Causes of chickenpox in adults
Chickenpox is an infectious disease, the pathology is caused by the herpes virus type 3 or Zoster, which is transmitted by airborne droplets. An adult can become infected from a child while being in the same room with him, but pathogenic microbes also penetrate through the ventilation system.
All adults who did not have chickenpox as children can become infected. A separate risk group is people with weakened immune systems; they suffer the disease especially hard.
What factors activate the virus:
- primary and secondary immunodeficiency;
- the presence of malignant neoplasms, undergoing a course of chemotherapy, long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- prolonged emotional stress, frequent stress;
- antibacterial therapy.
The chickenpox virus practically does not survive in the external environment, so it is impossible to become infected through household items; infection occurs only through direct contact with a sick person, or when treating wounds without protective gloves. Animals cannot be carriers of infection.
Chickenpox prevention and treatment methods
Vaccination is a modern method that has proven highly effective in combating the spread of chickenpox in adults. In Russia, drugs containing a weakened strain of the virus have been registered for quite some time. Vaccinations are given on a voluntary basis to any person who goes to a medical center or clinic at their place of residence.
There is no specific treatment for chickenpox, since herpes viruses develop inside biological cells. And it is very difficult to directly influence their vital activity without affecting a living cell. Therefore, the main recommendation of specialists is the practice of observing proper patient care during quarantine.
For typical, moderately severe chickenpox, treatment of the rash with external agents based on zinc oxide is allowed. It is also possible to use antihistamines and complex medications that can relieve itching and inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes. In more complex situations, the patient will be offered immunostimulating therapy using synthetic antiviral drugs.
But under no circumstances should you self-medicate! The entire set of necessary medications will be indicated only by the doctor after examining the patient and studying the test results. Otherwise, there may be a risk of complications and additional health problems.
It is also worth considering strengthening your immune system throughout your life. This is easy to do by giving up bad habits, switching to a fortified diet and a sports lifestyle.
Stages and symptoms of chickenpox
In adults, the disease has some peculiarities; it almost always occurs in a moderate or severe form; the older the patient, the greater the likelihood of complex bacterial complications.
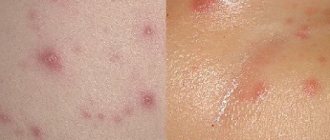
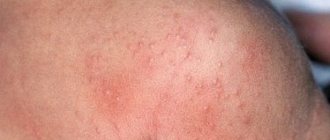
At the initial stage of development of the pathology, 28–30 hours before the appearance of characteristic vesicles, a person begins to be bothered by the first signs similar to a cold - headache, aches in the lower back, limbs, weakness, the disease occurs without fever, or the indicators rise to a low-grade level. After 48–72 hours, the acute phase of the disease occurs, which is accompanied by a characteristic rash, what it looks like can be seen in the photo.
Acute phase of the disease
The main manifestations of chickenpox:
- the temperature rises to 40 degrees, does not decrease well even after taking medications;
- symptoms of severe intoxication - loss of strength, nausea, frequent vomiting;
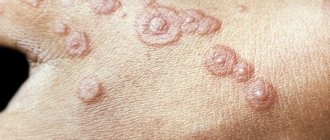
- a rash appears on the skin, every day this is approximately 3–4 days of the disease - numerous small tubercles of a pale red color, gradually they burst, a crust forms on their surface, they can be single, the rashes can be single, or merge with each other;
- rashes on the mucous membranes - red spots up to 5 mm in size can be seen on the gums, palatine arches, they gradually transform into nodules, vesicles, ulcers;
- severe itching;
- lymph nodes in the groin, behind the ears, under the lower jaw, in the armpits become enlarged and painful;
- the rashes have a wave-like character and completely disappear within 10 days;
- with severely weakened immunity, fasciitis and abscess develop.
Sometimes adults experience an atypical latent form of pathology without a rash - the clinical picture is erased, the disease is mild, temperature readings are normal, and symptoms of intoxication do not appear. This type of pathology is diagnosed in people who have been administered immunoglobulins for prevention.
Important!
The incubation period of chickenpox is 10–21 days, but the first obvious manifestations of the viral disease in adults are observed 3–5 days after infection.
Rash that itches
Herpes of the third type is not only particularly contagious, but is also one of the most dermatotropic microorganisms. Its own DNA structure allows it to penetrate into epidermal skin cells and cause destruction of surface tissues and capillaries. As a result, small pimples appear on the body of an infected person.
Read: When a rash appears due to chickenpox, you can’t say for sure what could have happened
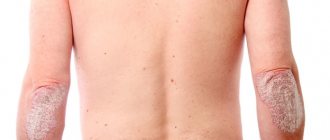
Chickenpox rashes last an average of 10-12 days. It takes 3-4 weeks for complete recovery from chickenpox. Therefore, most often the symptoms of herpes zoster infection last for a whole month. It is known that chickenpox in adults occurs with great complications when an atypical form of infection occurs. Then the fight against additionally attached diseases significantly increases the duration of the disease.
The period of rash is characterized by complications of intoxication of the body. The main symptoms may vary in appearance. The course of the acute phase of chickenpox in adults varies depending on a number of factors, but the following phenomena are most often observed:
- body temperature rises to 40 degrees, chills and weakness occur;
- The rashes are profuse and quickly spread throughout the body, causing severe itching. Enanthems may form in the oral cavity and on the mucous membranes. The rash affects the mucous membranes of the genital organs, complicating urination with severe pain;
- The lymph nodes (behind the ear, submandibular, axillary, inguinal) noticeably increase in size; severe pain is felt when palpating them;
- weakened immunity leads to suppuration (sepsis) of tissues during the period of illness;
- complications can lead to nausea and severe vomiting. Irritation from sounds and light occurs, and coordination of movements is often impaired.
Throughout the entire period of the disease, the elements will have varying degrees of development, since the signs of the acute phase are wavy in nature. In other words, the rash continues to change over the course of ten days. First, a pink spot appears, over time it turns into a bubble with liquid and a hole in the center (papule). The bubbles burst, resulting in vesicles. Over time, dried crusts form on their surface. The dense structure at the stage of skin tissue restoration simultaneously protects wounds from mechanical stress and also prevents the entry of pyogenic bacteria.
Herpes zoster viruses multiply very actively in the areas where the rash occurs, so already with the appearance of papules, the patient feels severe discomfort due to itchy pimples. Regular treatment of elements from the very beginning of their occurrence with modern antiseptic agents (except brilliant green solution) can reduce itching and prevent the formation of residual scars on the skin.
If the rules for treating areas with a rash are not followed, the wounds can be affected by a secondary infection, after which scars form on the skin.
Forms of chickenpox
The clinical picture and speed of recovery depends on the severity of chickenpox, but almost always adults are seriously ill with chickenpox.
Average form of chickenpox
- With a mild course of the disease, the temperature may remain within subfebrile levels, there is little rash, acne affects only the skin, and isolated rashes may be observed on the mucous membrane. Improvement in well-being is noticeable on days 2–4.
- The moderate form is characterized by pronounced manifestations of intoxication, temperature values rise to 38.8 degrees or more, a rash covers the entire body, accompanied by unbearable itching. The duration of the illness is up to 7 days.
- The severe form lasts more than a week, is accompanied by multiple rashes, high fever, vomiting, and may have several development options.
Varieties of severe chickenpox:
- Hemorrhagic - occurs when there is a history of hemorrhagic diathesis, vasculitis, poor blood clotting, is accompanied by numerous subcutaneous hemorrhages, hematomas, bleeding gums, and intestinal bleeding are observed.
- Bullous - in addition to the usual rash, at the early stage of the disease large folded blisters with cloudy liquid inside form, leaving ulcers that do not heal for a long time.
- Gangrenous - diagnosed in elderly, exhausted people, the disease occurs against the background of infection penetrating into the papules. A black border appears around the rash, which consists of dead tissue cells; the disease occurs against the background of severe hyperthermia and severe intoxication.
Important!
You can become infected not only from a person with chickenpox, but also from patients with herpes zoster.
Chickenpox vaccine for adults
The chickenpox vaccine is not included in the mandatory vaccination schedule and is used only at the request of the person. Vaccination against chickenpox among adults can be used at any time, especially if the person has not previously suffered from this pathology in an active clinical form. In most situations, persons whose work involves daily contact with children are interested in vaccination against chickenpox, since chickenpox is a fairly common infectious pathology among organized children's groups.
In addition, often young women of reproductive age who did not have chickenpox in childhood go to medical institutions for routine vaccination. Infectious disease specialists identify a certain category of people who are recommended to be routinely vaccinated against chickenpox (persons suffering from severe diabetes mellitus, leukemia, as well as cancer patients taking long courses of chemotherapy).
In order for persistent immune reactions against chickenpox to form in the body of an adult, vaccination should be carried out in two doses. In addition, emergency immunization of a healthy person in contact with an infected person can have a good therapeutic effect if used in the first three days after contact.
Currently, vaccines such as Okavax and Varilrix, which exhibit identical effectiveness, are used to vaccinate against chickenpox in adults.
The Okavax vaccine is a live chickenpox vaccine and is approved for use in both children and adults. Vaccination using Okavax is a subcutaneous injection of one dose of the drug in the projection of the outer surface of the shoulder. In most situations, vaccination against chickenpox in adults proceeds without complications, however, in some situations, the patient may experience a short-term local reaction in the form of slight swelling, thickening or hyperemia in the projection of the direct injection. An absolute contraindication for vaccination against chickenpox using a live vaccine is any trimester of pregnancy and severe somatic pathology accompanied by immunodeficiency.
Vaccination using the Varilrix vaccine is used in most situations as an emergency preventive measure, and its effectiveness directly depends on the time of use. Thus, in a situation where more than 72 hours have passed since a healthy person came into contact with a chickenpox-infected patient, vaccination is considered irrational. Vaccination against chickenpox using the Varilrix vaccine should be carried out twice at intervals of three months. Among the contraindications to the use of the Varilrix vaccine, it should be noted that the patient has signs of immunodeficiency or any acute infectious pathology.
In a situation where vaccination against is carried out routinely in relation to a woman of reproductive age, it should be carried out no later than three months before the expected pregnancy. Active synthesis of specific antibodies against the chickenpox virus in adults, which is observed after vaccination with a live vaccine, may be accompanied by the appearance of a low-intensity rash on the skin, the pathomorphological elements of which are similar to those of chickenpox. This condition is considered by infectious disease specialists as reactive and does not require drug correction.
The effectiveness of chickenpox vaccination has a limited duration of thirty years.
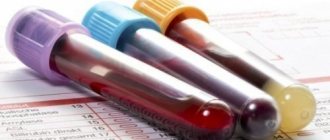
Diagnostics
Chicken pox has a pronounced clinical picture, which allows the doctor to make a diagnosis after examination and history taking. But sometimes chickenpox can be confused with herpes zoster, erythema multiforme, vesicular rickettsiosis; for a more accurate diagnosis, additional examination is prescribed
Chickenpox usually has a pronounced rash, but additional tests are always done to be sure.
Research methods:
- clinical blood test - with chickenpox, the ESR increases, the level of monocytes increases, and plasma cells appear;
- clinical urine test - the presence of protein, red blood cells, and leukocytes indicates that the kidneys are damaged by the virus;
- analysis of the contents of the rash is carried out using silvering and immunofluorescence;
- ELISA - determines the presence of antibodies to type M, G viruses in the blood.
Since chickenpox can provoke the development of severe complications, during the examination the doctor listens to the heart, lungs, bronchi, and palpates the abdomen and liver.
Treatment of chickenpox in an adult
Chickenpox in adults cannot be fought on your own; complications often rapidly develop against the background of the disease, which can result in the death of the patient. Medicines are used in therapy, and traditional medicine recipes are used as additional remedies.
General recommendations
In case of chickenpox, the patient is prescribed strict bed rest; in case of severe infectious pathology, hospitalization is required.
If you have chickenpox, hot showers and baths, as well as baths and saunas, are prohibited
What not to do if you have chickenpox:
- You can take hot baths or wash under a warm shower after the end of the acute phase of the disease, but rubbing the skin is contraindicated;
- comb the blisters, otherwise ulcers will appear, and after they heal, scars and scars will remain;
- touch pimples with dirty hands;
- eat spicy, fried, salty and smoked foods.
Until complete recovery, it is necessary to change bed linen daily, use all medications prescribed by the doctor, drink at least 2 liters of water per day, consume more dairy products, and ventilate the room every 2-3 hours.
Medicines
There are no special medications for the treatment of chickenpox; therapy includes drugs that help eliminate the manifestations of pathology, speed up the recovery process, and reduce the risk of complications.
How to treat:
Immunity booster
- antiviral drugs in the form of tablets and ointments - Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Valacyclovir;
- specific immunoglobulins – Zostevir;
- antipyretics – Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Aspirin;
- antiseptics for treating vesicles - Chlorhexidine, Miramistin;
- rinsing solutions – Sodium sulfacyl, Furacilin;
- antihistamines to relieve itching and swelling - Tavegil, Suprastin;
- intravenous detoxification agents – Reopoliglyukin;
- vitamin complexes, immunomodulators.
Adults with chickenpox are almost always prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics - Oxacillin, Cefazolin - to reduce the risk of developing secondary bacterial infections.
Doctors do not recommend lubricating wounds with brilliant green or Fukortsin - these products have a pronounced drying effect and increase the feeling of itching.
Folk remedies
At home, when treating a typical or latent form of chickenpox, you can use folk remedies; they effectively eliminate the unpleasant signs of the disease, but they should only be used in combination with medications.
What to do at home:
In case of severe itching, you need to make compresses from a solution of water and soda.
- In case of severe itching, prepare a solution of 200 ml of water and 5 g of soda, apply compresses to the affected areas, and leave for a quarter of an hour.
- Dissolve 10 g of mumiyo in 100 ml of warm water, take the drink morning and evening to strengthen the immune system, speed up the skin regeneration process, and reduce the risk of bacterial infections.
- Pour 1 kg of chopped oats into 5 liters of water, simmer over low heat for half an hour, pour the broth into the bath. Carry out water procedures before bed to eliminate itching.
Important!
People with chickenpox need to eat only warm food in pureed or liquid form - vegetable broths, steamed cutlets, purees, pureed soups, fruit mousses.
Treatment of chickenpox with medications
When pathology develops, certain groups of drugs are prescribed for a speedy recovery.
- Considering that the pathology is provoked by viruses, one cannot do without antiviral agents. The doctor prescribes: “Acyclovir”, “Famciclovir”.
- To reduce the intensity of itching, Suprastin and Cetirizine are prescribed.
- If you have a high temperature, you should definitely take antipyretic medications.
- If there are a large number of purulent rashes, antibiotics are indicated. These are, for example, Oxacillin, Cefazolin.
- To reduce intoxication in severe cases of the disease, intravenous glucose solution and rheopolyglucin are prescribed.
- In the most severe cases, specific antibodies to the virus may be administered.
Any self-medication is unacceptable; it is fraught with the development of complications.
Features during pregnancy
Chickenpox during pregnancy is extremely dangerous; the disease poses a threat not only to the woman, but also to the fetus. The result of the disease can be a miscarriage if the infection occurs before the 12th week.
When infected with chickenpox in the first trimester, the disease almost always negatively affects the development of the fetus - pathologies and deformities, diseases of the bone and nervous system, and disturbances in the formation of sensory organs can develop. If an ultrasound reveals such problems, the woman is recommended to have an artificial termination of pregnancy.
If chickenpox is detected in a pregnant woman, termination of pregnancy is recommended.
After 20 weeks, the virus does not particularly affect the condition of the mother and child, but a relapse may occur immediately before birth. Infection with chickenpox in the later stages provokes the development of pneumonia, which is often fatal for a newborn.
Important!
Women who have not had chickenpox are recommended to get vaccinated when planning pregnancy.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
If a woman did not suffer from pathology in childhood and did not get vaccinated against the disease, then infection during pregnancy can become especially dangerous for her. The symptoms and treatment of chickenpox in adults are discussed above; the photos demonstrate the severity of the disease. A pregnant woman who comes into contact with a sick person without immunity will definitely become infected. During this period, the immune system is under heavy stress, so re-infection is not excluded, but in this case the pathology will be much easier.
During the primary development of chickenpox, the features are as follows:
- The symptoms are pronounced.
- High risk of developing hemorrhagic, gangrenous forms of pathology.
- The risk of developing respiratory failure increases; in severe situations, death may occur.
- There is a high probability of neurological complications.
- There is a risk of miscarriage.
- A child may develop a congenital form of chickenpox.
The most dangerous infection for a woman and her baby is during the first three months and the last. Chickenpox at the beginning of pregnancy is fraught with damage to the fetal cerebral cortex and underdevelopment of the limbs. At a later stage, developmental delay and convulsive syndrome may occur.
Treatment of chickenpox in a woman in an interesting position categorically does not allow self-medication. This can be dangerous for the expectant mother and her baby.
Possible consequences and complications
In adults, chickenpox often causes severe complications that can cause disability or even death.
Why is chickenpox dangerous?
- severe dermatological pathologies - occur when scratching rashes, non-compliance with hygiene rules;
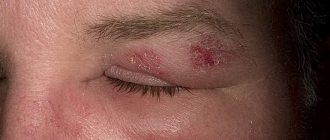
- blindness – develops when the virus penetrates the mucous membrane of the organs of vision;
- neurological disorders, paralysis of the facial nerves;
- subcutaneous, internal bleeding, hemoptysis, thrombophlebitis, myocarditis;
- chronic gingivitis, stomatitis, laryngitis;
- inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- sepsis, encephalitis, meningitis, cerebral edema;
- arthritis, synovitis, myositis;
- purulent otitis media, pneumonia;
- hepatitis, infection of the spleen and pancreas by the virus.
One of the complications of chickenpox in adults is blindness.
If a man's chickenpox rash affects the genitals, balanoposthitis develops - inflammation of the head and foreskin. Less commonly diagnosed is orchitis, an inflammatory process that affects the testicles.
For women, chickenpox is fraught with the development of vulvitis and other gynecological inflammatory pathologies, since rashes often appear on the vaginal mucosa.
Important!
If the Zoster virus affects the central nervous system, death can occur within 24 hours.
Severe fever in adults
The mechanism of thermoregulation in adults with chickenpox is very different from the process of fever in children. Fever is a response to irritating substances released by viral agents during their active life in the human body.
As a result of high heat production in organ cells, as well as limitation of the heat transfer process, spasmodic phenomena are formed in the skin vessels. Therefore, the patient in the initial stage of fever feels severe chills. When you have infectious chickenpox, it is quite difficult to bring down the temperature, since the pathogens produce pyrogens in large quantities.
It should be noted that with each new wave of rashes the body temperature will increase. Against the background of bacterial infection, adults also experience high readings, reaching 40-41 C.
Then the patient suffers from severe ailments in the form of:
- muscle weakness;
- headaches;
- delusional states;
- febrile seizures;
- loss of spatial orientation.
With this development of infection, special quarantine conditions should be followed. Bed rest is required for the entire period of elevated temperature. Like a small child, heat can cause rapid dehydration for an adult. Therefore, it is imperative to replenish the water balance in the body. Accelerating metabolism will allow you to remove a large number of toxins from tissues in a short time.
Read: Chickenpox in children under one year of age: danger and treatment methods
Taking some medications that are familiar to many is prohibited by medicine today. It has been proven that the effect of Acetylsalicylic acid on the body during viral infections leads to the development of Reye's syndrome. In this case, the process of fat breakdown is disrupted and liver edema occurs, followed by damage to brain cells.
Prevention
The best way to prevent chickenpox infection is vaccination; vaccination with Varilrix and Okavax is given to all adults who are at risk.
How to avoid secondary chickenpox:
- regularly strengthen the immune system - follow a daily routine, eat right, give up bad habits, lead an active and healthy lifestyle;
- avoid stress;
- limit contact with sick people; if a child is sick, you need to use protective medical masks.
To avoid chickenpox, you should regularly strengthen your immune system.
Compliance with all preventive measures significantly reduces the risk of infection and the development of complications, but there is no recipe that can guarantee protection from the disease.
You can get vaccinated against chickenpox as a preventive measure, or after contact with a sick person within 72 hours. Live vaccines are contraindicated in pregnant women, people with AIDS, primary immunodeficiency, or taking immunosuppressive drugs.
Disease prevention
If you were unlucky enough to get the chickenpox virus as a child, check out the preventive methods to avoid getting chickenpox:
- Avoid completely contacting someone in your environment if they have signs of chickenpox. The same goes for family friends whose children have chickenpox;
- If you are at risk of contracting chickenpox, try not to attend children's parties or other events/places where carriers of the chickenpox virus may be present. If this is not possible, take preventive measures regarding hygiene (gauze bandage on the face, rubbing hands with antiseptic, etc.).
Remember that the use of pharmaceutical drugs to completely eliminate the likelihood of infection with the chickenpox virus in adults is not carried out. The main condition for preventing chickenpox is your awareness and caution.
Quarantine conditions
If there is a child or other adult with chickenpox in the house, in order to prevent the spread of the disease, a quarantine regime is established :
- A patient with chickenpox is isolated in a separate room, the doors to which must remain closed;
- Each family member is given their own set of dishes and cutlery. The same goes for towels;
- If possible, quartz treatment is carried out indoors;
- In an apartment where there is a person with chickenpox, wet cleaning and ventilation are carried out daily (3 - 5 times a day);
- If you need to enter the room of a patient with chickenpox, put on a gauze bandage. Ideally, you should also wear latex gloves, but you can simply treat your hands with an alcohol antiseptic;
- The clothes of a person infected with chickenpox are washed separately.
If you follow these measures, the risk of chickenpox infection will be minimized. It is important not to neglect personal hygiene and strengthen some aspects of it (for example, make hand washing more frequent). The chickenpox virus is highly contagious, but it is possible to avoid being affected by it.
Emergency prevention for pregnant women
A woman who is expecting a child and becomes infected with chickenpox as an adult cannot receive vaccination. The solution would be to prescribe antiviral therapy, in particular, taking immunoglobulin. It should be prescribed by the doctor observing the pregnancy, so at the first symptoms of chickenpox infection, you should immediately inform him of what is happening.
Treatment of chickenpox in children
Why do red spots appear on the body?
Papillomas in children: causes and treatment
Chagas disease or American trypanosomiasis symptoms
Blastocystosis treatment for children and adults
Isosporosis in humans: symptoms and treatment
Question answer
How long does chickenpox last in adults?
The duration of the disease depends on the person’s immunity and the severity of the pathology; on average, recovery occurs after 15 days, the temperature begins to subside after 1–3 days. In severe forms, which are accompanied by complications, recovery may take 1.5–2 months.
Relapse in an adult
If a person has had chickenpox in childhood, then lifelong immunity is developed, but if the body’s defenses are weakened, repeated chickenpox is often diagnosed, and the pathology manifests itself in the form of shingles.
In an adult, relapse rarely occurs, but if this happens, it manifests itself in the form of herpes zoster
Chickenpox leaves behind antibodies in the human body that prevent re-infection, but they do not always work. Secondary infection with chickenpox is diagnosed in people with weakened immune systems; the disease in adults is severe and accompanied by complications.
Find out more on the topic: Infections
Signs of the initial stage of the disease
The first signs of pathology begin to appear 14-17 days after contact with a patient with chickenpox. It is important to know the initial symptoms so as not to confuse it with an infectious disease. The photo perfectly demonstrates the first symptoms of chickenpox in adults. They are:
- Muscle pain.
- General weakness.
- Headache.
- Increased body temperature.
At this stage, rarely does anyone go to the doctor, believing that the manifestations are caused by a cold or ARVI.