin, introduce infection into the wound, cause suppuration, which subsequently results in long-term healing of the wound and formation of a noticeable scar.
Ointment for burns with boiling water “Levomekol”
"Levomekol" is a water-based drug, hydrophilic. The ointment is easily washed off and can be used with other medications. This is a highly effective ointment, since penetration into the skin of the affected area occurs instantly. In addition, the product has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. The main active ingredients included in the ointment are chloramphenicol and methyluracil. These components eliminate dangerous microorganisms that can cause suppuration.
A burn that was promptly treated with Levomekol festers less and the healing process proceeds faster. Methyluracil stimulates metabolic processes in cells, due to which the affected structures are restored very quickly. Also, this component of the ointment causes leukocytosis, which is very important in the fight against microbes, since the first defenders of the body are leukocytes. A single action of the medicine lasts approximately 20 hours. Subsequently, the burn must be treated again. In ordinary cases, a single use of the ointment leads to a reduction in inflammation in the area of the burned area, removal of swelling and removal of purulent mass. If the degree is severe, then the doctor prescribes the ointment for use at a later stage, after preliminary therapy. The method of using the ointment is as follows:
- the burn site is pre-washed with cool water;
- "Levomekol" is applied to a bandage made of gauze or a sterile bandage;
- a bandage with ointment is applied to the damaged area.
It is recommended to change dressings with Levomekol after 20 hours. If the effect is not noticeable, it is necessary to change the bandage more often. This ointment for burns has no contraindications. It can be used even during breastfeeding. Before you start using the ointment, it is recommended to check the expiration date. The ointment should not have a destroyed composition or changed color. The color should be white and even.