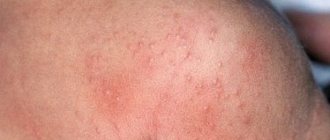
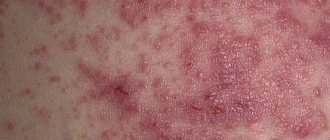
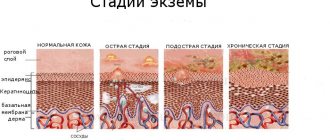
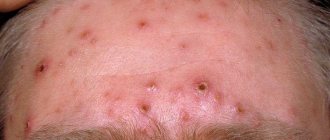
Skin lesions indicate disruption of the body's functioning and decreased immunity due to aggressive environmental influences. External and internal factors provoke the development of one of the most unpleasant forms of skin diseases - weeping dermatitis. This condition is characterized by the appearance of ulcers on the body, from which ichor or pus is released. The disease affects patients of any age: both men and women. Treatment of pathology requires an integrated approach and correctly selected means.
The main causes of the disease
Weeping dermatitis develops against the background of a malfunction of the stomach and intestines . The ability to break down proteins, fats, carbohydrates and beneficial micro- or macroelements is impaired; food is not completely digested. There is an accumulation of toxic substances, which are manifested by damage to the epidermis. Improper functioning of the kidneys, liver, and pancreas also aggravates the situation.
Other factors that provoke the formation of wet ulcers on human skin include:
- Frequent stress, irritation, and depression cause emotional instability and, as a consequence, the appearance of skin disease.
- Intolerance to certain foods causes an allergic food reaction.
- Taking medications may cause symptoms of dermatitis (as a side effect).
- Direct exposure to chemical reagents at work or inhalation of toxic fumes provokes the development of pathology. Allergens from household chemicals can also penetrate into the deep layers of the dermis, causing swelling and redness.
- The proliferation of a fungal or bacterial infection in the folds of the body leads to the appearance of weeping infected areas covered with blisters. The skin suffers the most from constant friction against synthetic or woolen clothing, shoes, and belts. A prerequisite for the growth of pathogenic microflora with further transformation into dermatitis are microcracks or scratches in the epithelium.
- The unfavorable ecology of the area of residence has a negative effect on human skin.
Depending on the cause, the types of disease are distinguished:
- professional;
- pyococcal (bacterial);
- fungal;
- domestic.
Among the numerous subspecies, the form of weeping atopic dermatitis is considered separately. There is a high risk of developing the disease in a child if dermatological problems are observed in both parents.
In this case, the impetus for the development of pathology may be:
- dysfunction of the nervous system;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- consumption of non-traditional products;
- moving to a country with different climatic conditions;
- exposure to highly allergenic substances (cosmetic products, plant extracts, contact with animals).
Causes
Weeping dermatitis develops due to 2 groups of causes - internal and external. The first group includes diseases:
- stomach and intestines;
- liver;
- pancreas;
- kidney
All these ailments lead to the appearance of “wrong” and even toxic substances in the body that normally are not formed or are quickly eliminated. The body tries to remove them percutaneously, and as a result it is damaged.
External causes of inflammatory skin disease are: contact with chemicals (for example, at work or at home), ingestion and subsequent reproduction of fungal or bacterial flora on the skin. The latter is possible only under conditions of damage to the skin: microcracks, in places where friction occurs on clothing, belts or shoes.
Depending on the underlying causes, weeping dermatitis can be:
- professional (occurs as a result of contact with harmful substances at work);
- pyococcal, when it was caused by bacterial flora;
- dermatomycosis (its cause is a fungus);
- household is a weeping dermatitis that occurs due to frequent skin contact with household chemicals.
There is also weeping atopic dermatitis. It occurs in people with a hereditary predisposition: if both parents have this pathology, the chance of getting sick is 81%, if only one parent is sick - 56%. Certain circumstances provoke the occurrence of the disease: disruptions in the functioning of either the central or autonomic nervous system, allergens (substances that cause an incorrect reaction from the immune system) on the skin, chronic stress, consumption of unusual foods, travel to an area with a different climate.
Also in the section: Atopic dermatitis
When contact with an allergen occurs in a person who does not have hereditary disorders in the immune system, allergic weeping dermatitis develops. It does not tend to recur constantly, unlike its atopic counterpart, unless the person is constantly in contact with allergens.
Atopic dermatitis is a hereditary disease. The word "atopy" is translated from Latin as "strangeness." And in modern medicine, this is what we call a genetic predisposition to allergies.
An allergy is a disruption of the body’s normal reaction to foreign substances (immunity). People prone to the disease often experience various abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system. First of all, this consists in increasing the synthesis of immunoglobulin proteins IgE, which are important for the immune system, compared to the norm (in 90% of cases). Increased immune reactivity leads to the formation of inflammatory mediators - histamines.
There are other factors that contribute to the occurrence of atopic dermatitis. Firstly, these are disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. They are expressed in an increased tendency to spasm of small vessels, including those on the skin. Patients also often experience:
- disruption of the synthesis of certain adrenal hormones responsible for the body’s anti-inflammatory reactions;
- decreased functionality of the skin sebaceous glands;
- impairment of the skin's ability to retain water;
- decreased lipid synthesis.
All this leads to a general weakening of the barrier functions of the skin and to the fact that irritating agents penetrate the skin into all its layers, causing inflammation.
Dermatitis is often accompanied by chronic gastrointestinal diseases that reduce intestinal barrier function:
- Dysbacteriosis,
- Gastroduodenitis,
- Pancreatitis,
- Biliary dyskinesia.
However, the hereditary factor still plays a leading role. The disease develops in 4 out of 5 cases when both parents suffer from it. If only one parent is sick, then the probability of illness in the child also remains quite high - 55%. The presence of allergic respiratory diseases in the other parent increases this figure.
Racial factors also influence the development of the disease - it is more common in children with fair skin.
In addition to heredity, other factors contribute to the development of atopic dermatitis in infancy:
- Lack of breastfeeding or too early transfer to artificial feeding,
- Toxicosis of pregnancy in the mother,
- Improper nutrition of the mother during pregnancy or lactation.
Less significant, but also contributing factors to the disease in children:
- high air temperature leading to increased sweating;
- weak immunity;
- presence of stress;
- poor skin hygiene or, conversely, too frequent washing.
In early childhood, food allergens most often act as irritants. These can be substances that come from food or from breast milk (for nursing women).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsen-GB
In adult patients, the list of allergens can be much wider. In addition to food allergens, irritants can be:
- House dust,
- Medicines,
- Household chemicals,
- Cosmetics,
- plant pollen,
- Bacteria and fungi,
- Pet hair.
Factors contributing to the manifestation of atopic dermatitis in adults:
- Poor environmental conditions;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Metabolic diseases;
- Acute infectious diseases;
- Complicated pregnancy;
- Sleep disorders, stress, psychological stress.
Often the disease is aggravated by self-medication, including with the help of herbal medicines, which may also contain allergens.
The course of pathology in an adult
Weeping dermatitis is characterized by the formation of a lesion in the deep layers of the dermis and the appearance of significant inflammation of the skin. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- rashes in the form of vesicles on the surface of the skin;
- separation of liquid (ichor) from the blisters (in case of infection, pus is released);
- swelling of the skin.
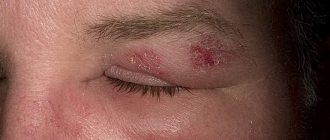
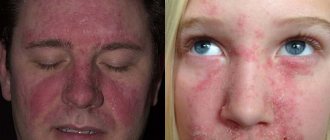
In adult patients, the disease manifests itself as extensive redness and irritation of the epidermis, on which oozing blisters gradually form, transforming into small ulcers and eczema with a cracked crust . Skin lesions are localized in the following places:
- natural body folds;
- on the backs of the hands and feet;
- on the ankles;
- in joint bends;
- on the face or neck.
Inflammation in open areas additionally causes psychological discomfort in the sick person. The acute phase of the pathology is accompanied by severe itching, burning, and a feeling of tightness in the affected areas. In photographs, patients often show wet, oozing wounds.
Causes of appearance in adults
The disease appears more and more often in adults - people over 18 years of age. That is why it is no longer classified as a children's game. Weeping dermatitis can occur in adolescents, middle-aged or elderly people. This feature is associated with differences in the course of the disease - symptoms manifest themselves in different intensities. The main reasons for the emergence and further development of the problem:
- disruptions of varying intensity occurring in the gastrointestinal tract;
- there is a problem with the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates and fats (in adults it occurs in 20% of all cases);
- food allergies;
- intolerance to certain elements in food;
- liver dysfunction;
- kidney disease;
- problems with the pancreas;
- diseases caused by exposure to a bacterial infection (manifested by the appearance of blisters);
- various stressful situations;
- hypersensitivity to certain components and substances;
- overwork;
- disorders of the nervous system of varying intensity;
- poisoning with various substances;
- negative effects of chemicals on the skin.
The following disturbances in the functioning of the body can also lead to the development of weeping dermatitis:
- diabetes of various types;
- disorders observed in the endocrine system;
- weakened immunity.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that helminthic infestation can lead to the development of the disease. In accordance with the existing classification, the disease can be contact, appearing under the influence of various irritants.
Principles for getting rid of weeping dermatitis
Measures aimed at eliminating the disease are comprehensive and include:
- special hypoallergenic diet;
- maintaining hygiene of affected areas of the body;
- taking medications;
- application of local drugs.
Additionally, they try to eliminate the negative impact of the environment and other external factors.
Traditional medical solutions
Among the main drugs for treatment, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs for weeping dermatitis are primarily selected to eliminate itching and irritation:
Potent hormonal ointments:
Prescribed in case of severe disease and lack of therapeutic effect from other pharmaceutical products.
To eliminate severe sputum, it is better to use drugs in the form of an emulsion or cream.
For young patients, the use of such drugs is unacceptable. Getting rid of the external symptoms of childhood dermatitis is carried out using zinc-based ointments, which have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties.
Safe drugs are:
- "Desitin";
- "Zinocap";
- "Sudocrem".
The patient’s recovery depends on the correct identification of the main cause that provoked the spread of weeping dermatitis . If neuralgic disorders are diagnosed, sedative (calming) medications additionally help treat the disease:
In case of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, allergenic products are excluded:
If dermatitis develops in a breastfed baby, the baby’s mother adjusts her diet.
Dysbacteriosis, which can provoke skin lesions, is eliminated with the help of probiotics (Linex, Bifidumbacterin). Additionally, it is necessary to consume fermented milk products.
In case of constant sputum production, drying lotions and compresses based on the following drugs are used:
After the crusts dry, apply coloring solutions (brilliant, fucorcin) or universal ointment “Levomekol”. Only the edges of the affected areas are allowed to be treated with iodine to prevent an increase in the area of inflamed skin.
If weeping dermatitis is accompanied by the formation of small blisters, they must be opened under sterile conditions. The procedure is performed by a dermatologist. After this, the surface of the wounds is treated with disinfectants containing aniline dyes.
If necessary, the process of curing dermatitis is strengthened by physiotherapeutic procedures:
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- laser exposure;
- healing mud.
Weeping dermatitis in adults: effective creams and ointments
Skin lesions indicate disruption of the body's functioning and decreased immunity due to aggressive environmental influences.
External and internal factors provoke the development of one of the most unpleasant forms of skin diseases - weeping dermatitis. This condition is characterized by the appearance of ulcers on the body, from which ichor or pus is released.
The disease affects patients of any age: both men and women. Treatment of pathology requires an integrated approach and correctly selected means.
The main causes of the disease
Weeping dermatitis develops against the background of a malfunction of the stomach and intestines.
The ability to break down proteins, fats, carbohydrates and beneficial micro- or macroelements is impaired; food is not completely digested.
There is an accumulation of toxic substances, which are manifested by damage to the epidermis. Improper functioning of the kidneys, liver, and pancreas also aggravates the situation.
Other factors that provoke the formation of wet ulcers on human skin include:
- Frequent stress, irritation, and depression cause emotional instability and, as a consequence, the appearance of skin disease.
- Intolerance to certain foods causes an allergic food reaction.
- Taking medications may cause symptoms of dermatitis (as a side effect).
- Direct exposure to chemical reagents at work or inhalation of toxic fumes provokes the development of pathology. Allergens from household chemicals can also penetrate into the deep layers of the dermis, causing swelling and redness.
- The proliferation of a fungal or bacterial infection in the folds of the body leads to the appearance of weeping infected areas covered with blisters. The skin suffers the most from constant friction against synthetic or woolen clothing, shoes, and belts. A prerequisite for the growth of pathogenic microflora with further transformation into dermatitis are microcracks or scratches in the epithelium.
- The unfavorable ecology of the area of residence has a negative effect on human skin.
Depending on the cause, the types of disease are distinguished:
- professional,
- pyococcal (bacterial),
- fungal,
- domestic.
Among the numerous subspecies, the form of weeping atopic dermatitis is considered separately. There is a high risk of developing the disease in a child if dermatological problems are observed in both parents.
In this case, the impetus for the development of pathology may be:
- dysfunction of the nervous system,
- vegetative-vascular dystonia,
- consumption of non-traditional products,
- moving to a country with different climatic conditions,
- exposure to highly allergenic substances (cosmetic products, plant extracts, contact with animals).
The course of pathology in an adult
Weeping dermatitis is characterized by the formation of a lesion in the deep layers of the dermis and the appearance of significant inflammation of the skin. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- rashes in the form of vesicles on the surface of the skin,
- separation of fluid (ichor) from the blisters (in case of infection, pus is released),
- swelling of the skin.
In adult patients, the disease manifests itself as extensive redness and irritation of the epidermis, on which oozing blisters gradually form, transforming into small ulcers and eczema with a cracked crust . Skin lesions are localized in the following places:
- natural body folds,
- on the backs of the hands and feet,
- on the ankles,
- in joint bends,
- on the face or neck.
Inflammation in open areas additionally causes psychological discomfort in the sick person. The acute phase of the pathology is accompanied by severe itching, burning, and a feeling of tightness in the affected areas. In photographs, patients often show wet, oozing wounds.
Principles for getting rid of weeping dermatitis
Measures aimed at eliminating the disease are comprehensive and include:
- a special hypoallergenic diet,
- maintaining hygiene of affected areas of the body,
- taking medications,
- application of local drugs.
Additionally, they try to eliminate the negative impact of the environment and other external factors.
Traditional medical solutions
Among the main drugs for treatment, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs for weeping dermatitis are primarily selected to eliminate itching and irritation:
- "Claritin"
- "Telfast"
- "Tavegil".
Potent hormonal ointments:
- "Afloderm"
- "Advantan"
- "Sinaflan"
- "Flixotide".
Prescribed in case of severe disease and lack of therapeutic effect from other pharmaceutical products.
To eliminate severe sputum, it is better to use drugs in the form of an emulsion or cream.
For young patients, the use of such drugs is unacceptable. Getting rid of the external symptoms of childhood dermatitis is carried out using zinc-based ointments, which have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties.
Safe drugs are:
- "Desitin"
- "Tsinocap",
- "Sudocrem".
The patient’s recovery depends on the correct identification of the main cause that provoked the spread of weeping dermatitis . If neuralgic disorders are diagnosed, sedative (calming) medications additionally help treat the disease:
- "Novo-Passit"
- "Glycine",
- "Valerian".
In case of pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, allergenic products are excluded:
- chocolate,
- citrus,
- honey,
- eggs.
If dermatitis develops in a breastfed baby, the baby’s mother adjusts her diet.
Dysbacteriosis, which can provoke skin lesions, is eliminated with the help of probiotics (Linex, Bifidumbacterin). Additionally, it is necessary to consume fermented milk products.
In case of constant sputum production, drying lotions and compresses based on the following drugs are used:
- manganese,
- boric acid,
- saline solution
After the crusts dry, apply coloring solutions (brilliant, fucorcin) or universal ointment “Levomekol”. Only the edges of the affected areas are allowed to be treated with iodine to prevent an increase in the area of inflamed skin.
If weeping dermatitis is accompanied by the formation of small blisters, they must be opened under sterile conditions. The procedure is performed by a dermatologist. After this, the surface of the wounds is treated with disinfectants containing aniline dyes.
If necessary, the process of curing dermatitis is strengthened by physiotherapeutic procedures:
- magnetotherapy,
- electrophoresis,
- laser exposure,
- healing mud.
Using folk recipes
The following tools have proven themselves well:
- A decoction of chamomile and oak bark. It is allowed to wipe the affected areas with the healing solution several times a day.
- One of the folk remedies for severe itching is a compress soaked in an infusion of birch buds.
- At the initial stage of the appearance of bubbles, you can prepare a decoction of celandine.
- Sage, calendula, string, and hop cones have drying and cleansing properties. Based on these plants, herbal infusions are prepared and medicinal lotions are made.
- If the cracks begin to get very wet, you can eliminate the problem using raw potatoes: the grated mass is placed in a gauze bag and fixed in the desired area overnight.
Attention!
The site administration advises you not to self-medicate, and in any controversial situations, consult a doctor.
Source: //fr-dc.ru/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/moknushhij-dermatit-osobennosti-bolezni-i-puti-lecheniya
Causes of weeping dermatitis
Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the fact that the human body does not receive enough of the beneficial microelements it needs for normal functioning. Improper functioning of the liver, kidneys, and pancreas inhibits the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. They accumulate and negatively affect the operation of all internal systems. Against this background, a pathological reaction develops, which leads to damage to the skin. This is not the only reason that can explain the mechanism of development of weeping dermatitis.
Such a disease can act as a complication of poisoning with toxic substances. This occurs when the skin interacts directly with chemicals. People who work in hazardous industries and those who often use aggressive household chemicals at home without additional protection suffer. If there is a history of hereditary predisposition or high skin sensitivity, this increases the risk of developing weeping dermatitis.
The third most common cause is bacterial and fungal infection. Invasion of the skin by staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and fungi is facilitated by any injury and neglect of personal hygiene rules. The lesions in this case are often localized in places where the skin comes into contact with clothing. Too tight underwear creates friction; clothing items made from synthetic fabrics create a greenhouse effect that irritates the skin and causes damage. Having studied the influence of all provoking factors, doctors have identified several types of dermatitis of the described form:
- professional (due to contact with chemical allergens);
- pyococcal (associated with bacterial skin lesions);
- household (develops after interaction with household chemicals);
- dermatomycosis (occurring after infection with fungi).
A separate group should include types of pathology that arise after suffering severe emotional stress.
Weeping dermatitis: causes of development, therapy with folk remedies and diet
Weeping dermatitis is a dermatological disease in which ulcers and cracks appear on the skin, constantly oozing ichor. The pathology is almost always complicated by the addition of a fungal infection or a bacterial component, which creates the threat of blood poisoning. It most often affects adults and children who have a history of digestive system dysfunction.
Causes of weeping dermatitis
Disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract lead to the fact that the human body does not receive enough of the beneficial microelements it needs for normal functioning.
Improper functioning of the liver, kidneys, and pancreas inhibits the absorption of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. They accumulate and negatively affect the operation of all internal systems. Against this background, a pathological reaction develops, which leads to damage to the skin.
This is not the only reason that can explain the mechanism of development of weeping dermatitis.
Such a disease can act as a complication of poisoning with toxic substances. This occurs when the skin interacts directly with chemicals.
People who work in hazardous industries and those who often use aggressive household chemicals at home without additional protection suffer.
If there is a history of hereditary predisposition or high skin sensitivity, this increases the risk of developing weeping dermatitis.
The third most common cause is bacterial and fungal infection. Invasion of the skin by staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and fungi is facilitated by any injury and neglect of personal hygiene rules.
The lesions in this case are often localized in places where the skin comes into contact with clothing. Too tight underwear creates friction; clothing items made from synthetic fabrics create a greenhouse effect that irritates the skin and causes damage.
Having studied the influence of all provoking factors, doctors have identified several types of dermatitis of the described form:
- professional (due to contact with chemical allergens),
- pyococcal (associated with bacterial skin lesions),
- household (develops after interaction with household chemicals),
- dermatomycosis (occurring after infection with fungi).
A separate group should include types of pathology that arise after suffering severe emotional stress.
Types of dermatitis in children and adults
In children under two years of age, the main cause of symptoms of the described disease is associated with food allergies. It can develop for various reasons. Sometimes the mother is to blame for not following nutritional principles when breastfeeding.
In formula-fed babies, the main provoking factor for dermatitis is the wrong choice of formula. Many people today have an innate predisposition to allergic reactions. It may be associated at this age with lactose intolerance.
The first complementary feeding can also provoke the appearance of a characteristic clinical picture.
At this age, weeping forms on the surface of the face, on the extensor surfaces of the arms or legs. Very rarely, lesions spread throughout the body. If left untreated, the inflamed skin cracks, constantly oozing ulcers form, which become crusty as they dry out.
From three to twelve years of age, lesions appear mainly on the neck, on the elbow and in the popliteal region, on the back of the hands.
The skin first turns red and swells, then papules appear on it, the development of which ends in the formation of weeping erosions. The skin thickens and cracks.
Elements of the rash last a long time, after which pigmentation spots remain on the affected area.
Starting from adolescence until the end of puberty, such symptoms appear suddenly and also suddenly disappear even without treatment. During exacerbation, lesions form in places of natural folds, and from there they spread throughout the body. After eighteen years of age, dermatitis develops according to the same scenario as in children under two years of age.
In an adult patient, the disease manifests itself in the form of erythema covered with a vesicular rash. When its elements are opened, erosions of a weeping nature are formed.
Diagnosis of weeping dermatitis
Pathology is diagnosed by external manifestations. At the first examination, the doctor carefully collects and analyzes the patient’s complaints, asks about the patient’s diet and lifestyle. First of all, he must determine what is developing: weeping dermatitis or eczema. The following table of diagnostic criteria is used for determination.
| Weeping dermatitis | Eczema |
| Formed in the deep layers of the skin | Surface damage |
| Significant swelling | Mild redness of the skin |
| Presence of purulent discharge and ichor | The presence of serous wells from which fluid constantly flows |
| The appearance of a rash with papules and vesicles | Papular rash |
| Thickening of inflamed skin | Formation of peeling and crusts |
| The appearance of deep cracks |
To draw up a medication regimen, it is necessary to scrape the affected area and microscopically examine it. It will allow you to identify the provocateur and establish the cause of dermatitis. Without eliminating it, symptom therapy will be useless.
Biological material is also sent for bacteriological seeding in special culture media.
Using this laboratory analysis, the pathogen is identified and its sensitivity to existing medications is determined.
How to treat weeping dermatitis
To alleviate the patient’s condition, therapy is used, which involves:
- dieting,
- treatment of affected skin areas,
- oral medication,
- body hygiene,
- prevention of exacerbation.
If a breastfed baby suffers from dermatitis, mothers are advised to remove meat, chicken and fish broths, spicy foods, onions and garlic from the diet. It is useful to reduce the consumption of sweets and starchy foods (bread, pasta, baked goods) to a minimum.
Doctors recommend that sick children over the age of one year and adult patients adhere to a hypoallergenic diet. It involves eliminating potential food allergens from the diet.
These include chocolate, products containing cocoa powder, fruits and vegetables with red, yellow, orange skins, smoked delicacies, and spices.
To improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, it is useful to eat fermented milk products, boiled rice, green apples and pears, lean boiled or oven-baked meat.
If there is no therapeutic effect after changing the diet, patients are prescribed:
- antihistamines like Claritin, Tavegil, Telfast,
- probiotics (“Linex”, “Probiform”),
- sedatives (tinctures of valerian or motherwort),
- systemic enzymes,
- immunomodulators,
- membrane stabilizers.
Glucocorticosteroids (Elocom, Advantan ointments) are used to treat the skin on the affected area. They help relieve swelling, eliminate inflammation and relieve itching in a very short time.
If weeping dermatitis is bacterial in nature, aniline dyes (Fukorcil, brilliant green) and ointments with an antibacterial effect are used.
Combination products that contain hormones and anti-inflammatory components help well. If signs of suppuration are present, the affected areas should be smeared with Triderm and Celestoderm creams.
Zinc ointment is best suited for disinfecting cracks.
If the cause of the pathology is a fungal infection, the therapeutic regimen additionally includes systemic antimycotics and ointments that have an antifungal effect. The choice of drugs is based on the results of bacteriological culture.
Folk remedies for weeping dermatitis
Among the folk remedies for the treatment of weeping dermatitis, the following are most often used:
- oak bark decoctions,
- chamomile infusions,
- celandine-based products.
A strong decoction prepared from all parts of celandine (leaves, stems, roots) has a good drying effect.
First, the plant is crushed with a knife, the resulting mass is filled with cold water (two glasses of raw material, two liters of liquid).
The product is simmered under a closed lid over low heat for ten minutes, and then infused for three hours. Afterwards it is filtered and then used for lotions.
Types of dermatitis in children and adults
In children under two years of age, the main cause of symptoms of the described disease is associated with food allergies. It can develop for various reasons. Sometimes the mother is to blame for not following nutritional principles when breastfeeding. In formula-fed babies, the main provoking factor for dermatitis is the wrong choice of formula. Many people today have an innate predisposition to allergic reactions. It may be associated at this age with lactose intolerance. The first complementary feeding can also provoke the appearance of a characteristic clinical picture.
At this age, weeping forms on the surface of the face, on the extensor surfaces of the arms or legs. Very rarely, lesions spread throughout the body. If left untreated, the inflamed skin cracks, constantly oozing ulcers form, which become crusty as they dry out.
From three to twelve years of age, lesions appear mainly on the neck, on the elbow and in the popliteal region, on the back of the hands. The skin first turns red and swells, then papules appear on it, the development of which ends in the formation of weeping erosions. The skin thickens and cracks. Elements of the rash last a long time, after which pigmentation spots remain on the affected area.
Starting from adolescence until the end of puberty, such symptoms appear suddenly and also suddenly disappear even without treatment. During exacerbation, lesions form in places of natural folds, and from there they spread throughout the body. After eighteen years of age, dermatitis develops according to the same scenario as in children under two years of age.
In an adult patient, the disease manifests itself in the form of erythema covered with a vesicular rash. When its elements are opened, erosions of a weeping nature are formed.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
To make an accurate diagnosis, you should consult a specialist . Diagnosis is not particularly difficult. In this case, the possibility of developing an allergic reaction, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis and scabies should be excluded.
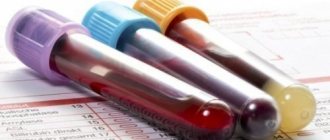
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient should undergo a biochemical and general blood test, scraping from the affected area to exclude a fungal infection.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by a blood test for the level of immunoglobulin E in the plasma, which will be slightly higher in case of illness.
Diagnosis of weeping dermatitis
Pathology is diagnosed by external manifestations. At the first examination, the doctor carefully collects and analyzes the patient’s complaints, asks about the patient’s diet and lifestyle. First of all, he must determine what is developing: weeping dermatitis or eczema. The following table of diagnostic criteria is used for determination.
| Weeping dermatitis | Eczema |
| Formed in the deep layers of the skin | Surface damage |
| Significant swelling | Mild redness of the skin |
| Presence of purulent discharge and ichor | The presence of serous wells from which fluid constantly flows |
| The appearance of a rash with papules and vesicles | Papular rash |
| Thickening of inflamed skin | Formation of peeling and crusts |
| The appearance of deep cracks |
Komarovsky's opinion
The commentary of Dr. Komarovsky, who discusses the treatment of weeping dermatitis in infants, could not be more appropriate.
In 85% of cases of itching and eczema on the skin in children under 2 years of age, this is not an allergic reaction to certain foods that were eaten by a child or a nursing mother, but atopic dermatitis, which is absolutely not related to food. Dr. Komarovsky
Curing weeping dermatitis is not always as easy and quick as it might seem. And due to the fact that the disease is not at all pleasant, no matter what age it occurs, it is best to adhere to preventive measures. Dermatitis often occurs due to some kind of internal failure, so the treatment process should be approached comprehensively, because skin rashes are just a signal that the body is suffering. Taking preventive measures as a rule is elementary, especially since now you can find a lot of necessary information on any website.
How to treat weeping dermatitis
To alleviate the patient’s condition, therapy is used, which involves:
- diet;
- treatment of affected skin areas;
- oral medication;
- body hygiene;
- prevention of exacerbation.
If a breastfed baby suffers from dermatitis, mothers are advised to remove meat, chicken and fish broths, spicy foods, onions and garlic from the diet. It is useful to reduce the consumption of sweets and starchy foods (bread, pasta, baked goods) to a minimum.
Doctors recommend that sick children over the age of one year and adult patients adhere to a hypoallergenic diet. It involves eliminating potential food allergens from the diet. These include chocolate, products containing cocoa powder, fruits and vegetables with red, yellow, orange skins, smoked delicacies, and spices. To improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, it is useful to eat fermented milk products, boiled rice, green apples and pears, lean boiled or oven-baked meat.
If there is no therapeutic effect after changing the diet, patients are prescribed:
- antihistamines like Claritin, Tavegil, Telfast;
- probiotics (“Linex”, “Probiform”);
- sedatives (tinctures of valerian or motherwort);
- systemic enzymes;
- immunomodulators;
- membrane stabilizers.
Glucocorticosteroids (Elocom, Advantan ointments) are used to treat the skin on the affected area. They help relieve swelling, eliminate inflammation and relieve itching in a very short time.
If weeping dermatitis is bacterial in nature, aniline dyes (Fukorcil, brilliant green) and ointments with an antibacterial effect are used. Combination products that contain hormones and anti-inflammatory components help well. If signs of suppuration are present, the affected areas should be smeared with Triderm and Celestoderm creams. Zinc ointment is best suited for disinfecting cracks.
If the cause of the pathology is a fungal infection, the therapeutic regimen additionally includes systemic antimycotics and ointments that have an antifungal effect. The choice of drugs is based on the results of bacteriological culture.
Folk remedies for weeping dermatitis
Among the folk remedies for the treatment of weeping dermatitis, the following are most often used:
- oak bark decoctions;
- chamomile infusions;
- celandine-based products.
A strong decoction prepared from all parts of celandine (leaves, stems, roots) has a good drying effect. First, the plant is crushed with a knife, the resulting mass is filled with cold water (two glasses of raw material, two liters of liquid). The product is simmered under a closed lid over low heat for ten minutes, and then infused for three hours. Afterwards it is filtered and then used for lotions.
Traditional methods of treating weeping dermatitis
It is not recommended to use any folk methods on your own. Otherwise, an adverse reaction may occur and complicate the course of the disease.
For this illness, a homemade decoction of oak bark and an infusion of medicinal chamomile have worked well.
To dry out the source of inflammation, doctors recommend applying a decoction of celandine. Prepare the decoction at home using 2 cups of raw materials and one liter of boiling water. Mix everything well and simmer for 30 minutes over low heat. After this, leave for 2-3 hours and strain. Use this folk recipe as lotions, see photos of how to make lotions.
Pay special attention! If you notice the first signs, you should immediately consult a doctor. If you start treatment on your own, this can lead to serious complications, especially if the dosage is not followed or the medication is incorrectly selected. Therefore, you should not self-medicate; consult a doctor.
Weeping dermatitis can be treated with almost the same means as other types of dermatitis.
The main treatment methods include:
- boosting immunity;
- follow a strict therapeutic diet;
- taking medications;
- try to avoid all stressful situations;
- use of ointments, lotions;
If we talk about stressful situations, experts have long found out that the patient’s constant stress contributes to the development of weeping dermatitis faster.
Therefore, if possible, patients should not only take all medications prescribed by specialists, but also visit a sanatorium for relaxation.
Ointments
Many patients ask the same question, what to apply to weeping dermatitis.
If exudation is observed, lotions with a solution of potassium permanganate or boric acid are prescribed.
And then they use various pastes - fucorcin, chloramphenicol.
In order for wounds to heal as quickly as possible, ointments, lotions, and gels are used. For example, solcoseryl and bepanthen heal wounds well.
Those areas where the skin has become rough are lubricated with naphthalene ointment and other products that have a resolving effect.
In recent years, topical glucocorticoids have begun to be actively used. They are produced in the form of ointments, lotions, and creams.
They can be used even for children in the first years of life.
If a secondary infection occurs, drugs with antibacterial properties are prescribed.
For example:
- triderm;
- celestoderm;
- pimafucort;
During periods of remission, the skin must be constantly moisturized using medicinal cosmetics.
Medicines
To treat the disease, experts prescribe the following drugs:
- antiallergenic drugs. With weeping dermatitis, all symptoms can be relieved by taking medications such as Tavegil, Telfast, Claretin. The important thing is that all these drugs rarely cause side effects, which means the patient can lead his usual lifestyle.
- anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. In order to have these effects on the affected areas, hormonal medications should be taken. Doctors almost always prefer topical medications. Their main substance is zinc;
Folk remedies
There are several ways to treat this disease with folk remedies:
- potato treatment. Grate the potatoes; both juice and gruel are used for treatment. For example, if you use porridge, then it is simply applied to the affected areas of the skin. It stays on for two hours and then goes away. Simply wipe the skin with potato juice several times a day;
- Geranium oil. It is used externally and has an excellent healing effect. To do this, you can take leaves, flowers or twigs. The plant is thoroughly crushed, two tablespoons are taken and a glass of vegetable oil is poured. The product should be infused in a dark room for five days. After which it is placed in the sun and kept for one month. Only after this can you strain and start using. Problem areas are lubricated for several hours, then washed off with warm water;
- periwinkle. Take 1 tbsp. spoon of the plant and pour a glass of water. All this is cooked over low heat for 10 minutes. The decoction is added to the bath or lotions are made from it;
- tea with lemon balm. Many claim that drinking this tea in the morning and evening will relieve symptoms of the disease;
Find out what it means
Dühring's dermatitis
.
Why does dermatitis appear on the head? See the article.
Disease prevention
To exclude the possibility of a relapse, doctors recommend to their patients:
- Carefully follow the rules of hygiene.
- Try to avoid nervous shocks.
- Eat right, stick to a hypoallergenic diet.
- Avoid direct contact with agents that can trigger allergies.
- Treat diseases of the digestive system in a timely manner.
- When the first signs of weeping dermatitis appear, stop self-medicating and seek help from a dermatologist.
Only rapid elimination of the manifestations of the disease and its complete cure guarantee recovery. If the pathology becomes chronic, then during remission it is important to carry out therapy to strengthen the immune system. To prevent the birth of a child with a genetic predisposition to weeping dermatitis, a woman carrying a baby should give up bad habits, minimize the use of medications, and eat right.
The skin acts as a protective barrier from external influences, participates in thermoregulation, metabolic and other processes, and is the largest organ in area. “Problems” in the functioning of the body primarily affect the condition of the skin. Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system and metabolic processes are often accompanied by the development of various forms of inflammation of the epidermis. Weeping dermatitis is one of the most unpleasant forms of the disease.
Like other types of pathological process, it is characterized by painful rashes on the skin. The lesion progresses rapidly and after a short period, bubbles with liquid are observed at the site of the rash. The disease has no age restrictions and occurs with equal frequency in children and adults. You can learn about dermatitis in children here.
The following reasons and factors can provoke “wet” dermatitis:
- Impaired functioning of the digestive system, gastrointestinal diseases. The result of such processes is insufficient digestion of the food consumed, which leads to minimal absorption of beneficial microelements. Vitamin deficiency can lead to the development of inflammation of the skin, in particular, weeping skin.
- Hypersensitivity to certain foods and substances. This is a condition in which the human body's immune system responds to normal stimuli with an exaggerated defensive response. Allergies can be triggered by: pollen, dust, dust mites, products of the sebaceous glands of pets, drugs, food and more.
- Imbalance of the nervous system. Prolonged stay in stressful situations and depression becomes a provoking factor in the development of the disease.
- Liver and kidney dysfunction. Organs act as a kind of filter. The liver is involved in processing, detoxifying and removing potentially harmful substances and waste products. The development of liver failure leads to the accumulation of toxins in the body, which can be expressed as a dermatous reaction.
- The presence of pathogenic microflora in the stratum corneum of the epidermis. The presence of bacteria often causes dermatitis in infants.
- Inadequate nutrition, deterioration of immunity. Inadequate nutritional intake, especially protein and vitamin deficiencies, has an adverse effect on the functioning of the immune system. Acute deficiency of selenium, an important antioxidant, also leads to a decrease in the protective functions of the immune system and an increased risk of dermatous lesions.
Weeping Dermatitis: Symptoms, Photos, Treatment and Prevention
Skin pathology: distinctive features Causes, triggers and typification of MD Symptoms of MD and diagnosis Basic principle of treatment: complexity Traditional medicine recommends Preventive measures
Skin pathology: distinctive features
The skin is subjected to destructive processes, resulting in erosions, wounds, and ulcers with secretions of ichor and pus. The disease can affect people of any age and gender, this is where its main features lie.
Weeping dermatitis causes the patient a lot of trouble: pain, burning and itching. All these details negatively affect the psychological state, as a result of which complexes and depression appear. This is a fertile ground for disruptions in the functioning of internal organs and systems, including the skin.
Causes, triggers and typification of MD
When the digestive system is unstable, a person suffers from the accumulation of toxins that are not eliminated from the body. In addition, the intestines lose the ability to absorb nutrients and are unable to break down carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract is reflected in the condition of the skin and becomes one of the main internal causes of weeping dermatitis. This category of motivating factors also includes disorders of the pancreas, thyroid gland, liver, and kidneys.
The genetic predisposition that triggers atopic MD is also considered an intrinsic cause.
External factors include:
- Strong experiences leading to stress, emotional swings, depression.
- Allergies to certain foods.
- Side effects of pharmacological drugs, in particular, individual components intolerable by the body.
- Harmful fumes, contact with toxic chemicals that can penetrate deep into the dermis.
- Infection with fungi or harmful bacteria that are found in skin folds.
- Mechanical impacts on the skin with the appearance of scratches and microcracks create ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microbes. These may be ordinary injuries, the result of friction between folds of skin or the edges of clothing.
- Unfavorable environmental background present in certain geographical areas of residence.
The type of disease in question is divided into the following types according to the reasons for its occurrence:
- Occupational – associated with hazardous work conditions that can cause skin disease.
- Bacterial (pyococcal) – the causative agents of the disease are pathogenic microorganisms.
- Fungal – the name itself requires no comment.
- Household – interaction with aggressive chemicals used in everyday life.
The classification of the disease includes many types and subtypes, among which weeping atopic dermatitis is serious and difficult to treat. This disease has hereditary causes; the likelihood of transmission to a child increases significantly if both parents have skin problems.
The main triggering mechanisms include:
- Dysfunction of the central and/or peripheral nervous system.
- VSD.
- Consumption of rare, exotic foods.
- Change of residence associated with moving to a different geographical area with a sharp climate change.
- Direct contact with and/or living near pets.
- Cosmetics components.
- Plant pollen.
- Worm infestation.
- Diabetes.
MD symptoms and diagnosis
Inflammation of the skin, penetrating deeply, forms foci of the disease, which are characterized by the following symptoms:
- Rashes (vesicles) appear on the top layer of skin.
- The appearance of blisters with sanguineous or purulent (if infected) contents.
- Swelling at the site of redness.
Adult patients are characterized by large-scale affected areas with the appearance of blisters that ooze, crusts constantly crack, then turn into the form of ulcers and/or eczema. Most often these manifestations are observed:
- In the folds of the body.
- On the backs of the hands and feet.
- In the ankle area.
- On the elbows and knees.
- On the skin of the face and neck.
The patient experiences a burning sensation, tightness of the skin, the affected areas constantly itch and get wet. This causes a person not only physical suffering, but also negatively affects the neuropsychic state.
Children experience similar symptoms, but depending on the age category, the course of the disease progresses differently. In newborns and up to one year old, weeping spots, blisters, peeling and itching may appear. In infants, the disease is quickly treatable and leaves no traces.
Photo of weeping dermatitis in infants:
Photo of weeping dermatitis in infants
As for children from 3 to 12 years old, MD proceeds almost the same as in newborns, but swelling, redness, and painful erosions are added to the listed symptoms. Treatment does not give a quick effect; it will take a lot of time to achieve complete recovery.
Weeping atopic dermatitis in children in the photo:
Weeping atopic dermatitis in children
In adolescence (13-18 years), due to hormonal imbalance characteristic of the period of puberty, the disease can arise spontaneously and disappear in the same way.
It is very important to correctly diagnose MD, because the quality of treatment and the result depend on it.
During the examination, the doctor examines the nature of the symptoms and makes a preliminary diagnosis. To prevent mistakes, a sample of skin tissue is taken in places of pathology, and the composition of the blood is examined. After analyzing the obtained medical history, the doctor confirms the presence or states the absence of MD.
It is very important to accurately determine the cause of the disease in order to make the right decision on which specialist to participate in treatment: a dermatologist, an allergist, a geneticist or an infectious disease specialist.
The main principle of treatment: complexity
Doctors have developed an algorithm according to which a patient is prescribed a course of treatment; it presents the following measures in the following sequence:
- Elimination of irritating factors, triggers and other external causes.
- Following a special diet.
- Drug treatment with tablets or other medications taken orally (injections, droppers).
- The use of external medications.
- Physical procedures.
MD on the hands and other parts of the body in adults requires treatment with antihistamines and medications that eliminate inflammation, itching and pain. The most effective tablets are: Tavegil, Claritin, Telfast.
Hormonal ointments are indicated for patients who have not received the desired effect from previously prescribed medications: Flixotide, Advantan, Sinaflan, Afloderm.
Children suffering from MD are prescribed drug therapy using drugs with minimal side effects: Sudocrem, Zinocap, Desitin.
When developing a treatment program, many aspects related to the cause of MD, age, and individual characteristics of the patient’s body are taken into account.
If the nervous system (neurological disorders) is to blame for the onset of the disease, such a patient is required to take sedative medications:
- Tincture or valerian tablets.
- Glycine.
- Novo-Passit.
Such patients are also not recommended to consume foods and drinks containing caffeine. You will have to forget about your favorite coffee and strong tea even in the morning. Bad habits such as smoking or drinking alcohol must be eradicated. In other words, if the desire to get rid of weeping dermatitis is great, you should maintain a healthy lifestyle.
MD, which appears against the background of a disordered digestive system, is recommended to be treated with the following pharmacological drugs: Probifor and other probiotics. This type of disease can be aggravated if the following foods are not excluded:
- Oranges, tangerines, apricots, strawberries.
- Chocolate and cocoa.
- Eggs.
- Whole milk.
- Spicy, fried foods.
The diet should be dominated by greens, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products.
In case of weeping dermatitis in a baby, the nursing mother should follow the diet.
To normalize the baby’s intestinal function, you will need probiotics: Bifidumbacterin, Linex.
Weeping wounds can be healed well, thanks to compresses using potassium permanganate (pink solution), boric acid, and saline solution. Then you can enhance the therapeutic effect of Levomycetin paste.
Dried wounds turn into crusts, which are recommended to be lubricated with Levomikol, Fukortsin or regular brilliant green. You need to be extremely careful with iodine so as not to burn your already affected body.
In order to prevent infection, iodine treatment is allowed only along the edge of the wound.
Otherwise, the inflammation may increase in size due to the destruction of the epithelium under the influence of alcohol.
When using external dosage forms, it is necessary to take into account an important nuance: some ointments and creams are indicated for weeping wounds, others for dry ones. If you miss this moment, you may either not achieve a result at all, or provoke an exacerbation. A case like this is further confirmation of how important it is to consult a doctor and a reminder of responsibility for your own health.
Small blisters must be opened, but only with the participation of a doctor. Intervention on your own may not have the most desirable consequences. In sterile hospital conditions, a dermatologist performs an opening procedure, then treats the sore spot with antiseptic preparations with aniline dye.
At the final stage, physiotherapeutic methods are indicated; they help consolidate the achieved results of previous therapy or autopsy:
- Laser irradiation.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Electrophoresis.
- The mud is therapeutic.
Traditional medicine recommends
There are thousands of species of medicinal plants known in nature that save people from infection, relieve pain, and heal wounds. It is from these herbs that you can prepare infusions with unique properties that will help solve the problem of prolonged weeping dermatitis.
Chamomile with oak bark
Pour equal parts of crushed bark and chamomile inflorescences with hot water in an enamel bowl and simmer over low heat for about 20 minutes. After half an hour of infusion, you can begin treatment - wipe the dermatitis wounds.
Birch buds
Prepare the buds and tops of young birch shoots in a similar way, only leave for 1.5 hours. The resulting drug relieves severe itching.
Hops with sage
An infusion prepared from a collection of plants such as marigolds, sage, string, hops (cones) is also quite good for compresses and wiping affected areas.
Potato gruel
If wounds due to dermatitis begin to ooze more, a homogeneous mass of raw potatoes placed in a bag of thin gauze will speed up the drying. It is attached to the sore spot for the whole night.
Healing geranium
Mix crushed flowers, stems and leaves (2 tablespoons) with purified vegetable oil (200 g), place in the dark, keep for 5 days in a dark room, then transfer to a well-lit room for 1 month. Pour the strained medicinal oil into a dark glass bottle. Used to treat wounds and cracks.
Periwinkle petal baths
Boil the plant petals (2 tablespoons) with two glasses of water for a quarter of an hour. Can be used as compresses or prepared as a medicinal bath.
Diagnosis and symptoms
The clinical picture depends on the patient’s age and is determined by the following gradation:
- Children under 3 years old. Weeping inflammations are observed on the child’s skin, which eventually become crusty. The clinic is not so extensive, the main localization is elbows, knees and wrists.
- Children 3-12 years old. The inflammatory reaction is localized on the palms, neck, bends of the arms and legs. There is an itchy, red rash, swelling, and thickening of the epithelium. Occasionally the inflammation spreads to the face.
In patients aged 3-12 years, the rash is always weeping, difficult to treat, and after therapy leaves skin defects in the form of dark spots.
- Adolescent dermatitis (12-18 years). The clinical picture is typical for patients of the previous age group, but there is a certain difference - the disease is prone to sudden appearance and rapid disappearance. The exacerbation of the disease is rapid, and every element of the body can be affected, including the knees, wrists, groin, neck, chest, and toes.
- Adult and old age. Rashes are observed in the armpits and neck. Pronounced redness is accompanied by the formation of vesicles filled with serous exudate.
The diagnosis is usually determined by a dermatologist, allergist or pediatrician, and can be made based on the clinical picture and external signs. Family history is also important because genetics have a significant influence on the development of allergies. There are no specific markers of the disease. A laboratory blood test is performed to determine proallergic IgE antibodies and eosinophils (a type of white blood cell). With weeping dermatitis, the indicators of both analyzes are overestimated. Specific allergens can be found using skin tests performed by a qualified physician.
It is important to carry out differential diagnosis with other types of dermatous lesions.
Symptoms
At different ages, weeping dermatitis manifests itself in different ways:
- In children under two years of age, crusts form on the skin in the face and on the bends of the knees and arms.
- If a child is over 12 years old, then he develops a rash almost all over his body. In this case, all affected areas are red, the skin swells, and cracks form.
- Adults experience the same symptoms as children. But at the same time their skin thickens greatly.
Weeping dermatitis on the hands.
The main symptoms of the development of weeping dermatitis include:
- At an early age, small rashes appear on the body, from which ichor is released.
- At the age of 2-3 years, you can notice small cracks and ulcers on the skin in the knee area and on the bend of the arms.
- From 3 to 12 years of age, dermatitis manifests itself as symptoms in the form of a rash on the arms, neck, and face. You may notice redness of the skin, itching, and dryness of the dermis.
- In adolescence, the disease is characterized by swelling of the body, ulcers affect most of the surface.
- In adults, symptoms such as redness of the skin, the appearance of ulcers on the face, neck, and hands appear. Severe itching, copious discharge of ichor.
When the first signs of pathology appear, you should consult a dermatologist. The doctor will examine the lesions, identify the type of disease and prescribe comprehensive treatment. To visually understand whether this is the type of disease in a person, you can look at a photo of weeping dermatitis. Its nature will directly depend on the patient’s age, location and etiology.
In a child and an adult, the disease will have slightly different symptoms, so they are considered separately.
Weeping dermatitis in infants and children under 3 years of age is manifested by the formation of redness, in place of which weeping ulcers soon appear, and clear liquid is released from them. These areas are then covered with crusts. Inflamed areas are localized on the cheeks and behind the ears, on the elbows and knees. Very rarely, skin lesions affect the trunk.
In children 3-12 years old, the disease is characterized by the appearance of swelling and redness in the neck, back of the hands, elbows and under the knees. In place of the redness, separate redder areas and blisters soon appear, which, when opened, form shiny pinkish “islands” - erosions. Then the areas of inflammation crack and become painful, and clear liquid is released from the cracks.
The affected areas are very itchy. The child scratches them, as a result, an infection is introduced here, and instead of ichor, pus begins to come out of the cracks. The healing of inflammation is indicated by the appearance of crusts and a decrease in redness. Where there were pockets of weeping dermatitis, spots remain darker than the surrounding skin.
In adolescents aged 12-18 years, the manifestations of weeping skin inflammation are not much different from those described earlier. The difference is that the affected areas can disappear spontaneously, or just as suddenly grow.
Weeping dermatitis on the body of an adult looks like areas of redness and swelling, on which blisters soon appear, which are then replaced by smooth and oozing erosions, cracks and crusts. Favorite places for inflammation: natural folds of the body, bends of joints, back surfaces of the hands and feet.
Treatment
Inflammatory processes are successfully eliminated by certain groups of drugs. Steroids, analogues of cortisol, are often used. They inhibit allergic processes and also significantly reduce skin itching. Corticosteroids are a powerful treatment for weeping dermatitis, particularly when used as ointments. They suppress the immune response (and therefore the allergic reaction) on the skin and have a rapid therapeutic effect. You will learn about other ointments for dermatitis in this article.
After stopping the use of corticosteroids, a relapse of the disease may occur, so they are used exclusively in accordance with the decision of the treating dermatologist.
The patient is prescribed a diet with the exclusion of foods with increased allergic potential, details here. For dermatitis caused by stress, an additional course of sedatives is administered.
Antihistamines are prescribed for oral and local use. Their name comes from their ability to block a compound known as histamine, released from certain cells after contact with an allergen. Blocking histamine also suppresses the entire allergic reaction.
There are also modern immunomodulatory therapies. Treatment consists of the use of special drugs to relieve hypersensitivity of the immune system and prevent the occurrence of allergic reactions.
In combination with medications, it is recommended to undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures: magnetic therapy, phonophoresis, laser exposure.
Preventive actions
To avoid the development of weeping dermatitis, you need to follow the recommendations of doctors regarding prevention:
- strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoid nervous disorders, stress and depression; if necessary, you can and should seek help from a psychologist or neurologist;
- timely treatment of diseases of internal organs;
- control your diet and diet to avoid digestive system disorders;
- If you have allergies, avoid contact with allergens.
If the patient promptly sought professional medical help for weeping dermatitis, then competent treatment will prevent the development of the acute form of the disease into a chronic one. If weeping dermatitis has already taken a chronic form, then during periods of remission, patients should strengthen their immunity and strictly follow all the recommendations and prescriptions of the attending physician.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical observer, therapist of the highest qualification category
21, total, today
( 41 votes, average: 4.71 out of 5)
Erythrasma - treatment and prevention of superficial pseudomycosis
Dermatitis: types, clinical picture, treatment
Related Posts
List of ointments and creams prescribed for dermatitis
Corsticosteroids
Hormonal drugs of synthetic origin similar to the hormone cortisol. When treating weeping dermatitis, the following medications for topical use (cream, gels) may be prescribed:
- Prednisolone;
- Advantan;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Akriderm;
- Beloderm;
- Diprosalik;
- Symbicort;
- Trimistin.
Tar ointment
Available with the addition of sulfur, it is a combined product for external use. Has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effect. Reduces the severity of itching and speeds up recovery.
Naftalan ointment
Used as a local anesthetic. It has a positive effect on the regenerating abilities of the epidermis, relieves inflammation, swelling, and redness. Apply according to instructions in the instructions.
Antiallergic
More often, antihistamine ointments are prescribed to children for dermatitis. Their pharmaceutical action is aimed at eliminating itching, inflammatory reaction, redness, and accelerating epithelization. Most popular:
Hormonal antihistamines:
Antiallergic with bacteriostatic component:
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing the disease, you must adhere to a number of recommendations from a dermatologist:
- Maintain personal hygiene, daily water procedures.
- Minimize exposure to stressful situations.
- Promptly carry out therapy for emerging diseases.
- Avoid contact with allergens and control your diet.
Timely seeking medical help at the first signs of dermatitis will help avoid the disease becoming chronic. If the disease has taken this form, then the patient will need to regularly monitor the functioning of the immune system, strengthen it, and take immune-modulating drugs.
Disease prevention
In order to prevent the development of weeping dermatitis, as well as to avoid relapse, it is important to adhere to preventive measures.
They are not difficult, absolutely anyone can do them:
- rules of personal hygiene;
- exclude all nervous disorders. Do not overwork, try not to be stressed;
- Healthy food. Do not consume allergic foods, they will only provoke the development of dermatitis;
- completely eliminate contact with the irritant;
- treat pathologies in a timely manner. When the first signs of dermatitis appear, you should immediately go to a dermatologist or allergist;
There are often cases when weeping dermatitis becomes chronic. In this case, it is important to carry out therapies to strengthen the immune system.
Read what it should be like
treatment of facial dermatitis in adults
.
How to choose an ointment for dermatitis on the legs? Find out here.
What should be the diet for allergic dermatitis? All recommendations below.
To avoid health problems and protect yourself from dermatitis, you should follow certain precautions. As a preventative measure, experts recommend:
- Regularly observe personal hygiene rules.
- Adjust your diet (exclude unhealthy, heavy foods from it).
- Protect yourself from contact with allergens.
- Avoid emotional stress, nervous breakdowns, and excitement.
- Treat chronic diseases in a timely manner.
- Strengthen the immune system.
- Walk in the fresh air for 2-3 hours every day.
- To live an active lifestyle.
Preventing yourself from getting sick is not that difficult. The main thing is to follow all the recommendations and regularly visit the hospital for routine examinations. There is no need to self-medicate. If any signs of pathology appear, you need to seek medical help and undergo a full diagnosis. Only timely treatment will help avoid health problems for adults and children.