General information
Itching is a sensation characteristic of the skin, which is accompanied by the need for mechanical irritation. There are physiological itching, as a response to irritation, and pathological, which is associated with diseases and affects the general condition of a person, causing nervousness , insomnia , and in severe cases, depression .
Itching is a common complaint in various dermatological diseases in which an allergic or inflammatory process occurs in the skin. Healthy skin has a pH of 4.5-5.5 (slightly acidic). Natural acidity protects it from the harmful effects of bacteria and fungi. If the pH and water balance are disturbed (heat, cold, endocrine diseases, use of low-quality cosmetics, stress), the skin becomes sensitive, dry, itching appears, and when scratched, inflammation occurs. Excessive itching and, accordingly, scratching of the skin leads to damage to the hair follicles, thinning hair and hair loss. If itching becomes regular, you need to establish the cause, and if it is based on simple factors - dry skin and improper care, they can be easily eliminated. But if there is severe itching of the scalp or the head itches and hair falls out, this indicates serious dermatological problems or disorders of the internal organs and endocrine system.
If it's lice
A disease whose main causative agent is lice, insects that parasitize humans. The main habitats of lice are the armpits, pubis, eyebrows, mustaches and, of course, the head.
Pediculosis is accompanied by severe itching and the appearance of red dots on the skin from insect bites, since lice feed exclusively on blood.
A parasitic disease develops when the rules of personal hygiene are grossly violated. For example, if you use someone else's hair brush or hat.
The cause of constant debilitating itching of the scalp is lice bites. However, once the parasites are eliminated, the painful symptoms disappear.
The drugs Spray Pax and Para Plus are considered effective. After the first application, lice are destroyed, and after the second treatment a week later, nits are destroyed.
Pediculosis is a disease of the scalp caused by head lice. It can be recognized visually: upon examination, live individuals or nits (white capsules tightly attached to the hair) are found.
On the head, lice live mainly on the temples, in the area of the ears and the back of the head. They feed on fresh blood, so bleeding wounds appear at the site of the bites, which can become inflamed and subsequently fester, which causes itching.
Treatment consists of killing parasites and treating the skin with anti-inflammatory agents. Nowadays, it is easy to purchase specialized aerosol preparations at any pharmacy, which, after a single use, completely eliminate lice.
At the same time, you need to purchase a spray for treating hats, pillows, bed linen and clothing that cannot be thermally treated. Chamomile decoction or a ready-made hair rinse with an anti-inflammatory effect is suitable for healing wounds.
Pathogenesis
Itching is caused by various types of stimulation of unmyelinated nerve fibers. Free nerve endings (itch receptors) are located in the papillary layer of the dermis. They are excited either directly by a mechanical/chemical stimulus, or by various mediators - histamine , serotonin , neuropeptides , proteases . CNS receptors are involved in the perception of itching.
With itchy dermatoses, the number of mast cells increases significantly, which release various inflammatory mediators ( tryptase , histamine ), prostaglandin D2 , interleukins and leukotrienes, which provoke itching. the main mediator of itching is histamine , the source of which is basophils migrating into tissues to cause inflammation. In pruritic dermatoses, eosinophils release eosinophilic protein, the level of accumulation of which affects the intensity of itching. The pathogenesis of this condition involves substance P, which is released from nerve endings and attracts proinflammatory cells to the inflammatory focus. It also stimulates mast cells. Interleukin-31 also plays a major role in the formation of itching, the level of which in the blood correlates with the severity of dermatitis.
If we consider the occurrence of itching with dry skin, then what is initially important is the overdrying of the skin and loss of moisture. With dry skin, micro-inflammations appear, which leads to skin irritation and itching.
If itching exists for a long time, a focus of excitation is formed in the cerebral cortex and itching becomes a constant reaction of the skin to irritants - external or internal.
Classification
According to the degree of prevalence, itching occurs:
- Localized (limited to certain areas of the skin).
- Generalized.
Localized itching is caused by local causes. So, for skin diseases ( contact dermatitis , seborrheic or atopic dermatitis , eczema , psoriasis , dermatophytosis , scabies , pediculosis , lichen planus ) local action occurs. However, with psoriasis it is not limited to the area of the rash. In somatic diseases, itching is diffuse.
By intensity:
- Weak.
- Moderate weight.
- Severe (leads to sleep disturbance).
By time of occurrence:
- Constant.
- Night.
- Day.
- Seasonal.
Why does my head itch, causes of itchy scalp
The causes of itchy scalp are different and are associated with skin diseases or somatic ones. The most common cause of an itchy scalp is scalp disease and the presence of parasites. Why does my head itch? Let's look at the main reasons:
- Severe itching is caused by dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis . Both diseases are caused by a fungus of the Malassezia genus, but they differ in severity. Dandruff is a mild manifestation of seborrheic dermatitis that affects only the scalp and is caused by an overgrowth of fungus. Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin disease of the face, trunk and scalp, which is associated with increased production of sebum and changes in its chemical composition. In this disease, the level of Malassezia is normal, but the body produces an abnormal immune response. Malassezia fungi are representatives of normal microflora, but become pathogenic due to an increase in lipase activity, which causes inflammation. Fungi are concentrated near the sebaceous glands and their secretions are used for their development. Under the influence of these microorganisms, the pH of the skin changes to the alkaline side. Malassezia produce substances that cause irritation, inflammation and increased proliferation of the epidermis. Why does the back of the head itch with seborrheic dermatitis? In the dry form of seborrhea, there is a decrease in sebum secretion, and horny scales densely cover the scalp. Peeling starts at the back of the head, spreads throughout the head, and it is very itchy.
- Bacterial infection. Purulent inflammation of the skin and purulent folliculitis cause pain and itching of the scalp.
- Mycoses. Among mycoses of the scalp, trichophytosis and microsporia . Rounded, delimited areas of baldness with peeling appear on the scalp. Inflammation is mild. Within the lesions, the hair changes color and breaks off - with microsporia above the skin level, and with trichophytosis at the skin level, leaving a black “stump”. Pathogens also cause an infiltrative-suppurative form of dermatophytosis: the lesion becomes covered with purulent crusts and protrudes above the skin level, hair falls out.
- Follicular form of lichen planus . The initial signs of this disease are itching and rashes. Scars and baldness appear on the scalp (crown, back of the head, temples). Round bald patches merge, the skin in the lesions is atrophic and shiny, the color is pink-bluish.
- Itchy scalp is associated with dermatoses that include contact dermatitis , psoriasis and eczema . Contact dermatitis is caused by hair care products (shampoos, conditioners, balms). Some immediately note that after washing their hair, redness, itching and even a rash appear. Some people experience a cumulative effect and these symptoms appear after several uses of a particular product. Most often, itching and irritation occurs after hair coloring using aggressive dye components.
- Rosacea . The disease is manifested by the presence of areas of redness and the formation of pustules. Such skin changes are limited to the face and scalp. The development of rosacea is associated with Demodex mites, bacteria, dietary errors, and diseases of the digestive system.
- Presence of parasites. Lice cause pediculosis , and mites cause demodicosis . The presence of lice and their nits can be determined independently, but mites can only be identified using laboratory methods.
- Chronic stress. Many people notice that their scalp itches “from nerves” (as soon as they get upset or nervous). There is an explanation for this. Stress is accompanied by the release of substance P , which causes an itching sensation. Consequently, constant lack of sleep, stress, fears or constant fatigue cause the scalp to itch. A more serious problem is psychogenic itching in mental disorders. Psychogenic itching develops without the presence of skin pathology. Patients have chronic itching due to depression , anxiety , obsessive-compulsive disorder or neurotic hypochondria . Most often this phenomenon is observed in women over 40 years of age. This type of itching is felt on the head in the form of a sensation of insects crawling or biting, which causes constant scratching.
- Alopecia areata. This is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the hair follicles. Associated with endocrine disorders. Manifests itself in the form of circular hair loss on the head.
- Dry skin. It occurs due to insufficient sebum production and is aggravated by improper care. The skin has a protective layer of nourishing lipids. This protective barrier is destroyed if, for any reason, lipid loss occurs. Dry skin leads to burning, flaking and a constantly itchy head. Frequent hair coloring and improper care (frequent washing with aggressive shampoos, over-drying with a hairdryer, straightening, perm) leads to loss of natural moisture and irritation of the skin. The loss of the protective skin barrier allows the entry of pathogens that cause inflammation.
- An unbalanced diet and vitamin deficiencies aggravate dry skin. A lack of vitamins A, B, C and a sufficient amount of polyunsaturated fats in the diet affects the condition of the hair and skin, which becomes sensitive, irritated and dry. Establishing a diet and a course of special vitamins significantly improves their condition.
General diseases of the body are less likely than dermatological pathologies to cause itching. If there are no rashes, redness, or peeling of the skin, a somatic disease can be suspected. The following diseases are most often accompanied by general and local itching:
- Allergic.
- Polycythemia vera .
- Oncological diseases.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Lymphogranulomatosis (intense itching of the head is an early symptom of this disease).
- Chronic renal failure .
- Diabetes.
- Leukemia.
- Neurological diseases.
- Liver pathology with symptoms of cholestasis (stagnation of bile).
Factors that provoke itching include:
- use of aggressive care products;
- contact of the scalp with irritating tissues;
- changes in ambient temperature (increase or excessive decrease);
- psychological impacts;
- hairstyle features (wearing braided braids for a long time);
- smoking and poor nutrition;
- environmental pollution.
Having considered the main causes and factors that cause itching, you can try to correct the situation yourself if it is not associated with dermatological diseases. If they are present, you need to contact a dermatologist to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Oils with antipruritic effect
The most popular are 3 folk methods. They can easily be implemented at home. The effectiveness of these methods has been proven by many people.
Tea tree oil
This oil is an effective anti-inflammatory and soothing agent. To help with itchy scalp, apply a few drops of oil to a cotton pad and wipe the disturbing area. After 5-10 minutes, you need to repeat the procedure. The itching will disappear within a few hours. When it appears, lubricate the head with oil again. The product has a drying effect and is effective for oily seborrhea.
Rosemary oil
This oil can normalize the microflora on the scalp and has a tonic and healing effect. Apply the oil to a cotton pad and treat itchy areas. It has been noticed that rosemary-based preparations help quickly get rid of dandruff.
Jojoba oil
If tea tree oil is recommended for oily seborrhea, then jojoba is recommended for dry seborrhea. This drug moisturizes the skin well, promotes softening and rapid exfoliation of dead cells. Thus, it cleanses and heals the scalp. Jojoba oil is used in the same way as previous products: by lubricating itchy areas with a cotton pad.
Symptoms
When examining the head, attention is immediately paid to lice and their eggs. If there are no lice, carefully examine possible skin changes. Itching and flaking occur if dandruff appears. This is such a common phenomenon that everyone notices its presence and, if the process is not expressed, they do not pay attention to its presence. If keratinized scales quickly form, the skin peels off significantly, then “snow dust” constantly covers the clothes, causing inconvenience. Dandruff and itching always go together.
If sores appear on your head and itch, you need to think about a primary dermatological disease of the scalp. It could be seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis , which are the most common causes of this. Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis at the onset of the disease are the appearance of floury white scales. With this option, there is no inflammation, but itching is present.
Seborrheic dermatitis causes constant itching of the head. Itching and scratching lead to inflammation, traumatization of the skin and excoriations (sores) appear, which are covered with greasy scales or scale-crusts. These are manifestations of a more severe oily form of scalp seborrhea. Sebum is secreted in excess from the sebaceous glands, and the hair becomes greasy and sticks together in strands. They also show abundant yellowish scales.
In the dry form, there is a decrease in sebum secretion; horny scales cover the scalp like a continuous cake. Peeling begins from the occipital region and spreads throughout the head. The scales come off easily and constantly fall on clothes. Hair becomes thin, dry and brittle.
Most often, the back of the neck under the hair (nape area) and temples are affected. When the skin of the face is affected, the rashes are localized in the area of the eyebrows, nasolabial folds and are combined with dermatitis of the scalp.
The eyelids are involved in the process - blepharitis . Unlike dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis is a more serious disease, since there is a risk of transition to seborrheic eczema , the addition of erythroderma and pyoderma . Seborrheic dermatitis is accompanied by hair loss. Therefore, if your head itches and hair falls out, you need to think about seborrheic dermatitis. Hair loss also occurs with psoriatic scalp lesions.
With this disease, scaly spots (plaques) form on the head, having a silvery color and an inflamed area of outline. With psoriasis, the itching is localized and disturbing in the area of psoriatic plaques, observed more often in the evening. The patient feels a tickling (“goosebumps”) or burning itch. If there are local plaques on the crown, the crown itches. With a more extensive lesion, the back of the head and neck itches, since the favorite localization of psoriatic plaques is:
- back of the head (the area under the hair);
- earlobes;
- forehead (in the area of the front edge of hair growth);
- ears and the area behind the ears (weeping cracks may form here).
Most often, psoriasis worsens in winter, which is associated with wearing a hat, cold outside and dry indoor air, and lack of sunlight.
Why does my face itch? There may be different reasons - demodicosis and seborrheic dermatitis . If the skin of the face is inflamed and swollen, or itching of the skin of the face appears, first of all you need to think about these dermatological diseases. Demodicosis is a chronic disease of the facial skin caused by opportunistic parasites Demodex mites. They live in hair follicles and sebaceous gland secretions and are found on the scalp, eyebrows and eyelashes. Under certain conditions, mites become pathogenic, causing an inflammatory reaction of the skin. A favorable factor is dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract (liver and intestines), endocrine glands and the presence of foci of chronic infection.
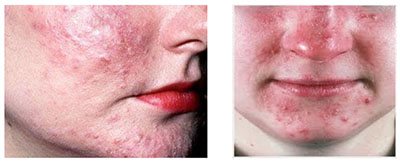
The main elements are erythematous spots located around the hair follicles. On the surface of the spots there is fine- or large-plate peeling. In the area of redness, red papules form and often contain purulent contents.
The pathological process is localized in the T-zone of the face. In patients, the face is red, itches and burns, there is a burning sensation, crawling sensations and fullness.
In advanced forms, thickening of the skin (focal or diffuse), decreased elasticity, a feeling of tightness, and bloody purulent crusts appear.
Characteristic symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis of the face are inflammation and peeling. The pathological process affects the forehead, nose, chin, eyelashes, eyebrows, and mustache area. The beard, scalp (hair growth line) and itchy eyebrows are also involved.
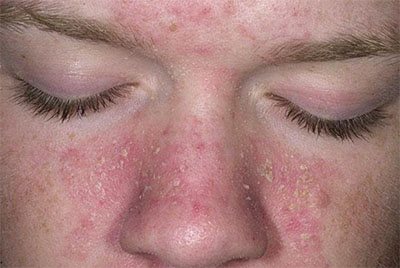
It is possible to differentiate seborrheic dermatitis and demodicosis only with laboratory analysis (acarogram).
Medications
Traditional methods will help to cope with unpleasant sensations and also prevent scratching of the scalp:
- A simple but very effective folk method is onion peeling. Fill it with a liter of water and boil for an hour. Rinse your hair with the resulting decoction after each wash. After just a couple of procedures, the itching will disappear.
- Dandelion and lemon. Take a handful of dandelion flowers, chop them, pour 50 ml. vodka. Next add 1 tsp. honey, juice of one lemon. Place the mixture in a warm place for 2 weeks, then strain. Before washing your hair, make a mask of this lotion for 40 minutes under a film and a warm towel.
- Apple vinegar. It also needs to be rubbed into the scalp, but this should be done five to ten minutes before washing. Before use, vinegar must be diluted with water.
To treat itchy scalp caused by fungal infections, you can use special shampoos.
Folk remedies often prove to be highly effective. You can make a mixture of garlic and onions, add vegetable oil and lemon juice to them. This folk remedy should be used immediately after washing your hair. The mixture is applied to the hair and left for half an hour. The mask should be washed off with acidified water.
Grated apple is an excellent option. This folk remedy should be applied with massaging movements to dry hair immediately before washing your hair. This method should be used a couple of times a week.
Dandelion tincture is also valued as a treatment. This kind of folk remedy moisturizes the skin and quickly relieves itching.
5 tbsp is enough. l.
Mix flowers with lemon juice, 5 ml of honey and 50 ml of vodka to get an excellent mask. Mix all ingredients and leave to infuse for two weeks.
Then strain everything and apply to the scalp with rubbing movements right before washing. This mask strengthens the hair roots, moisturizes the scalp and eliminates flaking.
READ MORE: Cellulite treatment with ultrasound reviews
Information about the treatment of itching of the scalp when this aesthetic pathology reappears can be obtained from the doctor who performed the therapeutic procedures. Typically, the treatment option is selected based on the nature and cause of the disease.
A specialist may prescribe local, oral and other medications. You should not prescribe medications on your own, in this case there is a risk of worsening the problem. Treatment is often performed using drugs with different directions and therapeutic effects:
- Seborrhea is treated with antifungal agents, vitamins B2, E and A.
- If a person has increased nervousness, antidepressants and sedatives are prescribed.
- Hormonal imbalances are treated with drugs that can normalize hormone levels.
- If the cause of itching is allergies, then antihistamines are needed.
People who have this problem often turn to doctors asking them to recommend remedies to relieve itching at home. Specialists can also prescribe folk remedies. Among them are medicated masks that have been found to be safe and effective.
Your scalp and hair will be fine if you pay enough attention to your diet:
- Be sure to include dairy products in your diet, give up sweets and fatty foods;
- Make it a habit to eat eggs, almonds, and consume yeast at least once a week;
- Drink more water daily;
- Fresh fruits and vegetables must be on the table. Apples, plums, carrots, broccoli and more.
- You also need to eat enough fiber, which includes nuts, berries, potatoes, and cabbage.
This is very important, because even if the itching of the scalp is caused by an infection, good and proper nutrition will greatly speed up your recovery.
Traditional medicine offers its own methods for eliminating itchy scalp:
- This remedy is suitable if the scalp is itchy and flaky after dyeing your hair. You need to squeeze out the juice from the onions and garlic, add the same amount of vegetable oil and lemon juice. The product is rubbed into the head immediately after washing for 30 minutes. The mask is washed off in acidified water;
- For dermatitis, itching is eliminated by a mask made from an apple grated on a fine grater. The resulting mass is applied to the head before washing twice a week;
- The itching goes away after three procedures of rinsing with a decoction of onion peels removed from several onions. Boil the husk for 30 minutes, and use it after it has cooled to a comfortable temperature. The decoction should replace hair rinse;
- Dandelion tincture helps effectively. To prepare it you need 5 tablespoons of flowers, the juice of one lemon and 5 ml of honey with 50 ml of vodka. All components are mixed in a glass jar and left to infuse for two weeks. After filtering, the product is rubbed into the skin before washing your hair.
Tests and diagnostics
- Diagnosis includes a thorough examination of the skin not only of the head, but also of the torso and limbs. Traces of scratching indicate the location of the itching.
- General laboratory tests are carried out to exclude pathologies of internal organs and the endocrine system.
- Acarogram. Performed to detect ticks. Scraping is performed and the number of Demodex larvae, eggs and adults is counted. Scraping is done in places where demodex accumulates (forehead, nose, chin). An analysis of eyelashes, eyebrows and follicle contents is performed. The diagnosis of demodicosis is considered valid if more than 5 mites per 1 cm2 are found on the skin, and more than 4 individuals are found on the eyelash. However, it is often not possible to detect mites in the sebaceous glands. Scraping is not considered a highly informative method and a negative analysis does not indicate the absence of a mite.
- Skin biopsy with immunofluorescence. It provides information in cases where the skin is apparently healthy. Histological examination allows us to establish a specific skin disease.
Diet
Diet for skin diseases
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after a month
- Time frame: three months or more
- Cost of products: 1400-1500 rubles per week
Diet for dermatitis
- Efficacy: Therapeutic effect after 3 weeks
- Timing: Constantly
- Cost of products: 1300-1390 rubles per week
Diet for psoriasis
- Efficacy: healing effect
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of products: 980-1150 rubles per week
Diet for facial demodicosis
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 30 days
- Timing: during exacerbation/permanently
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
Considering that any dermatological disease has an allergic component, the diet should not contain products with high sensitizing activity, artificial food additives, as well as products containing histamine and promoting its release. These products include: strawberries, cocoa, chocolate, coffee, orange juice, tomatoes, cow's milk, hazelnuts, all cheeses, smoked meats, herring, tuna.
Products with weak allergenic activity: beef, lamb, turnips, zucchini, chicken, pumpkin, squash, apples (green), fermented milk products, green gooseberries, plums, white currants, butter, dried fruits, cucumber, offal, olive oil, pearl barley and rice porridge, green pears.
To extract nitrates from vegetables, they need to be kept cold (especially potatoes to reduce the starch content), cereals must be soaked and boiled in a third of water (drain the water twice after boiling), and when preparing broths, also drain the water several times.
In the diet for atopic, seborrheic dermatitis and demodicosis, easily digestible carbohydrates are limited: sweet pastries, confectionery, jam, sweets, honey, jam, sugar, condensed milk. Excludes sausages, red meat, smoked meats, seafood, marinades and sauces, pickled vegetables, rich broths, mushrooms in any form, spicy dishes, sauces and seasonings (horseradish, vinegar, mustard, mayonnaise, ketchup), canned fish and meat, fatty sour cream. and animal fats, sugary drinks and alcohol. Salt is subject to restrictions. A strict diet must be followed during the period of exacerbation (3-4 weeks).
Prevention
Prevention of dry skin, itching and skin diseases includes:
- Choosing the right shampoo according to your hair type, especially for sensitive skin.
- Exclusion of alkaline shampoos (pay attention to the pH of the shampoo).
- Infrequent hair washing, since frequent washing reduces the protective properties of the skin and the lipid layer.
- Using shampoos with natural ingredients, allantoin, zinc, ceramides, tar, herbal extracts and panthenol.
- Avoid blow-drying using gels, mousses, varnishes and foams.
- Fighting stress (meditation, yoga, special gymnastics, leisurely walks, moderate sports).
- Strengthening general health, taking care of liver and intestinal health.
- A nutritious and healthy diet, excluding the contraindicated foods mentioned above.
- Rejection of bad habits.
Allergic reactions are to blame
Allergic skin can react to anything: shampoo, hair mask, new cosmetics, etc. In this case, you should immediately abandon the skin irritating product and switch to a neutral shampoo without sodium lauryl sulfate.
The scalp is predisposed to allergies to hair care products, decorative makeup, and synthetic detergents used to treat laundry during washing. Less commonly, allergic reactions to food may occur.
An itchy scalp is usually associated with using new products that have not been used before. To make a diagnosis in this case, you need to consult an allergist, who will clarify the type of reaction, identify the allergen and prescribe rational therapy.
Treatment here comes down to avoiding contact with the allergen and taking antihistamines.
Consequences and complications
Itching in dermatological diseases has unpleasant local and general consequences:
- When scratching, excoriations (scratches, abrasions) and increased pigmentation of these areas occur.
- Wounds in the epidermis are “gateways” for infection, which is further complicated by pyoderma and inflammation of the hair follicles ( folliculitis ).
- Traumatization of the follicles when combing, which leads to hair loss.
- At the site of permanent injury, lichenification (sharp thickening) of the skin and fibrosis develop - this is dangerous because scars form at the site of the follicles, they die, and along with them hair falls out.
- Changes in emotional state: attention and performance are impaired, irritability appears, self-esteem and self-confidence decrease.
- Sleep is disturbed.
Essential oils to combat dandruff and itching
There is another effective way to treat itchy scalp and dandruff. It is based on the use of essential oils. They are included in many shampoos with cosmetic and therapeutic effects.
The most popular in folk medicine are tea tree and burdock oils. At home, they can be used in their pure form. They will not only help get rid of itchy scalp and dandruff, but will also make your hair look healthy.
Using essential oils is quite simple. You just need to rub them into the scalp and hair roots, leave for a while, wrapping your head in a plastic bag and a towel.
The main medicinal properties of oils:
- Burdock oil - eliminates dandruff and reduces hair loss. After use they become strong and shiny.
- Tea tree oil - removes dandruff caused by fungus within 7 days after starting use.
- Lavender oil - promotes hair growth, eliminates dandruff and gives hair shine. Mix a few drops of oil with shampoo and wash your hair.
- Castor oil - relieves itching, dandruff and prevents hair loss.
- Coconut oil has a wonderful antibacterial effect and strengthens thinning hair. Prevents the appearance of dandruff and gray hair. Can be added to shampoo.
- Almond oil - nourishes hair roots, eliminates split ends and dandruff. Can be used several times a day by placing a few drops on the comb.
- Flaxseed oil, jojoba oil and sea buckthorn oil effectively eliminate dandruff, strengthen and nourish hair.
Severe itching of the scalp can be easily relieved with essential oils. They are found in shampoos with cosmetic and therapeutic properties. For example, one of the most popular in folk medicine is tea tree and burdock oil. At home they are used in their pure form. With them you can eliminate itchy scalp and dandruff, as well as make your hair healthy.
Using esters and regular oils is easy. They should be rubbed into the scalp and hair roots, leaving for a while. It is important to wrap your head with a plastic bag and a towel after this.
The following types of oils are considered popular:
- Burdock. Allows you to eliminate dandruff and reduce hair loss. After the procedures, the curls will be strong and shiny.
- Tea tree. Treats dandruff, itchy scalp. Within a week the results will be noticeable.
- Lavender. Treats dandruff, accelerates hair growth, makes it shiny. A few drops are enough to add to shampoo and wash your hair with this product.
- Castor oil. Oil is needed to eliminate itching, dandruff and protect against hair loss.
- Coconut. It has an excellent antibacterial effect and strengthens thin strands. The oil serves as protection against dandruff and gray hair. Can be mixed with shampoo.
- Almond. The product nourishes the roots of the strands, eliminates split ends and dandruff. It is used several times a day, applying drops to a comb.
- Flaxseed, jojoba, sea buckthorn. These oils treat dandruff, strengthen and nourish strands.
READ MORE: Dizzy during pregnancy - causes of dizziness. What to do for dizziness during pregnancy
List of sources
- Albanova V.I., Kalinina O.V. Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp: the role of Malassezia // Advances in medical mycology. 2016. No. 14. pp. 11–14.
- Belousova T. A., Goryachkina M. A., Katranova D. G. Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp: modern ideas about etiology, pathogenesis and therapy // Bulletin of Dermatology and Venereology. 2013. No. 6. pp. 132–138.
- Samgin M.A., Netrunenko I.Yu. New opportunities in the treatment of psoriasis of the scalp // Clinical dermatology and venereology. 2004. No. 3. P. 1–4.
- Danilova A. A., Fedorov S. M. Parasitic skin diseases. Demodicosis // Russian Medical Journal. 2001. T. 8, No. 6, p. 249–254.