Specialist: Dermatologist
Symptoms of urticaria in children Locations Causes of occurrence Mechanism of occurrence Forms of the disease How to treat urticaria in a child? Possible complications and their consequences Prevention of urticaria Urticaria is an acute or chronic disease accompanied by skin rashes with peripheral hyperemia. The name of the disease is due to the fact that outwardly it looks like a nettle burn - the skin turns pink and swells, while small blisters can merge into large local spots (angioedema) of irregular shape. Papules cause itching and discomfort; when scratched, the wound surface can become infected, and then dermatitis and other complications join the underlying disease. The disease is very common; every third person on the planet has suffered from urticaria in one form or another.
How to tell if this rash is hives
Hives are itchy, flat, raised, pale pink blisters, similar to nettle stings. They can be large or small, red or the same color as your skin.
Blisters may come and go quickly or remain on the skin for a long time.
Manifestations of the disease can be observed throughout the body or only in one or two localized areas.
Symptoms and causes
The itching that accompanies hives can be intense or mild, long-lasting or short-term. Often the appearance of blisters caused by the disease is preceded by itchy skin. In other cases, blisters and itching appear at the same time.
Hives usually appear as clusters of blisters that can occur anywhere on the body. Its manifestations can be tiny, pinpoint or much larger. Their size and shape may also vary.
In some cases, individual blisters merge to form very large itchy areas. The skin surrounding the area where the rash appears may appear red, swollen, or irritated.
The blister usually disappears within 24 hours, although it may appear elsewhere. The rash may remain on the body or recur for weeks, months, or even years.
Causes of urticaria
Acute urticaria that lasts less than 6 weeks may be caused by the body releasing too much histamine or overproducing it. Also, acute urticaria is a common manifestation of a true allergic reaction.
Allergies are believed to be the main cause of blisters. It can occur if you eat or drink something. Or have had contact with an environmental factor to which you are allergic.
Other factors that cause hives may include:
- medicines;
- ambient temperature;
- sunlight;
- anxiety and nervousness;
- certain bacterial or viral infections, such as streptococcal infections and urinary tract infections;
- autoimmune diseases.
In some cases, the causes of the rash may remain unidentified.
Treatment of the disease
Depending on the severity of the disease and the causes of its occurrence, treatment for urticaria may vary. If the appearance of a rash is an autoimmune disease (caused by improper functioning of the immune system), then the patient is prescribed antistaminic drugs (Zodak, Telfast, Cetrinax). In addition, you need to strengthen the immune system (fish oil, echinacea tincture, “Immunal”) so that it can function normally.
To prevent the acute form of urticaria from reappearing, the baby will be prescribed the following procedures:
- Identification and destruction of factors that provoke allergies.
- Eliminating allergens from the diet. The child must follow a hypoallergenic diet . Its essence is to exclude the most allergenic foods (lemon, honey, pineapple and others). The patient is recommended to eat more: apples, pears, boiled meat, cottage cheese, vegetable oil and other products.
- The use of antihistamines (Telfast, Zyrtec, Clarotadine). Reduces the risk of Quincke's edema. The course of application is up to 10 days.
- The use of corticosteroids (“ Florinef”, “Lemod”, “Urbazon”, “Medrol”, “Celeston”, “Cortinef” ) . If antihistamines do not have the desired effect, then these drugs are prescribed. In severe cases, medications are administered intramuscularly and intravenously. The course of use is up to 7 days, prescribed individually by a doctor. There are contraindications and age restrictions.
- The use of enterosorbents (remove harmful substances from the body) . These drugs remove many allergens from the body: activated carbon, Enterosgel, Laktofiltrum.
- Local treatment. Ointments “Fenistil”, “Advantan”, etc. are applied to the places where blisters appear.
- Removing harmful irritants from the body. For this, diuretic decoctions and medications are used (decoction of St. John's wort or wild pear, Furosemide).
The above measures will reduce the risk of recurrence of urticaria. But they do not always allow you to completely get rid of the disease. It would be useful to approach the issue of treatment comprehensively, using additional folk remedies.
Symptoms and causes of rash
The rash of urticaria may be similar to skin manifestations of other infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Skin rashes can be completely different:
- scaly, red, moist in appearance;
- in the form of blisters, ulcers or scars;
- painful, itchy and/or makes the skin hot to the touch;
- sometimes - edematous.
Depending on the underlying cause, the rash may be localized to one area or spread throughout the body.
Rashes as a symptom
A fairly large number of skin diseases are accompanied by a rash:
- contact dermatitis;
- allergic eczema or atopic dermatitis;
- psoriasis;
- seborrheic dermatitis;
- erythema infectiosum (fifth disease);
- impetigo;
- bites from fleas, bed bugs and other insects;
- viral and bacterial skin infections;
- other.
Diagnosis of urticaria
In most cases, establishing a diagnosis of acute urticaria does not pose any particular problems. However, the situation is completely different with the chronic form of the disease. It is not uncommon when, after an initial examination, it is not possible to establish the cause of the disease; in such cases they speak of “idiopathic urticaria”). In such a situation, there is no need to despair; the main thing is to strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations and get tested regularly.
In most situations, in the chronic form of urticaria, it is necessary to take a clinical and urine test, as well as tests for blood biochemistry, total protein, albumin, ALT, AST, sodium, potassium, calcium, uric acid, glucose, cholesterol and triglycerides) and C-reactive protein . It is necessary to do a chest x-ray, ultrasound of the abdominal organs
. In the future, the mandatory stages of additional examination should be:
- Rule out autoimmune diseases.
- Exclusion of intestinal parasitic infections.
- Exclusion of blood diseases (paraproteinemic hemoblastoses), as a rule, requires special blood and urine tests.
Symptoms of urticaria
The disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- Convex pink and red rashes appear that turn pale when the skin is pressed or stretched. When the blisters merge, the edges of the spots become more intensely colored.
- The appearance of blisters, their disappearance or merging into vast shapeless foci occurs chaotically, and their migration over the surface of the body is unpredictable.
- The rash is accompanied by severe itching.
- The temperature may rise, either slightly or to high values.
- Often - weakness, malaise, joint pain and headache.
- In the complicated form, difficulty breathing or swallowing, nausea and vomiting, and bowel movements.
- An even more severe manifestation is angioedema on the lips, oral mucosa, eyelids, cheeks or genitals.
In most cases, urticaria manifests itself in children only as an itchy rash that does not last long, from several hours to several days. Often other pathologies give similar symptoms; in this case, urticaria is not considered as an independent disease. Information for parents! If hives are accompanied by even slight swelling, especially in the face and neck, you should immediately call emergency services!
Cold urticaria
Cold urticaria appears when the skin is exposed to low temperatures. Its occurrence is explained by the production under the influence of cold of special proteins - cryoglobulins, which have the properties of antibodies. In addition to the typical skin pinkish-red itchy blisters, significant swelling of soft tissues and mucous membranes is observed. The rash lasts from 2 hours to a day, then disappears, leaving no pigmentation.
Solar urticaria
Solar urticaria is one of the types of photodermatoses. Appears when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation while in the sun or in a solarium. It most affects women with liver pathology and acute photosensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. There is a profuse rash of oddly shaped pinkish blisters on open areas of the body, which is combined with painful itching. Spending many hours in the scorching sun is fraught with the appearance of symptoms of sunstroke: headache, drop in blood pressure, fainting.
Causes of urticaria
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of hives. In addition, it can be caused by different factors in the same person at different ages. Among the most common pathogens in children, the following groups can be distinguished:
- Food products (citrus fruits, nuts, eggs, seafood, strawberries, tomatoes, etc.).
- Food additives, primarily sulfides, salicylates and various chemical dyes.
- Household allergens (dust, fluff, cigarette smoke, pollen, cosmetics and detergents, synthetic clothing, fumes from furniture varnishes, paints, etc.).
- Medicines and contrast agents for radiography.
- Blood (donated) and drugs created on its basis.
- Vaccinations.
- Insect bites, helminthic infestations.
- Physical, including thermal phenomena (overheating and sweating, cold, physical activity, direct sunlight).
- Psychogenic factors.
- Various infections.
All of these factors can become both the cause of primary urticaria and the impetus for its exacerbation during the chronic course of the disease. In children under two years of age, the vast majority of cases of urticaria are caused by food allergens.
Liver and urticaria
Manifestation of demographic urticaria
This form of the disease is one of the varieties of photodermatosis, whose development occurs in patients against the background of one or another liver disease as a result of increased reactive sensitivity to exposure to sunlight, as well as in individuals for whom porphyrin metabolism disorders are relevant.
Mostly this form of the disease is diagnosed in women.
As for its characteristic manifestations, urticarial rashes in this case are concentrated in the area of open areas of the skin (upper limbs, face, etc.). Also, this form of urticaria is characterized by seasonal manifestations; accordingly, it develops during the period of increased solar activity in spring and summer.
When patients are exposed to direct sunlight for a long period of time, a specific reaction to this effect may develop, which, in particular, involves disturbances in cardiac activity and breathing. The extreme manifestation in this case may be a state of shock.
Cold urticaria develops a few minutes after contact with such influencing factors as cold water or excessively cold air, icy wind.
Manifestations of symptoms are reduced to the appearance of itching, burning, erythema (severe redness of the skin), as well as a blister and/or swelling.
The predominant concentration of these manifestations is similar to the previous case with solar urticaria. Often, maximum manifestations are observed during the period of warming up of areas that have undergone such hypothermia; their disappearance occurs after about half an hour to an hour.
In some cases, cold urticaria is accompanied by urticarial rashes of a permanent nature. Such rashes, as a rule, form a few minutes after the corresponding exposure to the irritant; their persistence on the skin lasts for a week, although a longer period is not excluded.
A variant of cold urticaria cannot be excluded, in which urticarial rashes are concentrated in slightly different areas, and not in the immediate area of exposure to the irritant.
So, they can appear around this area, which also determines a slightly different form of the disease, such as reflex cold urticaria. It is noteworthy that some patients experience the development of cold allergies even after eating cold foods or foods, which is accordingly accompanied by swelling of the tongue, lips and pharynx.
In addition to rashes, patients also experience disorders related to the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, and gastrointestinal symptoms (in the form of diarrhea, abdominal pain) often appear.
The peculiarity of cold urticaria is that the more pronounced its symptoms are, the more severe the disease is.
Of course, the severity of symptoms is directly related to how large the cooling area turned out to be, as well as how strong the impact of the irritating factor itself (that is, cooling) was.
For example, patients who are extremely sensitive to the effects of cold, when cooling a large area of the body surface, may experience an anaphylactoid reaction, manifested in the form of a complex of symptoms: nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, dizziness, low blood pressure, shortness of breath, etc.
In practice, there have been cases in which exposure to cold was fatal for the patient, that is, it led to death.
As a rule, it is not difficult for parents to notice this disease, as well as to carry out an initial diagnosis based on characteristic manifestations. It should be noted that urticaria, the symptoms of which in adults determine approximately the same course of the disease in children, also begins suddenly, without previous symptoms.
Acute forms of the disease predominate; it is extremely rare in children under 6 months of age.
It manifests itself in the appearance of rashes, concentrated on the body and limbs, accompanied by unbearable itching. The location of the blisters can be concentrated not only within the skin, but also on the mucous membranes (gastrointestinal tract, lips, eyes). Itching leads to scratching, and swelling also appears. Temperatures can reach 39 degrees.
The duration of the disease can be on the order of several minutes, but a duration of the order of several hours and days is also possible, which is determined based on the degree of severity relevant to the response.
As in the general consideration of the disease, urticaria in children can occur in an acute form or in a chronic form.
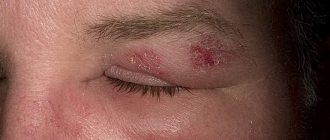
The most dangerous option is Quincke's edema, characterized by the appearance of a large area of rash along with looseness and swelling of the tissue in the surface area of the lips, eyelids, cheeks, tongue, larynx, and genitals.
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is a significant problem, leading to serious difficulty breathing, resulting in severe coughing, the child becomes nervously excited, and, ultimately, begins to choke. Such manifestations require immediate calling an ambulance.
In the case of swelling of the gastrointestinal tract, children develop diarrhea (quickly passing), nausea and vomiting also appear, nervous system disorders, dizziness, headache, some inhibition of reactions, and lethargy are noted.
Acute urticaria in children determines an equally significant risk of transition to a chronic form, therefore it is extremely important to adequately approach the treatment of this disease at this particular stage.
Treatment for urticaria is determined based on the overall severity of its manifestations.
An important role is given to the identification and subsequent elimination of all those pathogenetic factors that provoke the development of this disease. A certain role is assigned in treatment to such components as regimen, diet, state of the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system.
It is necessary to identify and subsequently cure all those foci that are relevant for chronic infections; in addition, it is necessary to exclude the influencing irritants (allergens). Consultations with a neurologist and an ENT specialist are important, as well as examinations related to the identification of helminths (with subsequent disposal of them).
The diet largely consists of including products of dairy and plant origin in the diet.
As for specific drugs, these are antihistamines, magnesium sulfate, sodium hyposulfite, calcium-containing desensitizing drugs, sedatives.
Acute urticaria requires the use of laxatives and diuretics, as well as the use of cleansing enemas; the establishment of metabolic processes is ensured by taking B vitamins, iron supplements, etc. Severe disease requires the administration of glucocorticoids and histaglobin. A number of external therapy measures (baths, ointments, etc.) are often used, but they do not determine a significant result.
If you suspect urticaria, you must contact an allergist-immunologist, infectious disease specialist and dermatologist; consultations with an ENT specialist and a neurologist are required during treatment.
If you think that you have Urticaria and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then an allergist-immunologist (or infectious disease specialist, dermatologist) .
We also suggest using our online disease diagnostic service, which selects probable diseases based on the entered symptoms.
Source: https://oballergii.info/lechenie/pechen-i-krapivnitsa.html
Why does urticaria develop?
The main risk factor for the development of urticaria is the accumulation of substances that are the immune system's response to contact with an irritant. They provoke skin reactions and inflammatory processes. This may develop as a result of contact with the following irritants:
- insect bites;
- some food products;
- medicines;
- cold, UV rays;
- parasitosis, etc.
Altered reactivity of the body can manifest itself not only upon first contact with an irritant, but also in cases where a person has already encountered an allergen before.
Appearance and symptoms
The symptoms of the disease will depend entirely on the type of disease and the degree of damage to the body. Common symptoms are redness of the skin, blistering and severe itching at the site of the lesion. A feature of the disease is the complete reversibility of symptoms. That is, after the provoking factor has been eliminated, all symptoms of the disease completely disappear.
In the acute form of the disease, rashes appear profusely and completely suddenly. All blisters are round, dense and pink in color. Often the bubbles merge with each other and flow into one dense large cake. But in addition to the rash, the patient often experiences a general deterioration in health, a rise in temperature, and severe chills. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system and gastrointestinal tract, and insomnia.
Quincke's edema is often associated with the symptoms of urticaria. The patient has swelling of the mucous membranes and subcutaneous fat on the face. The latter condition is extremely dangerous, because suffocation can begin, which leads to death.
The disease progresses to the chronic stage when symptoms accompany the disease for three months. But the symptoms become less pronounced, the rash becomes slightly pinkish, and swelling may be completely absent. In this case, exacerbations will often be replaced by periods of calm, when the symptoms will completely disappear. Exacerbations can be accompanied by severe headaches, neurotic disorders, and fever.
If treatment of the disease is not started in time, it develops into a chronic papular form, which mainly affects the limbs and is much more difficult to treat. At the same time, the disease remains completely non-contagious to others, which does not require isolation of the patient.
The mechanism of occurrence of urticaria
The human body contains mast cells or mast cells, which are specific elements of connective tissue. They are the central element in the development of urticaria, activators of inflammation. When an allergen enters the body for the first time and in small doses, the child does not experience any external manifestations or reactions, but sensitization occurs, which can be represented as the first acquaintance with the allergen, resulting in the production of histamine. It is this substance that causes redness, swelling and other inflammatory factors. It gradually accumulates in mast cells, and when its amount reaches a critical threshold, the cell membrane is destroyed with the release of histamine into the bloodstream and a subsequent cascade of pathological changes in the body.
First aid for hives
As a rule, an allergic rash goes away on its own within a couple of minutes or hours. But if a child begins to experience allergic swelling or severe itching, then first of all you need to:
- isolate a person from external irritants and allergens (cats, food, medicine, etc.);
- if you are allergic to a bite, then apply a tourniquet above the injury site;
- give the child clean water to drink;
- Give the child antiallergic drugs (if previously prescribed by a doctor) or a sorbent to destroy the allergen (activated carbon, Polyphepan, Polysorb).
The following actions are aimed at reducing itching so that the child does not scratch the blisters:
- apply anti-itch cream to the skin (fenistil gel, soventol);
- if there is no cream, then make a compress from a mixture of clean water (a regular glass of 200-300 ml) and a tablespoon of vinegar;
- cut your nails;
- dress the baby in clothes made of cotton or other natural fabric.
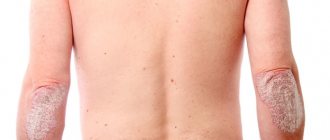
Forms of urticaria disease
According to the nature of the course, acute and chronic forms are distinguished. In the first case, the disease manifests itself abruptly; the symptoms of urticaria continue to bother the child from several hours (usually 6-12) to 1-2 weeks. The rash is accompanied by severe itching, the surface of the skin at the site of the rash becomes hot to the touch. If the outbreak is caused by an allergen, then when contact with it is eliminated, the symptoms disappear quickly and without a trace. With an exacerbation of chronic urticaria, the itching and rashes are less intense, but in this case they can persist for a long period - several weeks and sometimes months. The condition is accompanied by weakness, nausea, loss of appetite, headaches, and, less commonly, stool disorders. Sometimes, against the background of sluggish urticaria, neurotic disorders develop, and since the child constantly scratches the itchy papules, a secondary infection occurs and dermatitis develops. According to the severity of the disease, Mild form - external manifestations are almost invisible, the child feels well, there is no itching or intoxication of the body. A minor rash goes away within a day at most. Moderate - characteristic rashes are clearly visible, accompanied by fever and itching; intoxication of the body in the form of nausea and headache may be present. The papules merge, swelling appears, and there is a risk of the first signs of Quincke's edema appearing.
Severe - pronounced symptoms. Severely itchy rash, general intoxication of the body with a gastrointestinal reaction, development of Quincke's edema. Requires urgent medical attention. Depending on the provoking factor
- Contact - has an allergic origin, in 1st place among the causes are pharmacological and biological factors. When contact with them is eliminated, it goes away without a trace.
- Idiopathic - occurs for unknown reasons. It does not respond well to standard treatment and retains symptoms for a long time.
- Vibration - occurs against a background of strong mechanical vibrations.
- Dermatographic - provoked by mechanical irritation of the skin (tight or synthetic clothing, skin folds, etc.). After eliminating the irritant, it goes away very quickly, usually within half an hour.
- Cholinergic - caused by high physical activity, characterized by the appearance of small rashes.
- Thermal - provoked by uncomfortable (high or low) ambient temperature. Accompanied by particularly severe itching and is the most common cause of edema.
- Aquagenic - a reaction to contact with water. The rash is usually small or absent, but is accompanied by severe itching.
What complications does urticaria cause?
Complications of urticaria can be dangerous to the health and life of the patient. This disease must be taken seriously, and the patient must be examined and treated in a timely manner. In this article, we reviewed the main complications of urticaria in children and adults, the mechanisms, causes and symptoms of their development.
What can be the complications of acute urticaria?
What does acute urticaria look like? Acute urticaria develops due to contact with an allergen. Anything can be an allergen: food, plant dust, animal hair, cosmetics, sun, stress, cold, etc. Urticaria is a manifestation of an acute allergic reaction. It may be complicated by the development of Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
Quincke's edema, or angioedema, is a life-threatening condition for the patient. When it occurs, swelling of the subcutaneous tissue occurs due to the accumulation of fluid in it. It may be a consequence of the use of antibiotics or other medications.
Often, angioedema develops in children after insect bites. In adults, it can occur after visiting a solarium or using cosmetics. Please note that angioedema can be triggered by any allergen upon repeated contact of the patient with it.
The danger of this condition is swelling of the gap, which can result in suffocation.
Below are the main symptoms of Quincke's edema:
- Severe itching of the skin, which, with increased swelling, changes to pain and burning.
- Rapid development of swelling of the skin and submucous membranes.
- Pale skin, which may be accompanied by rashes, like urticaria.
- With pronounced progression, the patient may begin to choke, shortness of breath develops, a cough appears, and hoarseness of the voice appears.
Treatment of angioedema should begin immediately. When the first symptoms appear, you should call an ambulance. Treatment consists of intravenous administration of antihistamines and corticosteroids. In severe cases, hospitalization in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit is required.
If the cause of the edema was a food product, the stomach is washed through a tube, and the patient is prescribed sorbents (charcoal, smecta, enterosgel, atoxil, sorbex).
Anaphylactic shock is the most dangerous complication of urticaria, which can occur in both adults and children. Symptoms develop immediately after contact with the allergen.
Most often, such contact is not the first in the patient’s life. A substance that previously caused urticaria may, with the accumulation of inflammatory mediators and allergic reactions, provoke anaphylactic shock.
In children and adults, it is often triggered by medications.
Symptoms of anaphylactic shock:
- Loss of consciousness.
- Severe pallor.
- Rapid decrease in pressure and development of tachycardia.
- If left untreated, death occurs.
Anaphylactic shock can lead to the death of an adult or child in a matter of minutes. The consequences of delaying calling an ambulance are dire.
Treatment for this condition begins with the emergency medical team and continues in the intensive care unit. The patient is given intravenous adrenaline, corticosteroids, antihistamines, artificial respiration is started, and if necessary, doctors perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Complications of the chronic form of the disease
Complications of urticaria, with its chronic course, are not as dangerous as with the acute form of the disease. Most often, they are caused by an infection joining the area of the skin rash. Complications of urticaria most often arise due to ignoring the recommendations of the treating doctor.
The consequences of chronic urticaria include:
- Attachment of a bacterial or fungal infection. This especially often happens in children who scratch the rashes and introduce infection there. A fungal infection can occur after treatment with antibiotics. To identify an infection, it is necessary to undergo a series of laboratory tests (complete blood count, culture of the infected wound).
- Skin hyperpigmentation. It develops when the patient is exposed to direct sunlight or in a solarium. Sunbathing is contraindicated for patients with chronic urticaria, since the area of the rash does not tan, but burns, and dark pigment spots remain in its place. It is worth noting that visiting a solarium can provoke an exacerbation of the disease. In itself, solarium is very dangerous and is a common cause of skin cancer.
Treatment of the above complications is carried out by a dermatologist. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are used. It is best to use these drugs topically. Systemic antibiotics are prescribed for severe purulent skin lesions.
Laser, ultrasound and whitening cosmetics can be used to treat hyperpigmentation. This therapy is carried out by a dermatologist and a cosmetologist.
When to see a doctor
If you experience prolonged hives or any other rashes, be sure to consult an allergist or dermatologist. They will help you determine the cause of the symptom and create an effective course of treatment.
Hives and any other rash may be the result of an allergic reaction or a medical condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Consult your doctor immediately if, in addition to your skin condition worsening, the following symptoms occur:
- labored breathing;
- itching or feeling of constriction in the throat;
- severe pain at the site of the rash;
- severe pain in the head, neck or abdomen;
- swelling of the face, eyelids, lips, throat or limbs;
- fever;
- dizziness;
- confusion;
- muscle weakness or sudden lack of coordination;
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- formation of open sores or blisters;
- developing a rash around the mouth, eyes, or genitals.
Just as in adults, newborns and young children can develop any rash. This may be caused, for example, by a bug bite or exposure to foods new to children.
If your child has a rash and you are unsure of its origin, call your pediatrician. Especially if you notice at least one of the symptoms listed above.
Treatment of urticaria. Treatment routes
The most effective method of treating urticaria is identifying and eliminating the allergen. When this is not possible or the disease appears only once, topical medications or antihistamines are used. Symptoms usually go away quickly.
Only a doctor can determine how to cure hives. However, in general, treatment is characterized by the following features:
- The type of drugs used is determined by the severity of the pathology. In mild cases, topical ointments can be used.
- Treatment of chronic urticaria lasts quite a long time (from 2-3 weeks to several months).
- In 50% of patients, the disease goes away on its own - without any treatment.
- During the therapeutic course, the patient should eliminate infectious foci and restore the intestinal microflora.
- The patient is advised to follow a diet that excludes possible allergens and is aimed at strengthening the immune system.
- It is not advisable to use perfume products during the course.
If the pathology is caused by taking medication, this medicine cannot be consumed throughout life.
How to treat urticaria after identifying an allergen - directions of therapy:
- hyposensitization (the patient’s body is “accustomed” to the allergen by introducing a provoking substance in small dosages);
- elimination of skin irritation and itching through medications (internal administration or ointments);
- prevention of infectious foci;
- examination to detect the presence of stomach problems (and appropriate treatment if they are detected);
- deworming (measures to eliminate parasites and the consequences of their presence in the body).
Key remarks:
Hives and other types of skin rashes have a wide range of causes and are very common.
Hives are a type of rash, although not every rash looks like one. Both skin conditions can be acute or chronic.
It's important to try to determine the root cause of your hives or other rash to help determine the best treatment.
Breathing problems that occur in combination with hives may require immediate medical attention.
Reasons for development
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of urticaria, and it is not always possible to identify them in time. But in most cases, concomitant pathologies become the trigger for the development of the disease:
- endocrine pathologies;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- dysbacteriosis;
- systemic diseases;
- liver diseases;
- malignant tumors;
- allergic reactions to taking any drug;
- frequent stress;
- factors of natural origin.
All these factors lead to disturbances in the body, which ultimately cause the formation of rashes and swelling on the skin.
How to treat urticaria in a child?
Most often, the acute form of urticaria goes away quickly, even before the child receives medical attention. However, it is important for parents to be able to provide first aid.
First aid The primary task is to identify and eliminate the provoking factor. The main problem during this period is not rashes, but itchy skin. When providing first aid, it is important to eliminate it if possible - gently trim the nails, put on protective gloves for infants, apply an available non-hormonal anti-allergic cream (for sunburn, mosquito bites, etc.) to the site of the rash. If there is no cream, you can use a cool compress. Provide plenty of fluids; if urticaria develops after an insect bite on an arm or leg, apply a tight bandage above this area. All this is done before medical assistance, which should be provided immediately. In case of development of edema and severe symptoms, it is necessary to call an emergency team. Treatment of urticaria Treatment tactics are directly related to the form of urticaria. Only a doctor can prescribe competent treatment for the disease after an accurate diagnosis. The basic principles of therapy are the elimination of provoking factors, the prescription of medications to eliminate symptoms and the treatment of concomitant pathologies. The doctor makes the choice of antihistamines and other drugs based on the individual clinical picture. Modern medicine offers new generation drugs that minimize the risk of side effects, have a high level of safety and are easy to use for young children. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required. Is it possible to bathe a child with hives? If the disease is not aquagenic in nature, you can and should bathe your child, but it is important to follow the recommendations:
- do not heat the water above +37C;
- do not use washcloths and hygiene products with dyes and fragrances;
- maximum bathing time - 10 minutes;
- the use of herbal decoctions and potassium permanganate should be agreed with a doctor;
- Do not rub the inflamed skin with a towel.
Hives
Urticaria is one of the most difficult diseases in terms of diagnosis and treatment, with which one can come to see an allergist-immunologist.
Skin rashes like urticaria can have many causes, which requires a thorough examination of the patient and a balanced approach to his treatment.
This article is devoted to modern views on the cause of the development of this pathology and highlights the existing standards for the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria. 15-25% of the population will experience urticaria or angioedema at least once during their lifetime.
Urticaria is a term that unites a whole group of diseases of different nature, but having a similar clinical symptom: skin elements like blisters, reminiscent of a nettle burn.
Hives
- a fairly common disease. There are no exact statistics on its occurrence, but a number of domestic studies have shown that it occurs at least once in a lifetime in 31% of the population. Particularly difficult for patients are chronic forms of the disease (urticaria lasting more than 6 weeks).
The first detailed description of the symptoms of urticaria dates back to 1882, although similar symptoms are described in the works of Hippocrates.
Cause of hives
Urticaria is a classic polyetiological disease. This means that there can be many causes for the same symptoms.
One of the most common types of disease is allergic urticaria, which is based on immediate hypersensitivity. This mechanism underlies many allergic reactions.
It is characterized by the rapid development of symptoms after the allergen enters the body.
This type of allergy is typical for hives after an insect bite or associated with the consumption of food products.
Immune complex mechanism of urticaria development. Here, the basis of the pathological process is the excessive formation of antigen-antibody complexes.
(An antigen is a substance that causes an immune reaction, and an antibody is a protein produced by the human immune system to fight extracellular antigens. More about this in the article on immunity).
This mechanism is often observed in reactions to drugs, for example to the administration of serums.
Also, the development of anaphylactoid reactions may be the basis of skin problems.
Their distinctive feature is the increased ability of mast cells (a special type of cells, located, as a rule, under the skin and mucous membranes, and carrying a large amount of biologically active substances) to release the enzymes and active proteins accumulated in them. Moreover, this process occurs without the involvement of immune cells in this reaction.
Cause of hives
there may be liver pathology leading to impaired destruction of histamine, one of the most active participants in allergic inflammation.
Often urticaria
is
a consequence of autoimmune inflammation
. Conditions when the immune system begins to react to the body’s own tissues as if they were foreign.
These are just a few of the most common mechanisms for the development of urticaria. This problem is currently being actively studied, and every year more and more new aspects are being discovered.
Direct provocateur or stimulator of exacerbation of urticaria
may be
the use of medications, food, insect bites
. Chronic urticaria is most often based on some kind of chronic pathological process. Old manuals wrote that skin rashes are a reflection of internal pathology.
Diseases associated with chronic urticaria, that is, capable of triggering the above mechanisms leading to the appearance of skin symptoms:
1) Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, colitis, cholecystitis, intestinal dysbiosis, fermentopathy).
2) Infections: bacterial (Helicobacter pylori, chronic foci of infection in the oropharynx or urinary tract, gynecological infections), viral (Herpes simplex, etc.), fungal (Candida, Trichophyton, etc.), parasitic infestations (helminths).
3) Endocrine diseases (autoimmune thyroiditis, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, dysfunctional ovarian disorders, etc.). 4) Systemic connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
)5) Lymphoproliferative diseases (myeloma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Waldeström macroglobulinemia, etc.). 6) Tumors (carcinoma of the colon, rectum, liver, lungs and ovary, etc.).
7) Other diseases (sarcoidosis, amyloidosis).
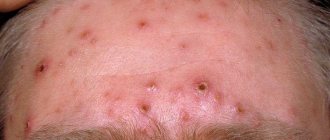
Symptoms of urticaria with photos
The main symptom of urticaria is the appearance of blisters on the skin. Externally, a blister is a protruding area of skin that resembles an insect bite or a burn left by a nettle. Skin element - accompanied by itching. The skin around the blister may be red. Elements can merge, acquiring gigantic sizes. Most often, the rashes are symmetrical.
A characteristic feature of urticaria is the complete reversibility of the elements. That is, after stopping the attack of the disease, the skin returns to its original state. There are no white spots, hyperpigmentation, or scars left. Elements can appear on any part of the skin and can migrate. For example, today on your arms, tomorrow on your stomach.
Urticaria in children
Acute forms of urticaria predominate in children. Hives rarely occur in children younger than 6 months. The most common forms of urticaria are allergic.
Children suffering from urticaria are characterized by severe exudation: the elements are swollen and rise sharply above the skin. The itching is usually worse than in adults. Possible increase in body temperature, joint pain...
Urticaria during pregnancy
During pregnancy, an increased amount of estrogen (female sex hormones) is produced, which is a risk factor for the development of urticaria. Often the occurrence of urticaria is a symptom of developing gestosis in pregnant women. Characteristic features of urticaria in pregnant women are severe itching, insomnia, irritability, and scratching of the skin.
What tests will you need to take for urticaria?
If hives appear, you should consult either a dermatologist or an allergist.
As we have already said: a symptom such as urticaria can be caused by a huge number of reasons. In this regard, a patient with urticaria is always offered to undergo a fairly large number of tests. This, of course, can be scary, but there is no other way! If the exact cause is not established, treatment may be ineffective.
Treatment of urticaria:
An obligatory component of the treatment of urticaria is adherence to a diet and a special lifestyle (more details in the section Features of nutrition and lifestyle with urticaria).
It should be noted that for urticaria, a number of medications that may be prescribed to treat concomitant diseases of a patient with urticaria are prohibited. These drugs include: aspirin and its derivatives, codeine, ACE inhibitors (enap, enam, capoten, etc.).
If you suffer or have suffered from urticaria, you should definitely warn your doctor about this so that he does not prescribe you medications that can provoke an exacerbation.
Traditionally, treatment for urticaria begins with antihistamines. It is preferable to use 3rd generation drugs: Telfast, Zyrtec, Erius, etc. Sometimes (with chronic urticaria) long-term medication is required, up to three months or more.
Treatment of urticaria with folk remedies
There are no remedies from the arsenal of traditional medicine that could be recommended for patients with urticaria. In addition, many recommended treatments for hives may make the condition worse. Conversations that certain recipes have helped someone are most often based on self-hypnosis.
Features of nutrition and lifestyle with urticaria
For all forms of urticaria, stress, alcohol consumption, and smoking are contraindicated. Prolonged exposure to the sun is not recommended, especially for patients with solar urticaria. Overheating is not recommended. Sunbathing is strictly forbidden.
Pressure on the skin should be avoided. To do this, you need to give up tight clothes, belts, and suspenders. Work involving heavy physical exertion is not recommended.
It is possible to prescribe local protective agents. For example, for solar urticaria, it is necessary to actively use sun creams with a protection factor of at least 40; for cold urticaria, protective creams against low temperatures, for example, Morozko baby cream or Mustella cream with mink oil.
During an exacerbation, it is necessary to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Possible complications of urticaria and prognosis
The prognosis for life is usually favorable. It is possible to develop Quincke's edema, which occurs with the development of edema of the upper respiratory tract. This condition is already life-threatening.
In addition, urticaria can be a manifestation of internal pathology, including cancer, which, of course, worsens the prognosis for the patient.
In 30% of cases, chronic forms of the disease occur.
Prevention of urticaria
No measures have been developed to prevent the development of urticaria. It is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle, timely detection and treatment of concomitant diseases. In the presence of frequent infectious diseases, sanitation of all possible foci of infection.
Save on social networks:
Related publications:
Source: https://krasgmu.net/publ/simptomy_i_lechenie/krapivnica/58-1-0-581
Features of treatment
Treatment of urticaria is carried out taking into account the basic principles
1. hypoallergenic diet, normalization of the diet and exclusion of allergenic foods (the doctor will recommend a dairy-vegetable diet excluding red fish, chocolate, honey, nuts and other foods that can trigger a reaction);
2. if possible, avoid contact with the allergen;
3. taking medications that normalize the level of biologically active substances responsible for skin reactions with urticaria;
4. symptomatic therapy as necessary.
Treatment involves the use of drugs with systemic action (latest generation antihistamines), as well as local ointments/creams. The latter are prescribed to reduce the severity of symptoms. In some cases, it is advisable to prescribe hormonal ointments; they should be used under the strict supervision of a specialist. Other drugs that are in demand for urticaria include anti-inflammatory drugs that accelerate healing, relieve itching and burning, and moisturizers.
Physiotherapeutic methods, immunomodulatory therapy, vitamin therapy, taking sorbents, pro- and prebiotics to improve intestinal microflora and strengthen the body's resistance can be used as a supplement. The doctor will definitely give recommendations not only regarding dietary habits, but also tell you about a lifestyle that excludes contact with the allergen or reduces it to a minimum. All this is the key to preventing frequent relapses (exacerbations) of a chronic disease.
Treatment of different forms of urticaria
Drug treatment is prescribed and adjusted only by a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable. Dosages of drugs depend on the patient’s body weight, age and severity of the disease.
For allergic etiology, it is necessary to take antihistamines. For cold and cholinergic forms, histamine receptor blockers are used. In severe autoimmune forms and ineffectiveness of conventional therapy, hormonal drugs (glucocorticosteroids) are added to treatment.
When selecting drug therapy, it is necessary to take into account the presence of concomitant diseases and contraindications, as well as possible adverse reactions.
Doctor's recommendations
During treatment and after relieving acute symptoms, it is important to follow the following recommendations:
- take a warm shower, avoid hot baths;
- choose soft detergents and towels;
- give preference to clothes made from natural fabrics;
- stop tanning;
- take anticoagulants only under the strict supervision of a doctor;
- You can contact a neurologist to prescribe sedative therapy if itching and the presence of a rash cause psychological irritation, insomnia and other symptoms.
Characteristics of the symptom
With hives, the skin becomes inflamed and a pink rash appears that is very itchy. The pathology affects different bodily areas, mainly localized on the limbs, neck, face and abdominal area. The disease is also called polyetiological dermatosis.
Urticaria is common and occurs due to internal disorders or external unfavorable factors. The acute form is characterized by a rapid course; with effective treatment, symptoms disappear within a few hours or days. If there is no therapy, the disease becomes chronic and lasts up to 7 weeks.
With polyetiological dermatosis, histamine is released into the circulatory system due to the high permeability of capillaries and their expansion. According to research results, it has been established that an allergic reaction in most cases provokes hives, so blisters on the body appear due to an allergy to external adverse factors.
When pathology appears, not only skin symptoms are noted, but also mental disorders. The disease can go away on its own, but in severe cases it requires treatment. With prolonged contact with the irritant, the rash grows and covers new areas of the epithelium. It tends to merge into large spots of uneven shape; damaged skin feels hotter than healthy areas to the touch.
Possible complications and their consequences
Urticaria, despite its apparent harmlessness, can lead to serious consequences, primarily to Quincke's edema. Its characteristic initial symptoms, in addition to the swelling itself, are difficulty breathing and paroxysmal cough with whistling (bronchospasms). Swelling of the internal mucous membranes is dangerous due to disruption of the housing and communal services, the first signs of which are a gag reflex and stool disturbance. From the nervous system, severe cases of urticaria are dangerous due to damage to the meninges, which can be fatal in the absence of medical assistance.
Why is urticaria dangerous?
Hives can lead to very severe allergic reactions - swelling of the tongue and throat, breathing problems and even anaphylactic shock. If these symptoms occur, it is important to immediately call an ambulance, otherwise the patient may suffocate.
In 1/3 of patients, urticaria becomes chronic, that is, even after treatment, from time to time it reminds itself of relapses. In 15% of patients it contributes to the development of depressive disorders.
It is important to know that urticaria can be a symptom of another, more serious disease - oncology.
Prevention of urticaria
It is impossible to predict the body's reaction to a particular allergen, however, every parent can protect their child as much as possible from contact with the most active well-known allergens, do not bundle up or overcool, and do not use cosmetics and detergents with dyes and strong fragrances. If possible, prevent the presence of children in rooms with a strong smell of paints and varnishes, avoid stress, infections and excessive physical exertion. It is recommended to examine the child’s endocrine system and not ignore signs of weak immunity. Unfortunately, urticaria is often not taken seriously; however, it is a disease that, if unfavorable, can threaten the life of a child. SM-Doctor pediatricians are always ready to come to the aid of your child; their experience and attentive attitude towards each little patient are the key to a quick and correct diagnosis and well-chosen treatment tactics.
Patient participation in treatment
In addition to taking prescribed medications, the patient needs to maintain a healthy lifestyle and monitor the body’s reaction to allergens and triggers.
If you have food allergic urticaria, you should adhere to a hypoallergenic diet - exclude everything to which a reaction was previously observed, and use foods containing histamine liberators with caution. This group includes cow's milk, eggs, many types of fish, caviar and seafood, spices and seasonings, marinades, alcohol, as well as all products containing dyes, flavors and preservatives.
You should be careful about skin hygiene to avoid pustular diseases. It is recommended to take a warm, but not hot, shower with liquid hypoallergenic soap and carefully use a soft washcloth so as not to injure irritated skin.
Ointments with hormones will help relieve skin itching due to urticaria.
Consultations with an allergist
Name of service | price, rub. |
| Program “Advanced diagnosis of allergies” (consultation with an allergist-immunologist, spirography, inhalation panel “Fadioton”, immunoglobulins (A, M, G, E), clinical blood test, Eczema panel, blood sampling, treatment regimen) | 13,500 rub. |
| Primary consultation with a doctor of the highest category, allergist-immunologist | 2,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation with a doctor of the highest category, allergist-immunologist | 1,800 rub. |
Love yourself, take care of your own health! Feel confident with our specialists. We will help!
Call or fill out the form
Make an appointment daily from 9 to 21
Or leave your phone number, we will call you back at a time convenient for you
Our specialists
Our specialists have extensive experience, modern knowledge and use the latest diagnostic and treatment technologies in their daily practice.
If you are lucky enough to not know what an allergy is, then you probably have a couple of friends who suffer from this disease. Household chemicals, plant pollen, animal hair - this is just the beginning of the list of things that provoke allergies. Moreover, today this disease is in the TOP of modern diseases. Is it possible to cure allergies? And at what symptoms should you not rush, but run to the doctor? Boris Pukhlyk, president of the Association of Allergists of Ukraine, told Mіst about this, as well as about the features of the problematic disease.
— Judging by the active advertising of drugs, the number of people suffering from allergies is growing in Ukraine?
— At one time, I worked on my dissertation, studying how many people actually have allergies. Unfortunately, there are no accurate statistics on allergy patients in Ukraine, and we can only guess about the real situation. Back in the days of the Soviet Union, the largest study in Europe to date was conducted in the Vinnytsia region, covering over 100 thousand people. In 1981, the number of sufferers was 6.03%, although it was then believed that only 1% suffered from allergies. After the research, they even called us to the KGB and burned 150 thousand questionnaires... Over the next 10 years, the figure grew to 9.05%. No other large studies of this kind have been conducted in Ukraine.
According to data from various sources, 35-40% of the population suffers from allergies today. My opinion is 20-30%. There are definitely half a million such patients in the Vinnytsia region. But the state does not agree with this and does not increase the number of allergists. But to examine Ukrainians for allergies, with the current number of specialists, it will take seven whole years. In Vinnitsa, for example, there is officially only one allergist-therapist - in the first hospital, and two more - in the regional one.
— What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
- There are four of them. First: long-term non-acute nasal congestion - more than two weeks. Second: choking, coughing, wheezing in the chest. Third: rash that itches, itching, swelling. And fourth: anaphylactic shock - loss of consciousness. The sooner a patient consults a doctor, the greater the chance of stopping the development of the disease. If you are late, the person will have to take medications for the rest of his life.
— What causes allergies?
— Plant pollen, dust, food, synthetic clothing, microfungi, emissions from enterprises... For example, in Ladyzhyn, when the enzyme plant and the state district power plant were still operating, 50% of the local population suffered from allergies. In general, there are two reasons for allergies: a failure in the human immune system or the presence of an excess of allergens in the environment. The huge number of different chemicals that have appeared in the last 100 years (which is a very short period in human evolution) causes an inadequate response to them in a significant part of people. About 1,500 chemicals are found in pesticides, 4,000 in pharmaceuticals, and 5,000 in food additives. The environment can modify allergens, making diagnosis and treatment more difficult. Allergy to pets - 1-4% in adults and up to 11% in children. Most often it is an allergy to cat and dog fur. In cats, the main source of allergen is saliva. By the way, cats, unlike cats, also excrete allergens in their urine and are more dangerous. Even when the animal is removed from the premises, allergens remain in it for up to 24 weeks.
— Is the allergy problem seasonal?
- If we are talking about hay fever, then yes. These are the periods when trees gather dust, starting in March, then meadow grasses, cereals, and weeds. The number of patients with polynosis reaches 20% of the population.
— What treatment methods?
— All medical technologies today are designed so that you take medications for life, relieve symptoms, but do not recover, and are tied to such treatment. Antihistamines are a good remedy, but only symptomatic. I’m not saying that these drugs are not needed - after all, a person needs, say, to relieve a rash, an exacerbation, and alleviate the general condition. But an allergy is essentially a breakdown in the immune system; the body’s defense reaction becomes so activated and becomes inadequate that it begins to destroy the body itself. An allergy is not a weak immune system, but a special condition of it, in other words, a failure. The way out of the problem is to “get into” our genes and make corrections - but we have not come to this yet. The second method that can really help is developing tolerance to allergens, i.e. non-response. For example, if an allergy is caused by birch pollen, you need to be treated with the same pollen - the allergen. Even if your genes react inadequately to the allergen, you already stop reacting to it and feel great.
Many diseases require lifelong treatment, but allergology has a solution, but only for those who see a doctor in a timely manner. Then you will be healthier and save a lot of money. It’s especially offensive when they bring a child and tell him that 10 years ago he began to choke. But he could have been cured! According to statistics, 75% of adults and 95% of children who were treated with allergens do not have allergy symptoms after 10 years. In children, the immune system is rebuilt much better and more deeply. I will say that many do not want to be treated - it is easier for them to survive the flowering period of plants once a year with the help of pharmacological agents, rather than seriously take care of their health. Unfortunately, this is our mentality: everyone wants it immediately, quickly and cheaply, and is satisfied with the temporary effect.
— What foods should a patient with allergies exclude from their diet?
- Everything is individual. For example, if you are allergic to birch pollen, you should not eat apples. For hay fever - no honey or citrus fruits. In general, products of protein origin have the highest allergenic activity. The most allergenic are milk, eggs, fish, and meat. However, this is no longer hay fever, but a different problem (food allergies, urticaria).
— Can you be allergic to the sun?
— Here we can talk about allergic dermatosis, where the sun acts as a provocateur. For example, urticaria occurs. But the sun itself is not the cause. Most likely, the person has some problems with internal organs. You may also be allergic to cold. They say that quite a long time ago our fellow countrywoman, the wonderful Olympic champion Yulia Ryabchinskaya, suffering from cold urticaria, fell into the water and died due to anaphylactic shock.
— And if allergy tests show nothing, how then to treat?
— The point is that there is a pseudo-allergy, and there is more of it than a true allergy. The doctor must figure this out. With hives, for example, everyone goes to an allergist, although only 10% of cases turn out to be an allergy. Hives, by the way, can be a sign of gallbladder disease, hepatitis, helminthiasis and even cancer. The most difficult patients for an allergist are those with urticaria. They rush between therapists, allergists, neurologists - and no one can help. Multilateral surveys are not cheap these days.
— How quickly is the cause of an allergy determined?
—Hay fever is established within 15 minutes. You need to “play around” with hives and other skin rashes for a month. The diagnosis of bronchial asthma is also easy to establish. But it is difficult to treat.
— Are allergies inherited?
— If one of the parents has an allergy, the probability of its occurrence in offspring may be 20-30%. If both parents have it, the risk of development is up to 70%. A predisposition to allergies in general is inherited, and not to its specific manifestation.
— Can stress cause allergies?
- Can not. They can only aggravate, just like any other disease. If a person gets nervous and then begins to choke, you should figure out what caused it.
Types of urticaria
Urticaria is usually classified according to several criteria: form, provoking factor and course variant.
The doctor’s task is to determine the specific type, because the treatment regimen depends on the type. The following types are distinguished by form:
- Acute urticaria. The rash appears suddenly, the blisters are round or elongated. As the spots develop, they merge, forming wide affected areas. The patient's condition is impaired, body temperature increases, chills and general weakness are observed. The rash primarily affects the arms, buttocks, and area near the feet. The disease can affect the tongue, larynx and nasopharynx, causing people to complain of difficulty swallowing. Acute urticaria occurs due to a food or drug irritant; with proper treatment, the blisters disappear within a few days.
- Chronic urticaria. It is determined in people whose rashes do not go away for more than 6 weeks. The disease is explained by autointoxication and is observed in pathologies of the digestive organs and liver. Provoking factors are caries, pathogens in the gallbladder and larynx, and worms. The chronic form appears if the patient has not treated acute urticaria.
- Chronic relapsing type. The disease lasts 10-20 years and can last a lifetime. The pathology has periods of improvement when the rash disappears. Quincke's edema often appears against the background of skin problems. The rashes are very itchy, causing patients to tear the skin with their nails until blood appears.
When urticaria begins, symptoms and treatment depend on the factor that provoked the pathology. The rash is usually classified depending on the cause of its appearance. The body's reaction to the food consumed is considered common. It is mainly diagnosed in infants during the introduction of complementary foods and in school-age children.
The figure shows types of urticaria and a photo of the disease. Symptoms and treatment methods are discussed in detail in the article.
After consuming a prohibited product, a rash appears on the skin, the lips and larynx swell, and angioedema develops. Patients note heaviness and pain in the abdomen, and during a food reaction, stool upset occurs. Allergens include red vegetables and fruits, chicken eggs, chocolate, milk, honey and nuts.
Stress urticaria begins after a nervous shock, with large blisters forming, merging into one spot. With neurogenic pathology, severe itching is always present. The risk group includes people prone to irritability, aggressiveness and mental instability.
With cold polyetiological dermatosis, rashes begin after exposure to low temperatures. The pathology often occurs in middle-aged women, but can also be diagnosed in men. The skin is adversely affected by icy air, raindrops, and snow flakes, which causes a rash.
There are other types of urticaria: solar, aquagenic, drug-induced, dermographic and cholinergic. The types of the disease differ in provoking factors, while the symptoms of the pathologies are similar. After stopping contact with the pathogen, the rash goes away on its own, but recovery can be accelerated by taking medications.
Today in medicine there are several types of disease, each of which requires a special approach to treatment and patient care:
- Acute form. It begins quite suddenly, bubbles suddenly begin to cover the entire body of the patient after contact with the irritant. The rash can disappear as quickly as it appeared. The duration of this stage of the disease most often lasts from several hours to two days. The rashes are accompanied by general malaise. The patient may develop a fever, headache and nervous disorders.
- Acute stage with the development of Quincke's edema. This type of disease is accompanied by swelling of the fatty tissue and mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. Such swelling in the larynx area is most dangerous, because it can lead to asphyxia and death of the patient. The disease at this stage is accompanied by white-pink blistering rashes, severe itching and blurred vision.
- Chronic urticaria with a recurrent nature. This variety is considered the heaviest. The patient experiences repeated attacks of severe itching, which lead to insomnia and bring the patient to complete nervous exhaustion. This form of the disease is extremely difficult to cure. Over a long period of time it can progress and develop.
- Chronic persistent papular form. This type of disease is also characterized by a long course and can bother the patient for up to several weeks. Swelling and rashes become persistent, and it is no longer possible to determine the true cause of the disease. Most often, blisters are localized in the areas of extension of the limbs. A little later, it is in these places that erythema nodosum forms, which have a dense consistency. This type of urticaria is most often classified as one of the forms of prurigo.
But urticaria generally differs in the irritant that causes it. According to this factor it happens:
- Solar is one of the types of photodermatosis. Skin rashes begin to appear only when exposed to sunlight. Most often, this type of disease affects women.
- Heat or cold, most often observed in people whose bodies do not tolerate overheating or hypothermia. Cold urticaria begins to appear after the onset of cold weather, and heat urticaria - after overheating in a sauna or bathhouse.
- Contact urticaria occurs after strong squeezing or rubbing of objects on the skin. It can occur when wearing clothes or shoes that are too tight. At the point of contact, blisters appear that are very itchy, but after a while they usually go away.
- Allergic - occurs after a person comes into contact with any allergen. You should under no circumstances ignore its symptoms, because in most cases it is accompanied by swelling and high body temperature.
What are the health benefits of oatmeal?
Method of preparation: Mix soda with flour. Fill a bowl with warm water and add flour and soda to it. Mix thoroughly. Take a bath for about 15 minutes. You can also apply oatmeal directly to the sores (if you don't have oatmeal, use cornstarch or talcum powder).
Aloe vera
It is difficult to find a product more beneficial for the skin than aloe vera.
This plant relieves redness, accelerates healing and prevents the wound from becoming infected. Cut one aloe vera leaf, extract the pulp and apply the released gel to the affected area. Let it air dry. All about urticaria
Main symptoms
Itchy skin is the first symptom of urticaria in adults and children. If you start scratching the skin, redness begins, against which pale red blisters appear. They usually have a round appearance, but as the area of redness grows, a variety of large plaques form.
A hives rash can affect any area of the skin and usually appears suddenly. The bubbles are dense, pale pinkish in color. The nettle rash is very itchy, the blisters can be small or large in diameter.
The rash lasts for several hours, then the level of the rash decreases, sometimes blisters may appear in other places on the body. But usually nettle fever in adults disappears, leaving no noticeable traces.
Typically, urticaria lasts several hours or days. With chronic nettle fever, the rash lasts for months. Sometimes rashes and itching are accompanied by fever, lethargy, and upset stomach.
What are the causes of hives?
For most people, hives are the result of an allergic reaction. The body responds to the allergen by releasing a number of chemicals into the blood, such as histamine. They cause blisters and swelling.
The most common allergens that cause hives include:
- pollen
- poisonous plants
- insect bites
- medicines
- various products and preservatives
- shellfish
- microscopic particles of animal skin
- materials such as wool or latex.
Urticaria can also be caused by:
- allergic rhinitis
- stress
- infection or disease
- excessive sweating
- increased fatigue
- wearing tight clothes
- sudden changes in body temperature
- extreme weather conditions such as extreme heat or cold.
Vasculitis is a rare disorder in which blood vessels become inflamed. It may also be accompanied by the appearance of blisters, only more painful.
Methods of treating pathology
Urticaria can be distinguished from other skin pathologies by its external manifestations. After contact with unfavorable factors, within 5-7 minutes the body becomes covered with numerous rashes. On the limbs, abdomen, neck and other parts of the body, obvious red or white spots and blisters appear like a nettle burn.
The size of the rash covers the skin by several millimeters and the nature of the disease is mild. With a strong reaction, a solid red spot is formed, affecting the entire abdomen, feet, arms, and neck.
The rash is characterized by mild or intense itching, burning, and the person complains of feeling as if his skin is burning. Depending on the extent of the lesion, the patient may experience severe weakness, drowsiness, nausea and headache. With urticaria, an elevated temperature occurs, which reaches 38-39 degrees.
Without treatment, urticaria symptoms can progress and cover the clear surface of the skin. If the pathology is mild, the rash disappears in 5-20 minutes or 3-4 hours, leaving no traces on the skin. In severe forms of the disease, the skin reaction lasts up to two to three weeks or months.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8uL3Mke1LZI
Characterized by a wave-like course, in which the rash partially disappears, but then reappears. Without treatment, acne becomes hemorrhagic, and after it disappears, pigment spots will remain on the body.
Treatment of urticaria is prescribed based on the causes of the pathology and exacerbation factors. When fighting the disease, symptoms are eliminated and human immunity is strengthened.
With the help of medications, the appearance of a new rash is prevented, the likelihood of anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema is reduced. The treatment regimen is determined individually by the doctor, depending on the form of urticaria and the age of the sick person.
Contact with the allergen is immediately excluded, regardless of the nature of its origin. The patient’s diet is adjusted, the premises are thoroughly cleaned, and medications that cause a rash are avoided. The doctor prescribes medications to the person to remove the allergen and restore the body’s strength.
For systemic therapy the following are prescribed:
- Antihistamines. Doctors prescribe Cetrizine, Diphenhydramine and Loratadine. They have an antiallergic effect and block histamine H1 receptors.
- Medicines for desensitization. Unithiol, calcium cholate or Cocarboxylase are prescribed. Immunotherapy is effective for allergies and is prescribed to patients if indicated.
- Systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs are necessary for the generalized type of urticaria. Representatives of this group: Prednisolone and Dexamethasone.
- Adrenaline hydrochloride. Used for patients with acute, life-threatening edema.
After identifying the allergen, you need to relieve skin irritation, for this you use Suprastin or Tavegil. A doctor may prescribe hypersensitization to reduce the body's sensitivity to an irritant. A recommended preventive measure is sanitization of foci of infection. If parasites are detected in the body, deworming is prescribed.
To treat chronic urticaria, Polysorb and other sorbents are used. They remove toxic substances from the body and speed up recovery. To reduce itching, patients use ointments and gels, which are divided into hormonal and non-hormonal drugs.
Non-hormonal ointments moisturize and nourish damaged epithelium. Gels based on zinc are prescribed, which has a drying and antimicrobial effect. Doctors prescribe Fenistil, Bespanten, Scan-cap and others.
With an integrated approach, urticaria quickly disappears. People with a chronic form of the pathology should know the symptoms and treatment in order to take timely measures. Mild rashes can be dealt with at home; acute pathologies cannot be dealt with without medical help.
In severe cases, detoxification measures are carried out in hospital conditions: injections of Glucose, Hemodesis and Plasmapheresis. The speed of recovery is different for all patients; the rash can disappear in a few hours or in a month.
Why urticaria is dangerous and how to treat it using traditional and alternative medicine
Pathology therapy must be comprehensive. Etiotropic treatment consists of eliminating contact with the allergen, as well as eliminating it from the diet. If the occurrence of urticarial rash and other manifestations is provoked by taking medications, their use is prohibited for life.
In addition, it is necessary to carefully treat surfaces from dust, as well as limit or completely eliminate contact with pet hair, pollen and other allergens. Urticaria is a dangerous disease. If the disease develops during pregnancy against the background of toxicosis (no matter at what stage, early or later), it can pose a danger not only to the woman who is carrying the fetus, but also to the child.
If not treated promptly, urticaria can cause suffocation. In addition, pregnant women are not allowed to take all medications. Most medications can have a toxic effect on the fetus. As a result of inappropriate medication use, children may be born with pathologies and anomalies. Therefore, if a pregnant woman develops the disease, before taking any drug, it is necessary to consult a doctor regarding its appropriateness. Every person should know the dangers of urticaria and be able to provide emergency care.
Drug treatment
Systemic treatment of pathology involves the use of medications. Often prescribed:
Local therapy consists of the use of ointments, creams and gels: Fenistil, Soventol, Psilo-balm, Cloveit, Advantan, Flucinar. In order to minimize itching, it is recommended to wipe the areas affected by the rash with a vodka solution, a solution of vinegar, diphenhydramine, and use a hot shower. It is also recommended to carry out a course of hepatoprotective therapy, taking enzymes and choleretic drugs. In order to restore the intestinal microflora, the use of Colibacterin and Bifidumbacterin is prescribed.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Both patients and their families have legitimate concerns about whether urticaria may pose a serious health threat. Let's try to figure this out.
Why is urticaria dangerous?
The rash itself does not have a poor long-term prognosis. A blister is an element without a cavity, resulting from swelling of the papillary layer of skin. It disappears, as it appears, quite quickly and without traces - without forming any erosions or wounds. Therefore, with isolated urticaria, although the patient is irritated and frightened due to the rash, there is no direct threat to health and life.
At the same time, one should ask the question: why did the urticaria make itself felt? What disease led to its development? After all, if you do not pay attention to episodes of rash, over time they may become more frequent, and the underlying pathology (for example, intestinal damage accompanied by dysbacteriosis) worsens.
You should also remember the risk of developing Quincke's edema. This is a swelling of dense consistency that can be localized externally (cheeks, eyelids, lips), in the digestive and respiratory tract, and affect the nervous system. Because of it, there is a risk of asphyxia (suffocation), due to the blocking of the lumen for the passage of air in the larynx area.
In addition to what has already been listed, it is worth keeping in mind that urticaria can be part of the clinical picture of dangerous immediate hypersensitivity reactions due to allergies. In addition to Quincke's edema, these are bronchospasm (narrowing of the airway due to muscle contraction) and anaphylactic shock (a critical drop in blood pressure, leading to oxygen starvation - hypoxia; has a high risk of mortality).
What complications exist in adults?
If the reaction is mild and limited to blisters that last a few hours on isolated areas of the skin, usually no adverse effects should be expected. The greatest danger in such cases is scratching: due to increased friction of itchy areas, tissue trauma occurs and infection can penetrate into the resulting “entrance gate” (scratches, wounds).
If we are talking about a severe course, the consequences of urticaria in adults may include such conditions as:
- development of respiratory failure and asphyxia (suffocation) with swelling of the larynx, bronchospasm;
- injuries and neurological disorders as a result of a seizure;
- anaphylactic shock.
Types and forms
Each form of urticaria has its own course and type of symptoms. There are acute, chronic and chronic papular persistent varieties. In international practice, it is about form, that is, without external influence from outside, and physical - providing any effect on the skin. The physical form of urticaria in adults has several types:
- Dermographic. It appears after mechanical impact. Signs are detected after squeezing the skin for a long time. Often occurs after wearing a backpack, tight shoe straps in the summer, or adults sitting motionless.
- Cold. Skin manifestations occur against the background of external influences - cold wind, water, wind, temperature.
- Thermal. Symptoms appear due to thermal influence.
- Solar. Signs are related to exposure to light or UV radiation. You can learn about solar urticaria here.
Some types of urticaria occur due to emotional stress, overexertion, skin itching and rash due to the release of adrenaline. There is contact urticaria, which appears as a result of skin contact with an allergen, and aquagenic urticaria, which occurs when the epidermis is exposed to water.
It is noted that most often spontaneous urticaria is diagnosed in adults in the acute and chronic phase, dermographic (delayed) and contact.
Acute urticaria
An acute form of urticaria on the skin can occur at any age. Typically, people with a predisposition to allergies and a tendency to atopic dermatitis are at risk. The signs of the acute form are clearly expressed and can be easily diagnosed visually.
A dense rash with pink blisters covers a certain area of the body, accompanied by hard-to-quench itching. Blisters can merge into one spot, resulting in a large affected area.
In the complex version, nettle fever may be accompanied by swelling and headache. Rashes sometimes affect the mucous membranes, in particular the lips, nasopharynx, and larynx. In this case, there are complaints of difficulty breathing.
Urticaria rashes occur from a couple of hours to several days. The acute form of the rash is accompanied by a short period of time, usually as a reaction to some irritant.
Causes of the acute form:
- Drug and food allergies;
- Pollen, insect bites;
- Chemical cosmetics;
- Hepatitis B, dysbacteriosis, poisoning.
With an atypical course in adults, there is no itching, and the blisters have a linear shape. An atypical type of rash usually occurs when the skin is exposed to mechanical irritants. This group sometimes includes contact urticaria. Read more about acute urticaria in this article.
Quincke's edema is described as a giant nettle fever that affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes, in particular the larynx, genitals, tonsils, lips, eyelids.
In some cases, swelling of the esophagus, intestines, and respiratory tract is observed. The patient suffers from swallowing problems, intestinal obstruction, vomiting, and barking cough. A dangerous outcome is asphyxia.
If with urticaria the rash is localized without swelling and with severe itching, then with Quincke's edema there is often no burning sensation. Usually the swelling subsides after a few hours, but relapses are possible. Sometimes Quincke's edema accompanies manifestations of typical urticaria.
Long-term rashes can develop into a papular form of the disease. The nature of the rash with papular urticaria looks like papular nodules. The papules have a burgundy hue, blisters of a dense structure and are very itchy.
Papules are accompanied by swelling, itching, and redness of the skin. They may be joined by a secondary infection - purulent blisters, pustules. When they heal, small scars remain in their place. Papular nodules are most often concentrated on the bends of the limbs, in the folds of the skin.
The chronic form occurs when the body's sensitivity to the influence of irritants that cause an allergic reaction increases. Chronic foci of infections can aggravate the process. These include caries, tonsillitis, inflammation of the tonsils, cholecystitis.
In the chronic form of urticaria, the rashes do not have a wide girth. They can affect any area of the skin, but the blisters are not profuse.
Acne is sometimes accompanied by a headache, general malaise, and painful sensations in the joints. The cause of the chronic stage can be found out after a blood test and a general examination of the body.
Cold
After exposure to low temperatures, some adults develop blisters on the skin; the pathology occurs at any age, but is more often diagnosed in women. The cold form can be triggered by cold air, snow, draft or cold shower.
The main symptom is severe itching with a rash. Urticaria-type rashes occur in two variants:
- Immediate form. The rash begins immediately after exposure to the cold factor.
- Slow form. Rashes are detected after 8-9 hours of exposure to cold.
Elements of rashes mainly appear at the site of direct contact with the cold factor - neck, cheeks, arms, legs. Sometimes they occur under the knees and calves. If the impact of the irritant was strong, then nausea, swelling, pain in the back of the head, and chills are added to the symptoms.
Dermographic
The form of urticaria appears due to some mechanical influence. The main sign of dermographism is the sudden appearance of a rash and its rapid disappearance. Belts, clothing straps, tight collars, and narrow shoes usually act as irritants.
The skin rash is light in color, and the surrounding areas of the epidermis are reddish in color. The appearance of the blisters is usually linear. There is urticaria of a dermographic appearance with white lines on the epidermis without signs of redness.
The main symptom of this type is severe itching and burning. The appearance of dermographism is influenced by the state of the environment and skin sensitivity. When the mechanical factor is eliminated, nettle fever in adults goes away on its own within a few hours.
Solar
This type is considered one of the most popular; nettle fever occurs when exposed to direct sun or ultraviolet rays. Symptoms begin after 20-30 minutes of exposure to direct sunlight.
Prolonged sun exposure worsens symptoms. In adults, blisters are small in size, pink in color and accompanied by an itchy sensation. If an adult or child has been under the sun for a long time, then the blisters can be larger, reaching 2 centimeters.
The condition can be aggravated by other symptoms - nausea, lack of air, dizziness, fever. What causes the solar form of urticaria? Causes:
- Skin sensitivity to the sun;
- Use of perfumery products with essential oils;
- Disease of internal organs.
Types of urticaria
The type of urticaria depends on the mechanism of triggering the disease.
- Allergic urticaria.
Caused by ingestion of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Commonly prescribed drugs include tetracycline, amoxicillin, flemoxin, aspirin, ibuprofen, and nise. Alcohol consumption can accelerate and intensify the course of the disease. Antibiotics accumulate in the body, so the problem does not manifest itself immediately. The course can be completed, and hives will appear in a couple of weeks. - Food urticaria.
It occurs more often in children after eating certain foods - fruits (citrus fruits and strawberries), fermented milk, fish products, nuts and sweets. This type of urticaria is not dangerous, goes away quickly, and occurs due to the body producing antibodies to a new product. - Contact urticaria
. Side effect during professional activities (reaction to latex in surgeons, allergies to chemicals in cleaners). - Reaction to the sting of a wasp, horsefly, hornet
. The most dangerous manifestation of allergies is angioedema, when the bitten person dies an hour after the bite. - Reaction to the presence of a virus in the body
. Sometimes the rash is provoked by intoxication due to fungal infections (staphylococcus, candidiasis (thrush), tonsillitis, pharyngitis). If the disease is cured, the redness on the skin will disappear. - Nervous urticaria
.
In a state of stress, the functioning of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems diverges, the signaling system fails, and our body incorrectly interprets the impulses sent by the brain. The stress hormone adrenaline is released, blood vessels dilate, their walls stretch and become permeable. Endothelial cells lining the vascular and capillary walls swell, forming red bumps on the surface. This condition is also urticaria.
Classification of urticaria by intensity
According to the intensity of its occurrence, urticaria can be:
- Spicy
. Caused by allergenic foods, medications, chemicals, insect bites. Lasts up to 6 weeks, after which it disappears completely. - Chronic.
Lasts over 6 weeks, after which in 60% the symptoms disappear. In 40% they remain and are observed throughout life.
Reasons for appearance
Urticaria is accompanied by many unpleasant symptoms, so patients are interested in quick treatment no less than provoking factors in order to prevent its occurrence in the future. For successful therapy, it is necessary to identify the cause of the disease and, if possible, eliminate it.
Causes of urticaria:
- Infectious diseases. A rash on the body may appear due to viruses or bacteria that have entered the human body. Polyetiological dermatosis occurs due to tonsillitis, caries, cholecystitis, adnexitis and other inflammatory processes.
- Food. The food consumed causes allergies, which leads to hives. Food products provoke a rash mainly in children, as well as in adults suffering from inflammatory processes in the body.
- Pathologies of the immune system. The body mistakes its cells for foreign agents and attacks them. A malfunction of the immune system leads to a skin rash that does not go away for a long time and is not relieved by antihistamines.
- Physical impact. External factors can provoke polyetiological dermatosis, which quickly disappears after the cause of the appearance is eliminated. The rash is formed due to a reaction to the sun, cold, water, mechanical irritation, a jump in body temperature, flowering, animals and other factors.
- Chronic diseases. Urticaria appears against the background of diabetes, herpes, hepatitis, gastrointestinal disorders and leukemia. A rash on the body occurs as the disease progresses and in the absence of professional therapy.
- Hormonal changes. In women, a rash on the epithelium forms during menopause, menstruation, pregnancy and when using oral contraceptives.
It is not always possible to find out the cause that caused polyetiological dermatosis. If the cause of the pathology is not determined after performing various tests, the patient is diagnosed with idiopathic urticaria.
First aid should be provided for Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock and other emergency conditions. You should immediately call an ambulance if a person begins to choke and turns red. While doctors are traveling, it is necessary to ensure good access to oxygen; it is recommended to open windows in the premises.
The patient should be laid horizontally and the neck should be straightened, and the oral cavity should be checked for the presence of foreign objects, for example, chewing gum, which could cause blockage of the airways.
It is necessary to elevate a person's legs to maintain blood pressure levels due to the flow of venous blood. An injection of adrenaline or another drug must be administered intramuscularly into the upper thigh. If the necessary medicine is not available, you will have to wait for an ambulance to arrive.