Everyone has probably experienced burns, even if only once in their entire life. Boiling oil, an accidental touch on a hot stove - such damage, as a rule, heals quickly, leaving no traces behind. But there are other types of burns, deeper and more serious. Such injuries are very painful and constantly remind of themselves with ugly scars on the skin.
Let's look at ways to help get rid of burn scars without causing negative consequences.
What kind of burns leave scars?
In order for the fight against post-burn skin changes to give a positive result, you need to know the cause of the burn and its degree. According to the nature of the occurrence of burns, there are:
- thermal, arising from exposure to high temperatures, for example, boiling liquid, fire, steam, sunlight, etc. 1st degree burns go away without a trace, since only the top layer of skin is affected. Grade 2 injuries may leave small scars and red spots. 3rd and 4th degree burns injure not only the epidermis, but also deep fatty layers, muscle and nervous tissue. Such injuries are the most serious - during the process of skin regeneration, the body forms scar tissue that is different from normal. The result is a noticeable scar that is unlikely to disappear on its own;
- chemicals that appear upon contact with salts of heavy metals, alkalis, acids and other harmful substances. With a 1st degree chemical burn, only the epidermis is affected, there is redness and a burning sensation. The second degree of damage is characterized by the formation of bubbles with liquid and swelling (traces usually disappear after some time). 3rd and 4th degree chemical burns are characterized by tissue necrosis and scab formation. Such damage takes a long time to heal, leaving noticeable scars in its place;
- electrical - formed as a result of exposure to electric current. As electricity passes through tissue, it is converted into heat, causing a burn similar to a thermal one. As with thermal burns, there are 4 degrees of damage.
During the formation of a scar, a crust forms, which cannot be touched, otherwise you risk making the damage even deeper and uglier. After scarring, you can choose a method to remove the burn scar and begin treatment.
Currently, there are surgical, medicinal and traditional methods of getting rid of post-burn scars. Depending on the degree of damage to the skin, you can give preference to one or another option.
What are burn scars?
A common scar is abnormally fused connective tissue with excess collagen fibers. A burn scar is a dense connective formation that also occurs during healing of an injury, but it also depends on the depth of damage to the epidermis, that is, it is not only a cosmetic problem, but often affects health issues if scars form in the extremities.
What happens to the skin during a burn?
The critical temperature at which you are guaranteed a burn is 43 C. Below, you should not be afraid of hot baths or a warm radiator on a winter evening - they are absolutely safe for you. In everyday life, you can get burned at 100-200 C by touching a hot source for no more than 1 second. In places of combat and in work shops, burns are especially dangerous and can occur at temperatures of 1000 C. You need to be very careful!
The degree of injury is influenced by its location on the body and the structure of the skin: the thermal conductivity of the dermis is higher than that of subcutaneous fat, since fat is a good insulator. Consequently, serious damage to the dermis may not affect the lower lipid layer, although too high temperatures lead to irreversible consequences: tissue, internal organs and even bones are destroyed. If first aid for a burn is not provided on time, irreversible intoxication of the body may begin.
Let's look at the degrees of burns in more detail.
Types of burns
Depending on the type, or degree, of the burn, the consequences will be of varying severity.
Typically the injury is classified into:
- superficial burns or 1st level burns;
- moderate or superficial burns of the 2nd level;
- deep - 3 levels.
A level 1 burn is the most harmless of all. Affects the upper layers of the epidermis, without reaching the dermis with hair follicles. After such a burn, there are no scars left, since enough keratinocytes come from the bottom of the follicle for normal tissue restoration.
Level 2 burn - can be superficial or deep. With a superficial burn, the entire epidermis and papillary layer of the dermis are affected, and with a deep burn, the reticular layer of the dermis is also injured. After the skin is damaged, macrophages are activated - particles that clean the wound of dead cells. Under the burned tissue, a new granulation tissue forms, which forms a scab. Thanks to this, the epidermis “heals” and a normotrophic scar appears (a scar that does not require correction).
However, if an infection gets into the wound during recovery, the rehabilitation stage may be delayed and a keloid or hypertrophic scar will form!
Level 3 burn - not only the epidermis is injured, but also the dermis, and subcutaneous fat with hair follicles. The latter are completely destroyed, which has a primary effect on wound healing. Since the hair follicles at the burn site are destroyed to the ground, keratinocytes come only from the edges of the wound, which is why rehabilitation is extremely slow.
Important! The longer the wound heals, the higher the likelihood of infection getting into it, which means the formation of keloid or hypertrophic scars that require immediate correction.
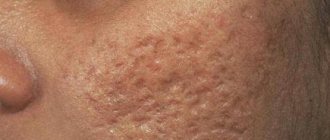
What is a keloid scar?
A keloid scar is often confused with a hypertrophic one. The difference is that, unlike a hypertrophic scar, a keloid scar brings a lot of discomfort: it quickly increases, growing beyond the wound, is accompanied by itching and pain, and has a bright burgundy or bluish color. The keloid scar does not shrink or resolve on its own, therefore, to get rid of it, you need to undergo several courses of physiotherapy with special means. It grows quite quickly and can extend beyond the burn in the form of peripheral cords.
The keloid scar itself does not shrink and does not resolve. To get rid of the scar after a burn, you will need to undergo a course of procedures.
What is a hypertrophic scar?
Unlike a keloid, it does not extend beyond the burn, but there is definitely nothing good about it. This defect is caused by excess collagen fibers at the burn site, which means it is dense and located above the skin level. Just like a keloid scar, it is not able to resolve on its own and requires treatment. Being in the area of the joints, such scars cause the greatest trouble, interfering with the normal functioning of the limbs.
Hypertrophic and keloid scars occur with deep burns, that is, with stages 2 or 3 or if the burn is very large. In affected areas, skin pigmentation is disrupted - it may be darker or lighter than the overall tone.
Sometimes scars grow in size over six months and then decrease over several years, but this is a rather rare occurrence in medical practice.
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing a burn scar
During recovery from injury, the effects can manifest themselves in many different ways. It depends on the:
- Patient's age. Children and adolescents have delicate skin, which means the risk of being left with a scar is higher, but at the same time it recovers faster, because the regenerative features of the skin are better developed than in an adult.
- Women are more prone to scars after burns than men.
- Injuries on the neck and upper extremities are hard-to-reach places that are more difficult to treat; the skin there is less elastic, which means less elastin is produced, and cell regeneration occurs more slowly.
- Surgery at the burn site more than once is often not a good solution, as it increases the risk of recurrence (re-formation of scars).
- Transplantation of a mesh skin flap at the burn site.
- It has been observed that dark-skinned people and people with Asian appearance are more prone to the formation of keloid scars due to their skin characteristics.
Radical removal methods
The following methods are effective in the fight against old scars and keloids:
- skin grafting. A post-burn scar is removed using a skin graft taken from another, healthy area of the body. This operation is indicated for 3rd and 4th degree burns, when the deep layers of skin and bone tissue are affected. If the patient does not have enough of his own skin, a donor's cover or special synthetic materials can be taken;
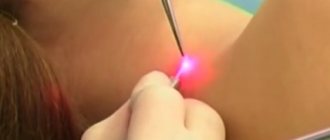
- laser resurfacing. This procedure is essentially a deep peeling, which removes the entire surface layer of skin (epidermis) and part of the dermis. Laser resurfacing can significantly smooth out the skin and remove deep scars. If the area of the burn scar is extensive, the procedure requires the use of local anesthesia or general anesthesia. The number of procedures, depending on the depth of skin damage, varies from 1 to 6, and their duration - from 30 minutes to 2 hours;
- scar excision. This is a simple surgical operation that involves removing scar tissue and applying a cosmetic suture. As a result, the scar thins out and becomes less noticeable;
- microdermabrasion. The essence of the method is to delicately polish the burn surface with microcrystals. During the peeling process, the upper keratinized skin particles are removed, the epidermis is renewed and scars become less noticeable. For the treatment of scars after a burn to be effective, an average of 5 to 10 procedures are required, depending on the depth of the damage. One procedure lasts 30-40 minutes. Microdermabrasion is absolutely safe and is carried out only under the supervision of a cosmetologist.
Medication methods
Medicines are effective only during the period of scar tissue formation and are precisely the means that can be used to smear a burn so that there is no scar left. The most popular are:
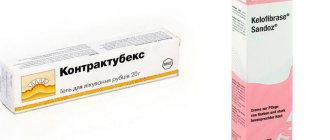
- Contractubex . The gel prevents the formation of post-burn scars, relieves pain and accelerates the process of tissue repair. Onion extract in the composition has a bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect. Heparin accelerates the healing process and the formation of connective cells. Allantoin softens pain and eliminates itching. The drug is applied daily to the damaged area 2-3 times. If the scar is fresh, 3 weeks of use will be enough. For old scars, the effect of application is much weaker, and the gel needs to be used longer - from 4 to 6 months;
- Kelofibrase . The main component of the cream is urea, which softens and fills rough skin with moisture, improving its elasticity. The composition also contains heparin and D-camphor, which have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and regenerating effects. The cream should be applied to the burn spot 3-4 times a day, rubbing in with massage movements;
- Dermatix . The drug is found on pharmacy counters in the form of a gel and ointment. It has a corrective effect on post-burn scars, making them less noticeable, and in some cases helping to get rid of defects altogether. The product contains siloxane polymers that saturate the skin with oxygen and nutrients, moisturize and relieve itching. Applications with the drug should be applied to the affected area at least 2 times a day, and the total duration of treatment is on average 1-2 months;
- Heparin ointment . The main active ingredient is heparin, present in many drugs for the treatment of scars. The ointment has a powerful anticoagulant effect, prevents the formation of blood clots and starts the process of resorption of old scars.
Care for post-burn scars and possible complications
Keloid and hypertrophic scars cause discomfort for a long period of time and can be itchy. A person feels such symptoms for 6–12 months. During this period, damaged areas of the dermis are vulnerable: slight tissue damage leads to a bacterial or infectious outbreak. A person gets sick, the immune system suffers, and the trail becomes larger. Self-medication for fever and severe pain is unacceptable. The real help for the patient is consultation with the attending physician.
After healing, post-burn scars require both medicinal and cosmetic care. Folk remedies with constant use also give excellent results.
The article has been verified by the editors
Traditional methods
The use of traditional methods for removing scars and scars from burns can be quite effective and can significantly reduce the defect. The most effective methods are:
- camphor oil compress. Soak gauze or a soft cloth with oil and apply to the defective area overnight. The optimal treatment period for post-burn scars is 1 month;
- Badyaga. A natural remedy obtained from freshwater sponge. It can be sold both in powder form and in the form of ointments. It has a local irritating and regenerating effect, improves blood supply to tissues and accelerates metabolic processes. The Badyagi mask is applied to the burn mark for 10 minutes, and then thoroughly washed off with warm water. It is recommended to repeat the procedure after 5-7 days - this time is enough to restore the top layer of skin after peeling with Badyaga;
- a mixture of melon seeds and eggshells. Grind equal parts of melon seeds and egg shells and pour in a little vegetable oil to obtain a thick, mushy consistency. Lubricate the defective areas with the resulting mixture for 2 months.
Do not delay the treatment of post-burn scars. The sooner you begin the process of getting rid of defects, the higher the likelihood of their effective elimination. Otherwise, you cannot avoid radical, expensive methods.
Which ointment is more effective for burn scars?
Burns are insidious injuries, since after their treatment scars remain on the body. Modern ointment for burn scars helps treat scars even before they form . In addition to ointments, other pharmaceutical products can help in the treatment of scars - gels, foams, silicone plates. Traditional methods and surgical treatment (if the scar is old) are also popular.
You can get a burn not only from fire or boiling water, but also from high concentration chemicals. If this type of injury is not treated correctly, it can lead to serious consequences (for example, infection of the wound at the site of the burn or accumulation of pus). An unpleasant consequence after severe burns is scars on the body. At the same time, it is possible to get rid of scars after burns. The desired effect can be achieved using currently existing methods and tools that can help in this long process.
Types of scar treatment
Formed scars are not a pleasant sight. Their healing is accompanied by constant painful sensations. And it is scars after burns that are difficult to remove completely (compared to other types of scars). A crust forms along the edges of the scar, and premature removal of it can provoke even greater localization of the scar on the skin. Therefore, treatment of post-burn scars should be carried out after preliminary consultation with a doctor (surgeon or dermatologist), who will select a suitable remedy.
# Image.јрдAll drugs that are used to treat types of injuries such as burns and scars that form after healing of a wound are divided into the following groups:
Antibacterial agents. This group includes antibiotics and antiseptics:
- products containing iodine (Iodinol, Vokadin ointment);
- products that include ammonium salts (Rokkal solution, catapol);
- products based on silver (Poviargola - solution or gel, Silvederm - ointments, creams).
Drugs that accelerate healing (Panthenol, Solcoseryl, sea buckthorn oil).
Composite compositions (Levomekol, Olazol).
In different treatment methods, several such drugs may be used and combined. Most often you can find a combination of antiseptics with painkillers and drugs that accelerate healing.
Before you begin to remove the scar, you should wait until it is completely healed. Treatment of scars after burns involves several methods that can be classified into the following categories:
- Pharmacy products (ointments, gels, sprays).
- Folk remedies (making your own ointments based on pumpkin seeds or bodyaga).
- Surgical treatment (laser resurfacing, microdermabrasion, skin grafting).
- stage of inflammation - dead areas melt, the wound is cleaned of decay products, contamination and damaged tissue;
- regeneration stage - connective tissue elements grow, new vascular tissue appears along the bottom and walls of the wound;
- stage of epithelium formation - the wound is closed with connective tissue, a scar is formed.
The first two methods can be effective if the burn scar is still fresh. In the case of an old scar, surgical methods can help.
Return to scar Formation, types of scars and reasons for removal
To successfully treat a burn, you should know the biological stages of wound healing. There are three main phases in this process:
Different treatment modalities are used during different phases of healing. First, antibacterial and antiseptic drugs are used, then agents are used that help in scarring. After the scar has formed, you can begin to treat it.
Scars appear as a result of normal wound healing and are made up of tissues that lack natural collagen structure. For successful therapy, different conditions are taken into account - the depth and size of the wound, the gender of the person, his age category, and heredity.
The main motives for getting rid of scars are:
For effective removal, one should take into account the types of scars, they are: keloid, hypertrophied, atrophic, normotrophic.
Return to medicineEffective treatment of burns and scars
This is a long process that requires a careful approach. Pharmacy methods help in eliminating scars even before their final formation.
# Image.јrdOintment Contractubex. The substances contained in its composition help not only treat scars, but also take an active part in wound healing:
- onion extract – relieves inflammation, has an antibacterial effect, helps avoid the formation of excess tissue during scar formation;
- heparin – gently affecting the tissue structure, relieves inflammation, helps in the restoration of connective tissue, stimulates collagen production;
- allanoin – moisturizes tissue, eliminates itching during scar formation.
Using the ointment is simple - just smear the injured areas of the skin. It belongs to the combined types of products; it is used for shallow types of scars.
Kelofibrase ointment. It contains urea, camphor and heparin, which improve blood circulation, soften scar tissue, have an analgesic effect, and accelerate the process of skin regeneration and scar resorption.
Suitable for treating old scars. Long-term regular use can lead to complete disappearance of the scar. Can be used to treat stretch marks.
Spenko silicone plates are an overlay for the scar, which helps to eliminate scar formations.
Zeraderm ultra ointment has an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective and restorative effect. To treat with this ointment, you must wait until the tissue is completely scarred.
Fermenkol ointment - helps in the treatment of scars and relieves itching. Injected into the scar using ultrasound or electrophoresis.
Kelo-Kot ointment contains two types of silicone; they are the most effective in the treatment of scars and stretch marks for external use.
Skargard ointment. contains:
- hydrocortisone hormone – promotes healing;
- vitamin E – softens and restores the skin;
- silicone – helps smooth out scars.
Strataderm ointment (analogs - Carboderm, Dermalexia). The main component of the ointment is silicone compounds, which are successfully used to heal scars, protect the skin from infection, and promote collagen restoration.
Using traditional methods to treat post-burn scars, you can achieve good results. Ointments made with one's own hands are used as homeopathic ointments:
Ointment based on bodyagi. Helps improve blood circulation, accelerates regeneration and metabolic processes in the tissue structure. Used in the treatment of shallow scars.
Ointment based on egg seeds and eggshells. The seeds and shells are crushed and any oil is added. The ointment is used as a compress by applying a bandage with ointment to the affected area of the skin.
As we can see, folk remedies can be successfully used in the treatment of scars if used correctly.
Return to zmistuWe can’t cure it by masking it like this
In addition to treating scars, there are methods to disguise them. Foundation or a special pencil perfectly hides the defect, but is not suitable in the summer. Self-tanning is often used. The method of applying a tattoo to a scar is not welcomed by doctors, since it can further injure the skin and cause infection.
Afterwards, burn scars can cause concern to their owner; if they are visible, the person becomes embarrassed and has a complex. When treating scars with ointments, you need to be prepared for a long process if you want to achieve the desired effect.
You must strictly follow the instructions, use regularly and complete the full course.
When choosing remedies for the treatment of this type of scars, it is necessary to proceed from the fact that such formations differ in shape and appearance, in addition, the characteristics and types of skin are individual for each person. Only by following the correct treatment will you get beautiful and healthy skin.