Urticaria pigmentosa is one of the most common forms of a rare disease called mastocytosis. In many cases, children are susceptible to this disease, but adult women and men can also get it.
Mastocytosis is a disease in which mast cells multiply and accumulate in living tissues. Mast cells are a fairly significant part of the human immune system, so many experts are confident that urticaria pigmentosa appears when the body’s immunity is impaired.
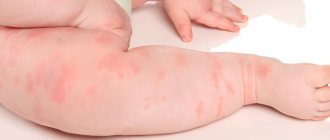
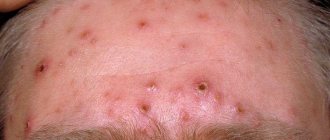
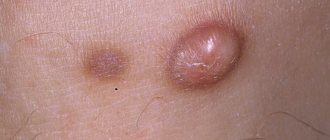
Children most often suffer from urticaria pigmentosa; spots appear on their body, red or pink, and later they change into subcutaneous blisters, inside of which there is water. After they heal, traces of a brownish tint remain on the body. Sometimes they disappear, and sometimes they remain and may even increase in size.
In adults, urticaria pigmentosa begins to occur in the form of spots that have a clear border and are absolutely smooth; nodular formations no larger than 5 mm may occur, and there may be rashes in the form of blisters. These inflammations can be seasonal or appear from any damage to the skin, sometimes they are with a person throughout his life, then disappearing, then appearing again.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms that characterize this disease directly depend on where exactly, in which layers of the epidermis, substances released from mast cells have accumulated.
Doctors are used to dividing the skin reactions that occur with urticaria pigmentosa into five types:
- Maculopapular. Many small nodules or dark spots form on the skin. Localization is clearly limited. If you apply mechanical force to them, small bubbles may appear.
- Nodal. With this type, many convex seals or nodules appear on a person’s skin. The color of the formations that appear is usually red, pink or yellow. Sometimes the nodules, due to their close proximity to each other, merge into plaques.
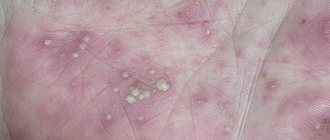
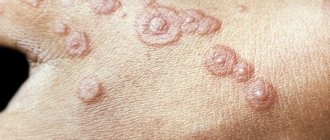
- Solitary. A knot no larger than 50 mm in size is formed; when you touch it, you might think that it is rubber. These nodes are called mastocytomas. Their localization is usually on the arms or neck, on the torso. Usually only one nodule appears, but it is possible to increase their number to four. They have the ability to disappear on their own.
- Telangiectatic. This type usually affects women in adulthood. They have red-brown spots on their body, mainly on their chest.
- Erythrodermic. Yellowish-brown areas appear on the human skin, quite dense, they have uneven edges, but the border is clearly visible. With this form of the disease, a person suffers from severe itching, which, as a result of scratching the affected areas of the body, leads to small ulcers and cracks.
With minor exposure, blisters may appear and the itching may become worse. There is a risk of developing a bullous form, when there are a lot of bubbles. The transformation into a systemic form occurs much less frequently, but then the entire skin will be affected, will peel off and be very difficult to treat.
In addition to the signs that appear with urticaria pigmentosa on the skin, the following symptoms may appear:
- the human body temperature rises;
- blood pressure decreases for unknown reasons;
- severe itching and redness of the skin;
- attacks of tachycardia.
These symptoms may indicate that the disease may have damaged a person's internal organs. And in this case, it already becomes quite life-threatening and requires good and professional treatment.
Causes of urticaria
Urticaria pigmentosa most often appears due to allergies to food, drugs and chemicals. In this case, you need to exclude the allergen from your diet or use. Can be transmitted from person to person by airborne droplets. There is even solar urticaria, in which rashes on the skin appear due to the influence of sunlight on it.
Often in adults, a rash is observed due to severe stress. You cannot cover stains with cosmetics to hide them. This can only worsen the situation, so the rashes will become even more pronounced.
Experts also believe that urticaria in children occurs due to hereditary factors. Therefore, if one of the parents has such a problem, then the child may also develop it. There is also an opinion that skin rashes are associated with inflammatory processes in the body caused by infection or toxins.
In general, the mechanism of development of mastocytosis is as follows. With excessive accumulation of leukocytes in skin cells, histamine and other active substances are produced, which are formed as a result of the breakdown of mastocytes. The produced components expand capillaries and increase vascular permeability. As a result, numerous rashes appear on the skin. This happens due to excess melanin in the lower layers of the skin. This phenomenon is called immune influence. With non-immune exposures, urticaria is caused by other factors: cold, heat, shock, sun, and so on.
Forms of mastocytosis
There are several forms of mastocytosis:
- systemic. It usually appears in adults and affects the tissues of the internal organs of a person, but there may or may not be skin lesions;
- cutaneous This form includes both infantile and adult mastocytosis. With this form, in infancy and adolescence, only the skin is affected; the disease does not spread to the tissues of internal organs. Cases of transition to the adult form are very rare;
- malignant. It degenerates mast cells into a malignant form. There may not be inflammation on the skin; it only affects the internal organs. Difficult to treat and can lead to death.
- adult or teenage form. It manifests itself as symptoms on the skin, but also affects the internal organs of a person, the heart, kidneys, and stomach. Although such lesions rarely progress and become systemic.
Symptoms
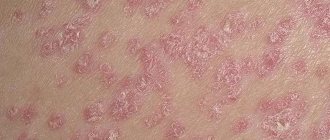
The main symptom of urticaria pigmentosa is a skin rash in the form of spots and papular mastocytes, the size of which can reach 4-5 cm. The color of the rash ranges from pale pink to brown. The rashes are most often distributed evenly throughout the body, but in the diffuse form they appear only on certain parts of the body: neck, abdomen, palms, back, face, legs and thighs. After the acute period has stopped, purple spots often remain on the skin.
A distinctive feature of cutaneous mastocytosis from other types of urticaria is the appearance of small papules on the skin. These are morphological elements of a skin rash in the form of nodules that rise slightly above the level of the skin and are not filled with exudate. After friction, these nodules increase in size (Unna-Tost syndrome).
Depending on the clinical form in which the disease occurs, the following symptoms may be present in the patient’s medical history:
- skin itching of varying intensity;
- the appearance of marks on the skin in the form of an inflamed swelling after interaction with any objects (dermatographism);
- headache;
- decreased performance, rapid fatigue;
- hypotension phenomena (low blood pressure).
In children, such symptoms can go away on their own without any treatment, subject to optimal correction of the diet, lifestyle and regimen. In adults, the pathology is more severe and often develops into a mixed form. With massive infiltration of internal organs by mast cells, multiple organ failure can develop, so treatment of adult patients is most often carried out in a hospital setting.
Note! Symptoms that cutaneous mastocytosis has become a mixed form may include the following: gastralgia (abdominal pain), vomiting, nausea, muscle and joint pain, depression, malignant hypotension and sudden fainting.
You should immediately report these symptoms to your doctor, since with an aggressive course, mastocytosis can lead to serious consequences, for example, the development of acute leukemia.
Treatment of urticaria pigmentosa
For this disease, treatment must be prescribed by a doctor; it is individual and depends on many factors:
- symptoms;
- age of the sick person;
- causes of the disease.
When mastocytosis affects children, but there are no strong symptoms on the skin, then no therapy is prescribed, since everything goes away on its own before adolescence. When cases are more complex, drug treatment is prescribed.
Antihistamines such as:
- Cetirizine;
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Diazolin et al.
Anti-bradykinin drugs such as:
- Anginin;
- Prodectin, etc.
Antiserotonin drugs such as:
- Ketotifen;
- Bicarfen;
- Periactin et al.
Corticosteroid drugs, drugs based on cromoglyceric acid, such as:
- Intal;
- Nalkrom;
- KromHexal et al.
Drugs from the group of cytostatics:
- Prospidin and others.
PUVA therapy may also be prescribed. This method involves exposing the skin to photoactive substances, medications and ultraviolet rays. If the symptoms on the skin are very pronounced, they can be removed through surgery.
The treatment prescribed by the doctor will always depend on the form of the disease. And in each case, the approach will be different. Therefore, at the first signs of this disease, you should immediately consult a doctor. He will conduct the necessary tests and studies, and, having determined the form of mastocytosis, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
You should always follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor; you should not prescribe or use drugs on your own that the specialist did not mention. If there is a definite need to find out about the drug that you want to use, then it is better to first ask your doctor about it, in case it is not suitable for you at all. And you will not only spend extra money, but you can also worsen your situation.
Elena Malysheva. Symptoms and treatment of urticaria
Prevention of complications
It should be noted that the release of mediators from mast cells can occur not only with systemic mastocytosis, but also with any other variant of the course of the disease. Therefore, to avoid the development of systemic complications, here are some useful recommendations:
- A syringe with Epinephrine, which you must carry with you at all times, will help you cope with anaphylactic shock. Especially when planning a trip to nature.
- Eliminate from your diet some foods that aggravate the disease. Be careful with seafood, alcoholic beverages, spicy foods, citrus fruits, etc.
- Not all medications can be used without restrictions. For example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, narcotic analgesics, etc. are prescribed with extreme caution. They can provoke degranulation of mast cells.
- If it is necessary to use X-ray contrast agents for diagnostic purposes, glucocorticosteroids are administered in parallel.
- Buy only high-quality cosmetics and detergents that do not cause skin irritation.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment of urticaria pigmentosa, in addition to medication and physiotherapy, also includes adherence to a special diet. With such a diet, all salty, fatty, smoked and spicy foods are prohibited.
It is advisable to steam foods or eat them boiled. It is imperative to exclude soda and drinks containing alcohol from drinks. Fans of spicy seasonings and sauces will also have to give them up.
You can also resort to old traditional methods of treatment, but you must first consult with your doctor. For example:
- Nettle infusion. Add a spoonful of nettle leaves to a glass of boiling water and let it brew for no more than thirty minutes. And then drink 4 or 5 times a day, half a glass of warm infusion.
- Celery juice. This method is not suitable for everyone, since celery has a rather specific taste, but if you don’t mind trying it, you should drink the juice three times a day, half a glass before meals.
- Beetroot infusion. Fresh beets, peel, cut into small pieces and add three liters of water. Keep this in a dark place for no more than six days. Next you need to drink one tbsp. l. three times a day. You can also apply compresses to the affected areas of the body.
- Potato compress. This type of home treatment is quite common and helps with many skin inflammations, soothes it, and relieves itching. You need to take fresh potatoes, grate them and, wrap them in gauze, apply the resulting compress to the inflamed and affected areas of the skin for no more than forty minutes.
- Baths with herbal infusions. You can also take medicated baths to soothe your skin. To do this, you need to mix celandine, chamomile, valerian, sage and string in equal parts, pour everything with plain water and boil for about 10 minutes. Next, it is infused for about half an hour, and then the resulting infusion must be added to a bath filled with warm water. It is not recommended to take such a bath for more than 10 minutes.
Hives. Types and signs of urticaria, causes and treatment
Causes
Like any phenomenon, for the development of urticaria pigmentosa there must be a reason. Nothing just happens, and most people know this. Sometimes it is useful to get to the cause that caused the development of the disease. By eliminating it, you can be free from the disease itself.
Chronic stress
This is the first thing a modern person should pay attention to. Most people live in a hurry, barely having time to solve everyday tasks and affairs. Lack of sleep, nervous shock, and unexpected expenses lead to chronic stress. This condition turns out to be extremely difficult to treat, especially when time has already been lost. Stress burns a person from the inside, taking away a large amount of energy necessary for everyday life.
Such a condition is dangerous not in itself, but because of its consequences. A person who spends a lot of time in a state of exhausting fatigue is not able to adequately make decisions or set achievable goals. He constantly worries, replays in his head negative events that could happen to him. And this is instead of focusing properly on the main goal.
Chronic stress may well cause the development of a disease such as urticaria pigmentosa. Most diseases appear just when a person is nervous a lot and spends his mental strength on something important to himself.
Climate change
Moving to another city can have a detrimental effect on your health. It is known that people get used to a certain time zone and adjust their individual schedule to it.
Climate change often causes a person to experience some kind of physical ailment: gastrointestinal disorders, palpitations, headaches, surges in blood pressure, and various skin rashes. Urticaria in this case is no exception.
Before you begin treatment of the disease itself, you should understand what factor could cause such a reaction. A change in climate or a sudden plunge into a different time zone may well provoke the development of the disease.
Taking medications
Some medications can cause significant harm to health. In most cases, there is an individual intolerance caused by an allergic reaction to certain components of the drug. In addition, not all medications can be taken without a doctor's prescription. Uncontrolled absorption of pills, of course, will also not lead to anything good.
Sometimes a slight malaise appears, in the worst case – poisoning. Urticaria pigmentosa is almost the most harmless scenario. That is why any medications can be taken orally only after consulting a doctor.
Food products
Some foods can cause a persistent allergic reaction in a person. Sometimes it is impossible to predict what consequences may occur after a delicious dinner in a pleasant, friendly company. Such products include, first of all, citrus fruits, chocolate, berries, alcohol, etc.
Urticaria pigmentosa can appear as a result of inadvertently ingesting large quantities of exotic fruits that have not been tried before. That is why you should be extremely careful when choosing a menu, try unfamiliar dishes, and try not to experiment too much with unfamiliar cuisine.
Psychological reasons
Almost always, so-called psychological reasons are to blame for the appearance of urticaria pigmentosa. The fact is that every day a person is faced with a large number of experiences that destroy his nervous system and have a negative impact on the condition of his internal organs.
It has been observed that people who have any skin problems suffer from a lack of self-confidence. They constantly find new reasons for dissatisfaction with themselves: appearance, relationships with relatives, personal development, financial situation, etc. A negative attitude towards one’s own person leads to the fact that soon it becomes really awkward to communicate with others.
People with skin problems, in most cases, are ashamed of it and perceive the disease as a significant disadvantage. Psychological reasons most strongly undermine a person from the inside. No allergic reaction to a specific product can cause as much harm as everyday experiences and worries do to a person.
Disease prevention
People who have been diagnosed with any form of mastocytosis should take preventative measures such as:
- Increase your immunity by taking vitamins or undergoing special therapy;
- Follow the diet prescribed by your doctor;
- Eliminate or replace certain medications that must be notified to your physician.
- Be sure to treat inflamed areas of skin with caution, do not injure them or apply mechanical stress.
Sometimes, in adults, urticaria pigmentosa sometimes disappears and then appears again; they need to very carefully monitor the symptoms of the disease, and at the first signs of its relapse, go to the doctor.
Treatment
If adults or children develop symptoms of mastocytosis, consult a dermatologist immediately. The doctor conducts a series of tests to determine what kind of disease the patient has. After all, the symptoms of many skin diseases are similar to each other.
A blood and urine test for histamine and a skin biopsy are performed. If a diagnosis of urticaria pigmentosa is made, comprehensive treatment is started. The doctor prescribes a number of medications, taking into account the individual and age characteristics of the patients.
If the rash in children is mild, treatment is not carried out. As a rule, such urticaria disappears on its own during puberty. In more complex cases, antihistamines and antiserotonin drugs, as well as corticosteroids, are prescribed. If the cosmetic defect is very noticeable in adults or children, surgical treatment is performed based on the removal of mast cells.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for such a disease will directly depend on its form. If a small child gets sick, then in almost all cases, the disease will go away on its own before puberty. In rare cases, it develops into an adult form.
If a teenager gets urticaria pigmentosa, the chance of completely recovering from it is about 50%. When urticaria pigmentosa affects an adult, it usually does not end with inflammation of the skin; internal organs are also affected. If the disease develops into a systemic form of mastocytosis, it can be fatal.
If urticaria pigmentosa affects only the skin of a person, then a dermatologist will treat him. And if the disease affects internal organs, then specialists in other fields will monitor the patient and treat him, for example, an oncologist or hematologist.
As you can understand from this article, this disease has various forms and can flow from one to another. In childhood, it is much easier to tolerate, therefore, if the disease has overtaken an adult, you need to carefully monitor the course of the disease and do not forget to visit your doctor.
Next Post
Previous Post
Effect on internal organs
As mentioned above, mastocytosis affects not only the skin, but also internal organs. We will now understand exactly how.
The liver enlarges, fibrous nodes appear and it thickens, the tissue changes to connective tissue.
Bones - areas of osteoporosis appear - the bones soften, and osteosclerosis also develops, naturally they begin to ache.
Lymph nodes become enlarged and painful.
Gastrointestinal system - peptic ulcers and diarrhea develop.
The spleen is greatly enlarged.
Causes of the disease
Today, scientists in the world of medicine have not yet fully studied this disease, however, there are several hypotheses that explain the cause of the disease, but all this data has not been officially confirmed.
Here are the most common hypotheses:
- genetic predisposition of the child;
- severe allergic manifestation;
- toxic effect on the child's body.
There are some known factors that influence the occurrence of urticaria:
- prolonged exposure of the child to the sun;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- consumption of harmful foods;
- inappropriate use of medications.
If an infant has symptoms similar in nature to manifestations of mastocytosis, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor. It is not recommended to delay this matter.
The causes of urticaria pigmentosa (mastocytosis) are still considered unclear. There is a version about hereditary prerequisites. This is supported by the fact that mastocytosis is often detected in relatives. But on the other hand, in approximately 50 percent of cases, no genetic predisposition is detected.
Modern science believes that urticaria pigmentosa can be of an immune or non-immune nature. A disease belonging to the second type often develops under the influence of the following factors:
- excess ultraviolet radiation;
- friction;
- overheating or hypothermia;
- nervous tension, stress;
- climate change;
- taking certain medications;
- unhealthy food;
- toxins;
- chronic urticaria.
forms of mastocytosis
What causes the disease
The exact causes of mastocytosis in children have not yet been clarified, but it is believed that the disease is caused by a gene mutation that leads to an increase in the number of mast cells. What, in turn, this mutation comes from is also completely unknown.
There are a number of factors that lead to urticaria pigmentosa, according to experts. At the same time, predisposing factors are divided for infants under 1 year and older children. In the first case, note:
- hereditary predisposition;
- overheating and hypothermia, which are possible if the correct temperature in the children's room is not maintained;
- errors in the introduction of complementary foods or the use of food products that are inappropriate for children by age;
- uncomfortable clothes that rub delicate skin;
- various viral and bacterial infections.
In older children, theoretically, the following can lead to the disease:
- prolonged overheating due to exposure to the scorching rays of the sun;
- stress and overwork;
- taking medications;
- weakening of the body's protective functions;
- eating food that can cause allergies;
- Alcohol and drug abuse affects adolescent children.