How it manifests itself
Cold urticaria is manifested by the following symptoms:
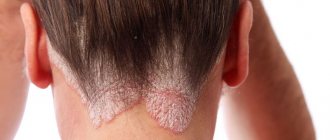
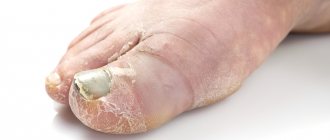
- Characteristic blisters protruding above the surface of healthy skin. The rash appears almost immediately after contact with low temperatures.
- Itching, which gives the patient very unpleasant sensations.
- The rash is localized in strictly defined places. This is the skin on exposed areas of the body that have been exposed to cold.
- In some cases, symptoms such as difficulty breathing, headache, fever, and deterioration in general condition occur.
Cold urticaria of some varieties has additional specific symptoms:
- Body hyperthermia.
- Edema with clear boundaries.
Why does cold urticaria occur?
- One of the most common causes of the disease is genetic predisposition. Scientists have found that the risk of transmitting the disease from mother to child is about 50%. This is typical for both the first and subsequent pregnancies.
- Another reason that provokes the development of cold urticaria is autoimmune disorders that occur when the body's defenses are not enough to resist the proliferation of invasive bodies.
- Infections, viruses (mycoplasma, mononucleosis, viral hepatitis, chicken pox and others) are quite common causes.
Types of cold urticaria
There are several varieties of this disease. They are characterized by certain symptoms and causes.
- Acute and chronic forms are characterized by a sudden onset and intense course. The characteristic rash appears first on open areas of the skin, then can spread to the entire body. In this case, the patient feels severe itching. The affected skin swells and blisters form. In especially severe cases, chills, weakness, rapid heartbeat, and discomfort in the joints and muscles are noted.
- The recurrent form appears in certain seasons. However, with frequent and prolonged exposure to cold water, symptoms may occur throughout the year.
- The reflex form most often manifests itself with general hypothermia. The rash can be located throughout the body, or in a specific area.
- The familial form is quite rare. The cause of the disease is the genetic predisposition of the child. After exposure to cold, rashes in the form of papules appear on the child’s skin, causing severe itching. Sometimes the rash appears a day after contact with the cold. This complicates the diagnosis of this form.
- Cold erythema is painful redness on the skin.
- Cold dermatitis is a scaly rash accompanied by severe itching.
- Cold rhinitis resembles a common runny nose, with the difference that symptoms of congestion occur only upon contact with cold air. On warm days, the symptoms of the disease disappear.
- Cold conjunctivitis is manifested by severe lacrimation, burning in the eyes, at a time when a person is in the cold.
Each person exposed to the cold exhibits certain protective reactions, which should not be confused with manifestations of cold allergies.
Diagnostics
Cold urticaria is diagnosed with a simple test that can be done even at home. You need to place an ice cube on your skin for 5 minutes. After its removal, a red bump will form. This examination is called the Duncan test.
An in-depth study of patients with cold urticaria reveals an increased content of special proteins – cryoglobulins – in the blood. During exacerbation of the disease, their concentration increases, during remission it decreases, but still remains above normal. This test is recommended for wider use in clinical practice for the correct diagnosis of cold allergy.
Most often, the disease appears in a child and goes away on its own, so the doctor may not prescribe any additional diagnostic methods. In adults, this condition can be a consequence of serious diseases that negatively affect the immune system. First of all, these are hepatitis and malignant tumors. Therefore, the doctor may order tests to diagnose these diseases.
List of studies required for chronic cold urticaria to exclude concomitant diseases:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests, urine analysis;
- examination for syphilis and viral hepatitis;
- rheumatic tests;
- stool analysis for worm eggs;
- detection of antibodies to antigens of various parasites;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- FGDS;
- ECG;
- X-ray of the chest, and, if necessary, the paranasal sinuses.
If the rash persists for more than a day, a skin biopsy is required to rule out urticarial vasculitis.
In female patients, as well as those who have relatives suffering from autoimmune diseases or diseases of the thyroid gland, it is necessary to conduct a screening determination of the level of antithyroid antibodies or conduct another examination of this gland.
In most patients, the cause of the disease cannot be identified. In such cases, they speak of primary idiopathic cold urticaria.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following diseases:
- urticarial vasculitis;
- bullous pemphigoid;
- erythema multiforme;
- Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis.
Folk remedies for cold urticaria
Treatment with traditional medicine will help relieve the unpleasant symptoms that characterize cold urticaria. It is good to treat with compresses from herbal decoctions, applying them to damaged skin for 30-40 minutes.
You can treat your skin with aloe juice and green tea. These products eliminate unpleasant skin symptoms, soothe the skin, heal damage, and relieve swelling. For general strengthening of the body, it is recommended to drink raspberry tea daily, or eat a few spoons of raspberry jam. It is very tasty and, most importantly, healthy.
Diet for allergies to cold
If allergies to cold worsen, it is recommended to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet. The following should be excluded from the diet:
- spicy, salty, fatty and fried foods;
- strong broths;
- spices;
- smoked meats;
- sausages;
- seafood;
- eggs;
- ice cream;
- processed and sharp cheeses;
- industrially made sauces (ketchup, mayonnaise);
- pickles and marinades;
- some vegetables (bell peppers, tomatoes, spinach);
- nuts;
- mushrooms;
- citrus;
- confectionery.
It is recommended to include in the diet:
- dairy products;
- cereal dishes (except semolina);
- lean meat;
- mild varieties of cheese;
- green apples;
- vegetable oil;
- dishes made from vegetables, preferably green (zucchini, cabbage, squash, green beans, green peas, dill, parsley, etc.).
Ways to prevent cold urticaria
Measures to prevent the onset of symptoms of the disease are quite simple:
- Maximum skin protection from cold. If it is not possible to cover all parts of the body with clothing, it is recommended to use a nourishing cream.
- Remember such items of clothing as a hat, gloves, and warm tights. Pay attention to the quality of the underwear you wear. It should be made of cotton, as others, such as synthetic materials, can cause an allergic reaction.
- Avoid hypothermia. If you feel discomfort, hurry to a warm room.
- Hardening is considered a good preventative measure. It should be started in the warm season, using water at a comfortable temperature.
- Adjust your daily diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty, fried, spicy foods. Make sure you have foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids on your table.
Therapy
Given the often combined nature of the allergic reaction, patients with cold urticaria need to adhere to a diet limiting allergenic foods (eggs, nuts, milk, chocolate and others). If such a diet does not protect against the occurrence of new cases of exacerbation within a month, it can not be followed.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease with medication. Treatment of cold urticaria is pathogenetic and symptomatic. This means that it is aimed at suppressing the mechanism of development of pathology and eliminating its symptoms.
The patient should be informed that he should not take the following medications:
- aspirin;
- codeine (for example, as part of terpincode and other prescription cough and pain medications);
- ACE inhibitors (captopril, enalapril and other drugs from this group can cause angioedema in predisposed patients).
Over-the-counter antihistamines are usually prescribed, but in some cases more serious therapy is required.
Antihistamines block the release of histamine from cells, the active substance that causes symptoms of the disease. Examples of these are fexofenadine and desloratadine. They are taken once a day until the rash disappears, and then for another month.
Anti-allergy creams can also be used, but they are less effective than tablets.
Cyproheptadine is a substance with an antihistamine effect that additionally blocks nerve impulses that increase symptoms.
Doxepin is commonly used to treat anxiety and depression. However, it may reduce symptoms caused by cold urticaria.
Omalizumab is a drug for the treatment of allergic bronchial asthma. In the case of urticaria, it is used when other remedies are ineffective.
In severe cases, the patient may be recommended:
- leukotriene antagonists: zafirlukast (Acolat), montelukast (Singulair);
- cyclosporine is an immunosuppressant that has shown good results in this disease, but more often if chronic urticaria has an autoimmune component;
- systemic glucocorticoids (prednisolone) for a short course with gradual withdrawal; with true cold urticaria they are ineffective, but with the combined nature of the pathology they can be useful.
The patient must always have one of the following medications with him:
- loratadine (Claritin, Loragexal, Erolin and others);
- fexofenadine (Telfast, Fexo, Fexadine);
- cetirizine (Zyrtec, Zodak, Cetrin);
- Levocetirizine (Xyzal).
It is necessary to avoid sudden changes in temperature, and also use protective creams for the face and hands when going out into the cold (Barrierderm).
For children and pregnant women, treatment with modern H1-histamine blockers, namely loratadine, is recommended. None of the studies in expectant mothers have shown any adverse effects of these medications on the fetus. When treating children, the age and weight of the small patient must be taken into account.
Treatment algorithm:
- H1-histamine blockers in the usual dosage;
- if ineffective within 2 weeks, increase the dose of the drug by 4 times (except for therapy in children);
- if there is no effect within another 2 weeks, use Omalizumab or Prednisolone.
To prescribe medications from other groups, a consultation is required, since their official indications do not include the treatment of chronic urticaria.
Episodes of cold urticaria are usually easily treated in an outpatient setting. The patient is hospitalized in the dermatology department only if there is no effect from taking medications. Another indication for hospitalization is widespread skin lesions, accompanied by deterioration of the general condition and intense painful itching.
If laryngeal angioedema or anaphylactic reaction develops, the patient is treated in the intensive care unit. In this case, histamine blockers are prescribed in the form of injections, prednisolone, norepinephrine, aminophylline.