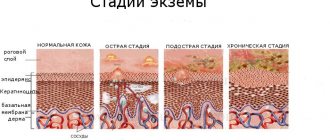
Features of the disease
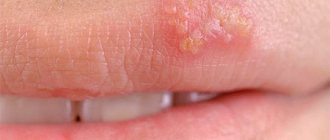
Herpes of internal organs is diagnosed much less frequently in comparison with a blistering rash on the genitals and lips. The causative agent of the disease is cytomegalovirus or herpes virus type 5.
After the pathogen spreads through the body through the bloodstream, the symptoms of the disease may manifest differently in each person. Internal herpetic infection is characterized by damage to several organs at once, but most often one of three forms of this disease is identified:
- Viral herpetic hepatitis.
- Herpetic pneumonia.
- Infectious herpetic esophagitis.
- Herpes of the anus.
If the symptoms of herpes type 1-2 are simply identified by the characteristic fine-bubble rashes on the mucous membrane of the larynx, urethra, bladder and vaginal walls, then the infection of the 5th strain is much more difficult to diagnose. The disease is often accompanied by serious complications that can lead to death.
Important: once it enters the body, cytomegalovirus remains there forever and manifests itself when the human immune system is weakened.
If a patient has herpes on internal organs, the symptoms of the disease can be very varied depending on which organ is affected. Scientists still do not know exactly how infection occurs. Many experts are convinced that infection occurs through biological fluids (saliva, blood, semen, urine). That is why it is generally accepted that this occurs through very close contact with a carrier of the virus.
In this case, there are the following routes of transmission from a sick person to a healthy one:
- airborne (this is not only sneezing and coughing, but also kissing, in which infected saliva reaches a healthy person);
- sexual mode of transmission;
- the infection can be transmitted to the baby during feeding with mother's milk;
- intrauterine (via the placenta);
- generic;
- blood transfusion.
Routes of infection
You can become infected with the herpes simplex virus through contact transmission. In this case, antibodies enter the body of a healthy person through interaction with a source of infection, which can be infected people or objects. The contact-household method involves infection during normal everyday activities: the direct route is handshakes, kisses, hugs, and the indirect route is through personal hygiene items, cutlery and other environmental objects.

Herpetic pneumonia: symptoms
If the patient has internal herpes, symptoms of damage to the respiratory system manifest themselves in a hacking cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain. The patient's temperature rises to significant levels and he experiences general malaise. Since herpes is often combined with other pathological processes in the body (for example, protozoal, fungal or bacterial infection of the respiratory system), the clinical picture of the disease is unclear.
At the moment when herpetic viral tracheobronchitis spreads in the lungs, the disease manifests itself in the form of necrotizing bronchopneumonia. Also, the cause of bilateral herpetic lesions of the lungs can be herpes simplex, which is localized on the face near the mouth at the time it enters the bloodstream.
Caution: The mortality rate from herpesvirus in patients with weakened immune systems who are not treated with specific antiviral drugs is approximately 80%.
It has been proven that distress syndrome of the lungs and respiratory organs in an adult is quite often accompanied by diseases that are associated with manifestations of herpes simplex, for example, a rash on the lip. However, the influence of this virus on the formation of such a pathological condition has not yet been studied.
Preparing for HSV analysis and deciphering it
Prevention
To prevent the manifestation of the disease, as well as possible repeated relapses, it is important to follow a number of simple recommendations:
- Create a balanced, rational menu. It is necessary to exclude heavy foods and harmful preservatives, fast food and genetically modified products. You need to eat regularly, in small portions up to six times a day. Don't overeat at night.
- Go out into fresh air more often. Sports, exercise and walking help strengthen the immune system.
- Do not neglect taking vitamin complexes.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene, especially wash the navel and abdomen area.
- In case of infectious diseases, adhere to bed rest and drink more fluids.
It is important not to forget that the therapeutic measures taken do not contribute to the complete elimination of the viral infection from the body, which significantly increases the risk of relapses. To prevent this, you must follow all recommendations for preventing the onset of the disease.
Herpetic hepatitis
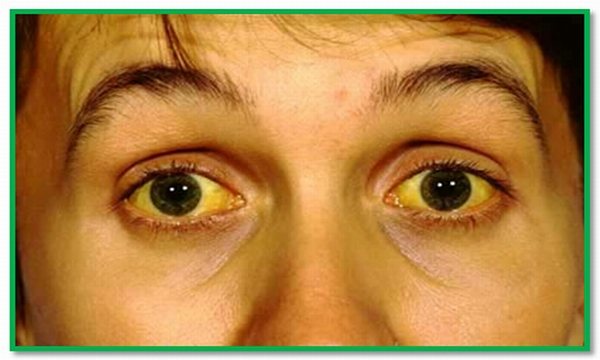
If a patient has herpes of internal organs, the symptoms of viral liver damage are very similar to other forms of hepatitis. The main symptom of this disease is jaundice. The patient's skin and sclera of the eyes turn yellow due to the increased level of bilirubin in the body.
The first signs of herpetic liver damage are as follows:
- temperature increase;
- there are headaches;
- general weakness;
- sometimes thrombohemorrhagic syndrome is formed;
- the amount of bile pigment increases rapidly.
The patient has severe pain on the right side, localized under the ribs, which can radiate to the shoulder and scapula. This is due to an increase in the size of the organ and a strong stretching of its membrane.
Causes
Why, other things being equal, do some people often suffer from herpes, while others never develop the disease? The answer lies in the activity of the immune system. There is a category of people with genetically strong antiherpetic immunity. But the main reason is the weakening of the body’s activity, caused by the following factors:
- Transfer of acute viral diseases and exacerbation of chronic ones;
- Unbalanced diet and vitamin deficiencies;
- Surgical interventions;
- Oncological processes;
- Impaired liver function; diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis;
- Use of drugs that suppress the immune system;
- Presence of HIV infection;
- Prolonged physical and emotional overload.
Since shingles is a purely dermatological problem, it is not a consequence of pathologies of the abdominal organs, except for the cases listed above.
In children, the list of factors is significantly reduced, which reduces the likelihood of the disease occurring.
Viral esophagitis
The symptoms and treatment of herpes infection in the esophagus are very similar to the usual inflammatory process in this organ. This affects the mucous membrane inside the digestive tract. This disease occurs due to the direct penetration of the cytomegalovirus virus into the esophagus through the pharynx. Sometimes this disease occurs as a result of reactivation of the herpes virus in the vagus nerve.
In this case, herpes of internal organs, namely esophagitis, is manifested by the following symptoms:
- it is painful for a person to swallow solid food and even saliva;
- the patient feels pain behind the sternum;
- rapid weight loss.
When examined using a gastroscope, multiple ulcers are revealed on the esophageal mucosa. The bottom of these ulcers is reddish with a fibrous film on the upper part. If treatment is not carried out in time, these films will contribute to loosening of the mucous layer.
In most cases, herpes inside the body affects the upper part of the esophagus. If the disease is very advanced, then the intestinal walls are also involved in the process. In the latter case, the entire surface of the esophageal mucosa will be affected by the herpetic infection.
Differential diagnosis of viral esophagitis will be difficult if carried out using x-ray or endoscopic examination, since the disease is very similar to thermal damage to the esophagus, its trauma, chemical burn or thrush. For diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a virological and cytological study of the biomaterial taken during esophagoscopy. It is with their help that the causative agent of the disease can be identified, which will make it possible to decide how to treat the patient.
Important! Internal herpes practically does not occur in people with good immunity.
Signs of an exacerbation of the virus
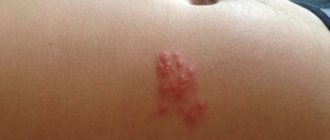
Herpes on the stomach makes itself felt with vivid symptoms:
- Numerous rashes appear on the body. They are like bubbles containing a translucent liquid. The skin around the ribs becomes reddish or pink. Sometimes the blistering elements merge together, and one red itchy area is formed, which is painful even to touch. After 3-5 days, the contents of the formations come out, and they turn into small ulcers.
- The skin on the body becomes hypersensitive, which is due to the location of the virus in the nerve ganglia. The patient feels pain in the ribs. The person becomes irritable and emotional.
- Itching occurs, which intensifies with overheating or hypothermia, stress, and nervous conditions.
- The local temperature in the affected areas rises and they become hot to the touch.
- General weakness appears, body temperature increases to 37-38 degrees. Possible migraines, loss of appetite, dizziness.
It is not recommended to touch herpes zoster on the body or, worse, try to pierce the blisters: in the “whole” state, the rashes are less painful.
To speed up the healing process, you can use acyclovir and other pharmaceuticals. After 5-10 days, the rash will begin to dry out and a dense, non-flaky crust will form.
You should not try to peel it off: after about 14 days it will fall off on its own, and the skin will return to its former color and uniformity.
If you follow the doctor's recommendations, the illness you have suffered will not leave scars or complications.
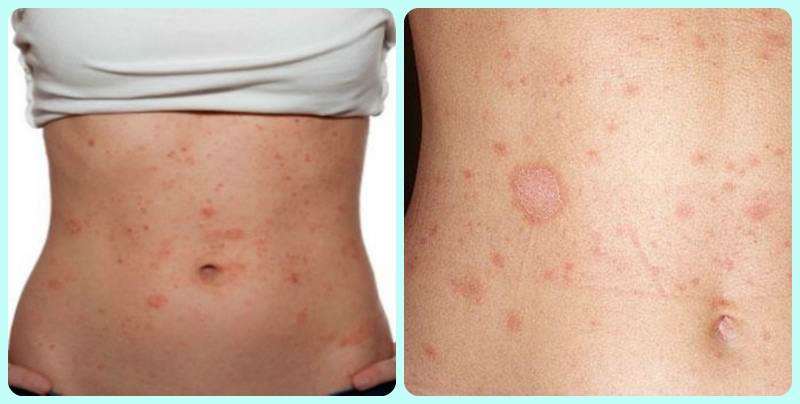
Herpes on the stomach photo
Anal herpes

Symptoms of herpes zoster during pregnancy and its treatment
This disease develops with the penetration of herpes type 1-2, which can affect peripheral nerve tissue. The manifestations of this disease can be different. In most patients, the main manifestation of the disease is severe itching in the anal area. In some patients, the disease can be expressed in severe pain in this area and the formation of a small blistering rash.
This form of herpes can also manifest itself with other signs:
- headache;
- sleep disturbance and insomnia;
- general malaise;
- increased irritability;
- heat;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
After spontaneous opening of the blisters, they become covered with crusts and heal. When a secondary infection occurs, scars remain forever in this place. The disease can easily develop into herpetic intestinal lesions. In this case, ulcers and erosions occur on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
If rectal herpes is not diagnosed and treated in time, the disease will progress and the symptoms will become more pronounced. In the future, this can lead to proctitis, when pus accumulates in the walls of the rectum. In this case, the patient suffers from severe constipation, pain during bowel movements, and inclusions of blood and pus in the stool.
Attention: other types of internal herpes are less common. These include herpetic glomerulonephritis, monoarthritis, adrenal necrosis and thrombocytopenic purpura.
Differential diagnosis
In order to accurately determine the type of disease, its nature and treatment tactics, a differential diagnostic method is used, in which possible diseases that are inappropriate for any symptoms are excluded. Thus, the diagnosis is reduced to the only possible disease.
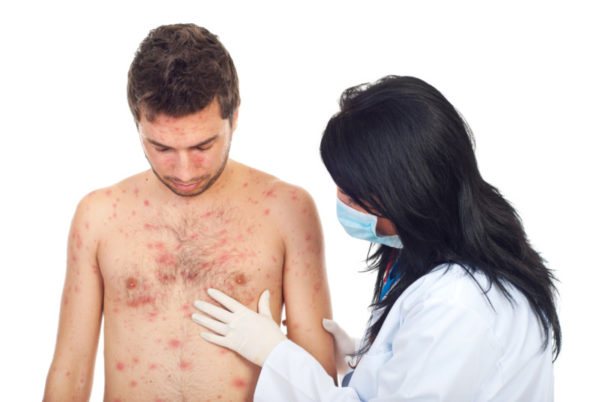
Herpes zoster is differentiated from the following infectious diseases:
- Erosive chancre is a manifestation of primary syphilis. With this disease, erosions are bright red in size and large in size. The outlines of the rash are round or oval. Enlarged lymph nodes are painless. Accumulations of cellular elements mixed with blood and lymph (infiltrates) are observed in the tissues.
- Contact dermatitis, which occurs in case of an allergic reaction. Characterized by a linear distribution of rashes and itching.
- Herpangina, characterized by erosions mainly on the palate, uvula and palatine arches.
- Bullous impetigo. Blisters or superficial erosions of a round shape are observed, which independently peel off from the epidermis. There are no deep localized blisters characteristic of herpes.
- Cystic dactylitis. The rashes are most similar to herpetic ones, but if with herpes they are multiple, then with dactylitis a single blister is observed.
- Streptococcal impetigo. It is characterized by small flat blisters with a superficial pustule (phlytena) filled with turbid liquid. These skin formations are surrounded by a pink inflammatory rim and occur most often on the face and hands.
- A thermal burn, similar in appearance to herpes, but caused by mechanical trauma.
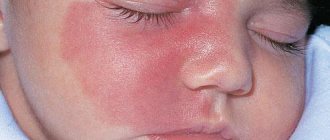
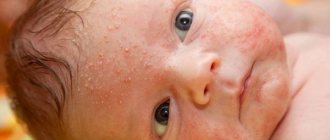
Herpes of newborns
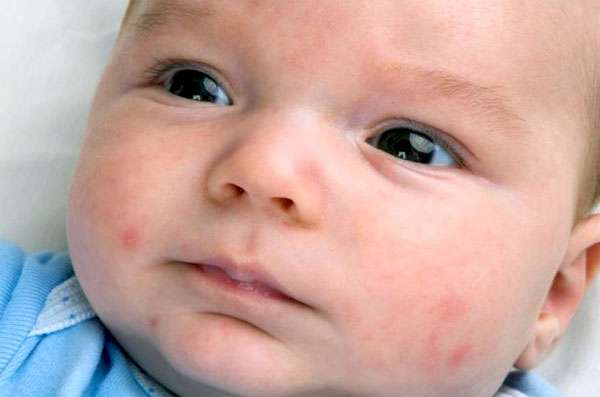
Cytomegalovirus poses a huge danger to infants. In them, the virus can affect both internal organs and the central nervous system. The likelihood of this is very high if the baby is not treated in a timely manner. Activation of cytomegalovirus in newborns leads to death in 65% of cases. Only one in ten children with central nervous system damage can develop and grow according to age norms.
The greatest risk of intrauterine infection of the child is present with primary infection of the mother. If a pregnant woman has reactivated the virus, then the risk of transmitting it to the baby is low. What is very important here is at what stage of pregnancy this happened. The fetus is considered most vulnerable in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Third type
The third type of virus can be defined as shingles. It causes the development of chickenpox in children aged 10 to 14 years. The symptoms in this case are almost always the same: first a spot becomes noticeable, gradually turning into a papule. As a result, a crust forms on the body. If the virus appears at age 35 or older, it affects the spinal and cranial nerves. Therefore, treatment of herpes in adults in this condition must be carried out competently and without delay, otherwise serious complications are possible.
Treatment
Treatment of internal herpes is often carried out with the use of Valacyclovir and Acyclovir. In this case, the chances of remission of the disease increase significantly. Viferon in suppositories is usually used as an immunostimulant. This drug can be used during pregnancy and even in newborns. If bacterial complications occur, a course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Also recommended:
- If you have esophageal herpes, you must adhere to the principles of a healthy diet;
- During treatment you should not smoke or drink alcohol;
- When treating pneumonia, medications are required to thin and facilitate the removal of sputum, as well as antiviral drugs;
- When rashes appear on the surface of the skin, be sure to use topical products, for example, special antiherpetic ointments;
- To protect yourself from a recurrence of the disease in the future, it is necessary to strengthen your immune system and take multivitamin complexes;
- It is beneficial to consume freshly squeezed juices daily.
Those who are at risk for internal herpes should be especially attentive to their health. These include pregnant women, people with cancer, people infected with HIV, all those who for one reason or another have a weakened immune system, as well as patients with diabetes.
It is better to cure internal herpes in a hospital setting under the supervision of doctors. The main components of therapy are immunomodulators and antiviral drugs. At high temperatures, use an antipyretic. Anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers are used as symptomatic treatment.
The causative agent of infection
The causative agent is a virus called Varicella-Zoster. This microorganism belongs to the group of herpes viruses, and along with shingles, it causes chickenpox. The herpes virus is unstable in the external environment and quickly dies when exposed to disinfectants or boiling. It is resistant to low temperatures.
Transmission of the causative agent of chickenpox and shingles from person to person is carried out by contact and airborne droplets. Infection most often occurs in spring and autumn.