Treatment after burns
There are four main degrees of burn injuries:
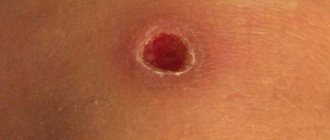
- With a first degree burn, damage occurs to the epidermis, that is, the surface of the skin. After a burn, slight swelling and redness of the skin is observed. As a rule, such a burn goes away within two to three days, leaving no traces.
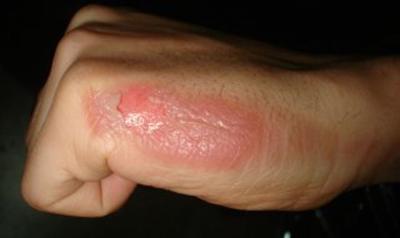
- With a second degree burn, blisters form. With proper treatment and the use of adequate therapy and remedies after burns, healing is possible within ten to twelve days.
- A more serious, third degree burn is characterized by tissue necrosis. In this case, a dry crust, the so-called scab, forms over the wound. In case of a third degree burn A, the epithelial cells of the skin are partially preserved, which contributes to the process of self-healing of the wound. And with a third degree burn B, all the skin dies, and the wound heals very slowly.
- A fourth degree burn is accompanied by charring of the skin and deep damage to the muscles, subcutaneous tissues and bones. In case of severe burns and a large area of damage, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
For small lesions, correctly provided first aid is of particular importance for rapid tissue healing.
First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the burn as soon as possible by stopping the exposure of the skin to fire or temperature. Cool the affected area by placing it in cold water or applying dry ice.
When providing first aid, you should not immediately apply ointments or creams after burns to the damaged tissue; you must first clean the undamaged surface around the affected area using ether and then alcohol.
An isotonic sodium chloride solution is usually used to remove dead tissue from a wound. If first aid is provided in a timely manner, the skin damaged as a result of a burn will heal much faster.
Skin restoration after a burn
At the stage of skin restoration, the main tasks are healing and disinfection. Often, immediately after a burn, a blister appears on the skin containing a clear liquid - plasma, which seeps through the damaged tissue.
If blisters after a burn are treated correctly, inflammation and suppuration can be avoided, and a new layer of skin will begin to form under the blister, and after one or two weeks the damaged area will dry out and separate. In place of the blister, as a rule, there remains a light pink spot - new young skin. The skin after a burn is very tender and sensitive; at this stage, to speed up its regeneration, it is recommended to use various ointments, creams and gels. They help restore damaged tissue and remove burn marks.
In case of unfavorable development of events, an infection may develop in the damaged area of the skin, then inflammation and suppuration of the blister occurs. The inflammatory process leads to increased temperature, chills, weakness, and recovery after a burn becomes longer. The resulting infection can lead to scarring and burn scars. If this happens, you should immediately consult a doctor who will prescribe tests. With their help, it will be found out what the cause of inflammation is.
Treatment of scars after burns
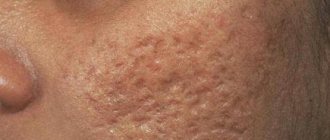
Scars that form where the skin is broken can become inflamed, often leading to the formation of a keloid scar that protrudes above the skin. The formation of a keloid scar is most often accompanied by itching and burning. Most often, large scars from burns are treated surgically. A burn scar is removed by excision of the scar followed by a cosmetic suture. Then, after the sutures are removed, the new scar is treated with special medications that prevent tissue growth.
Burn scars can also be treated with laser resurfacing. For less serious cases, a so-called chemical peel using fruit acids is used. In addition, it is recommended to use creams that contain active regenerating components.
Remedies for burns
Drugs used for treatment after burns at different stages come in several types - sprays, creams, ointments, gels and dressings.
Thus, ointments, for example Levomekol, are most often used to treat thermal burns. This medicine heals the wound and has bactericidal properties. In addition, it contains an analgesic component, which helps relieve pain in the first days of wound healing.
Povidone-iodine ointment contains active iodine, which disinfects the wound, as well as drugs that accelerate the process of tissue regeneration. The well-known balm “Rescuer” has a similar effect, made from natural ingredients without the use of hormonal and antibiotic agents, which actively restores the protective properties of damaged skin. Also, to avoid infection and speedy healing of the skin after a burn, Levomekol and Panthenol ointments are traditionally used.
In addition to ointments, another effective remedy for burns is cream. As a rule, it is used at the stage of restoration of damaged tissue, to prevent the formation of scars and scars. For sun and thermal burns, Panthenol cream foam can be used. Its action is similar to that of an ointment, but the cream, compared to the ointment, has a lighter texture and is more easily absorbed into the skin.
In case of serious damage, when contact with the wound causes severe pain, it is recommended to use sprays. They are easily sprayed onto the affected surface, avoiding additional contact with the painful area of skin.
Another means for treating skin after burns is various anti-burn dressings. They are impregnated with a special composition that relieves pain and has an antiseptic effect.
Gels are also an effective remedy for burns. Among such means is oh, “Apollo”. These gels combine the functions of an antiseptic for the initial treatment of a wound, a healing ointment and a local anesthetic. According to experiments, gels promote faster cleansing of wounds from necrotic tissue, preventing the development of the inflammatory process and suppuration, thereby preventing the formation of scars and scars.
Of course, it is better to prevent traumatic situations. However, if you have already received a burn, even a small one, it is better to go to the emergency room or the nearest clinic, where they will be able to give you more correct advice than you will find on the Internet or among friends. So, for example, vegetable or sea buckthorn oil, which is often recommended by everyone, is completely unacceptable to use immediately after damage occurs. Also, your first aid kit should always have a proven cream or gel for burns, for example, Panthenol.
How to get rid of burns at home
You can only treat superficial burns with your own hands (no more than second degree). If you receive a serious burn, we advise you to immediately seek help from a doctor.
After immersing the burned area in cold water, we recommend taking a few simple measures:
- Apply some Vaseline to the affected area and cover with a piece of sterile gauze.
- During the day, remove the bandage and try not to actively move your limbs.
- Take a pain reliever (such as ibuprofen).
- The next morning, remove the bandage to allow fresh air to blow on the burned area.
- Before removing the bandage, you need to moisten it a little so that the gauze does not stick to the wound.
- After 7 days, disinfect the wound and carefully remove dead skin using gauze dipped in an isotonic solution. Do not use excessive force when doing this, as dried skin will easily come off the wound.
Stages of burn healing depending on severity
Injury to the skin caused by exposure to high temperatures, chemicals, electricity and sunlight is called a burn. It is characterized by acute pain, burning and requires professional treatment. How a burn heals depends on the depth of tissue damage and other features. In severe cases, the recovery period drags on for several years.
Classification of burns
Many factors influence healing. To make a forecast, you need to know:
- degree of damage;
- type of injury;
- damage area;
- patient's age;
- general health.
Elderly people and children are at risk. Young skin is too thin, so it is injured as deeply as possible. Patients over 60 years of age have concomitant diseases that make it difficult to restore the epidermis.
Degrees
A special classification has been created, which includes 4 degrees of burns, characterized by different symptoms:
- the first is slight damage to the surface layer of the skin. It appears as redness and slight swelling. Pain and burning are felt, body temperature at the burn site rises;
- the second - the skin is affected up to the germ layer. Redness and swelling are accompanied by the appearance of blisters. Inside there is a clear liquid that gradually becomes cloudy;
- the third is divided into subgroups A and B. A degree A burn affects part of the dermis, leaving the sebaceous glands and hair follicles intact. At the site of injury, wounds appear that are covered with a soft scab. Sometimes large blisters filled with bloody fluid appear. A grade B burn destroys the dermis and can damage fatty tissue. Large-scale cell death occurs, the skin peels off;
- fourth is the most severe degree. The epidermis becomes charred and deep necrosis develops. All layers of skin, muscles and tendons are affected. Sometimes the injury extends to the bones.
Type of damage
The speed of healing depends on what exactly caused the burn. Doctors distinguish 4 types of injury.
- Thermal. Occurs upon contact with a heat source. This could be boiling water, hot oil, steam released by a kettle, the soleplate of a switched-on iron, or an open fire. Signs of damage include severe pain, blisters, inflamed and swollen skin.
- Chemical. Appears from exposure to aggressive substances. Salts of heavy metals, alkalis and acids pose a high threat. Such injuries rarely form blisters. Usually the affected area is covered with a scab. When it cracks, long-healing ulcers and weeping wounds form. In addition to contact with aggressive reagents in everyday life or at work, chemical damage to the epithelium is provoked by jellyfish stings and contact with certain plants.
- Electric. Occurs when an electric shock occurs at work, at home, or during a thunderstorm. Electrical injury is very dangerous. It disrupts not only the integrity of the skin, but also the functioning of internal organs. Such damage is manifested by redness, swelling, burning, and cardiac dysfunction.
- Solar. Occurs under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The cells of the surface layer die, irritation and swelling develop. Severe damage causes blistering. If they burst, open wounds appear.
Classification
Depending on the severity of damage to the skin, burns are classified according to degree:
| Burn degree | What is it characterized by? |
| First
| The superficial layers of the epithelium are affected, which is accompanied by redness of the skin, mild burning and pain. Typically, grade 1 injuries heal on their own without any consequences after 2-3 days |
| Second
| The layers of the epithelium are affected, which is accompanied by redness of the skin, swelling, burning and pain. With prolonged exposure to boiling water, small and large bubbles filled with a clear liquid form at the site of damage. 2nd degree burns heal within a couple of weeks, leaving no scars or skin changes. In severe cases, the injury site becomes infected and hospitalization is required. |
| Third (grade A and B) Blisters and deep skin lesions | The epithelium and deep layers of tissue are affected. With degree 3A, blisters form on the surface of the skin, covered with a thick scab (crust). With grade 3B, severe wet wounds are formed, often festering and poorly healing. After complete healing, a scar remains at the burn site |
| Fourth Deep lesions of all layers of the skin | Characterized by damage to all layers of skin and subcutaneous fat. In the case of a burn with boiling water, charring, as with exposure to fire, is not observed, but the wound is very serious. Often patients die from painful shock before the ambulance arrives, especially if a significant part of the body is burned |
Important! For 1-2 degree burns, treatment can be carried out at home after examining the wound by a doctor and accompanying recommendations. Patients with 3-4 degrees of burns, as well as persons who experience complications in the form of suppuration in 2 degrees, are subject to mandatory hospitalization. Children and adults who have burned about 20-30% of their body surface must be hospitalized in the burn department.
Area of injury
For the healing of burns, the area of the affected area is of great importance. Large-scale injuries provoke the development of burn disease and lead to many complications. The regeneration process takes a long time.
To correctly estimate the area, it is convenient to use the palm rule. This is a simple method accessible to everyone. Scientists have concluded that the open palm of an adult approximately corresponds to 1% of the total area of his body. If the size of the burn exceeds 5%, it must be treated in a hospital setting, regardless of the degree.
The method is not suitable for determining the extent of the lesion in a child. For patients under 15 years of age, specially designed medical tables and diagrams must be used .
Assessing the severity of the injury
In order to decide what action to take, it is necessary to assess how serious the injury is. If less than 10% of the skin is damaged by boiling water, such a burn is considered local, in other cases - extensive. For information, the palm of an adult makes up 1% of the surface area of the body.
Most often, small children receive injuries from just boiled water; their body surface is several times smaller than that of an adult, so even minor burns can lead to serious injuries.

The danger of boiling water for children
There are 4 degrees of burns resulting from spilled boiling water:
- The first degree is noted when, after a burn with boiling water, there is slight redness of the burned area, a sharp, burning pain is felt, and slight swelling of the damaged area may appear. Only the top layer of the epidermis is affected.
- The second degree is characterized by more significant redness of the affected area, blisters filled with liquid appear, and when damaged, the wound surface opens, where it is important not to introduce infection.
- Third degree injuries affect both the top layer of skin and soft tissue. Scabs appear under the blisters, and a purulent process develops.
- Deep wounds of the fourth degree affect all layers of skin, soft tissue, muscles, and sometimes even bones. Such terrible injuries to the body from boiled water practically never occur in everyday life.
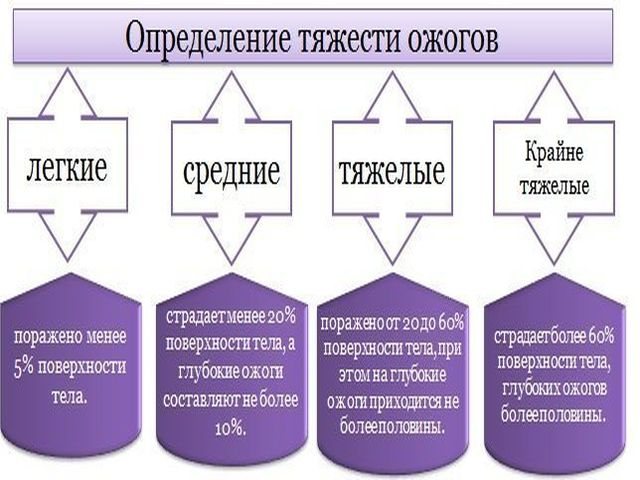
How to determine the severity of a burn
Important! When diagnosing 3rd and 4th degree burns, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Stages of healing
The rate of cell regeneration is individual for each person. Proper first aid is extremely important to alleviate the victim’s condition. A sequential algorithm of actions allows you to reduce the heating temperature in case of a thermal burn and neutralize the aggressive substance in case of chemical injury. This prevents deepening of the affected area and improves the prognosis for recovery.
First degree
Lesions of the 1st degree, in area not exceeding 5% of the skin, rarely provoke complications. The inflamed epidermis quickly recovers even without additional effort.
If you regularly treat it with products that can effectively heal damage, for example, Panthenol or Olazol, the symptoms disappear after 2-3 days. The redness subsides and peeling appears. The burn goes away without a trace, the skin is completely renewed.
Second degree
Stage 2 healing takes longer. If blisters have formed on the body, they should not be pierced. Inside there is a liquid containing white blood cells. They protect wounds from infection.
A burst bubble is an open gate for infection. Pathogenic microorganisms provoke inflammation and accumulation of pus. Such wounds take at least a month to heal and leave behind scars and scars.
Under normal conditions, recovery occurs within 2-3 weeks. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the doctor's instructions, regularly treat the blisters with antibacterial ointment, for example, Levomekol, and apply a sterile bandage. New skin forms under the blisters. Gradually they are blown away, the dead layer moves away, and in its place remains a pink spot of healthy epidermis.
Third degree
This degree of burn should only be treated in a hospital. Initially, severe inflammation develops. Necrosis and rejection of dead tissue is observed. To start the regeneration process, intensive therapy is needed, aimed at restoring immunity, suppressing infection, and relieving pain shock. A 3B burn requires surgery.
Only 20-30 days after injury, new cells begin to form, and healthy skin gradually appears . It may take several months to go through all stages of healing. Scars remain at the burn site, sometimes requiring plastic correction.
Fourth degree
Grade 4 damage is characterized by charring of tissue and death of all layers of the skin. They do not heal on their own. A person must lie in a room with a special microclimate and undergo complex treatment.
- In the first weeks, a scab appears in the affected area. It is important to avoid infection during this process.
- Granulation tissue slowly forms under the crust. This stage takes 1-2 months.
- When the granulation phase ends, skin grafting is prescribed. For transplantation, donor or the victim's own material is used.
The rehabilitation period after 4th degree burns lasts from 3 months to several years. The greatest danger is burn disease, damage to joints and bone tissue. Such patients often have impaired mobility and become disabled.
Any burns require the close attention of a specialist. Only a doctor can correctly assess the clinical picture and prescribe treatment that stimulates rapid healing.
What to do in case of a burn?

Our whole life is a daily encounter with dangers, all kinds of risks and problems. Pretending to be a wise minnow and hiding from the worries of the outside world in a cozy home is not a solution. Many unforeseen situations can happen to us within the walls of our own apartment: at any moment you can accidentally touch a hot iron, spill a cup of coffee on yourself, or burn your hand with steam over a boiling kettle. What to do if you are burned by boiling water? How to provide first aid to a victim injured by chemicals? In which cases you need to immediately go to the hospital, and in which burns you can get by with improvised means - we will find out in this article.

First aid for burns
A burn occurs as a result of exposure to high temperatures and immediately turns into an open wound, accessible to any microbes. Therefore, the first and most important thing to do is to free the damaged area from clothing and immediately cool the burned area. Ice from the refrigerator, snow, very cold water or any frozen product will do. Thanks to the cold, the pain subsides for a while, as unwanted inflammatory processes in the affected tissues are stopped. After providing first aid, you must carefully examine the burn and assess the location of the skin lesion - further actions depend on the degree of the burn.
Burn degrees
There are 4 degrees of burn, here they are:
- I degree is a mild and safe degree, in which only the upper layer of the dermis remains burned. There is noticeable redness and slight swelling on the skin;
- II degree - in addition to swelling and redness, blisters with cloudy contents appear on the affected area, and severe pain is observed. With proper treatment and emergency care, no traces of burns or scars remain;
- III degree - in this case, not only the surface of the skin remains damaged, but also deeper tissues; the burn can affect the muscles and damage them. Blisters with a cloudy liquid inside form on the burned area. Treating a third degree burn is difficult because there is a high risk of infection. Under no circumstances should treatment be carried out at home.
- IV degree is the most serious and dangerous degree of burn. High temperatures at this stage can damage the bone; skin and muscles may be absent. The most dangerous and difficult areas are the neck, face, inner arms and thighs. Patients tolerate burn injuries to their feet, back and arms (up to the elbow) more easily.
What actions are contraindicated for burns from boiling water?
How to properly treat a burn with boiling water, what can and cannot be done at home? In order to really help the victim without causing harm, you should remember what actions are prohibited for thermal household burns:
- Do not use medical alcohol, cologne or iodine to treat damaged skin. Such solutions irritate the skin even more and significantly worsen the condition;
- In order to properly and efficiently treat water burns, first aid at home should not consist of applying medicinal creams or ointments to the wound immediately after the injury. First you need to cool the wound and only then apply any means;

- It is strictly forbidden to puncture the blisters. Such actions not only slow down the treatment process, but also increase the risk of infection;
- As soon as a burn with boiling water occurs, treatment at home should exclude the use of fats and essential oils. Such products form a film on the skin, which in turn closes the pores and does not allow the skin to breathe. You can use oils as a medicine for burns, but a little later;
- If clothing is stuck to the burn site, it is forbidden to tear it off. It is necessary to carefully cut off the edges, and do not touch what is stuck to the wound surface;
- The first rinsing of the wound should be done with clean water. Acidic and slightly alkaline solutions are prohibited in such situations;
- It is not recommended to lubricate fresh wounds with kefir or sour cream. Although many consider these products to be highly beneficial, they contribute to the development of infectious processes. Dairy products contain acid, which has a detrimental effect on irritated skin.
If you do not know how to act in cases where there is a burn with boiling water, how to smear the resulting wounds at home, then the best solution would be to seek help from doctors. This will prevent negative consequences and help provide correct and safe treatment.
In case of a burn, it is strictly prohibited:
- lubricate the burn area with vegetable oil, alcohol-containing preparations, iodine, brilliant green;
- sprinkle with starch;
- apply burn ointment and other medical products to the hot surface of the skin;
- apply fermented milk products to the damaged area;
- pierce or cut through the formed blisters on the skin;
- independently clean the wound from dirt or remnants of clothing;
- wash the burn with water with the addition of soda or citric acid;
- apply a plaster to the burn.
Treatment of first degree burns
In case of a first degree burn, treatment can be easily done at home. As soon as the first emergency aid has been provided, the cooled surface of the skin should be lubricated with a medicine that will prevent the burn from spreading into the deep layers of the skin and will relieve swelling and pain. These are drugs such as:
- Panthenol - well restores burned mucous membranes and skin, has regenerative and metabolic effects on damaged tissues. The ointment perfectly relieves burning sensation and relieves pain.
- Sulfargin - this ointment with silver ions quickly copes with wounds of a wide variety of nature.
- Levomikol - first, lubricate a gauze bandage with the ointment, and then apply it to the burn site. This bandage needs to be changed every 20 hours - the swelling will gradually subside and the pus will be eliminated.
- Olazol is a spray containing an antiseptic and anesthesin. Thanks to this composition, the drug heals burns faster.
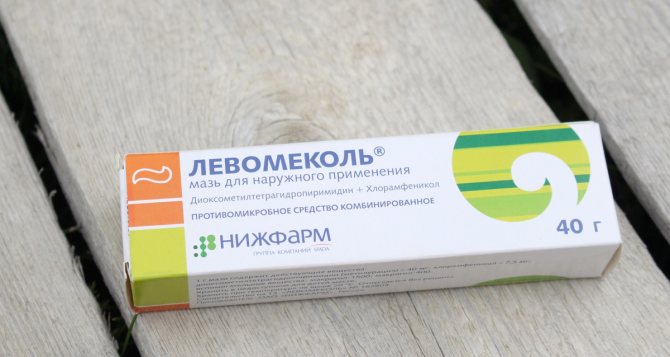
In addition to medications, homemade compresses are also suitable for treating minor first-degree burns:
- 100 grams of finely grated potatoes should be mixed with a teaspoon of honey. Make a compress on a bandage or gauze and leave on the burn site for 2-3 hours;
- finely chop the cabbage and mix it with raw egg white, and then brush the resulting mixture onto the burn;
- instead of lotions, you can leave cooled black and green tea on the damaged area;
- cut off a juicy aloe leaf, cut it lengthwise and apply to the burned area for a few minutes;
- freshly picked plantain leaves should be washed with boiling water, cooled and applied to the affected area of the skin;
- Place finely grated carrots on gauze or bandage and apply to the burn. The compress should be changed every 2-3 hours.

Burns caused by boiling water
This type of burn injury can be easily experienced at home. A pot or kettle of boiling water on the stove can be incredibly dangerous, especially if there are children at home.
Small but quite serious burns caused by boiling water happen, unfortunately, quite often. This is why you should always be very careful and boil water on the burner that is located further from the edge of the stove.

If a few drops of boiling water fall on your skin or you touch a hot object, you will immediately feel an unpleasant pain, which will disappear after a few seconds. The easiest way to relieve pain after such a burn is to place the burned area under a tap or immerse it in a vessel of cold water for at least five minutes to cool the affected area and relieve pain.
If you have received serious burns, we advise you to carry out the same procedure, but keep your hand in cold water longer. For second degree burns, place the burned area of the body under water for 15 minutes.
In fact, the type of treatment depends on which part of the body was burned. That is, if you cannot place the burnt area under running water or dip it in a bowl, you can apply a clean linen napkin soaked in cold water or a plastic bag with ice cubes inside to the affected area. Remember not to apply bare ice to burned skin!
Treatment of second degree burns
This stage is already considered a fairly serious injury, so assistance is provided first at a trauma center, and then at home. The doctor carefully treats the wound, performing the following algorithm:
- anesthesia of the affected area;
- treating healthy skin next to the burn with an antiseptic;
- removing dead skin, dirt and clothing;
- carefully removing the contents of burn blisters with a sterilized instrument. The membrane of the bladder remains intact to protect the wound from bacteria and infections;
- applying a bandage with a special bactericidal ointment to the wound.
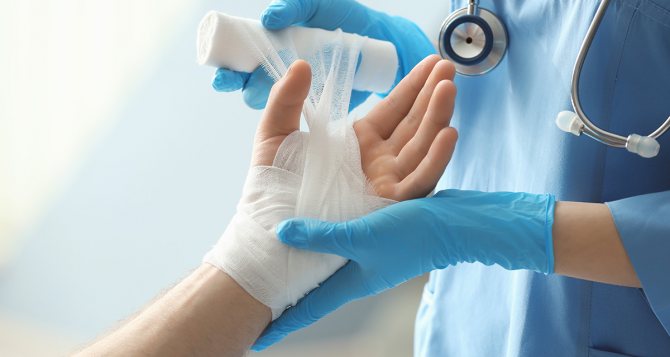
Why do boiling water burns occur?
Children are often burned with boiling water in an attempt to learn something new. Although such knowledge of the world around us is sometimes unsafe. A burn from boiling water can be caused by:
- a cup with just poured coffee, standing close to the edge of the table;
- a container of hot water that the baby can easily reach;
- It happens that a child suddenly runs up to a parent carrying boiling liquid.
There are many possible situations for receiving such an injury at home. There will be fewer complications from a boiling water burn if you quickly and competently provide first aid to the victim.

Burns of III and IV degrees
The first rule for third and fourth degree burns is no self-medication! Severe burns must be treated in a hospital. There, the doctor first carries out anti-shock therapy, surgical treatment (if it is necessary to remove dead tissue and perform skin grafting), and then hospital treatment.

What to do for burns from boiling water
- Get rid of clothing that is at the burn site as soon as possible.
- Inspect the affected area and determine the extent of damage.
- For a first or second degree burn, apply ice or make a cold compress, change the compress after a few minutes.
- If the burn is severe, go to the hospital immediately.
What to do for steam burns
- Remove clothing blocking access to the affected area of skin.
- Cool the burned surface.
- If the burn is on your hand, it should be kept elevated.
- If damage is more than 5%, go to the emergency room.
What to do for oil burns
- Cool the damaged area under running cold water.
- Apply a sterile, damp bandage to the burn site.
- If the burn is more than 1% (the palm makes up 1% of the whole body), call a doctor.
What to do for chemical burns
- Call an ambulance.
- Remove clothing from the affected area.
- Cool the burn area under running ice water.
- If the burn is caused by sulfuric acid, it must first be removed from the surface of the skin with a dry cloth.
- And if the burn is caused by quicklime, cold water will have the opposite effect! In this case, you need to remove the reagent from the affected area with a dry cloth, and then lubricate the burn with oil or greasy ointment.
How to correctly assess the extent of the burn surface?
The following features are typical for a first-degree boiling water burn:
- superficial lesion;
- hyperemia;
- edema;
- small bubbles.
With the second degree, the characteristics change slightly:
- the burn is also superficial, but a little deeper;
- the bubbles are tense or have already burst;
- swelling;
- redness;
- a thin scab is formed.
As for the third degree, the burn has the following features:
- the burn surface is so deep that it reaches the muscle fibers;
- small blisters have already burst;
- the presence of a dry crust.
The most severe, fourth degree, is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the lesion reaches the skeletal system;
- necrosis of surface tissue occurs;
- fabrics become charred and blackened.
If we talk about the first and second degrees of severity, then, as can be seen from the clinical picture, this is not so scary, so you can treat a burn at these stages at home.
The main point is that the burn surface area should be no more than one percent, which roughly corresponds to the size of a human palm.
Even in the first and second stages, if the lesion has affected the bone, face, genitals, then it is better not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor. The fact is that the scarring process may be associated with the occurrence of certain problems.
In case of third and fourth degree - serious injuries - you should immediately call an ambulance. The danger is posed by a burn of more than five percent; in this case, the risk of developing burn disease increases, a condition in which shock occurs and the functioning of the entire body is disrupted.
Regarding the specifics of treating young children, it is important to understand that the child’s body can react to injury individually and sometimes very unpredictably. There is a very high risk of complications, so it is better not to experiment, but to seek qualified help.
Serious burns: when to go to the hospital
Imagine that a pot of boiling water has been poured on you.
Even if your clothing is stuck to your skin, do not try to remove it yourself. Wet the burn area with cold water and call an ambulance immediately. Doctors will remove clothing so as not to cause further harm.
If blisters appear as a result of the burn, neither piercing them can make the problem even worse. This way you can prevent scars and wound infections.
It is better to wrap the bladder during the day so as not to accidentally touch it and cause a puncture, but in the evening you can free the bladder from the bandages for a few minutes so that it can be exposed to fresh air. If the blister from a burn is large, it is better not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor.
If the bubble causes you pain and severe discomfort, due to which you cannot move your limbs normally, you can make a small puncture to release the fluid. However, first be sure to disinfect the tool you will use to do this.
What further actions should be taken?
The main objectives of further measures include the following:
- cooling the burn surface;
- prevention of possible infection;
- anesthesia.
If you wash the burn surface with soap and water, this will be a good prevention of possible infection. Cooling can be continued by placing a cloth moistened with cold water on the affected area of the skin.
To relieve pain, you can give some analgesic drug; to reduce swelling, you will need to use antihistamines. It is worth understanding that the body loses a large amount of fluid through the wound surface, so the victim should drink plenty of plain water.
Treatments for burns
While the affected area is cooling, assess the extent of the burn injury.
If pain and redness do not go away after a few minutes and blisters appear, consult a doctor immediately.
If the redness and pain decrease, further treatment of the burn injury can be carried out further at home.
Take a small piece of gauze and moisten it with water. Wrap gauze around the affected area of the body and leave for 30 minutes. If necessary, change into clean clothes to prevent dirt and bacteria from entering the wound.
The best natural remedy for superficial burn injuries from boiling water, hot oil or sun rays is aloe vera. This plant should be in every home. To use the product, simply cut off one shoot and squeeze out the clear gel.
It is this thick liquid, which is found inside aloe shoots, that has the ability to moisturize the skin. Apply the gel to the affected area of skin and leave until completely absorbed.
You can wrap a piece of sterile gauze around this area, although we advise against doing this, because the wound needs to “breathe.”
How to properly treat a burn with boiling water?
There are two methods to properly treat a burn with boiling water, namely:
The open method does not involve applying a bandage, while the closed method involves the use of a bandage.
Although the open method is more productive, it is associated with risks of infection.
A specialist should determine the methods, but at first, bandages are always used to prevent infection.
The burn surface is treated with an antiseptic solution, a sterile napkin is applied, and then a bandage is applied.
Choose antiseptics that, in addition to their main action, have other properties:
- analgesic effect;
- regenerating features;
- reducing weeping;
- antibacterial properties.
Subsequently, when the damaged area stops oozing, it can be treated with fat-based ointments. This is effective, since at this stage it is necessary to accelerate the processes of epithelization and elastic scar tissue should form.
As you can see, in order to cure a burn with boiling water, a whole range of measures are needed, which are carried out in stages. But what mistakes are made when providing assistance and what should never be done?
What should you not do?
Let's talk about common mistakes that you should avoid:
- After a burn, immediately lubricate the affected area with fats of animal or vegetable origin. The fact is that fats help retain heat in the wound. Moreover, fats are a favorable environment for the development of the infectious process;
- treating the affected surface with irritating antiseptic agents, namely: alcohol, iodine, potassium permanganate, etc. The use of these agents causes severe pain, due to which it will be difficult for a specialist to assess the extent of the burn surface;
- Apply ice to the wound without wrapping it in cloth. This will worsen the situation, adding frostbite to the burn.